Introduction
The Role of Clinical Evaluation in Ensuring Safety and Efficacy
The clinical evaluation process plays a crucial role in verifying the safety and efficacy of medical devices. It involves a thorough appraisal of clinical data from various sources, such as clinical investigations and scientific literature, to construct a robust profile of the device's performance. Transparency is key during this evaluation, as it affects risk assessment and patient outcomes.
Furthermore, clinical evaluations must simulate real-world conditions to optimize user profiles and understand critical tasks and hazard scenarios. Post-market reporting of adverse events and product problems is also an integral part of the evaluation process. The insights provided by industry professionals emphasize the need for a comprehensive approach to risk management and clinical evaluation.
The Role of Clinical Evaluation in Ensuring Safety and Efficacy
The clinical evaluation process is pivotal in verifying that medical devices maintain their promised safety and efficacy throughout their lifecycle. This thorough appraisal of clinical data encompasses an array of sources, including clinical investigations, post-market surveillance, and scientific literature, to construct a robust profile of the device's performance.
It is during this evaluation that the device's advantages and potential hazards are meticulously weighed. A key aspect of this process is transparency, which entails the clear communication of information about the medical device, including its intended use, development, and performance, as well as the logic behind its operation.
This transparency is crucial as it affects risk assessment and patient outcomes. The clinical evaluation process must consider the needs of the intended audience and the context in which the device will be used, and it must employ the most effective methods and timing for communication.
Moreover, clinical evaluations must simulate the test environment and patient interaction with the device to optimize user profiles and understand critical tasks and hazard scenarios. This simulation is guided by standards such as IEC 62366-1 and the FDA's guidance document on applying human factors and usability engineering to medical devices.
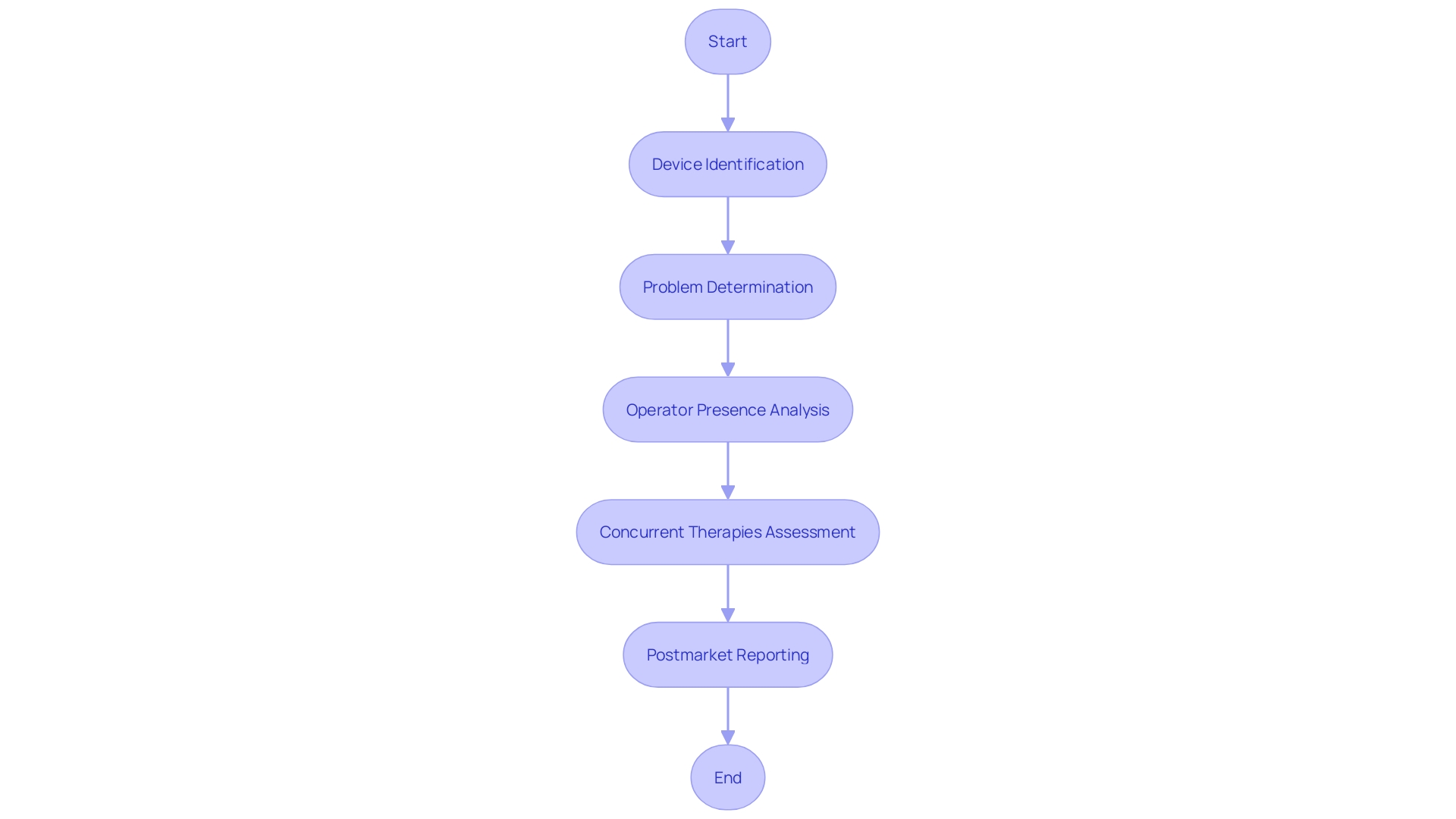
It involves replicating the actual conditions under which the medical device will be used, considering factors such as lighting, temperature, and noise, to ensure the device performs as expected in real-world settings. In addition to these rigorous protocols, post-market reporting of adverse events and product problems is an integral part of the clinical evaluation. This reporting includes detailed information such as the device type, manufacturer, brand name, and any issues encountered during operation, such as defects or malfunctions. It is essential to ascertain whether other therapies being used may have contributed to any reported event. Feedback from industry professionals, such as those provided by MedTech Safety, underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to risk management and clinical evaluation. These insights highlight the need for practical strategies and hands-on examples that go beyond the mere explanation of standards, enabling a deeper understanding of the complexities involved in ensuring medical device safety and efficacy.
Key Components of a Clinical Evaluation Report (CER)
The Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) serves as a cornerstone in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices. It is a meticulously crafted document that encapsulates the assessment of a device's clinical performance and its potential risks, presented in a structured format.
The report commences with a Device Description, presenting a comprehensive overview of the device's design, purpose, and technical attributes. This is followed by Clinical Data, which is gathered from an array of sources such as clinical trials, post-market surveillance, and scholarly literature.
It is here that the data is scrutinized to affirm the device's performance. A critical component of the CER is the Risk Assessment, where potential hazards associated with the device are identified and strategies to mitigate these risks are evaluated.
This assessment is crucial for maintaining patient safety and upholding product integrity. In parallel, the Benefit-Risk Analysis offers a balanced examination of the device's advantages against its risks, taking into account the patient demographics, intended application, and alternative solutions. Finally, the Clinical Evidence Summary consolidates all the clinical findings, encapsulating study methodologies, outcomes, and interpretations. This summary is not merely a collection of data; it is the narrative that supports the device's claims of safety and efficacy through rigorous analysis. The CER thus becomes an indispensable tool, accepted by regulatory authorities and Notified Bodies, that reflects the thorough investigation and substantiation of a medical devices clinical validity.
Importance of Robust Clinical Evidence in CERs
The clinical evaluation process is a cornerstone in the lifecycle of medical devices, from development to market delivery and beyond. It necessitates a meticulous approach to collecting, analyzing, and presenting clinical data in a Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) that meets the regulatory standards of authorities and Notified Bodies. This process involves a series of critical steps, including conducting thorough literature searches, understanding the current state of the art, and performing a comprehensive risk-benefit assessment of the data.
Mary-Ann from NAMSA, a leader in medical writing services, emphasizes the importance of assembling clinical evidence that is not only robust but also aligns with regulatory requirements. This includes preparing CERs and performance evaluation reports (PERs) that reflect a deep understanding of the medical device's clinical impact. Moreover, the clinical evaluation is integral to the medical device's development, ensuring that the safety and efficacy are continually assessed even after the product enters the market.
As per the insights from Kaplan, a researcher in clinical research standards, the FDA's recognition of a novel drug's approval based on substantial evidence—historically involving at least two well-controlled clinical investigations—underscores the significance of rigorous clinical evidence. Although the 21st Century Cures Act of 2017 has provided some flexibility, allowing for a single trial in certain cases, the underlying requirement for high-quality clinical data remains unchanged. Through case studies and template documents, healthcare professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the clinical evaluation process, ensuring they are equipped to produce clinical data evidence that is acceptable, reliable, and conducive to informed decision-making concerning medical devices.
Benefits and Risks: A Balanced Appraisal
In the dynamic world of medical device innovation, where cutting-edge treatments and technological breakthroughs are transforming patient care, the importance of a thorough clinical evaluation cannot be overstated. This evaluation is not just about recognizing the health benefits or quality-of-life improvements that a device may offer, or even the potential for reducing healthcare costs.
It is equally imperative to rigorously assess and address the risks that come with these advancements, such as adverse events or device malfunctions, to uphold patient safety. Classifying devices according to their risk levels, as done by the FDA, helps streamline the regulatory process and ensures that high-risk devices like pacemakers receive the scrutiny they deserve.
The FDA's three-tier classification system, from low-risk class one to high-risk class three, exemplifies the meticulous approach required to navigate the regulatory landscape, where approximately 10% of devices fall under the most stringent controls. As medical devices become more digitized and complex, keeping abreast of regulatory updates is crucial for manufacturers to avoid delays in bringing their products to market. This balanced scrutiny of benefits and risks is the cornerstone of patient safety and informed decision-making in the use of medical devices.
Regulatory Requirements for CERs Under the MDR
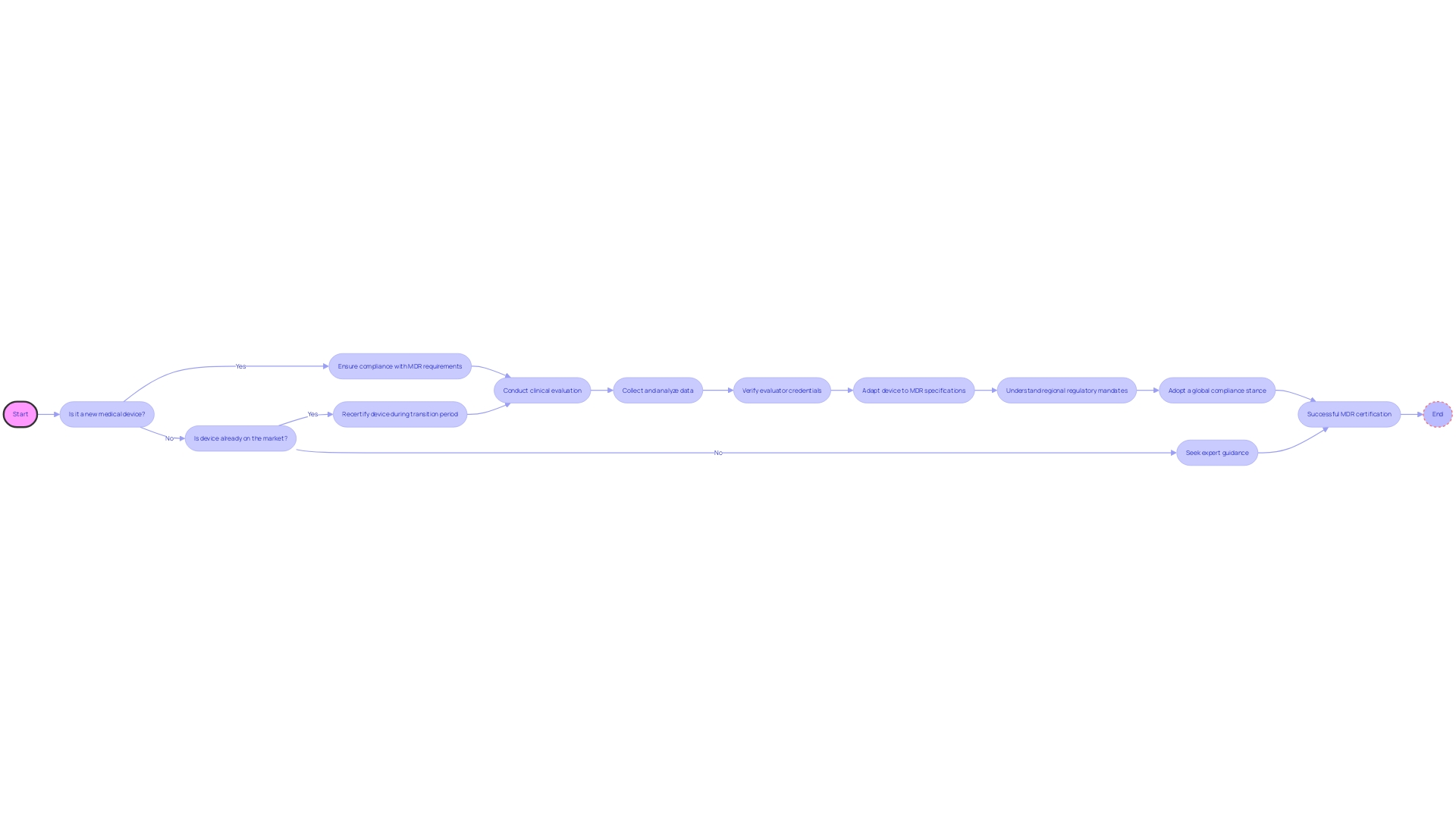
The European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) represents a significant shift in the legal landscape for medical devices, introducing stringent requirements to assure the safety and efficacy of products entering the European market. These regulations necessitate a thorough Clinical Evaluation Report (CER), which must encompass a comprehensive clinical evaluation plan, robust data collection and analysis methodologies, and detail the credentials of the evaluators involved.
To align with MDR, manufacturers must adapt to these specifications both for new medical devices seeking market entry and for existing products, which, during a transition phase, require recertification under the new criteria. It is imperative for manufacturers to be well-informed about the scope of their product's market, as some regulatory mandates are specific to certain regions.
Moreover, a global compliance stance is often adopted by companies to avoid the intricacies associated with variable market strategies and evolving regulations. Understanding regulations like RoHS, particularly relevant to those in the electronics supply chain dealing with Printed Circuit Board Assemblies (PCBAs), is crucial. Expert guidance is invaluable in navigating the complexities of MDR, ensuring manufacturers meet all necessary obligations for a successful certification in the European market.
Best Practices for Writing a CER
Crafting a Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) that is both thorough and compliant necessitates meticulous attention to several critical elements. The process begins with Comprehensive Data Collection, which involves collating clinical data from a myriad of sources such as clinical trials, post-market surveillance, and peer-reviewed scientific literature. This ensures a holistic assessment of the medical device in question.
Rigorous Data Analysis is the next pivotal step, where the data undergo rigorous statistical scrutiny and are subjected to appropriate methodologies to validate their significance. Clear and Transparent Reporting is paramount, detailing the methodologies employed in data collection and analysis with clarity, thereby ensuring stakeholders can readily comprehend and trust the findings. Regular Updates are crucial to maintain the CER's relevance; this involves consistent reviews and incorporation of new clinical data, reflecting the latest insights into the device's safety and efficacy.
Incorporating insights from experts in the field, such as Mary-Ann from NAMSA, who emphasizes the significance of assembling clinical evidence that meets the scrutiny of regulatory authorities, reaffirms the importance of these best practices. Moreover, understanding the regulatory landscape, as highlighted in the OECD's Conflict Minerals policy, can further inform the CER process by ensuring compliance with global standards. By adhering to these best practices, medical device manufacturers can produce Cars that not only fulfill regulatory mandates but also convincingly demonstrate their commitment to patient safety and product efficacy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the clinical evaluation process is essential for verifying the safety and efficacy of medical devices. It involves a thorough appraisal of clinical data from various sources, ensuring transparency and risk assessment. Simulating real-world conditions and post-market reporting are integral to this process.
The Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) serves as a cornerstone in ensuring device performance and risk mitigation. Robust clinical evidence is crucial to meet regulatory requirements and align with industry standards. Balancing benefits and risks is paramount in the dynamic field of medical device innovation, prioritizing patient safety and informed decision-making.
Compliance with the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) is necessary for market entry, requiring manufacturers to adapt CERs to stringent criteria. Crafting a comprehensive CER involves meticulous data collection, rigorous analysis, transparent reporting, regular updates, and adherence to best practices. Following these guidelines demonstrates commitment to patient safety.
In summary, the clinical evaluation process is vital for ensuring safe and effective medical devices. Transparency, simulation of real-world conditions, post-market reporting, robust clinical evidence in CERs, balancing benefits and risks, MDR compliance, and best practices all contribute to this goal. By prioritizing these elements, manufacturers can deliver innovative devices while upholding patient safety.




