Introduction
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices is crucial in the dynamic markets of Latin America. The region is home to a diverse range of countries, each with its unique healthcare demands.
To meet the stringent Medical Device Regulations (MDR), manufacturers must navigate through these varied markets by prioritizing target markets based on disease prevalence and other data-driven insights. Additionally, a targeted approach to Voice of Customer (VoC) research is key to aligning medical device utility with local healthcare gaps.
Collaboration with local partners and transparent communication are imperative to successfully meet regulatory benchmarks and ensure device evaluation resonates with the needs of the healthcare ecosystem. This article will explore the importance of clinical evaluations, systematic reviews, real-world evidence, and creating a clinical evaluation report (CER) in the context of MDR compliance. It will also discuss the role of equivalence in clinical evaluation, the significance of sufficient clinical evidence, device class requirements under EU MDR, best practices for clinical evaluation, and regulatory guidance and resources for clinical evaluation.
Overview of MDR and Clinical Evaluation Requirements
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices in the dynamic markets of Latin America necessitates a nuanced approach to regulatory compliance and clinical evaluation. Here, diversity is the norm; among the 128 countries classified as low- or middle-income countries (LMICs), regional powerhouses like Brazil stand alongside smaller economies, each with its unique disease patterns and healthcare demands.
As manufacturers strive to meet the stringent Medical Device Regulations (MDR) across these varied markets, it is essential to identify and prioritize target markets based on disease prevalence and other data-driven insights. The clinical evaluation process is as much about understanding the 'who' and 'where' of product deployment as it is about meeting regulatory benchmarks.
This targeted approach to Voice of Customer (VoC) research is key to aligning medical device utility with local healthcare gaps. By selecting representatives from these stratified markets, manufacturers can glean significant insights while accounting for the subtle, yet critical differences across regions.
Collaboration with adept local partners becomes indispensable for organizing site visits and engaging with stakeholders, ensuring that device evaluation resonates with the needs of the healthcare ecosystem. As the industry navigates these complexities, transparency in communication about a device's intended use, performance, and development logic stands paramount. As one expert puts it, 'Logic' and 'explainability' are not just components of transparency but are imperative to successfully communicating information that can impact patient outcomes and risk management. Effectual communication strategies, coupled with a comprehensive understanding of user environments and workflows, elevate the quality and applicability of clinical evaluations in Latin America, reflecting a commitment to meet medical needs with precision and care.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing Clinical Evaluation
A robust clinical evaluation is imperative to validate the safety and effectiveness of medical devices. Essential to this process is the meticulous collection and examination of clinical data alongside a systematic review of relevant literature, ensuring a comprehensive assessment of the clinical evidence at hand.
This evaluation should encapsulate not just scientific rigor but also clarity and accuracy in how the device's purpose, function, and role in healthcare workflow are communicated to medical professionals and stakeholders. Moreover, transparency is paramount—it involves lucidly conveying information regarding the intended use, development, and performance of medical devices, underpinned by 'logic' and 'explainability'.
These terms denote the ability to convey the rationale behind results or decisions understandably, which affects risk assessment and patient outcomes significantly. Addressing these points, the role of clinical experts becomes pivotal, as they bring insight into how the device interacts with and impacts healthcare decisions. Their expertise can illuminate the device's medical purpose for intended users and environments, targeting a coherent integration into health care practices. During this evaluation, it’s also crucial to consider detailed product information, such as device type, manufacturer, and any events associated with usage, ensuring that device evaluation is as thorough as it is transparent.
Importance of Systematic Reviews in Clinical Evaluation
The importance of systematic reviews in clinical evaluations cannot be overstated, particularly when assessing the safety and efficacy of medical devices. Unlike narrative reviews that rely on the subjective selection of literature, a systematic review addresses a specific question methodically by identifying, selecting, and appraising all relevant research, thus elevating its status in secondary literature.
Essentially, this type of review is a comprehensive 'study of studies' that provides a critical audit of both published and unpublished works to answer a precisely formulated question. Employing systematic reviews in clinical evaluation ensures an objective analysis grounded in expansive and meticulous research.
For example, when examining the use of nebulisers in the treatment of cystic fibrosis, a systematic review could identify the various advantages newer technologies might have over traditional systems in terms of treatment efficacy, adherence, and patient preference. However, it's crucial to consider that different nebulisers may not be compatible with all medications, suggesting an area where more research could improve the review's comprehensiveness.
Leveraging tools like DistillerSR, which uses artificial intelligence and intelligent workflows, can greatly enhance the efficiency of conducting systematic reviews, providing high-quality evidence in a more cost-effective and timely manner. Furthermore, adhering to structured methodologies such as the PICO framework—Patient, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome—can augment the precision of the review by ensuring all relevant aspects of a clinical question are addressed. Beyond healthcare, systematic reviews find their place across varied sociological fields, showcasing their adaptability and vital role in contributing to the robust evidence necessary for informed decision-making in medical interventions. Their systematic and explicit approach assists in not only summarizing existing knowledge but also in evaluating the appropriateness of medical interventions through thorough literature reviews and expert panel assessments, as noted by industry experts.
Role of Real-World Evidence in Clinical Evaluation
The significance of Real-world evidence (RWE) in clinical evaluation is burgeoning, especially regarding medical devices in Latin American healthcare settings. RWE encompasses a diverse array of data sources, including patient registries and electronic health records (EHRs), which offer additional insights beyond conventional clinical trial findings. These rich datasets enable researchers to observe the performance of medical devices amidst actual clinical practices, thereby uncovering information on safety and efficacy that complements controlled trial data.
As medical device companies contemplate the future, they often use forward-looking statements to project their products' performance and business strategies. Such statements are inherently based on current beliefs and estimations, emphasizing the potential of products like Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence medical devices (Names). Yet, the industry recognizes that similar to pharmaceuticals, these devices must surmount high hurdles during development and post-market studies to achieve commercial success.
The emphasis must be placed not solely on technological prowess but also on comprehensive, real-world implementation. Challenges arise when utilizing RWE; the data's varying quality, data privacy considerations, and interpretation can impose limitations on its utility. Despite these hurdles, the strategic use of RWE can offer a more nuanced understanding of medical device performance in real healthcare environments, shaping future business directions and fostering innovation grounded in practicality and patient safety.
Creating a Clinical Evaluation Report (CER)
Crafting a Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) is foundational in validating the safety and performance of a medical device. At its core, the CER encompasses a collection of clinical data, methodical evaluation processes, and systematic analysis drawn together to affirm the efficacy and safety of the device within its intended purpose. When embarking on the development of a CER, one must regard the global landscape of Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs), which includes a diverse array of economies and healthcare needs.
Specifically, it is essential to contextualize your research by focusing on pertinent markets that reflect your device's target demographic, utilizing disease prevalence and incidence rates as guiding metrics. This careful selection of representative locations will streamline your investigation, enabling an effective capture of meaningful clinical data that resonates across similar markets. As you delve into the particulars of constructing a CER, it becomes apparent that the process is multi-tiered: starting from a comprehensive literature search strategy to tease out current standards of care (the 'State of the Art'), conducting risk-benefit assessments based on collected data, and culminating with documentation that satisfies both regulatory bodies and Notified Bodies.
Furthermore, partnering with adept local entities can greatly bolster the depth and applicability of your clinical evaluation, allowing you to navigate the idiosyncrasies of each region effectively. It's worth noting that the clinical evaluation is not only a pre-market endeavor but also extends into post-market surveillance, underpinning the continuous affirmation of the device's clinical relevance and safety throughout its lifecycle. By understanding the clinical evaluation's integral role in both development and ongoing market analysis, you equip yourself with the know-how to assemble a robust CER, furthering the credibility and reliability of your medical device in meeting global health demands.
Ensuring Equivalence in Clinical Evaluation
Demonstrating equivalence in the clinical evaluation of medical devices—comparing a new device to a pre-existing one—is a critical yet complex task. Transparency regarding the logic and methodology underpinning device function and the explanation of results is essential to confer an assurance of safety and effectiveness.
For instance, in medical machine learning devices (MLMDs), myriad factors including intended use, development parameters, and performance must be openly presented. A comprehensive explanation should cover the device's medical purpose, functions, and how it integrates into healthcare workflows, aiding clinicians in their decision-making process.
Moreover, the impact of the device's outputs on healthcare decisions or professional judgment should be explicitly described. This approach not only fosters trust in medical devices but also addresses the explainability aspect—the 'why' and 'how' behind the device's output.
Yet, despite technological sophistication, many promising innovations stumble on the path to clinical usage due to the high demands of commercial viability. This underlines the importance of rigorous external validation studies, designed to detail a device’s predictive capabilities and clinical utility based on concrete characteristics. Unfortunately, as the landscape of clinical prediction models reveals, a significant gap often exists between the development of predictive tools and their practical application in patient care. Scholarly acknowledgment, evident through citations and academic acclaim, does not always equate to clinical adoption, as seen in the unfortunate underutilization of certain cancer subtype classification schemes. It is imperative, therefore, that clinical evaluations not only establish equivalence but also prioritize transparency and the translation of research into practice to realize tangible patient benefits.
Sufficient Clinical Evidence for MDR Compliance
Ensuring that medical devices conform to the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) by providing sufficient clinical evidence is crucial for maintaining access to the market. To ascertain adequate clinical evidence, a combination of clinical investigations, meticulous post-market surveillance data, and thorough literature reviews is utilized.
These data categories not only demonstrate device safety and effectiveness but also support ongoing regulatory compliance. Importantly, in the current global healthcare landscape, there is a growing emphasis on the proper use of antimicrobial agents and the drive to reinforce research and development in this field.
As reflected in the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare's trial project on antimicrobial drugs, similar principles of rigorous evaluation, appropriate use, and assured compliance are paramount across medical initiatives. This illustrates the international focus on the continuous assessment and validation of healthcare interventions, including the evaluation of medical devices as well as advanced practices such as the development of machine learning/artificial intelligence medical devices. With the bar set high for commercial success, similar to the pharmaceutical industry, medical devices must demonstrate their value within healthcare systems, ensuring that they meet the quality and relevance standards expected by clinicians and stakeholders.
Device Class Requirements Under EU MDR
Under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), the classification of medical devices plays an essential role in determining the level of regulatory scrutiny required before they can be brought to the European market. Class I devices are considered to have the lowest potential risk and therefore are subject to less stringent controls. Conversely, Class III devices include critical instruments such as pacemakers, which are deemed high-risk and, as such, undergo a rigorous examination process to ensure safety and efficacy.
It is important to understand that these classifications dictate not only the pre-market requirements but also the post-market clinical evaluation needed to continuously demonstrate compliance. Such evaluations are vital for all classes of devices to maintain market presence, especially considering that the MDR has introduced a more robust framework for monitoring medical devices. According to the U.S. FDA, Class III devices represent roughly 10% of the medical devices they regulate, indicating the smaller proportion of devices falling into this high-risk category, yet these devices often require a premarket approval (PMA) which is a more stringent process compared to the 510(k) clearance needed for Class I and II devices.
Navigating the MDR, with its stringent and complex requirements, is critical for manufacturers aiming to certify or recertify their products. Reassuringly, experts are available to aid in maneuvering through these regulatory intricacies to achieve successful product certification in the European market. Manufacturers must be prepared to address these classification-driven evaluation processes, as the MDR substantially reshapes the legal landscape for medical devices across Europe.
Best Practices for Clinical Evaluation Under MDR
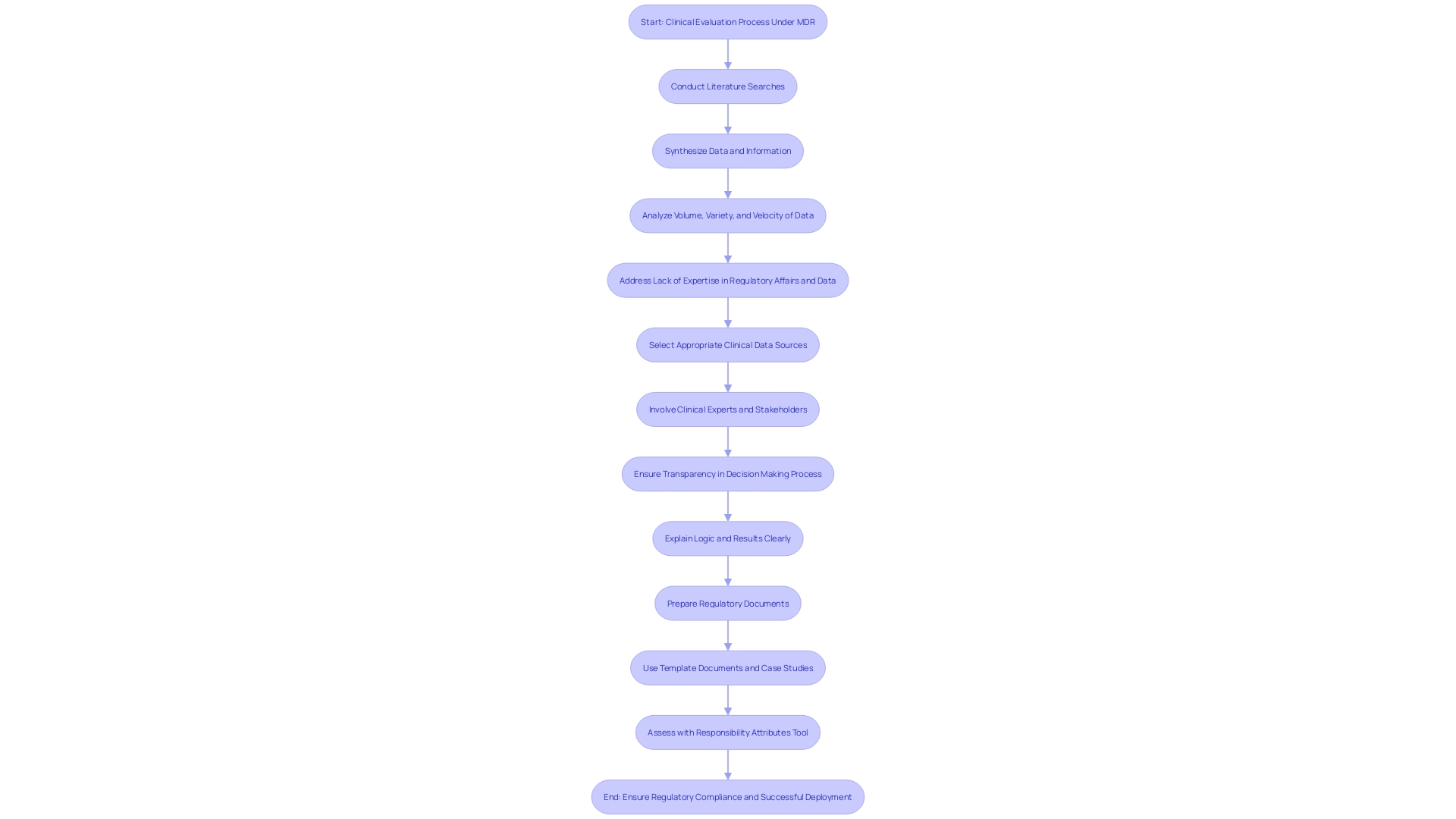
To ensure regulatory compliance and the successful deployment of medical devices, a refined approach to clinical evaluation under the MDR is critical. A comprehensive understanding of the clinical evaluation process is paramount for assemblage of clinical evidence that will stand up to the scrutiny of regulatory authorities and Notified Bodies. This involves mastering the ability to conduct precise literature searches and synthesize data that can establish a state of the art framework and risk-benefit assessment.
Selecting the right clinical data sources is essential. A meticulous strategy should be adopted for literature searches, ensuring that the question being addressed is clearly defined, using carefully selected key words for comprehensive research. The involvement of clinical experts is also vital, as they can guide the evaluation process with their expertise, ensuring that the clinical evidence is not only robust but also aligns with current medical practice and standards.
Transparency and explainability are key tenets; the 'logic' of decision-making and the results obtained need to be communicated in a manner that is understandable by intended users or audiences. This is particularly important in diverse markets such as Latin America where the efficacy and safety of medical devices need to be made clear across varying regulatory landscapes. Lastly, the challenges inherent in clinical evaluations should not be underestimated.
These include the complexity of document preparation, as highlighted by NAMSA's medical writing services experience. Utilizing template documents and leveraging case studies can greatly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of creating Clinical Evaluation Reports (CER) and other critical documentation. Armed with these practices, professionals can produce clinical data evidence that conforms to the highest of standards, ensuring a smooth pathway from device development to market.
Regulatory Guidance and Resources for Clinical Evaluation
Compliance with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) is an intricate endeavor, given the myriad facets and continual evolution of regulations. The FDA's mandate extends to guaranteeing the safety and effectiveness of medical devices and plays a pivotal role in regulatory oversight. To equip manufacturers with the necessary tools for clinical evaluation, various regulatory guidance documents and international standards are readily available.
Provisioned by regulatory authorities and professional organizations, these resources are a treasure trove of insights for developing and implementing rigorous clinical evaluations. An example of this regulatory guidance comes into sharp focus with the development and qualification of Digital Health Technologies (DHTs) for clinical trials. As highlighted in a recent public forum, the FDA shed light on the importance of selection, verification, and validation of such technologies, emphasizing the balance needed between consumer usability and stringent data integrity.
Furthermore, health-tech leaders underscore the significance of a robust regulatory strategy, drawing on courses and tool kits to crystallize the federal regulatory pathways applicable to their products. This not only expedites product development but also safeguards patient safety effectively. Strategic knowledge acquisition, as cited from the course, directly correlates to better market-readiness and streamlined processes, ensuring an adherence to the newest regulatory stipulations.
To solidify this practice, manufacturers must remain vigilant and continually integrate the latest regulatory changes into their clinical evaluation processes. This ongoing vigilance is critical as it directly impacts postmarket reporting mechanisms, such as documenting adverse events and product issues—an area where details on device type, manufacturer, and the circumstances surrounding an event are vital. By staying abreast of these developments and effectively utilizing the available resources, manufacturers can navigate the complex landscape of MDR compliance with greater confidence and precision.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices in Latin America requires a strategic approach to regulatory compliance and clinical evaluation. Manufacturers must prioritize target markets based on data-driven insights and align device utility with local healthcare gaps through Voice of Customer research. Collaboration with local partners and transparent communication are imperative.
A robust clinical evaluation process involves collecting and examining clinical data, conducting systematic reviews, and ensuring transparency and explainability in communicating results. Systematic reviews play a crucial role in evaluating device performance and identifying advantages over traditional systems. Real-world evidence (RWE) is increasingly significant in clinical evaluation, providing insights beyond controlled trial data.
Despite challenges, the strategic use of RWE fosters innovation grounded in practicality and patient safety. Crafting a comprehensive Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) is foundational in validating device safety and performance. Manufacturers must contextualize research, collaborate with local entities, and extend the evaluation into post-market surveillance.
Demonstrating equivalence in clinical evaluation requires transparency and explainability in device function and results. Rigorous external validation studies are essential for clinical adoption. Compliance with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) necessitates sufficient clinical evidence through investigations, post-market surveillance, and literature reviews.
Understanding device classification under the EU MDR is crucial for navigating the regulatory landscape. Best practices for clinical evaluation include precise literature searches, involvement of clinical experts, prioritizing transparency, and utilizing available regulatory guidance and resources. In conclusion, prioritizing target markets, conducting robust evaluations, leveraging systematic reviews and real-world evidence, creating comprehensive CERs, demonstrating equivalence, and providing sufficient clinical evidence are all crucial for ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices in Latin America.




