Overview
Best practices for clinical study data capture focus on leveraging Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems to enhance data quality, reduce costs, and streamline processes in clinical trials. The article supports this by highlighting the significant benefits of EDC, including improved accuracy, real-time data access, and customization options, which collectively contribute to more efficient and effective clinical research outcomes.
Introduction
The integration of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems has revolutionized the landscape of clinical trials, transforming the way data is collected, managed, and analyzed. As the industry shifts away from traditional paper-based methods, the advantages of EDC systems become increasingly apparent, including significant reductions in data collection costs and enhanced data integrity.
This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of EDC systems, exploring their role in:
- Improving data quality
- Overcoming implementation challenges
- Customizing solutions to meet specific research needs
Furthermore, it highlights emerging trends that are shaping the future of clinical study data capture, emphasizing the necessity for researchers to adapt to these innovations to maintain a competitive edge in an evolving marketplace.
Understanding Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems in Clinical Trials
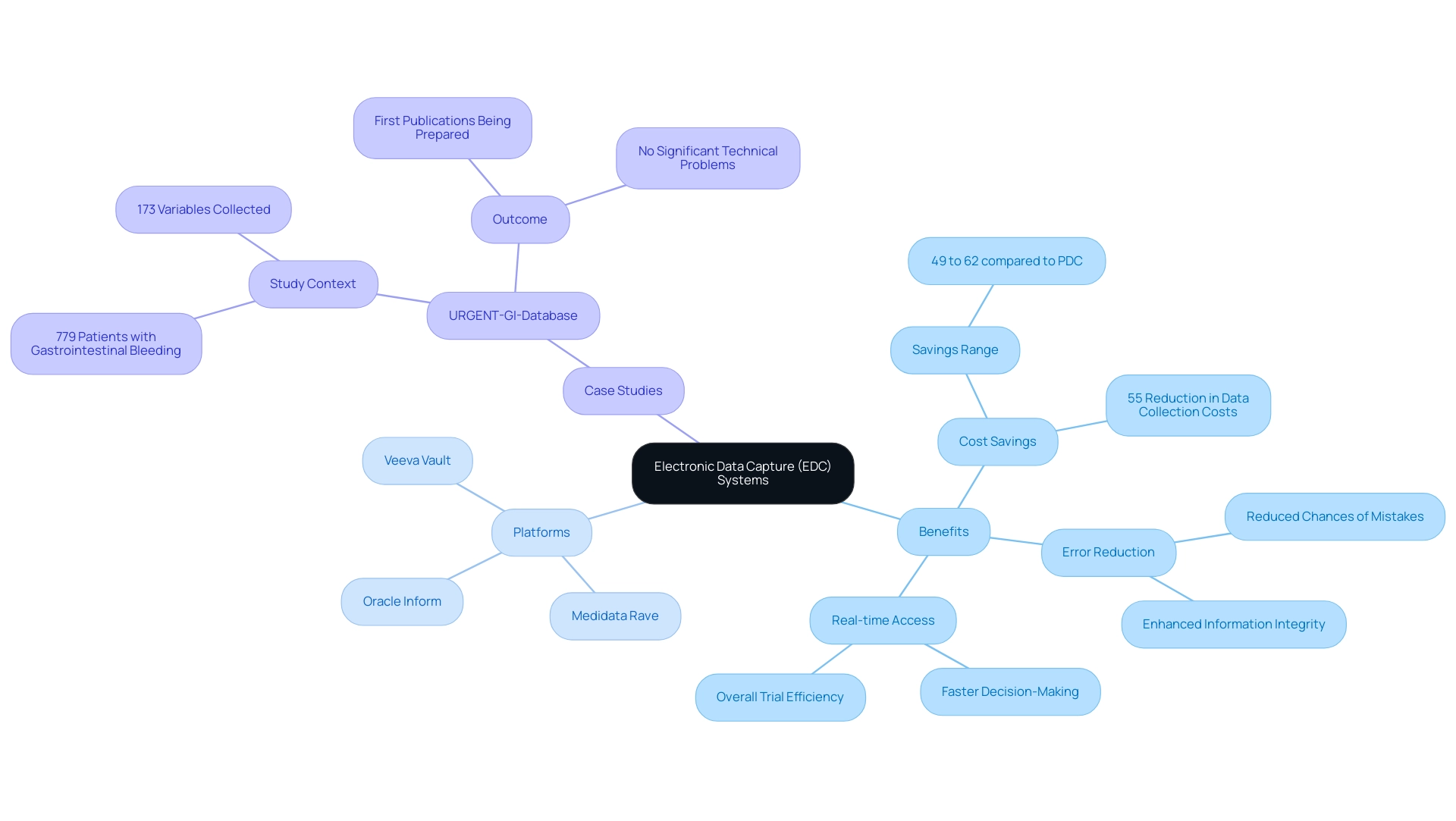
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) technologies signify a crucial progress in the field of research trials, enabling clinical study data capture through digital platforms for the effective gathering, management, and examination of information. Unlike conventional paper-based information gathering methods, EDC frameworks simplify the clinical study data capture process, significantly reducing the chances of mistakes and enhancing information integrity. Recent studies indicate that the clinical study data capture method using EDC can lower collection costs by as much as 55%, with potential savings ranging from 49% to 62% when compared to PDC, emphasizing the financial benefits crucial for clinical researchers operating within budget constraints.
Additionally, EDC networks support clinical study data capture by offering real-time information access, which promotes faster decision-making and enhances overall trial efficiency. Prominent EDC platforms, such as:
- Medidata Rave
- Oracle Inform
- Veeva Vault
offer a variety of features tailored to meet diverse research needs. For instance, the URGENT-GI-Database study, which examined a large cohort of 779 patients with gastrointestinal bleeding, reported no significant technical problems and is preparing its first publications, underscoring the effectiveness of EDC in managing complex information sets.
Additionally, advancements such as shinyMobile for mobile-ready applications further enhance the functionality of EDC solutions. As Adorjan, K. points out, 'Electronic information collection in resource-limited environments utilizing the lightweight medical information acquisition and recording framework' demonstrates the flexibility of EDC technologies. As healthcare researchers aim to enhance strategies for clinical study data capture and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements, grasping the features and benefits of EDC platforms becomes crucial.
Benefits of Implementing EDC Systems for Enhanced Data Quality
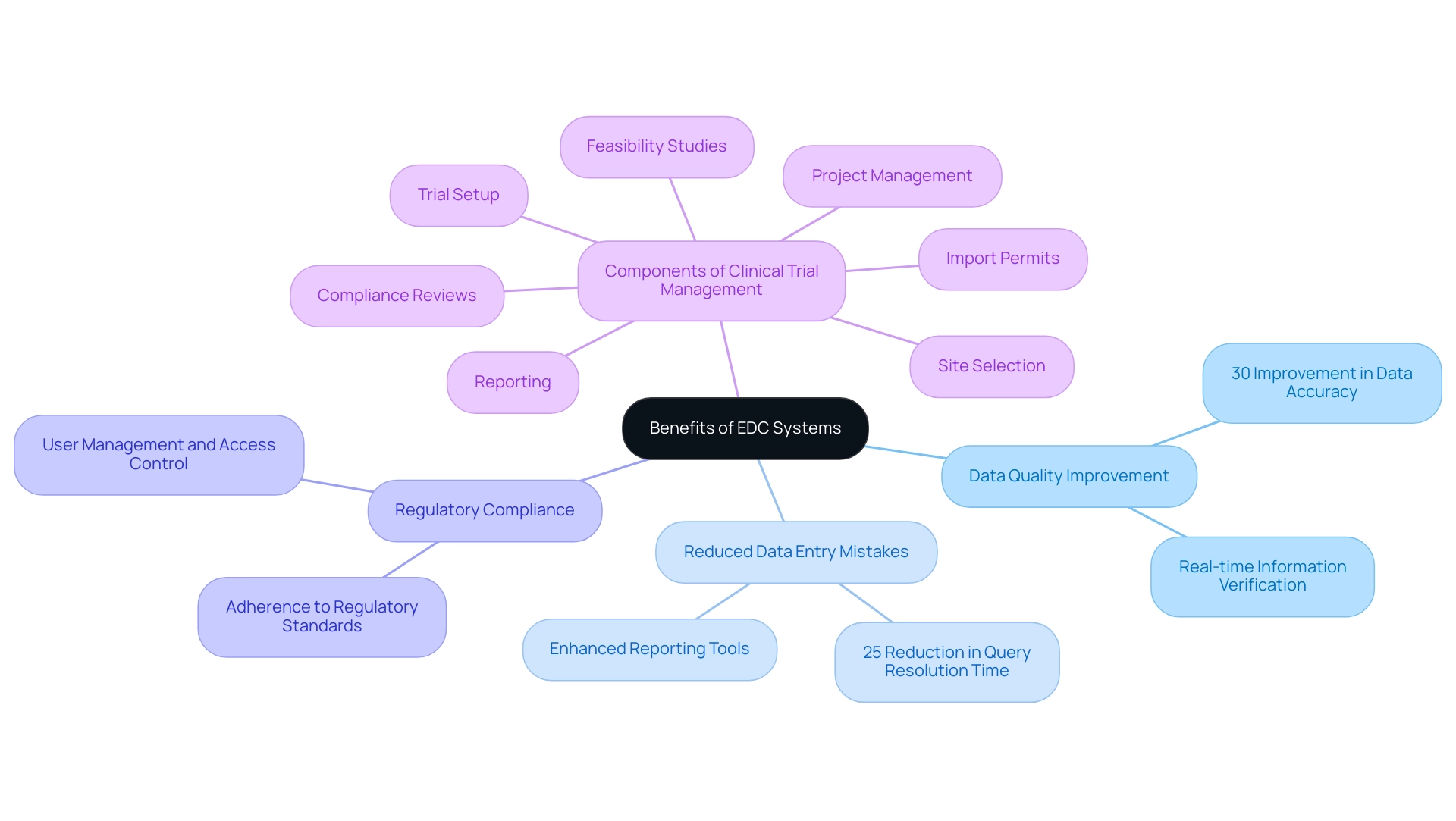
The adoption of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) tools in research trials provides numerous benefits, particularly in clinical study data capture, by improving data quality, reducing data entry mistakes, and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. This is part of a broader suite of comprehensive clinical trial management services that includes:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
The trial setup process involves meticulous planning and coordination with stakeholders to ensure all regulatory requirements are met, while project management encompasses ongoing oversight and communication to track progress and address any issues that arise.
According to market analysis, the North America EDC frameworks market is expected to grow at 9.4% during the analysis period, reflecting a growing recognition of the benefits these frameworks provide. EDC frameworks allow real-time information verification, ensuring that details are precise and comprehensive before analysis. Moreover, EDC platforms are often equipped with advanced reporting tools that empower researchers to track trends and identify discrepancies as they arise.
As a significant study emphasized, there was a 30% improvement in data accuracy along with a 25% reduction in query resolution time after the transition from traditional paper-based methods to electronic data capture. This efficiency contributes not only to improved healthcare outcomes but also drives economic growth and job creation in local economies, emphasizing the importance of international collaboration and innovation in Medtech. Effective communication strategies between research locations and sponsors, as discussed in the case study 'Communication Strategies for Sites and Sponsors,' are vital for the successful implementation of EDC methods.
This evidence underscores the critical role that EDC technologies play in clinical study data capture within modern clinical research, advocating for their widespread adoption to improve overall research outcomes.
Overcoming Challenges in EDC Implementation
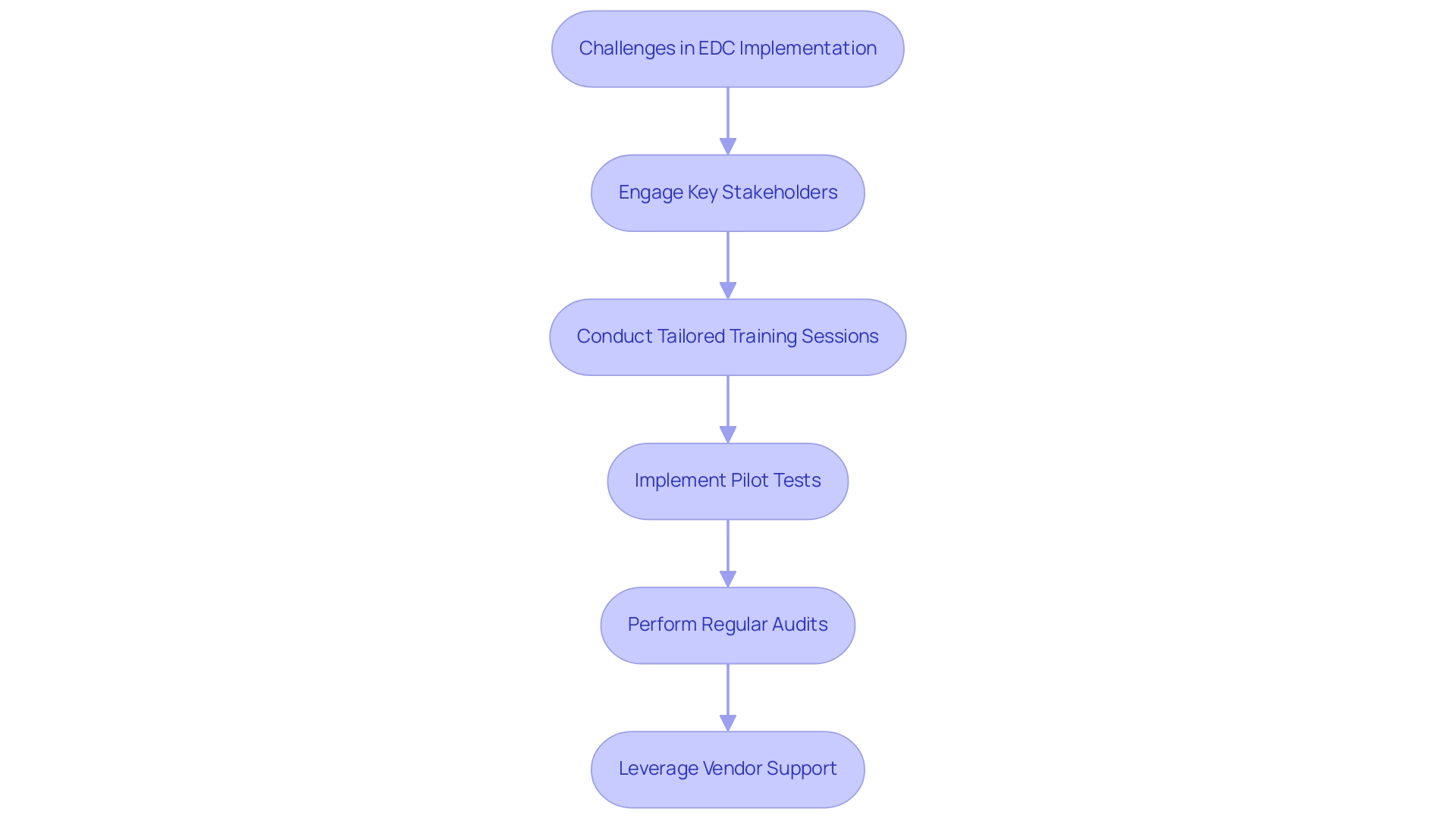
Implementing Electronic Information Capture (EDC) frameworks can present various challenges, particularly personnel resistance to change, migration complexities, and the requirement for extensive training. Recent reports indicate that the average source-to-database error rate stands at 14.3 errors per 10,000 fields, highlighting the critical need for meticulous implementation strategies. To navigate these hurdles effectively, engaging key stakeholders early in the process is essential, ensuring their input and buy-in.
- Tailored training sessions that cater to the varying technical proficiencies of different user groups can significantly enhance user comfort and confidence.
- Additionally, conducting pilot tests allows organizations to pinpoint potential issues before a full-scale rollout, creating a smoother transition.
- It is also crucial to implement regular audits and reviews to maintain information quality and system efficiency, as these practices are integral to successful EDC adoption.
The challenges of high initial costs and the need for ongoing technical support further complicate the implementation process, necessitating vigilance in regulatory compliance. Leveraging vendor support for data migration and customization can mitigate technical challenges. A practical case study titled 'Practical Implications of EDC Adoption' illustrates this well; a research organization that effectively navigated these barriers reported enhanced user adoption rates and a more seamless transition by prioritizing comprehensive training and continuous staff engagement.
As highlighted by industry specialists,
Better yet, they can develop alongside Castor as they enter the future of fully integrated studies,
emphasizing the potential for EDC frameworks to progress in accordance with organizational needs.
Customization: Tailoring EDC Solutions for Specific Study Requirements
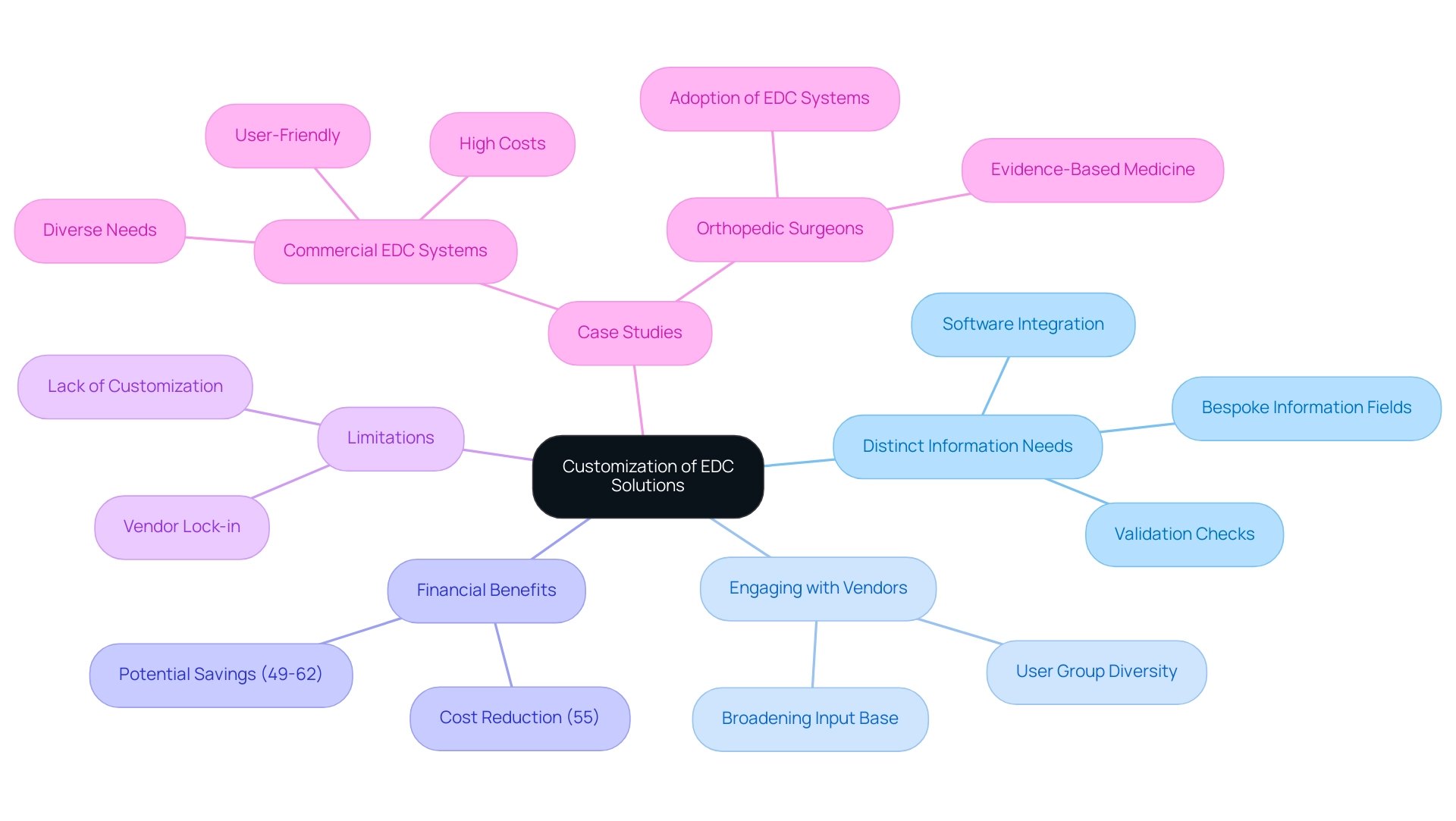
Customizing Electronic Data Capture (EDC) platforms is essential for effectively addressing the varied requirements of clinical study data capture. Each trial presents distinct information needs, patient demographics, and regulatory frameworks, making it imperative for researchers to tailor EDC solutions accordingly. By implementing customized EDC systems, researchers can enhance clinical study data capture, streamline information entry processes, and align the platform with the specific study protocol.
This customization might encompass:
- Creating bespoke information fields
- Establishing targeted validation checks
- Facilitating integration with other software platforms
Engaging with EDC vendors during the customization phase is crucial; as noted by James A. Welker,
All too frequently input is only obtained from a small user group that is technology oriented.
Broadening the input base during this phase can lead to significant enhancements in the efficiency and effectiveness of clinical study data capture.
Furthermore, the EDC process has been shown to decrease collection costs by 55% compared to paper capture (PDC), highlighting the financial benefits of customization. Recent trends suggest a shift towards more flexible EDC solutions that enhance clinical study data capture and address specific research requirements, offering a route for improved data management in trial settings. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of commercial EDC solutions, such as vendor lock-in and lack of customization, which can impede effective use in medical environments.
Case studies illustrate how customized EDC solutions can lead to improved clinical study data capture, resulting in better alignment with evidence-based practices and ultimately aiding more efficient research investigations. For instance, careful evaluation of existing EDC systems can assist orthopedic surgeons in adopting these technologies, thereby enhancing their practice of evidence-based medicine.
Future Trends in Clinical Study Data Capture: Innovations and Insights
The landscape of clinical study data capture is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by innovations such as Direct Data Capture (DDC) and remote patient monitoring. DDC enables the seamless collection of information directly from patients via wearable devices and mobile applications, effectively minimizing reliance on traditional entry methods. This pivotal shift not only enhances the accuracy of information collected but also fosters greater patient engagement and adherence to study protocols.
Furthermore, our comprehensive trial management services encompass:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Project management
- Reporting, including the management of study status, inventory, and adverse events
These services are essential for navigating the regulatory landscape in Latin America. The integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning promises to revolutionize analysis processes, allowing researchers to extract valuable insights with increased efficiency. As Florence Mowlem, PhD, Vice President of Science for ObvioHealth, stated, 'I hope this can be a turning point for the industry with regard to comparability testing.
We can stop having [comparability] conversations so frequently, and instead we can start talking about optimizing our electronic measures for all individuals.' With Walgreens recently signing 15 contracts for trial recruitment in Q3 2023, a notable increase from 8 contracts in Q2, it's evident that the industry is adapting to these changes. As CVS leaves the trial environment, the need for researchers to stay updated on these trends and to modify electronic information capture (EDC) systems accordingly is crucial for preserving a competitive advantage in trials.
A relevant example of this evolution is illustrated by the case study on Sensor-Based Coas, which highlights how digital measures are being utilized for remote patient assessment and validated to monitor meaningful aspects of patient health. Looking ahead to 2024, the evolution of clinical study data capture technology, including innovations in direct data capture and remote monitoring, will be critical for optimizing research outcomes and fostering international collaboration, ultimately contributing to economic growth and healthcare improvement in the region.
, with arrows indicating the flow and interconnections between components. Each box represents a key innovation or service in clinical study data capture, with arrows indicating the flow and interconnections between components.](https://images.tely.ai/telyai/moiirsvh-each-box-represents-a-key-innovation-or-service-in-clinical-study-data-capture-with-arrows-indicating-the-flow-and-interconnections-between-components.webp)
Conclusion
The implementation of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems in clinical trials offers transformative benefits, fundamentally enhancing the data collection process. With capabilities that significantly reduce costs and improve data integrity, EDC systems represent a crucial advancement over traditional paper-based methods. Their ability to provide real-time data access and validation not only minimizes errors but also accelerates decision-making, ultimately leading to more efficient trial management.
Despite the challenges associated with EDC implementation—such as staff resistance and data migration complexities—strategies like tailored training and stakeholder engagement can facilitate a smoother transition. The customization of EDC solutions to meet specific research requirements further enhances their effectiveness, allowing for the integration of unique data needs and regulatory considerations. As the landscape of clinical research continues to evolve, the adaptation of EDC systems to incorporate emerging technologies, such as Direct Data Capture and remote monitoring, will be vital.
In summary, embracing EDC systems is essential for clinical researchers aiming to improve data quality and operational efficiency. As the industry shifts towards more innovative data capture methods, staying informed and adaptable will ensure that researchers remain competitive in an increasingly complex marketplace. The future of clinical trials is undeniably digital, and those who leverage EDC technologies will be well-positioned to drive advancements in healthcare outcomes and research integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Electronic Data Capture (EDC) technologies?
EDC technologies are digital platforms used for capturing clinical study data, improving the gathering, management, and examination of information compared to traditional paper-based methods.
How do EDC technologies improve the clinical study data capture process?
EDC technologies simplify the data capture process, significantly reduce the chances of mistakes, and enhance information integrity.
What financial benefits do EDC systems offer?
EDC systems can lower collection costs by as much as 55%, with potential savings ranging from 49% to 62% compared to paper-based data collection (PDC).
What advantages do EDC networks provide for clinical trials?
EDC networks offer real-time information access, promoting faster decision-making and enhancing overall trial efficiency.
What are some prominent EDC platforms?
Notable EDC platforms include Medidata Rave, Oracle Inform, and Veeva Vault, which provide various features tailored to different research needs.
Can you provide an example of EDC effectiveness in a study?
The URGENT-GI-Database study, which involved 779 patients with gastrointestinal bleeding, reported no significant technical problems and is preparing for its first publications, highlighting EDC's effectiveness in managing complex datasets.
How do advancements like shinyMobile enhance EDC solutions?
shinyMobile provides mobile-ready applications, further improving the functionality and accessibility of EDC solutions.
What additional services are included in comprehensive clinical trial management alongside EDC?
Comprehensive clinical trial management services include feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting.
What impact has the transition to EDC had on data accuracy and query resolution time?
The transition from traditional paper-based methods to EDC has resulted in a 30% improvement in data accuracy and a 25% reduction in query resolution time.
What is the expected market growth for EDC frameworks in North America?
The North America EDC frameworks market is expected to grow at a rate of 9.4% during the analysis period, indicating a growing recognition of their benefits.
Why is effective communication important in the implementation of EDC methods?
Effective communication strategies between research locations and sponsors are vital for the successful implementation of EDC methods, ensuring smooth operations and adherence to regulatory requirements.

