Overview
Best practices for informed consent in Latin America emphasize the need for culturally sensitive and comprehensible consent processes that respect participants' autonomy and understanding. The article outlines strategies such as using tailored consent forms, community engagement, and technology integration to enhance clarity and trust, ensuring ethical compliance and effective communication in diverse populations.
Introduction
Informed consent stands as a cornerstone of ethical clinical research, embodying the principles of autonomy and respect for participants. This intricate process requires that individuals willingly engage in studies, fully informed about the potential risks and benefits involved.
In the diverse landscape of Latin America, where cultural nuances and varying literacy levels significantly impact comprehension, the importance of informed consent is magnified. Researchers must navigate a myriad of challenges, from language barriers to regulatory compliance, all while fostering trust and transparency with participants.
By examining best practices, legal considerations, and the role of technology, this article delves into the complexities of obtaining informed consent in Latin America, ultimately underscoring its vital role in maintaining the integrity of clinical trials and protecting the rights of human subjects.
Understanding Informed Consent: Definition and Importance
Informed Consent: Best Practices for Latin America is a fundamental element of clinical research, defined as the procedure through which a participant voluntarily affirms their readiness to engage in a study after receiving detailed information about the study's purpose, procedures, potential risks, and benefits. This procedure is crucial for safeguarding human subjects, ensuring that individuals are not unwittingly involved in research activities. In the context of Latin America, where cultural diversity and varying literacy levels significantly influence comprehension, the relevance of Informed Consent: Best Practices for Latin America becomes particularly pronounced.
Researchers are assigned to establish agreement protocols that not only comply with local regulations, such as those required by INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, but also show cultural sensitivity. This approach fosters trust and transparency between researchers and participants, which is essential for bridging gaps in clinical research and innovation. However, Medtech firms frequently encounter obstacles like language barriers and professionalism, which can complicate the understanding agreement.
The ethical importance of knowledgeable agreement is further emphasized by international guidelines, such as the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice (GCP), affirming that Informed Consent: Best Practices for Latin America is a crucial ethical responsibility in clinical research. A recent assessment demonstrated that, among 135 data sets, 79 offered insight on whether interviewers were the original trial investigators, emphasizing the significance of transparency in the approval process. The Latin American Consortium for the Investigation of Lung Cancer (CLICAP), founded in 2011, aims to advance lung cancer research in the area, showcasing efforts focused on improving research methods and underscoring the significance of Informed Consent: Best Practices for Latin America to uphold trial integrity.
Furthermore, a study named 'Evaluation Methods and Their Effect on Understanding' examined how various questioning techniques influenced individuals' comprehension of the provided information, indicating that those evaluated with open-ended questions were less likely to grasp essential elements compared to those evaluated with closed-ended questions. With these considerations, the ethical implications of awareness agreements extend beyond mere compliance to embody a commitment to the dignity and autonomy of research subjects, highlighting the need for comprehensive clinical trial management services in the region.
Best Practices for Obtaining Informed Consent in Latin America
To effectively secure informed consent: best practices for Latin America, researchers should adopt a series of best practices that address cultural nuances and enhance participant understanding.
-
Culturally Tailored Agreement Forms: It is crucial to develop forms that are not only linguistically accessible but also culturally appropriate for the target demographic.
Utilizing clear, simple language and minimizing jargon can significantly enhance comprehension. This method corresponds with the conclusions of Barutta J. in Directrices Anticipadas en América Latina, which highlights the necessity for ethical considerations in agreement procedures adapted to local contexts. Considering that the share of individuals who grasped informed agreement has not risen over the last 30 years, this customized method is essential to addressing ongoing difficulties in understanding.
-
Community Engagement: Early engagement with local communities fosters trust and ensures that research initiatives resonate with community values and needs. Such involvement can lead to increased participation rates and a deeper understanding of the consent process, ultimately improving ethical compliance. By actively involving community members, researchers can adapt their strategies to the unique needs of diverse populations, including the growing elderly demographic.
-
Use of Visual Aids: Incorporating visual materials, such as diagrams or videos, can assist attendees in grasping the study's objectives and procedures, particularly among populations with varying literacy levels. This technique can bridge communication gaps and promote clearer understanding. The case study on the effect of question types highlights that those assessed with open-ended questions were less likely to understand the purpose of the study, underscoring the importance of clarity in communication.
-
Ongoing Agreement Process: It is essential to see knowledgeable approval as a continuous discussion instead of a singular occurrence. Researchers should keep individuals updated on the study's progress and encourage them to ask questions throughout, ensuring their ongoing understanding and comfort with the research.
-
Training for Research Personnel: Ensuring that all team members involved in obtaining approval are well-trained in ethical considerations, effective communication skills, and cultural competency is essential.
This preparation allows researchers to interact purposefully with individuals, cultivating an atmosphere of trust and respect.
By applying informed consent: best practices for Latin America, researchers can greatly improve the agreement process. This approach not only ensures ethical compliance but also fosters greater understanding and trust among those involved, ultimately benefiting the research outcomes and the communities engaged.
Navigating Legal and Ethical Challenges
Researchers conducting studies in Latin America must navigate a complex landscape of legal and ethical challenges while adhering to Informed Consent: Best Practices for Latin America when acquiring agreement. These challenges can manifest in various forms, such as differing age regulations, cultural perceptions of medical research, and varying degrees of participant understanding. To effectively address these complexities, researchers are advised to adopt the following best practices:
- Consult Local Regulations: It is essential to familiarize oneself with the legal stipulations for awareness specific to the country or region of study. Laws can vary greatly, impacting the agreement procedure directly.
- Ethics Committee Approval: Securing approval from a local ethics committee or institutional review board (IRB) is crucial. This step guarantees that the agreement procedure follows ethical standards and honors the rights of participants. Recent discussions underscore the importance of maintaining the credibility of medical science through strict adherence to Human Research Subjects Protections, especially in light of ethical breaches observed during health emergencies. Obtaining informed approval is necessary for all research involving human subjects during a health emergency, unless waived by an REC.
- Addressing Vulnerable Populations: Researchers must pay particular attention to vulnerable groups, including children, the elderly, and individuals with limited autonomy. Tailoring approval procedures to safeguard their rights is paramount, as highlighted by expert opinions on the ethical considerations inherent in research authorization processes. As Gress Marissell Gómez-Arteaga noted, education suggested individuals research initial method cognitive training ethics, together with promotion behavior order encourage adoption reasonable policies field values, attitudes behavior.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Implementing rigorous documentation practices is critical. Maintaining comprehensive records of the approval process—including approval forms and participant communications—enhances transparency and ensures compliance with legal frameworks. Our service capabilities encompass comprehensive review and feedback on study documents to ensure adherence to country requirements, along with trial set-up, start-up, and approval procedures, which can assist in this effort.
- Continuous Monitoring: A proactive approach involves regularly reviewing and assessing agreement processes throughout the study's duration. This commitment to monitoring ensures that the agreement remains effective, ethical, and legally compliant. Our study project management and monitoring services can support researchers in maintaining ongoing compliance and oversight, including reporting on study status, inventory, and adverse events.
For instance, a recent case study involving ozone therapy for COVID-19 raised significant ethical concerns due to the lack of qualified researchers and inadequate safety measures. After multiple rounds of review, the ethics committee maintained concerns about the study's ethical issues, ultimately leading the principal investigator to withdraw the study. This example underscores the importance of ethical oversight in research practices.
By addressing these legal and ethical challenges head-on, researchers can cultivate a more trustworthy and respectful environment for participants, thereby enhancing the overall quality and integrity of the research conducted. Leveraging comprehensive clinical trial management services, including import permits and nationalization of investigational devices, can be instrumental in navigating these complexities effectively.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Informed Consent
Technology is essential in enhancing the agreement process, especially in regions marked by diverse groups and differing literacy levels. The subsequent strategies describe effective methods to utilize technology for acquiring knowledgeable agreement:
- Electronic Approval (eApproval): Utilizing electronic approval platforms facilitates the digital review and signing of agreement forms, significantly enhancing accessibility, especially for individuals in remote locations.
- Multimedia Presentations: Implementing audiovisual tools to convey study information allows for a more engaging experience, which is particularly advantageous for individuals who may find written text challenging. Research indicates that multimedia technology notably improves patient retention of information presented during preoperative education. This enhancement highlights the importance of utilizing multimedia in the awareness process, as it can assist in ensuring individuals completely grasp the risks and benefits of their involvement.
- Mobile Applications: The development of mobile applications can provide users with continuous access to study information, including real-time updates and frequently asked questions, thus fostering ongoing communication and engagement.
- Secure Data Management: It is essential that any technology used for approval adheres to data protection regulations, thus ensuring the safeguarding of individuals' personal information and maintaining confidentiality.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Integrating feedback features within technology platforms enables researchers to collect insights from individuals regarding the agreement framework, fostering ongoing enhancement and adjustment to better meet their requirements.
A trust-based approach to agreement may more accurately represent the realities of research involvement, acknowledging that informed consent: best practices for Latin America is not simply a checkbox but rather a significant conversation between researchers and individuals. By adopting these technological advancements, researchers can develop a more efficient and participant-centered approval process. This approach not only fosters higher levels of trust and engagement in clinical research but also aligns with the ethical obligations of autonomy and justice, as highlighted in contemporary discussions on the participant-researcher relationship.
The case study on sociodemographic factors affecting agreement illustrates that younger, more educated individuals are generally more willing to agree, while racialized individuals prefer detailed options for approval, indicating the need for customized agreement approaches. As Andrzej Michalski aptly notes,
Patient approval for surgery or for high-risk methods of treatment or diagnosis means that unlawful breach of the patient’s personal interests is avoided and the patient accepts the risk of surgery and takes the brunt of it.
Therefore, the incorporation of technology in the Informed Consent: Best Practices for Latin America procedures is crucial for improving individual autonomy and overall research integrity.
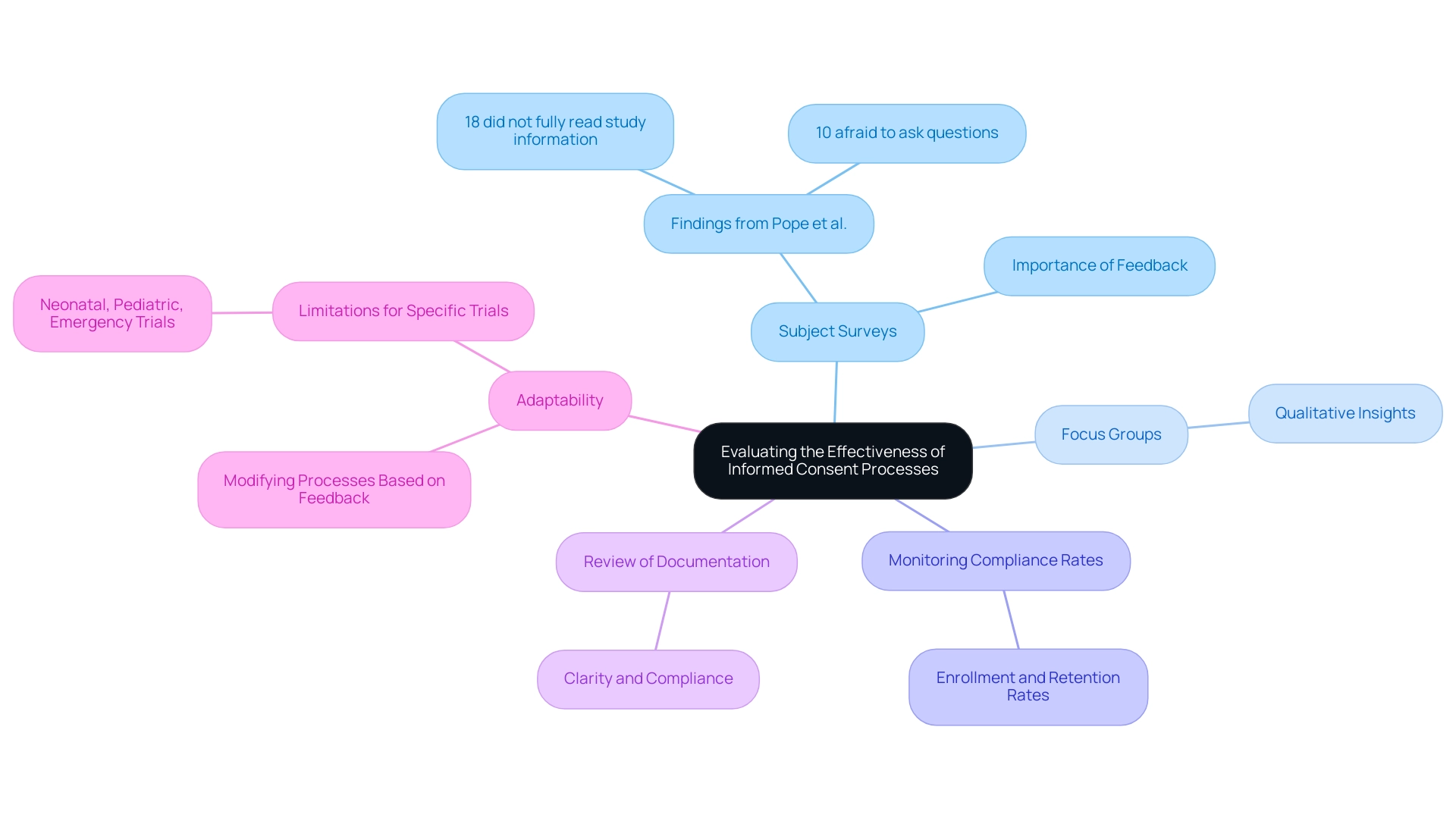
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Informed Consent Processes
To ensure the effectiveness of informed consent processes, it is essential for researchers to follow informed consent: best practices for Latin America by implementing a range of evaluation methods. These include:
-
Subject Surveys: Conducting surveys or interviews with subjects post-consent can provide critical insights into their understanding of study details.
For instance, research by Pope et al. revealed that 18% of individuals admitted they had not fully read the study information letter, with 10% expressing fear of asking questions. Additionally, a researcher reviewed the data entry for a random 20% of surveys, which bolsters the credibility of the findings.
Such feedback is invaluable for identifying areas of improvement.
-
Focus Groups: Arranging focus groups enables thorough discussions regarding individuals' experiences with the approval system, fostering qualitative insights that can result in improvements.
-
Monitoring Compliance Rates: Keeping track of enrollment and retention rates is essential, as high drop-out rates may indicate issues with the informed agreement process.
-
Review of Documentation: Regularly reviewing approval documentation ensures that it is clear, accurate, and compliant with regulatory standards. This is particularly important in high-stakes trials, where clarity can significantly influence understanding and trust.
-
Adaptability: Researchers must remain flexible, modifying approval processes based on feedback from individuals involved and evaluation results to ensure they stay relevant and effective for the target population. It is important to recognize that the findings discussed may not apply to neonatal, pediatric, or emergency patient trials requiring swift approval. For instance, the Harrison Study (1995) emphasized the efficacy of evaluation of awareness within the context of an HIV vaccine trial, where individuals showed a high comprehension of confidentiality (95-100%) and side effects (83-100%).
Additionally, the article named 'An assessment of the procedure of knowledgeable agreement: perspectives from research participants and staff,' published in Trials on August 18, 2021, highlights the continual necessity for efficient evaluation techniques in this area. By implementing these strategies, researchers can continuously refine their informed consent processes in accordance with 'Informed Consent: Best Practices for Latin America', fostering a more ethical and participant-centered approach to clinical research.
Conclusion
Informed consent represents a vital ethical foundation for clinical research, particularly within the diverse context of Latin America. As explored throughout this article, the informed consent process is not merely a formality; it embodies the principles of autonomy, respect, and transparency that are essential for safeguarding participants. The challenges faced by researchers, including cultural differences, varying literacy levels, and legal complexities, necessitate a thoughtful and tailored approach to ensure that participants fully understand their rights and the implications of their involvement in studies.
Implementing best practices such as:
- Culturally appropriate consent forms
- Community engagement
- The use of technology
can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the informed consent process. By fostering an ongoing dialogue with participants and integrating multimedia tools, researchers can improve comprehension and trust, ultimately contributing to higher participation rates and more ethically sound research practices. Moreover, addressing legal and ethical challenges—particularly for vulnerable populations—ensures that the rights of all participants are upheld.
The integration of evaluation methods further underscores the importance of continuous improvement in informed consent processes. By actively seeking feedback and adapting strategies based on participant experiences, researchers can refine their approaches, ensuring that consent remains meaningful and relevant. As the landscape of clinical research evolves, the commitment to informed consent will remain crucial in maintaining the integrity of studies and protecting the dignity of human subjects. Ultimately, a robust informed consent process not only bolsters the ethical foundation of research but also enhances the quality and credibility of scientific inquiry in the region.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is informed consent in clinical research?
Informed consent is the procedure through which a participant voluntarily affirms their readiness to engage in a study after receiving detailed information about the study's purpose, procedures, potential risks, and benefits. It is crucial for safeguarding human subjects and ensuring they are not unwittingly involved in research activities.
Why is informed consent particularly important in Latin America?
Informed consent is particularly important in Latin America due to cultural diversity and varying literacy levels that significantly influence comprehension. This makes it essential to establish agreement protocols that are culturally sensitive and comply with local regulations.
What are some challenges faced by researchers regarding informed consent in Latin America?
Researchers often encounter obstacles such as language barriers and professionalism, which can complicate the understanding of the informed consent process.
What international guidelines emphasize the ethical importance of informed consent?
The ethical importance of informed consent is emphasized by international guidelines such as the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice (GCP).
What is the role of the Latin American Consortium for the Investigation of Lung Cancer (CLICAP)?
CLICAP, founded in 2011, aims to advance lung cancer research in Latin America and showcases efforts focused on improving research methods, highlighting the significance of informed consent to uphold trial integrity.
How do questioning techniques affect understanding of informed consent?
A study found that individuals evaluated with open-ended questions were less likely to grasp essential elements of informed consent compared to those evaluated with closed-ended questions, indicating the importance of clarity in communication.
What are some best practices for securing informed consent in Latin America?
Best practices include: 1. Culturally tailored agreement forms that use clear and simple language. 2. Early community engagement to foster trust and ensure research resonates with local values. 3. Use of visual aids to enhance understanding among populations with varying literacy levels. 4. Ongoing consent processes that encourage continuous discussions and updates. 5. Training for research personnel in ethical considerations and effective communication skills.
How can implementing best practices for informed consent benefit research outcomes?
By applying best practices for informed consent, researchers can improve the agreement process, ensure ethical compliance, foster greater understanding and trust among participants, and ultimately benefit both research outcomes and the communities involved.

