Overview
The article centers on the imperative of enhancing patient diversity in Ecuadorian clinical trials through targeted recruitment strategies, community engagement, and the navigation of regulatory and ethical considerations. It underscores the significance of adopting culturally relevant approaches and fostering trust with diverse populations as essential components for elevating participation rates.
Successful initiatives have demonstrated that increased representation from underrepresented groups leads to more equitable healthcare outcomes. This focus on diversity not only enriches clinical research but also ensures that healthcare solutions are reflective of the communities they serve.
Introduction
In the realm of clinical research, the significance of patient diversity cannot be overstated. A homogeneous participant pool can lead to skewed results that fail to represent the broader population, ultimately impacting healthcare outcomes. By embracing diversity in clinical trials, researchers can uncover vital differences in treatment efficacy and safety across various demographics, including age, gender, and ethnicity. This pursuit not only enhances the relevance of findings but also fosters trust within communities, encouraging wider participation.
As the landscape of clinical trials evolves, the call for targeted recruitment strategies and community engagement becomes increasingly urgent, paving the way for a more inclusive approach that benefits all.
Understand the Importance of Patient Diversity in Clinical Trials
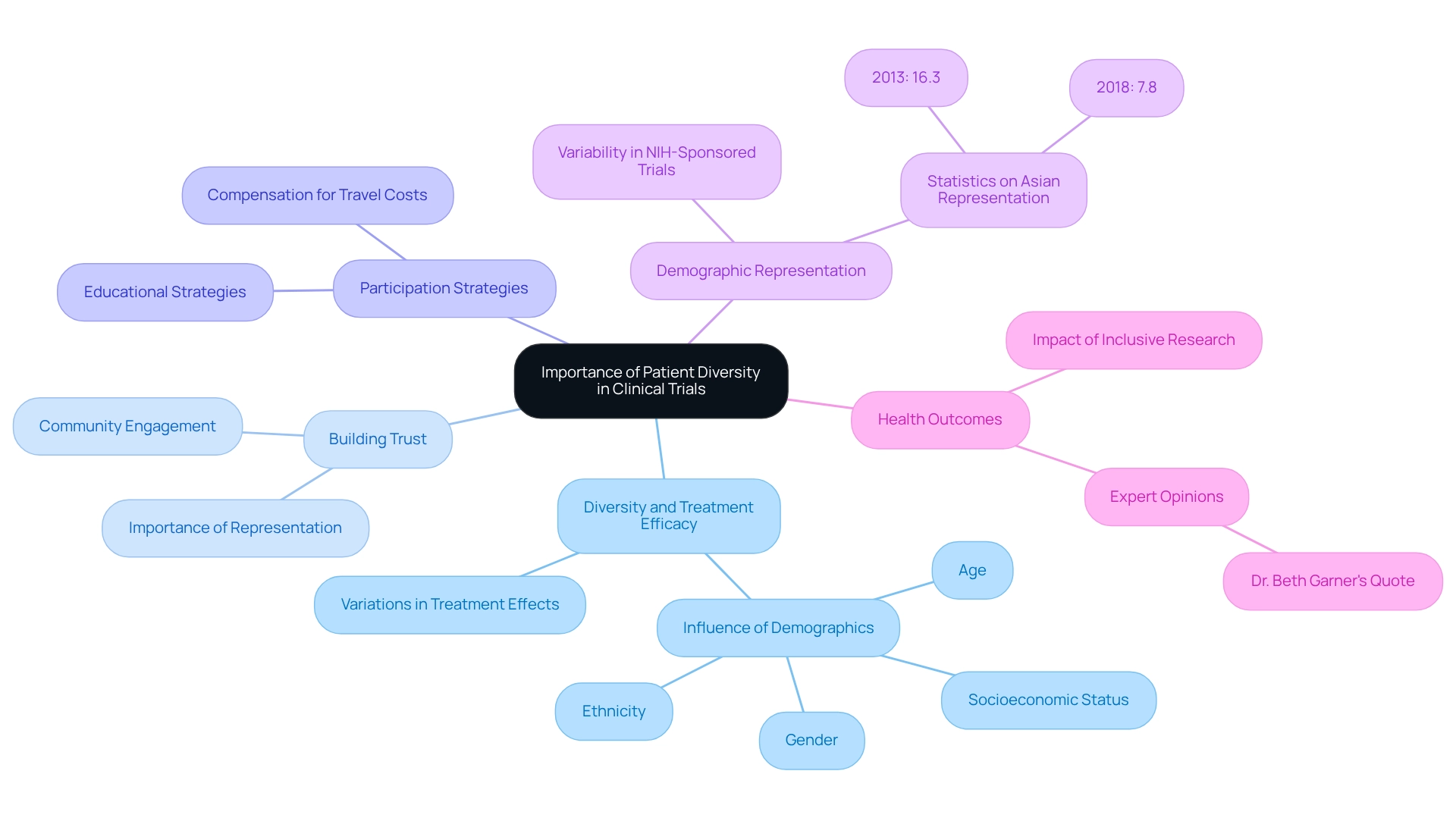
Variety among participants in medical studies is essential for guaranteeing that findings are applicable to the whole population. By incorporating diverse participant groups, researchers can investigate variations in treatment efficacy and safety across demographics such as age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. Recent studies indicate that certain medications exhibit different effects among various racial and ethnic groups, influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. This diversity not only helps identify potential disparities in treatment outcomes but also promotes more equitable healthcare solutions.
Furthermore, promoting varied representation cultivates trust among communities, which is vital for encouraging involvement in medical research. Educational strategies and compensation for travel costs have proven effective in increasing participation from underrepresented groups, thereby enhancing the overall quality of data collected. The statistic regarding Asian participant representation, which dropped from 16.3 percent in 2013 to just 7.8 percent in 2018, highlights the urgent need for targeted strategies to improve enrollment from minority populations.
The variability in participant diversity across research studies, as emphasized in investigations like the NIH-sponsored ones, underscores the difficulties encountered in attaining representative enrollment, particularly concerning patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials. As Dr. Beth Garner, Chief Scientific Officer of Ferring Pharmaceuticals US, aptly states, "We all know that when women are healthy, everyone is healthy. That's why it's important to include individuals in research trials who resemble the people who will be using your product once it's approved." This viewpoint strengthens the case for inclusive studies.
Moreover, the dedication of WBA leaders and partners to enhancing health outcomes for everyone highlights the broader significance of diversity in medical studies. As we approach 2025, the importance of patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials remains crucial, with expert views indicating that inclusive research results in improved health outcomes for all.
Implement Targeted Recruitment Strategies for Diverse Populations
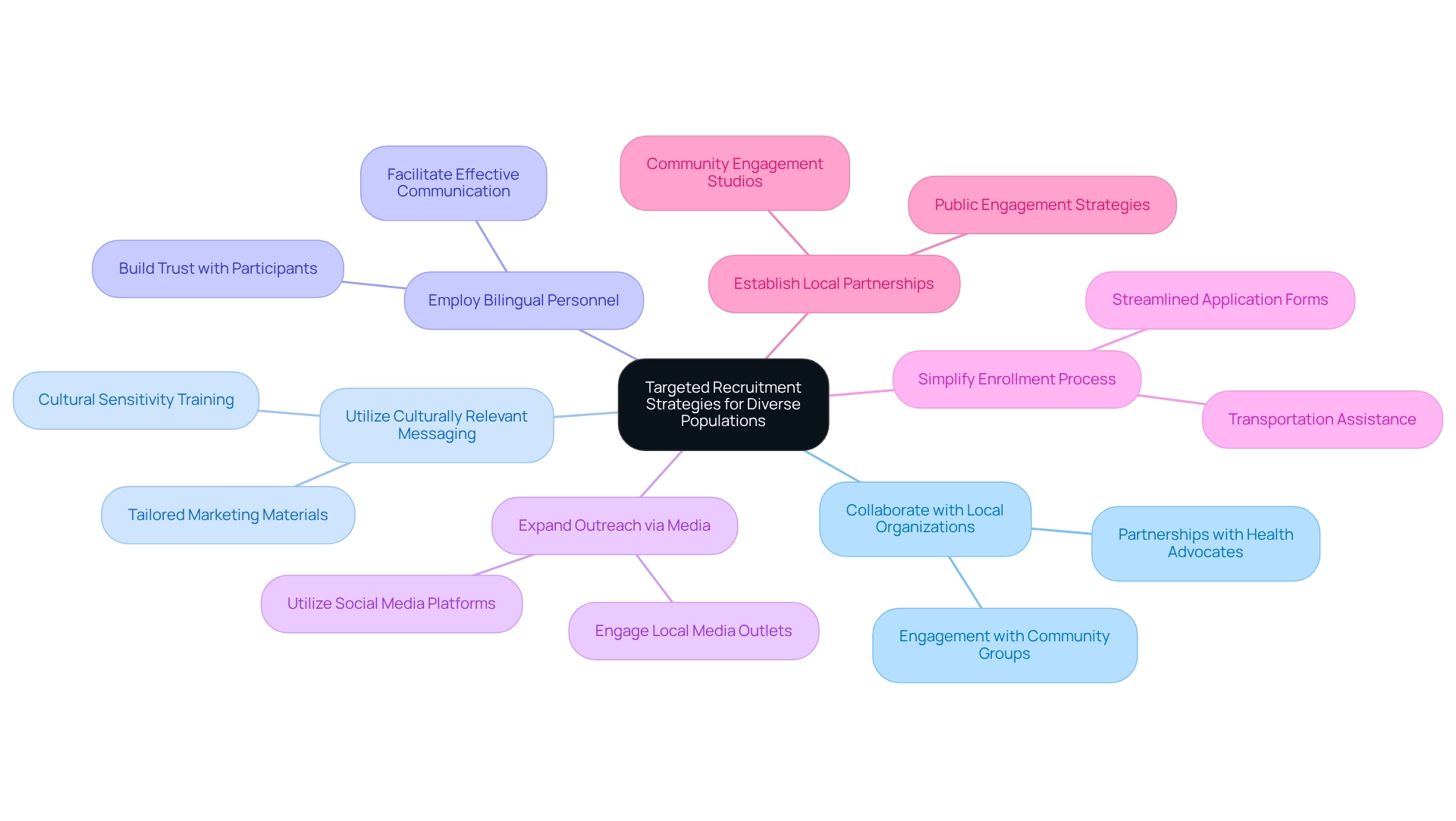
Improving patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials necessitates the implementation of targeted recruitment methods. Essential strategies include:
- Recognizing and collaborating with local organizations that cater to diverse populations
- Utilizing culturally relevant messaging
- Employing bilingual personnel to facilitate effective communication
Engaging with social media platforms and local media outlets can further expand outreach efforts. As Thompson articulated, 'Enhance inclusivity in studies more quickly and sustainably by concentrating on the populations you are missing,' highlighting the critical need for targeted recruitment initiatives that emphasize patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials.
For example, a successful initiative in Ecuador illustrated that partnering with local health advocates markedly increased participation from indigenous populations by addressing their specific needs and concerns. This aligns with findings from the case study titled 'Engagement of Populations in Research,' which underscores the importance of public involvement in enhancing recruitment and retention of underrepresented groups in health studies.
Moreover, simplifying the enrollment process and providing transportation assistance can effectively reduce barriers to participation, thereby fostering greater engagement from diverse groups in clinical trials, which is crucial for improving patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials.
Furthermore, as emphasized by industry leaders, the implementation of public engagement strategies is essential. For instance, establishing local partnerships and ensuring that marketing materials are culturally sensitive can bolster trust and communication with potential participants. The efficacy of these strategies is underscored by the establishment of engagement studios to evaluate recommendations, which has proven advantageous in enhancing diversity.
However, it is vital to remain vigilant about common pitfalls in these efforts, such as miscommunication or lack of trust among groups, which can impede recruitment. Proactively addressing these challenges will enhance the success of targeted recruitment strategies.
Foster Community Engagement and Partnerships for Enhanced Participation
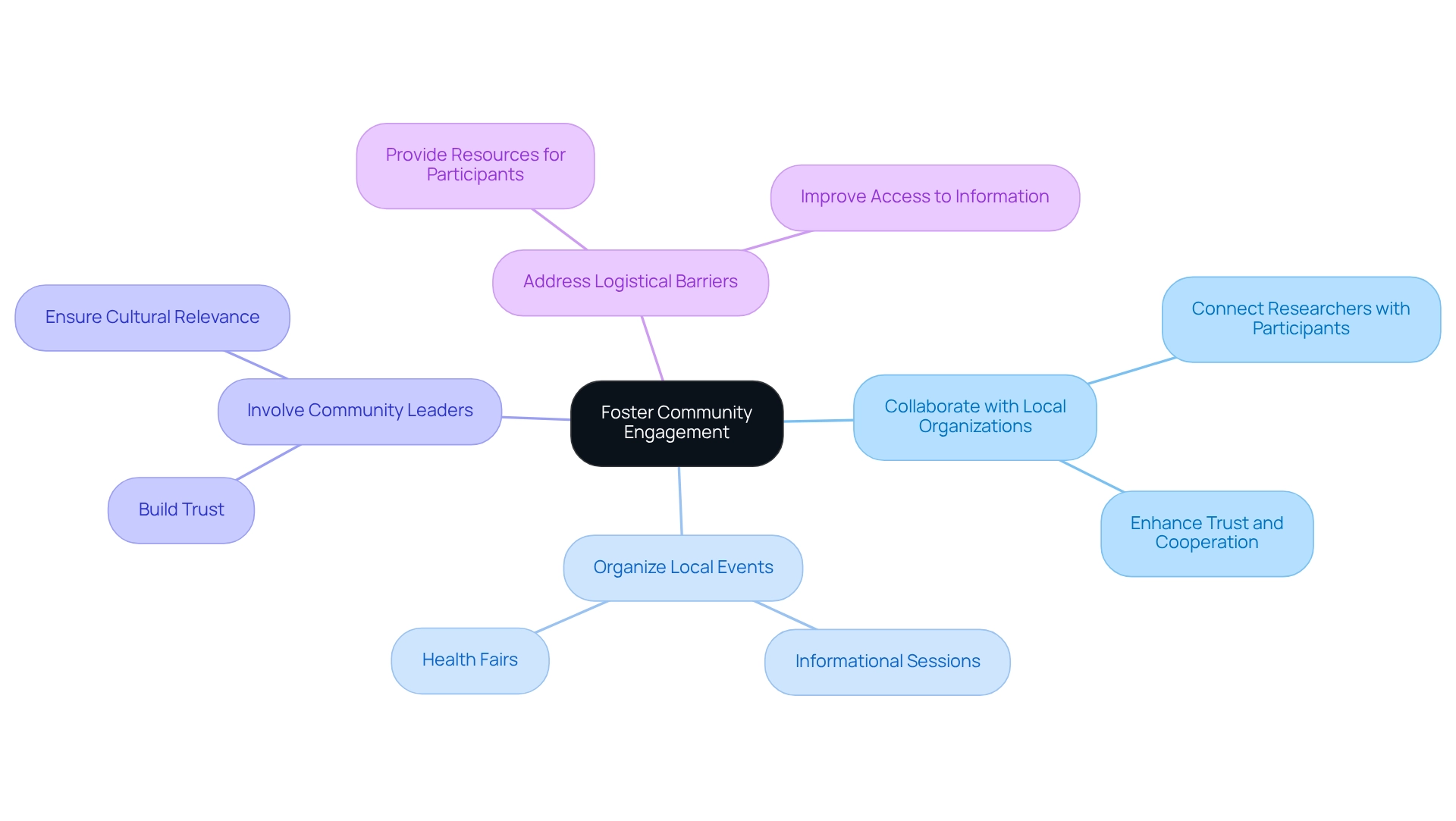
Encouraging public involvement is essential for increasing participation in research studies. Forming collaborations with local organizations, healthcare providers, and leaders in the area effectively connects researchers and potential participants. Involving groups through informational sessions, workshops, and health fairs raises awareness about the importance of research studies and helps clear up misunderstandings. For instance, bioaccess™ and Caribbean Health Group's partnership aims to establish Barranquilla as a premier location for medical studies in Latin America, with support from Colombia's Minister of Health, underscoring the potential for enhanced local engagement in investigative initiatives.
Statistics indicate that among 32,000 participants in a medical study, only 6% were Hispanic, highlighting the pressing necessity for patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials. As Bessie A. Young, MD, MPH, emphasizes, "We must do more to enhance diversity in medical studies as a scientific group and need to create and adhere to a strategy that can demonstrate effective involvement of populations at the start of investigation."
Moreover, engaging local members in the planning and execution of trials ensures that the study is culturally sensitive and relevant, thus improving participation rates. This approach not only addresses logistical obstacles—such as transportation and access to information—but also fosters trust and cooperation, which are vital for the success of research focused on patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials.
To effectively foster community engagement, consider the following strategies:
- Collaborate with local organizations to reach potential participants
- Organize local events to inform the public about research studies
- Involve community leaders in the research process to build trust
- Address logistical barriers by providing resources and support for participants
Furthermore, bioaccess™ offers extensive research management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance assessments, setup, import permits, project oversight, and reporting. By implementing these strategies and utilizing their services, researchers in healthcare can enhance participation and ensure that studies accurately reflect the populations they intend to serve, ultimately supporting the success of initiatives like those led by bioaccess™ in Colombia.
Address Regulatory and Ethical Considerations for Inclusive Trials
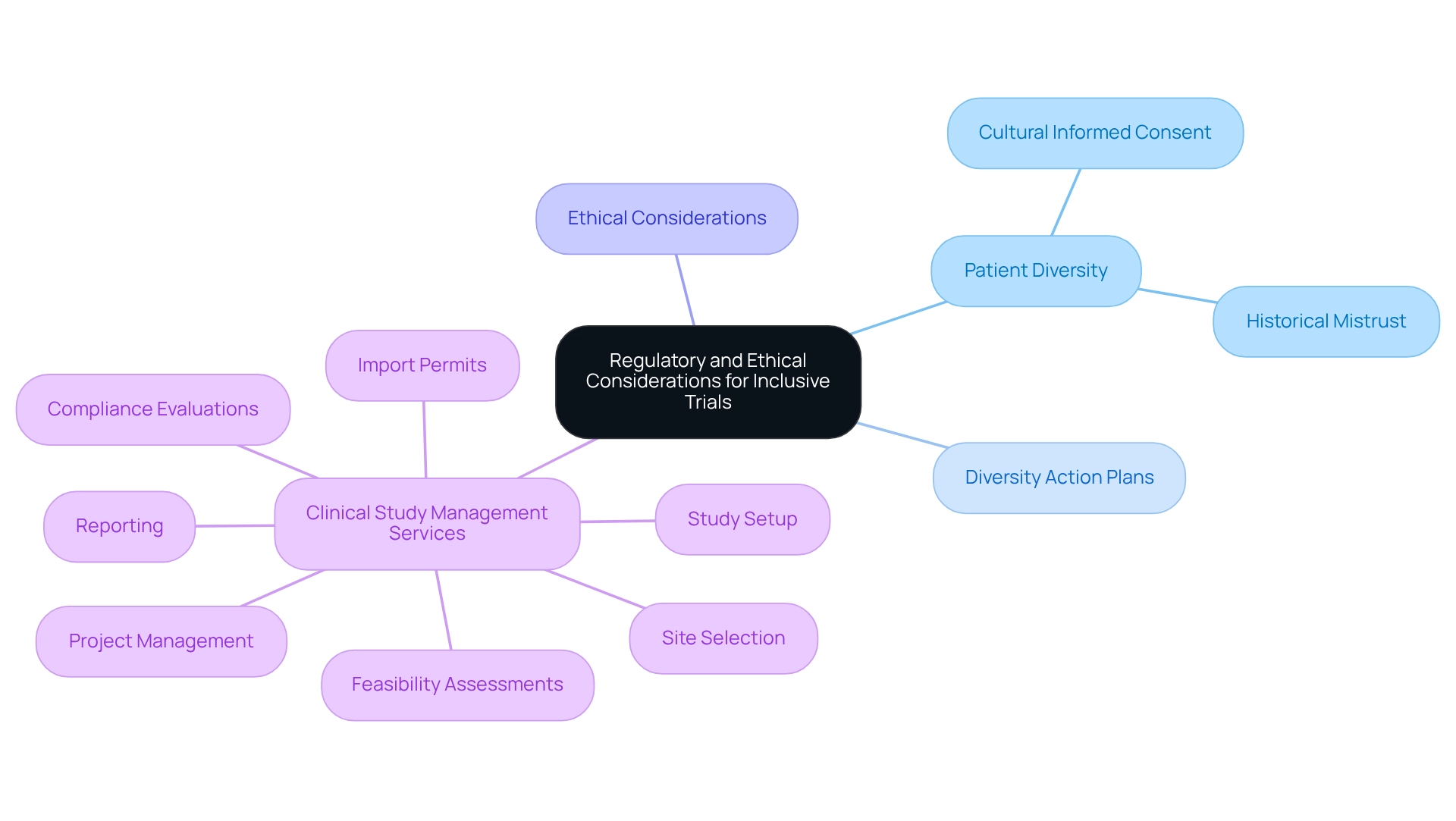
Addressing regulatory and ethical considerations is essential for conducting inclusive research studies. Adhering to directives from regulatory agencies, including the FDA, underscores the significance of patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials within study populations.
To ensure patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials, researchers must create diversity action plans that outline methods for recruiting underrepresented groups, ensuring that informed consent procedures are culturally suitable and reachable.
At bioaccess, our extensive clinical study management services encompass:
- Feasibility assessments
- Site selection
- Compliance evaluations
- Study setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
These capabilities assist researchers in managing the intricacies of regulatory requirements and ensuring that patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials is represented, making studies inclusive of varied populations.
Ethical considerations involve recognizing and tackling historical mistrust among underrepresented groups. This can be effectively managed through clear communication and active participation in the process. Community-focused studies demonstrate that involving local stakeholders to address ethical issues significantly enhances trust and readiness to engage.
By employing familiar environments and engaging community leaders, these trials not only enhance patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials but also cultivate a cooperative atmosphere that respects the distinct needs of varied populations.
Furthermore, the quest for zero fetal risk in clinical studies is complex, as it is unachievable and can unintentionally present considerable dangers to maternal and fetal health. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) emphasizes that studies conducted during pregnancy are crucial for examining interventions targeted at conditions specific to this population.
Their support for the autonomy of pregnant individuals in research participation underscores the importance of ethical guidelines that prioritize informed consent and respect for individual choices. This autonomy impacts the informed consent process, as it requires researchers to ensure that participants fully understand the implications of their involvement, emphasizing the importance of patient diversity in Ecuadorian trials.
Conclusion
Patient diversity in clinical trials transcends mere fairness; it is critical for the integrity and applicability of medical research. By integrating participants from diverse demographics, researchers gain invaluable insights into how different groups respond to treatments, ultimately leading to more effective and equitable healthcare solutions. The alarming statistics reflecting the decline in representation, especially among Asian populations, highlight the urgent necessity for targeted recruitment strategies that engage and empower underrepresented communities.
Implementing these strategies mandates collaboration with local organizations and community leaders to cultivate trust and facilitate participation. By addressing barriers such as logistical challenges and cultural sensitivities, researchers can foster an environment that encourages greater involvement from diverse populations. The success of initiatives in regions like Ecuador exemplifies how focused efforts can yield significant improvements in participant diversity.
Moreover, ethical considerations are paramount in this endeavor. Researchers must adeptly navigate regulatory guidelines while simultaneously addressing historical mistrust among marginalized communities. By promoting transparent communication and community engagement, clinical trials can evolve to become more inclusive and respectful of participants' unique needs and backgrounds.
In summary, the journey toward inclusive clinical research is multifaceted, encompassing strategic recruitment, community engagement, and ethical diligence. As the healthcare landscape continues to transform, embracing diversity in clinical trials is essential for generating relevant findings that benefit all populations. By committing to these principles, the research community can ensure that future medical advancements are safe, effective, and equitable for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is variety among participants in medical studies important?
Variety among participants is essential to ensure that study findings are applicable to the entire population. It allows researchers to investigate differences in treatment efficacy and safety across demographics such as age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status.
How does participant diversity impact treatment outcomes?
Participant diversity helps identify potential disparities in treatment outcomes, as certain medications may have different effects among various racial and ethnic groups due to genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
What are some strategies to increase participation from underrepresented groups in medical research?
Effective strategies include educational initiatives and compensating for travel costs, which have been shown to enhance participation from underrepresented groups and improve the overall quality of collected data.
What statistic highlights the need for improved enrollment from minority populations?
The representation of Asian participants in medical studies dropped from 16.3 percent in 2013 to just 7.8 percent in 2018, indicating an urgent need for targeted strategies to improve enrollment from minority populations.
What challenges are faced in achieving representative enrollment in research studies?
Challenges include variability in participant diversity across research studies and difficulties in attaining representative enrollment, particularly in trials conducted in specific regions, such as Ecuador.
Why is it important to include individuals in research trials who resemble the end users of the product?
Including individuals who resemble the end users is crucial because it ensures that the research outcomes are relevant and applicable to the population that will use the product once approved, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
What is the broader significance of diversity in medical studies?
The broader significance lies in the commitment of leaders and partners to improve health outcomes for everyone, as inclusive research is linked to enhanced health outcomes for all populations.




