Introduction
In the realm of clinical research, the integrity of electronic source data is paramount, serving as the foundation for reliable and valid study outcomes. The ALCOA-C principles—Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, and Complete—provide a robust framework for ensuring that data collected during investigations meets the highest standards of quality.
As organizations navigate the complexities of regulatory requirements and technological advancements, understanding and implementing these principles becomes essential not only for compliance but also for enhancing the overall effectiveness of clinical trials.
Recent advancements, including the integration of artificial intelligence and comprehensive clinical trial management services, further underscore the importance of maintaining data integrity in an increasingly digital landscape.
This article delves into the critical aspects of electronic source data management, exploring best practices, challenges, and the pivotal role of training and support in achieving success in clinical investigations.
Understanding ALCOA-C Principles for Electronic Source Data
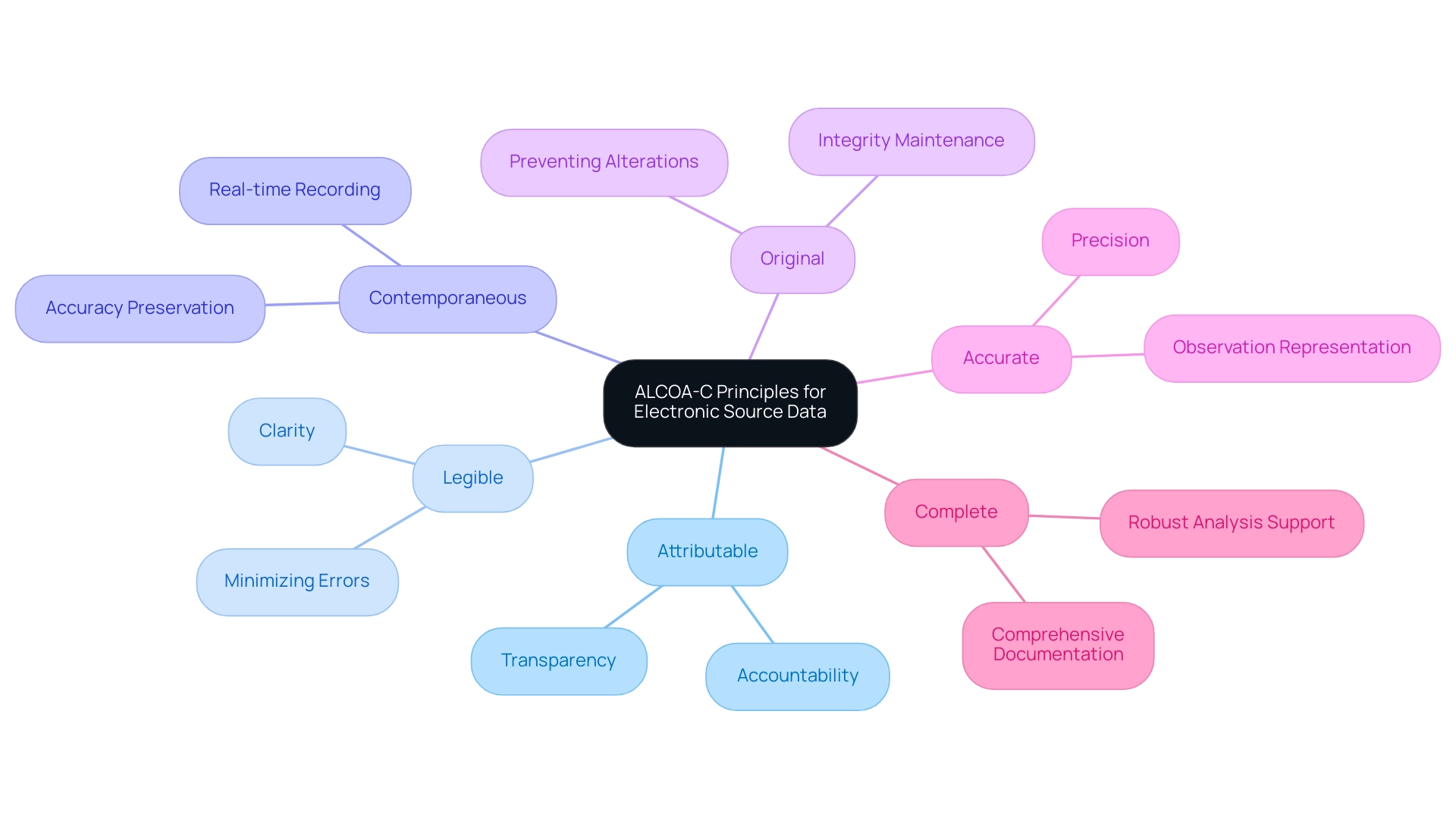
The ALCOA-C principles serve as an essential framework for assessing the quality of electronic source data in clinical investigations, ensuring that integrity is preserved throughout the research process. Each principle fulfills a distinct role in this framework:
- Attributable: It is essential that information can be traced back to the individual responsible for its collection, thereby ensuring accountability and transparency in the research process.
- Legible: Information must be presented in a clear and understandable format to minimize the risk of misinterpretation and errors.
- Contemporaneous: Recording information in real-time or as close to the event as possible is vital for preserving accuracy and ensuring that it reflects actual occurrences.
- Original: Retaining original information is crucial for upholding the integrity of the content, preventing unauthorized alterations.
- Accurate: Information must be precise, accurately representing the observations made during the study.
- Complete: All pertinent information should be documented to ensure that the dataset is comprehensive and supports robust analyses.
The importance of these principles is underscored by recent findings; as of May 2023, an impressive 94% of interventional studies have successfully posted their results. This statistic not only reflects a commitment to information transparency and integrity but also highlights the necessity of adhering to ALCOA-C principles to achieve such outcomes. Additionally, the adoption of ALCOA-C principles is associated with a notable enhancement in information integrity, which is increasingly acknowledged as crucial in advancing clinical research and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards regarding electronic source data in clinical investigations.
Furthermore, the execution of comprehensive clinical trial management services—covering feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, nationalization of investigational devices, project management, and reporting—plays a significant role in improving the quality of digital source information. As noted by industry experts, the integration of advanced technologies, such as AI, is transforming these practices. Mandis Beigi and colleagues discuss how AI-powered simulants can improve study efficiency, suggesting that by 2025, AI tools are expected to handle up to 50% of data-related tasks.
This evolution in technology further reinforces the need for meticulous adherence to ALCOA-C principles to maintain quality and integrity, driving global health improvement through international collaboration and innovation in Medtech.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements for Electronic Source Data
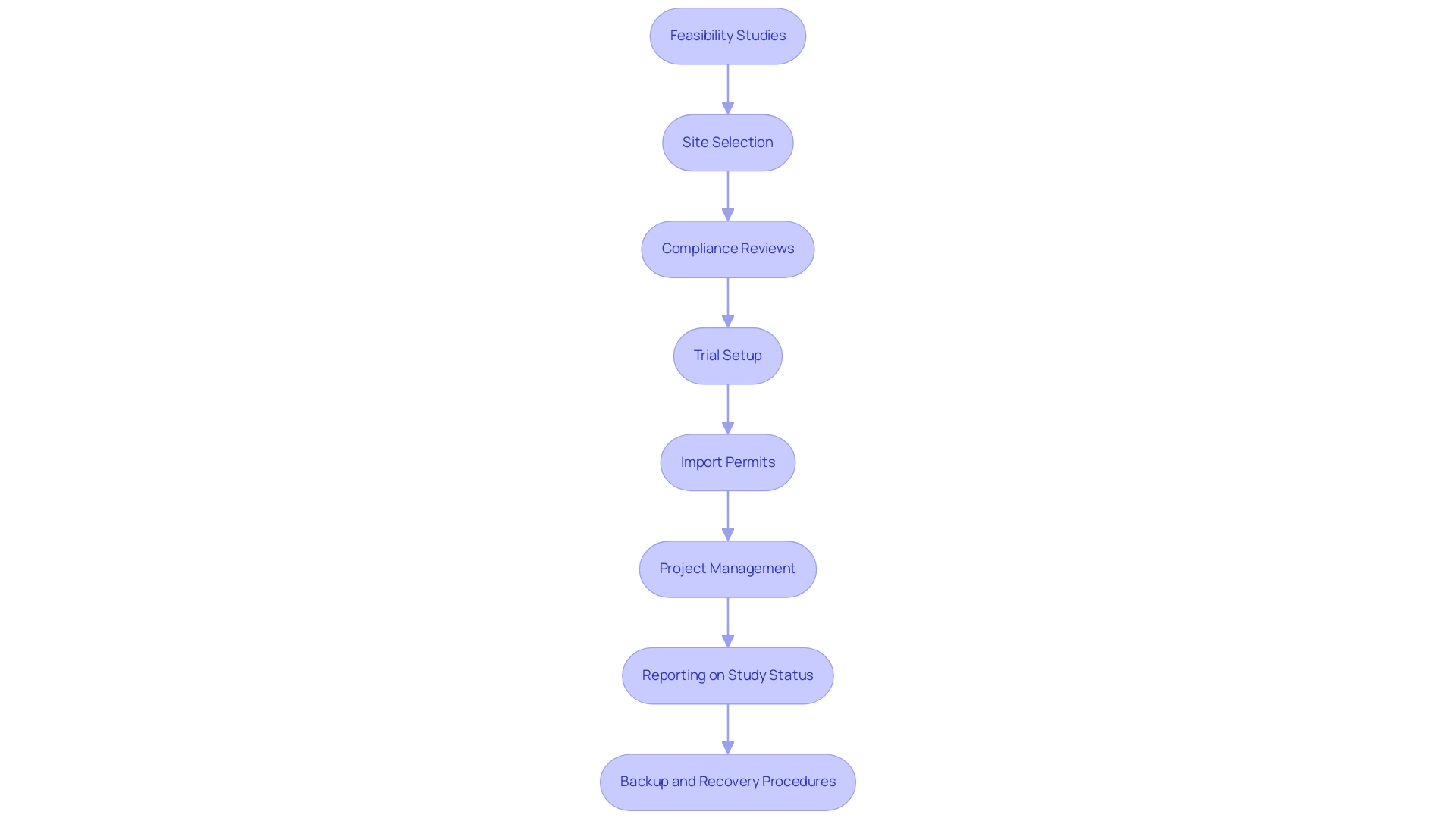
Navigating the regulatory landscape surrounding electronic source data in clinical investigations necessitates a comprehensive understanding of established guidelines and requirements. Our service capabilities encompass:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews, including review and feedback on study documents to comply with country requirements
- Trial setup
- Import permits and nationalization of investigational devices
- Project management
- Reporting on study status, inventory, and serious and non-serious adverse events
The FDA's 21 CFR Part 11 outlines specific directives regarding electronic source data in clinical investigations, emphasizing that digital records and signatures must be trustworthy, reliable, and accurate.
Compliance with these regulations is critical, as any failure to adhere can lead to significant penalties and jeopardize the integrity of research outcomes that utilize electronic source data in clinical investigations. Moreover, international guidelines like GxP (Good Practice) regulations strengthen the need for adherence to standards regarding electronic source data in clinical investigations within digital information systems. An example of the FDA's stringent approach is reflected in its record retention requirements, which mandate that both electronic source data in clinical investigations and traditional information be treated equally, ensuring that all records essential for reconstructing a clinical investigation remain accessible during inspections.
Consequently, regulated entities must implement robust backup and recovery procedures to ensure compliance with the requirements for electronic source data in clinical investigations and maintain data integrity. To stay compliant and efficient, organizations should prioritize regular updates and training focused on evolving regulatory changes, particularly regarding electronic source data in clinical investigations and the significance of these updates in the context of digital submissions. As stated by the FDA, 'Support for eCTD v4.0 digital submissions begins September 16, 2024.'
FDA will also continue to support eCTD v3.2.2 digital submissions, and it is suggested that sponsors incorporate a Study Data Standardization Plan (SDSP) for research sent to CBER, ensuring alignment with the latest FDA guidelines on digital records and signatures, particularly regarding electronic source data in clinical investigations. Notably, our Director of Regulatory Affairs, Ana Criado, brings invaluable expertise in regulatory compliance, having held leadership roles at INVIMA and providing consultancy for global companies. Her background in biomedical engineering and health economics enhances our commitment to navigating the complexities of clinical trials effectively.
Best Practices for Implementing Electronic Source Data Systems
To effectively implement digital source information frameworks, organizations should adhere to several best practices that not only streamline processes but also enhance information quality and compliance.
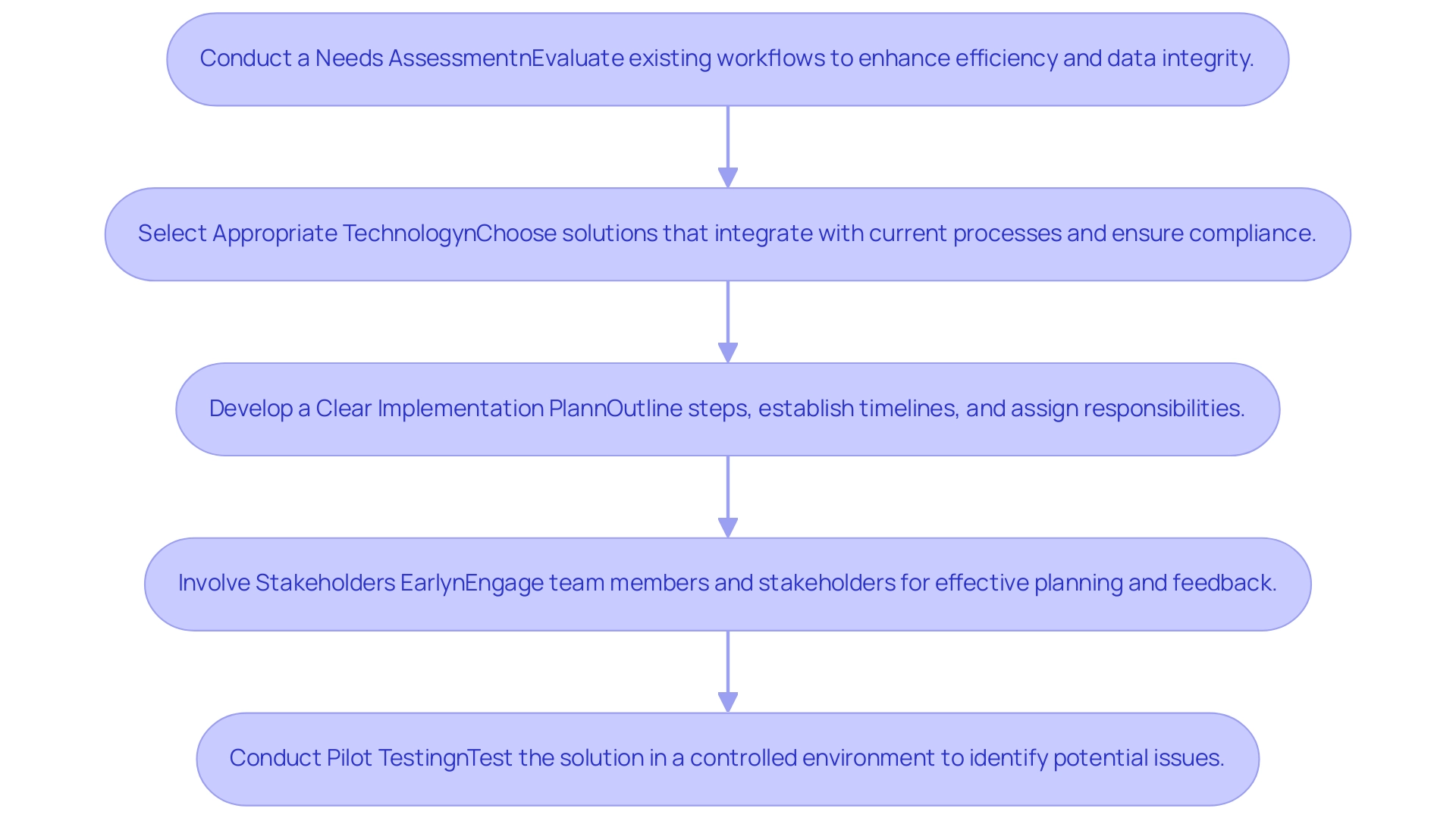
- Conduct a Needs Assessment: It is crucial to evaluate existing workflows thoroughly. This assessment identifies specific areas where electronic source data in clinical investigations can significantly enhance efficiency and data integrity.
- Select Appropriate Technology: Organizations should choose solutions that seamlessly integrate with current processes while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. The right technology selection can mitigate future interoperability challenges. As noted by Miriam Reisman, "Misaligned incentives are partly to blame for the lack of interoperability," emphasizing the need for careful technology selection that supports health information exchange (HIE).
- Develop a Clear Implementation Plan: A well-defined implementation plan should outline necessary steps, establish timelines, and assign responsibilities. This framework helps in managing expectations and enhances the likelihood of a successful transition.
- Involve Stakeholders Early: Engaging team members and key stakeholders in the planning process is essential. Early participation enables organizations to tackle issues effectively and collect valuable feedback that can influence the design and functionality.
- Conduct Pilot Testing: Before large-scale implementation, organizations should conduct pilot testing of the solution. This approach enables identification and resolution of potential issues in a controlled environment, minimizing disruptions during the broader rollout.
The challenges associated with EHR interoperability are exemplified in the case study titled "Barriers to EHR Interoperability," which highlights that despite the widespread implementation of EHRs, significant barriers persist, such as lack of cooperation among stakeholders and burdensome regulations. By 2015, only 12% of physicians completed stage 2 of meaningful use, and just 6% could share patient information across different EHR systems, underscoring the shortcomings of the HITECH Act's focus on EHR adoption rather than on HIE.
Furthermore, the Medicare health record (EHR) incentive program payment adjustment fact sheet published in 2017 provides historical context for the challenges of EHR adoption and its impact on interoperability. By following these best practices, organizations can significantly enhance the quality of information collection, improve operational efficiency, and address common challenges highlighted by critics of the HITECH Act, which will ultimately support the effective use of electronic source data in clinical investigations and lead to higher success rates in implementation and a more cohesive clinical research landscape.
Challenges and Solutions in Managing Electronic Source Data
Managing electronic source data in clinical investigations presents a range of challenges that can significantly impact integrity, user accuracy, and overall technological effectiveness. In 2024, as emphasized, information will ultimately determine business success, making it crucial to address these challenges effectively. Some of the most common challenges include:
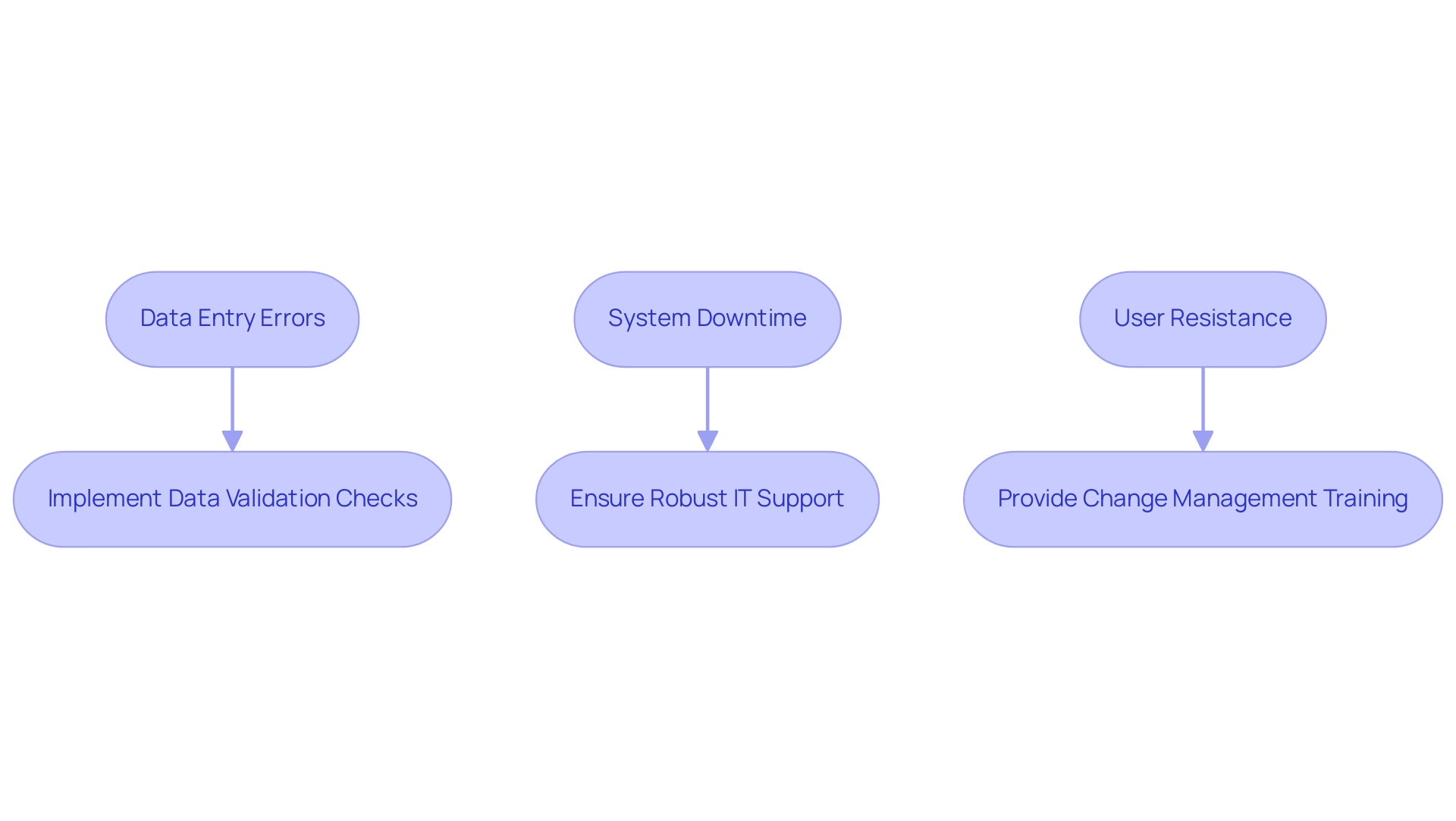
- Data Entry Errors: Manual data entry processes often lead to inaccuracies, compromising the reliability of the collected data.
- System Downtime: Unexpected technical failures can hinder access to critical information, disrupting the collection process and delaying research timelines.
- User Resistance: There can be reluctance among staff to embrace new technologies, stemming from a lack of familiarity or perceived complexity.
To effectively address these challenges, consider the following solutions:
- Implement Data Validation Checks: Automated validation processes can significantly reduce data entry errors, ensuring that only accurate data is captured.
- Ensure Robust IT Support: Establishing a strong technical support infrastructure is essential for promptly addressing technical issues and minimizing downtime.
- Provide Change Management Training: Offering comprehensive training that highlights the advantages of electronic systems can facilitate smoother transitions and foster a culture of acceptance among staff.
By proactively addressing these challenges, research professionals can enhance the quality and integrity of electronic source data in clinical investigations, ultimately leading to more successful results. As Tajammul Pangarkar, CMO at Prudour Pvt Ltd, emphasizes, "leveraging advanced technologies is crucial for navigating the complexities of modern clinical research." Furthermore, the case study on consumer concerns regarding AI and information privacy illustrates the growing importance of consumer trust in management, highlighting that while 60% of consumers worry about AI usage, 73% believe it can positively impact customer experience.
This emphasizes the necessity for strong information management practices to cultivate trust and guarantee integrity.
Training and Support: Key to Successful Electronic Source Data Management
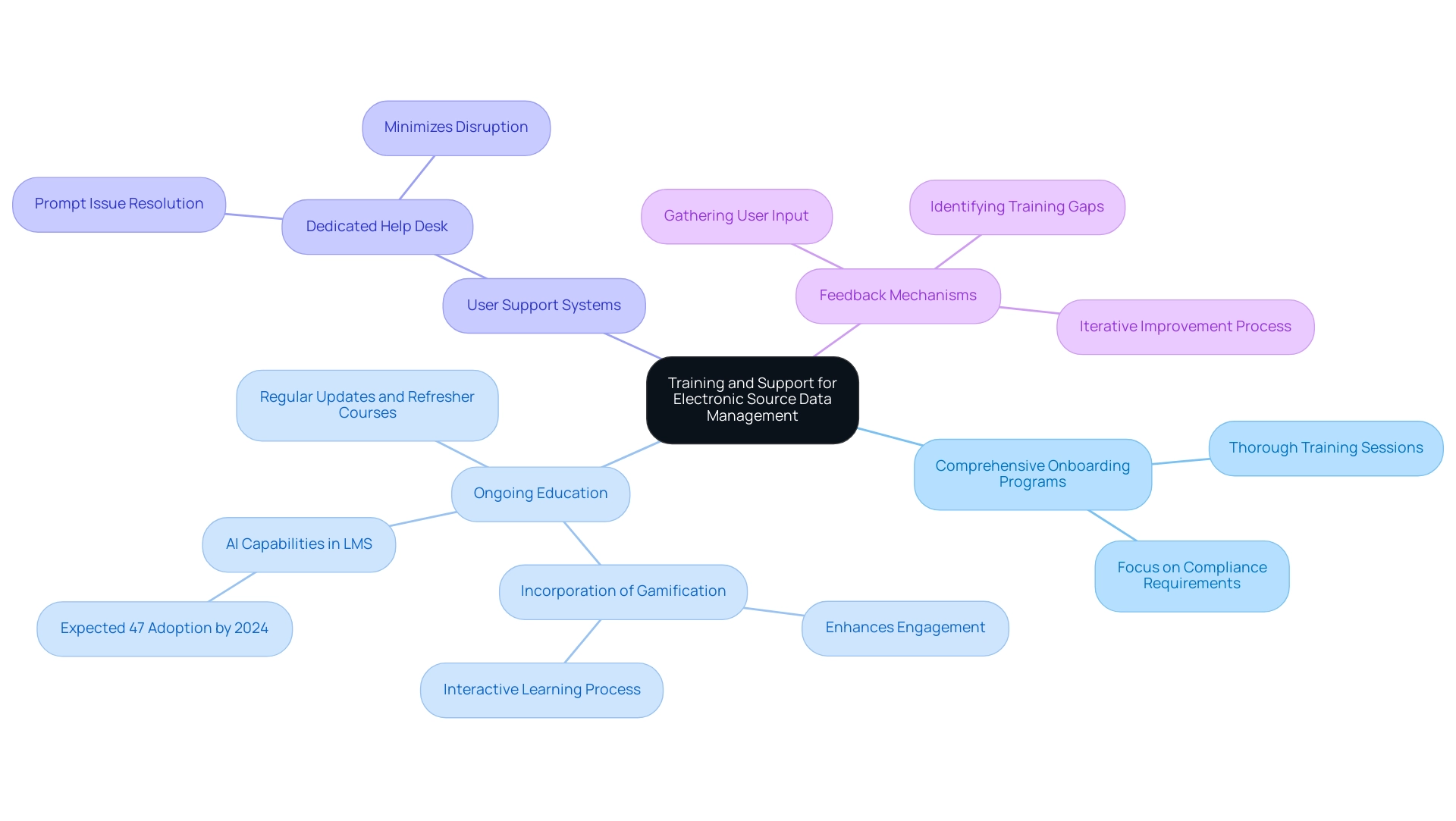
Efficient training and assistance constitute the foundation of successful management of electronic source data in clinical investigations, which is essential for upholding high standards. Key strategies to ensure staff competency include:
-
Comprehensive Onboarding Programs: Thorough training sessions are essential for new staff, focusing on electronic source data in clinical investigations and compliance requirements.
Such programs establish a strong foundation for understanding functionalities and regulatory obligations.
-
Ongoing Education: Regular updates and refresher courses are essential to keep staff informed about the latest functionalities and regulatory changes.
Incorporating gamification elements in these programs can further enhance engagement and motivation, making the learning process more interactive and effective. This continuous learning approach is particularly relevant, as recent trends indicate that by 2024, approximately 47% of Learning Management System (LMS) tools will incorporate AI capabilities, enhancing the learning experience.
-
User Support Systems: Establishing a dedicated help desk for technical assistance empowers staff to resolve issues promptly, ensuring minimal disruption to information management processes.
-
Feedback Mechanisms: Actively gathering user input allows organizations to identify training gaps and areas for improvement in system usability.
This iterative process not only enhances training effectiveness but also increases the overall quality of information collected.
The importance of training is further underscored by the findings from the 2016 Benchmark Report, which stated,
Technology has not decreased the demand for instructor-led training, but gives instructors new tools to reach learners.
Additionally, insights from the Training Industry Benchmark Report 2020, which surveyed respondents during the global Coronavirus pandemic, emphasize the critical need for robust training programs during challenging times.
By prioritizing training and support, organizations can significantly improve staff competency, ultimately leading to enhanced compliance and data quality in relation to electronic source data in clinical investigations. The recent surge in engagement among Gen Z learners—who dedicated 50% more hours to learning content in 2020, with 69% reporting increased time spent on educational resources—highlights the value of adaptive learning strategies in fostering an engaged and knowledgeable workforce, particularly through the gamification of training programs.
Conclusion
The integrity of electronic source data is fundamental to the success of clinical research, and adherence to the ALCOA-C principles is vital in achieving this goal. By ensuring that data is:
- Attributable
- Legible
- Contemporaneous
- Original
- Accurate
- Complete
organizations can enhance the quality and credibility of their findings. As highlighted, the integration of advanced technologies, including AI, alongside comprehensive clinical trial management services, further emphasizes the importance of maintaining these standards in an evolving digital landscape.
Navigating regulatory requirements is another critical aspect of managing electronic source data. Organizations must remain vigilant in complying with guidelines set forth by regulatory bodies, such as the FDA, to avoid penalties and safeguard the integrity of their research. Continuous training and support for staff are equally important, as they equip teams with the necessary skills to effectively utilize electronic systems and adapt to changes in regulatory demands.
Addressing the challenges associated with electronic data management—such as data entry errors, system downtime, and user resistance—requires a proactive approach. Implementing solutions like:
- Data validation checks
- Robust IT support
- Comprehensive change management training
will significantly enhance data quality and promote a culture of acceptance among staff.
In summary, a commitment to the ALCOA-C principles, coupled with a thorough understanding of regulatory requirements and a focus on training and support, is essential for successful electronic source data management. By prioritizing these elements, organizations can not only improve the reliability of their data but also contribute to the overall advancement of clinical research, ultimately driving better health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the ALCOA-C principles?
The ALCOA-C principles are a framework for assessing the quality of electronic source data in clinical investigations, ensuring integrity throughout the research process. They include Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, and Complete.
Why is it important for information to be Attributable?
Attributability ensures that information can be traced back to the individual responsible for its collection, promoting accountability and transparency in the research process.
How does the principle of Legible contribute to data integrity?
Legibility ensures that information is presented in a clear and understandable format, which minimizes the risk of misinterpretation and errors.
What does Contemporaneous mean in the context of the ALCOA-C principles?
Contemporaneous refers to recording information in real-time or as close to the event as possible, which is vital for preserving accuracy and reflecting actual occurrences.
Why is it necessary to retain Original information?
Retaining original information is crucial for upholding the integrity of the content and preventing unauthorized alterations.
What does it mean for information to be Accurate?
Accuracy means that the information must be precise and accurately represent the observations made during the study.
What is meant by Complete information in the ALCOA-C framework?
Completeness refers to documenting all pertinent information to ensure that the dataset is comprehensive and supports robust analyses.
What recent statistic reflects the importance of adhering to ALCOA-C principles?
As of May 2023, 94% of interventional studies have successfully posted their results, highlighting a commitment to information transparency and integrity.
How does the adoption of ALCOA-C principles enhance information integrity?
The adoption of ALCOA-C principles is associated with notable improvements in information integrity, which is crucial for advancing clinical research and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
What role do comprehensive clinical trial management services play in data quality?
Comprehensive clinical trial management services, which include feasibility studies, site selection, and project management, significantly improve the quality of digital source information.
How is AI transforming clinical trial practices?
AI is expected to enhance study efficiency by handling up to 50% of data-related tasks by 2025, reinforcing the need for adherence to ALCOA-C principles.
What regulations govern electronic source data in clinical investigations?
The FDA's 21 CFR Part 11 outlines directives for electronic source data, emphasizing that digital records and signatures must be trustworthy, reliable, and accurate.
What are the consequences of failing to comply with electronic data regulations?
Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties and jeopardize the integrity of research outcomes that utilize electronic source data.
What is the significance of record retention requirements by the FDA?
The FDA mandates that both electronic and traditional records be treated equally, ensuring that all records essential for reconstructing a clinical investigation remain accessible during inspections.
What should organizations do to maintain compliance with electronic source data regulations?
Organizations should implement robust backup and recovery procedures and prioritize regular updates and training focused on evolving regulatory changes.

