Overview
The article titled "Enhancing Patient Diversity in Chilean Clinical Trials" underscores the critical importance of increasing participant diversity in clinical trials within Chile. It asserts that diverse patient representation is essential for ensuring that medical research findings are relevant and applicable across all populations. To support this claim, the article discusses various strategies, including:
- Community engagement
- Digital outreach
- Ethical practices
These strategies can significantly enhance recruitment and participation among underrepresented groups.
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of clinical trials, the significance of patient diversity cannot be overstated. As research endeavors strive to produce findings that are applicable across various demographic groups, the need for inclusive practices becomes increasingly urgent. Diverse participation not only enhances the relevance of medical research but also plays a pivotal role in addressing health disparities and fostering equity in healthcare.
Alarming statistics reveal the underrepresentation of certain populations in clinical studies, particularly in regions like Latin America, presenting a critical opportunity to enact change. By prioritizing diverse recruitment strategies and ethical practices, researchers can ensure that their work resonates with the communities they aim to serve, ultimately leading to more effective and personalized healthcare solutions.
Understand the Importance of Patient Diversity in Clinical Trials
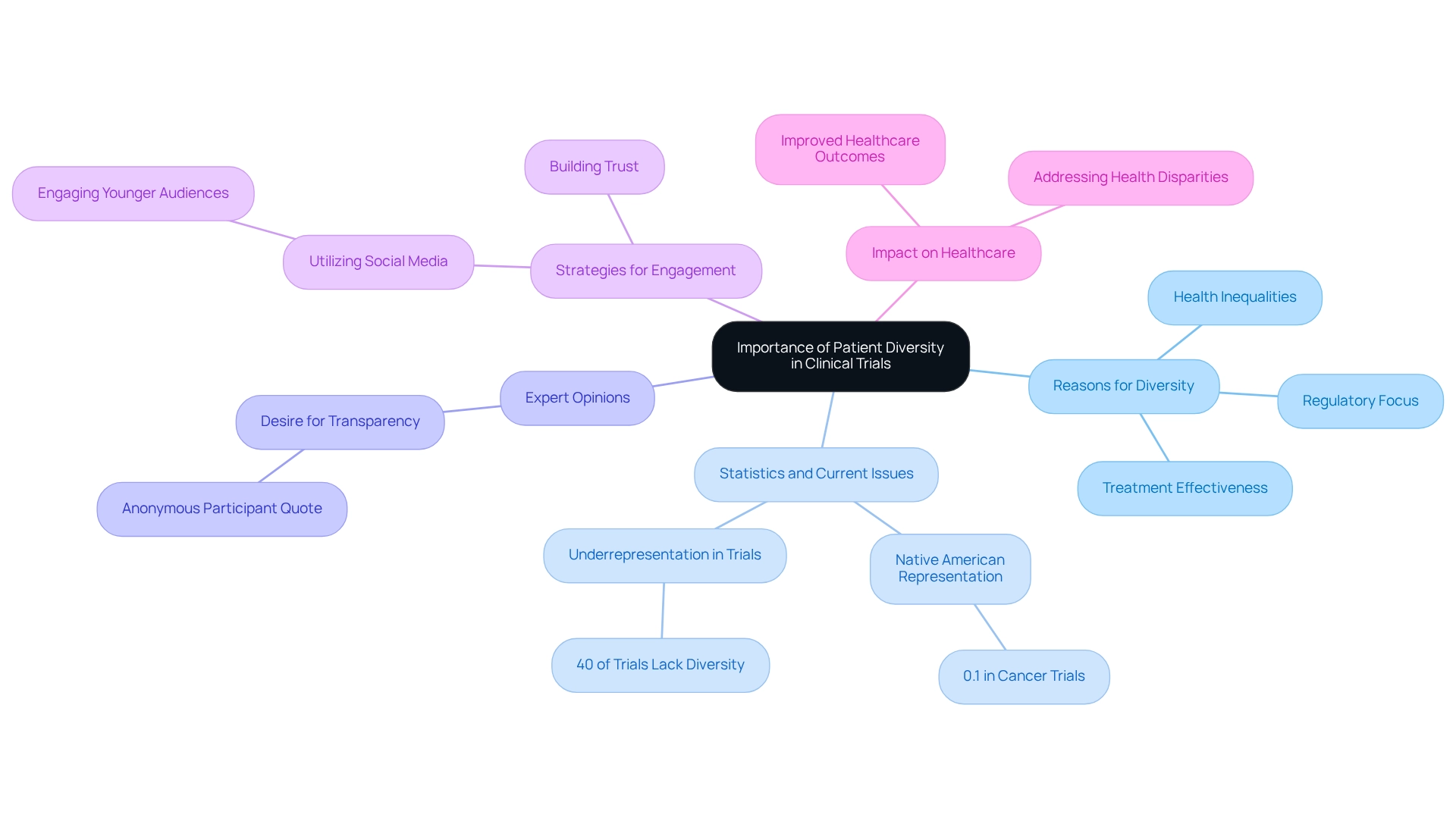
Patient variety in research studies is essential for multiple significant reasons. It guarantees that study findings are applicable to a wide range of populations, as different demographic groups may show diverse responses to treatments affected by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. For instance, investigations show that medications can exhibit varying effectiveness and safety characteristics among ethnic groups, emphasizing the importance of inclusive examination practices. Furthermore, involving varied populations in health assessments is crucial for tackling health inequalities and promoting fairness in healthcare. By examining how treatments impact various demographic groups, researchers can create more effective and personalized interventions. This method not only improves the relevance of medical studies but also corresponds with the increasing focus from regulatory agencies, like the FDA, on the significance of diversity in medical evaluations to guarantee that new therapies are safe and effective for all segments of the population.
Recent statistics highlight the urgency of this matter: in cancer treatment investigations, only 0.1% of participants were Native American, and over 40% of cancer studies in the U.S. fail to represent the incidence rates among various racial and ethnic groups. While these statistics are alarming, they also underscore a vital opportunity for Latin America, including Chile, to lead by example in promoting diversity in research. By prioritizing diverse participant recruitment, Chilean studies can better reflect the population's needs and enhance healthcare outcomes. Expert opinions further support this viewpoint, with many advocating for transparency and engagement to build trust and encourage wider involvement in research. As one anonymous participant noted, there is a strong desire for transparency and engagement to enhance healthcare decision-making. This feeling highlights the significance of incorporating trust-building approaches into research designs. Moreover, media attention, like that from Clinical Leader, plays an essential part in promoting awareness about studies in Latin America and Colombia, further stressing the necessity for varied participation. A case analysis on trust in social media for medical guidance demonstrates that younger participants are more inclined to seek health-related information online, while older demographics favor traditional sources. This variation in trust levels among different age groups highlights the need for tailored communication strategies to enhance participation across diverse populations in Latin America. For example, utilizing social media platforms to spread information about clinical trials could engage younger audiences more effectively.
Moreover, thorough clinical trial management services, including feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, are crucial in ensuring that trials are carried out efficiently and ethically. These services not only simplify the investigation process but also improve the quality and dependability of the findings, ultimately aiding patient care.
The emotional influence of Medtech analyses cannot be ignored either. These investigations frequently result in innovations that greatly enhance patients' quality of life, tackling both physical and emotional health requirements. By comprehending and incorporating these emotional elements into medical research, scholars can develop more comprehensive and effective interventions.
In conclusion, the emphasis on patient diversity in Chilean clinical trials not only enhances the research environment but also significantly contributes to promoting healthcare fairness and improving treatment results for all people. By adopting strategies that consider the distinct dynamics of the Latin American context, researchers can ensure that their investigations are inclusive and representative of the populations they aim to serve.
Implement Effective Recruitment Strategies for Diverse Populations
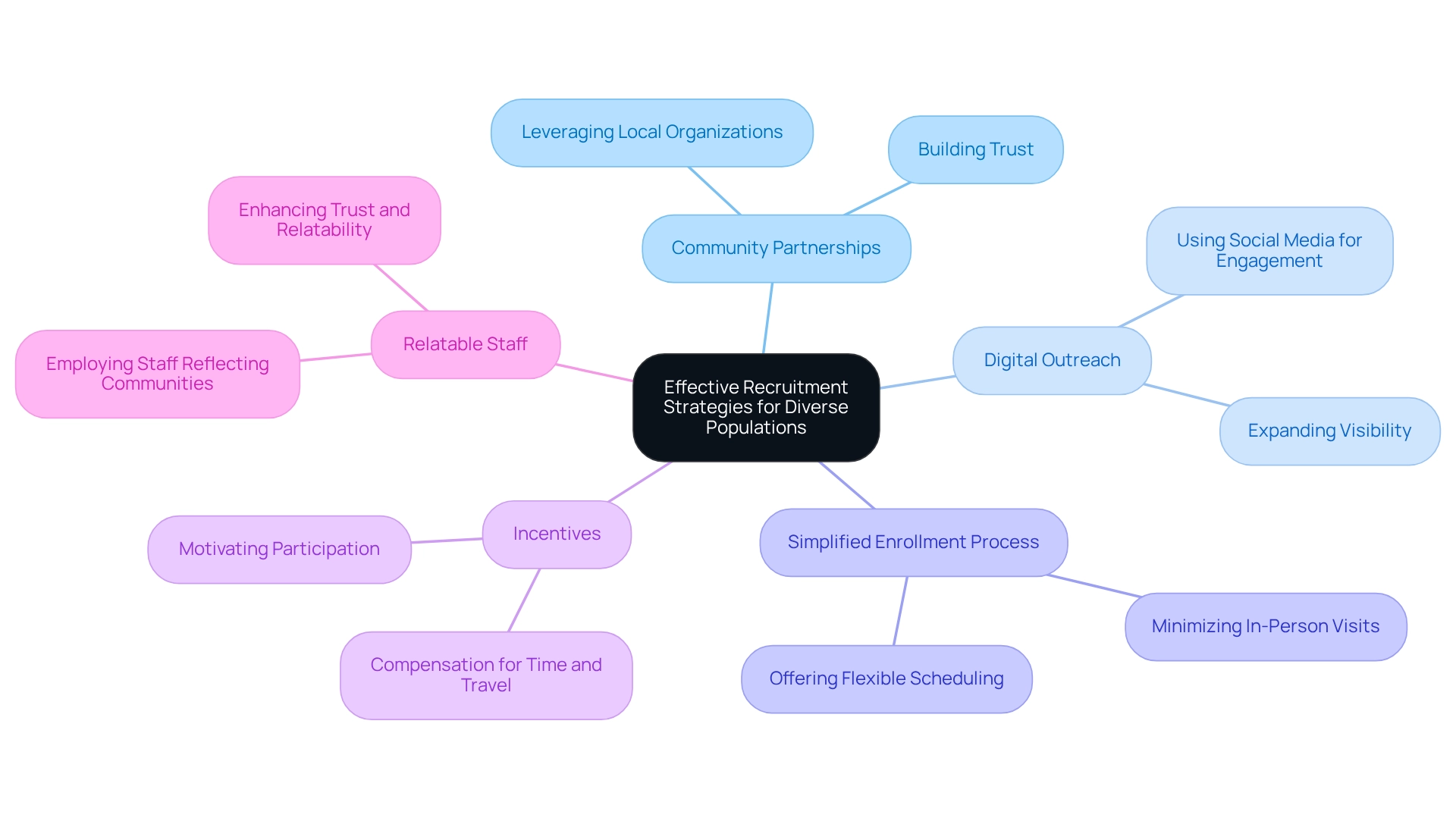
To effectively recruit varied groups for research studies, organizations must implement several key strategies. First, leveraging community partnerships is essential for building trust and facilitating outreach. Collaborating with local organizations that serve underrepresented groups enables researchers to gain insights into cultural sensitivities and improve communication. For instance, research highlighted that 1,178 women were enlisted via social media, significantly surpassing the 219 women gathered through conventional in-person techniques, illustrating the power of digital interaction.
Additionally, utilizing digital platforms and social media expands outreach and engages potential participants in their most active spaces. This approach not only enhances visibility but also fosters a sense of community among participants. Third, simplifying the enrollment process by minimizing in-person visit requirements and offering flexible scheduling options can greatly increase accessibility for diverse populations.
Moreover, providing incentives, such as compensation for time and travel, can motivate participation from underrepresented groups. Employing staff who reflect the communities being targeted further fosters trust and relatability, enhancing recruitment efforts. It is noteworthy that while the COVID-19 pandemic initially caused a slowdown in patient recruitment, it also accelerated an industry-wide shift toward new types of studies and innovative recruitment strategies.
Case studies, such as 'Engagement Strategies for Underrepresented Populations,' emphasize actionable steps for engaging these communities, including understanding their needs and building partnerships. By implementing these strategies, organizations can achieve significant progress in enhancing patient diversity in Chilean clinical trials, ultimately aiding in the advancement of medical devices and patient care. Furthermore, the workshop's suggestions for improving minority involvement in health studies provide a framework for both short-term and enduring strategies that can be enacted to reach these objectives.
Engage Communities to Foster Participation in Clinical Trials
Involving communities is crucial for increasing participation in research studies. Scientists must emphasize the importance of building strong connections with community leaders and organizations to enhance understanding of medical studies. With one-third of Gen Z males often turning to unreliable social media platforms for health information instead of consulting their physicians, providing trustworthy community engagement and education becomes imperative.
Hosting informational sessions and workshops can effectively educate community members on the benefits of participation while addressing prevalent misconceptions. Engaging community members in the design and execution of trials ensures that patient diversity in Chilean clinical trials is culturally sensitive and relevant to their needs. Furthermore, employing community health workers as liaisons can bridge gaps between researchers and participants, fostering trust and encouraging enrollment.
As Reed Tuckson, MD, states, "We have to build our skills in engagement, in trustworthiness, in countering misinformation throughout medical school learning, our residency experiences, and our continuing medical education." By actively involving communities, researchers can cultivate a more inclusive environment that not only promotes participation but also enhances the quality of data collected.
This method is essential, particularly in addressing the distinct health issues of marginalized populations, ultimately resulting in more equitable health outcomes, which underscores the significance of patient diversity in Chilean clinical trials. Moreover, researchers often hesitate to engage publicly due to fear of repercussions, as highlighted in the case analysis 'The Need for Public Engagement by Scientists.' By overcoming these challenges, researchers can effectively combat misinformation and build trust within communities.

Ensure Ethical Practices and Informed Consent in Diverse Trials
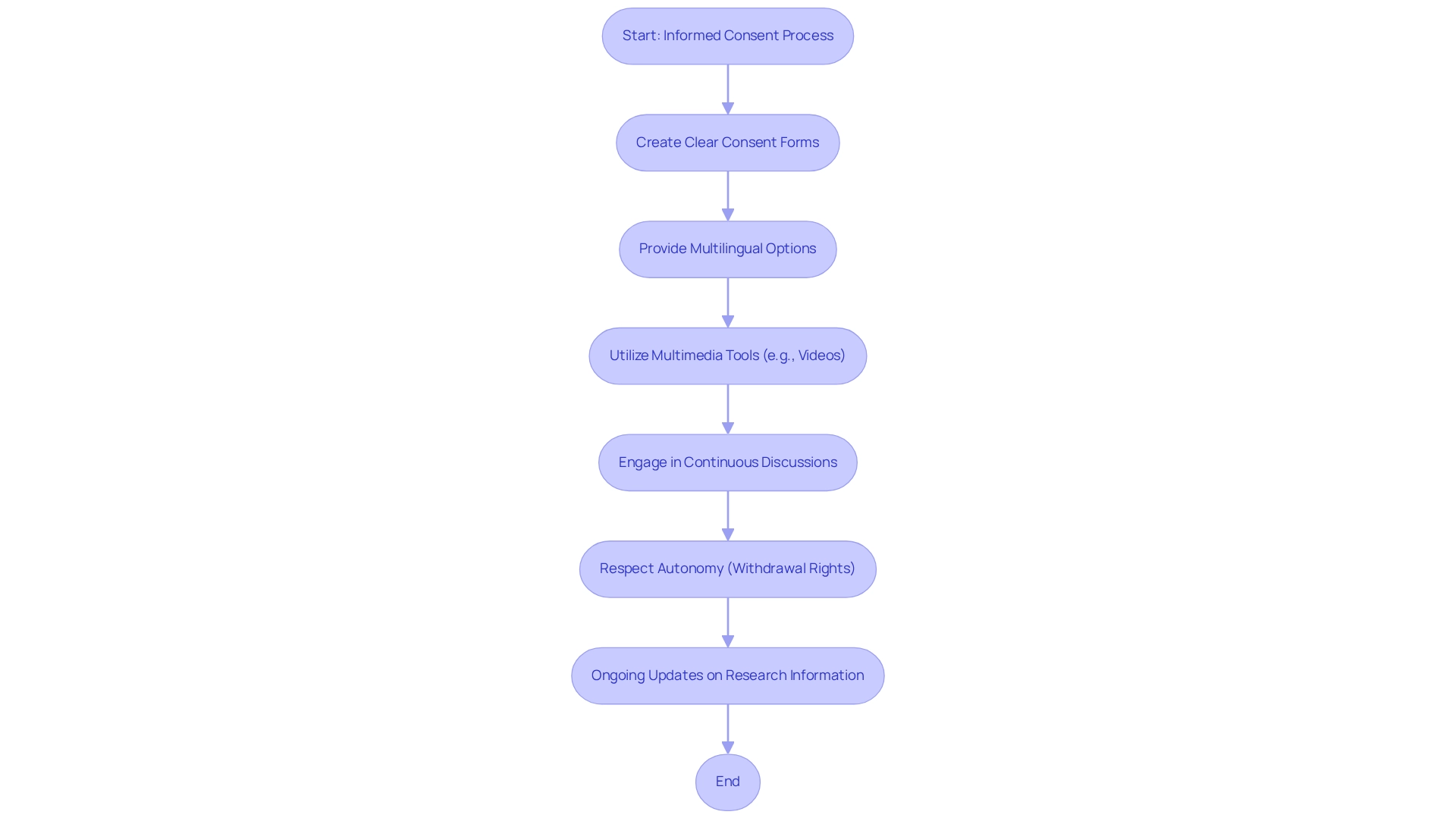
Informed consent stands as a cornerstone of ethical clinical research, particularly across diverse studies. Researchers must guarantee that consent forms are clear, concise, and available in multiple languages to effectively accommodate participants from various backgrounds. Providing thorough details regarding the research's purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits in an easily understandable manner is crucial. Furthermore, employing flow charts and instructional videos can significantly enhance understanding during the consent process. Engaging in continuous discussions with participants throughout the study allows researchers to address questions and concerns, fostering trust and empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their participation.
Ethical practices extend to respecting participants' autonomy, ensuring they can withdraw from the study at any time without penalty. This commitment to ethical considerations not only bolsters the integrity of clinical trials but also cultivates a culture of respect and transparency. The implementation of multilingual consent forms has proven effective in increasing participant comprehension, thereby enhancing the overall quality of the informed consent process. Moreover, ongoing informed consent practices, which involve regularly updating participants about new information that may influence their willingness to continue, reinforce the voluntary nature of participation and elevate ethical research practices. As highlighted in a case study on ongoing informed consent, continuous communication fosters trust and underscores the voluntary nature of participation.
By prioritizing these ethical principles—voluntariness, comprehension, and disclosure—researchers can significantly enhance the quality and inclusivity of medical trials, ultimately leading to more reliable and generalizable results that reflect patient diversity in Chilean clinical trials. As Rashmi Ashish Kadam, Quality Assurance Manager, asserts, 'Conducting a valid, meaningful, and complete informed consent process with emphasis on patient understanding and comprehension will be an important step toward inculcating 'Quality' in studies conducted in our country.' Additionally, the concept of broad consent for future research on biological samples or data is becoming increasingly relevant, underscoring the evolving nature of informed consent in clinical research.
Conclusion
Patient diversity in clinical trials is crucial for producing relevant findings that cater to the diverse health needs of various demographic groups. This inclusivity not only addresses health disparities but also enhances the effectiveness of medical interventions, promoting equity in healthcare. The underrepresentation of certain populations, especially in Latin America, presents a significant opportunity for improvement.
To enhance diversity, organizations must adopt effective recruitment strategies. These strategies include:
- Building partnerships with community organizations
- Utilizing digital platforms
- Simplifying enrollment processes
- Providing incentives
These strategies foster trust and make trials more accessible.
Engaging communities is essential for boosting participation rates. Researchers should establish strong relationships with community leaders to raise awareness and educate potential participants about the benefits of clinical trials. Designing culturally sensitive research and employing community health workers can further encourage enrollment and improve data quality.
Additionally, ethical practices and informed consent are foundational to conducting diverse trials. Clear and accessible consent processes, along with ongoing communication, build trust and empower participants throughout their involvement.
In conclusion, prioritizing patient diversity in clinical trials is vital for advancing healthcare equity and improving treatment outcomes. By implementing inclusive recruitment strategies, engaging communities, and adhering to ethical standards, researchers can ensure that trials reflect the diverse populations they aim to serve, ultimately leading to more effective healthcare solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is patient variety important in research studies?
Patient variety is essential because it ensures that study findings are applicable to a wide range of populations. Different demographic groups may respond differently to treatments due to genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
How do demographic differences affect treatment responses?
Investigations have shown that medications can exhibit varying effectiveness and safety characteristics among different ethnic groups, highlighting the importance of inclusive examination practices in research.
What role does diversity play in addressing health inequalities?
Involving varied populations in health assessments is crucial for tackling health inequalities and promoting fairness in healthcare. It allows researchers to create more effective and personalized interventions based on how treatments impact different demographic groups.
What are the statistics regarding diversity in cancer treatment studies?
Recent statistics indicate that only 0.1% of participants in cancer treatment investigations were Native American, and over 40% of cancer studies in the U.S. fail to represent the incidence rates among various racial and ethnic groups.
How can Latin America, particularly Chile, lead in promoting diversity in research?
By prioritizing diverse participant recruitment, Chilean studies can better reflect the population's needs and enhance healthcare outcomes, thus leading by example in promoting diversity in research.
What is the significance of transparency and engagement in research?
Transparency and engagement are vital for building trust and encouraging wider involvement in research. Participants express a strong desire for these elements to enhance healthcare decision-making.
How does media attention influence participation in research studies?
Media attention, such as coverage from Clinical Leader, plays a crucial role in raising awareness about studies in Latin America and Colombia, emphasizing the necessity for varied participation.
What differences exist in how various age groups seek health-related information?
Younger participants are more inclined to seek health-related information online, while older demographics tend to prefer traditional sources. This variation highlights the need for tailored communication strategies to enhance participation across diverse populations.
What are the key components of clinical trial management services?
Key components include feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, which ensure trials are conducted efficiently and ethically.
How do Medtech analyses impact patient quality of life?
Medtech analyses often lead to innovations that significantly enhance patients' quality of life by addressing both physical and emotional health requirements.
What is the overall impact of emphasizing patient diversity in clinical trials?
Emphasizing patient diversity in Chilean clinical trials enhances the research environment, promotes healthcare fairness, and improves treatment outcomes for all individuals.




