Overview
The article addresses the ethical considerations and challenges encountered in Ecuadorian clinical trials, underscoring the necessity of adhering to a comprehensive moral framework established by Ministerial Agreement 0075-2017. It stresses the importance of:
- Culturally sensitive practices
- Community engagement
- Transparent communication
to secure informed consent and ensure ethical compliance. This is particularly crucial in the context of historical mistrust among indigenous populations and the complexities introduced by health emergencies.
Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of clinical research, Ecuador distinguishes itself with its unique ethical frameworks designed to safeguard human subjects amidst the complexities of cultural diversity and historical mistrust. Central to this framework is the Ministerial Agreement 0075-2017, which establishes critical principles such as informed consent and risk minimization.
As the nation confronts the challenges of conducting ethical trials, particularly in urgent public health contexts, the role of community engagement becomes increasingly vital. Researchers are urged to adopt culturally sensitive strategies that not only uphold ethical standards but also cultivate trust and collaboration with local populations.
This article explores the ethical considerations surrounding clinical trials in Ecuador, highlighting the necessity for robust protections, innovative compliance strategies, and the significance of integrating community voices into the research process.
Explore Ethical Frameworks in Ecuadorian Clinical Trials
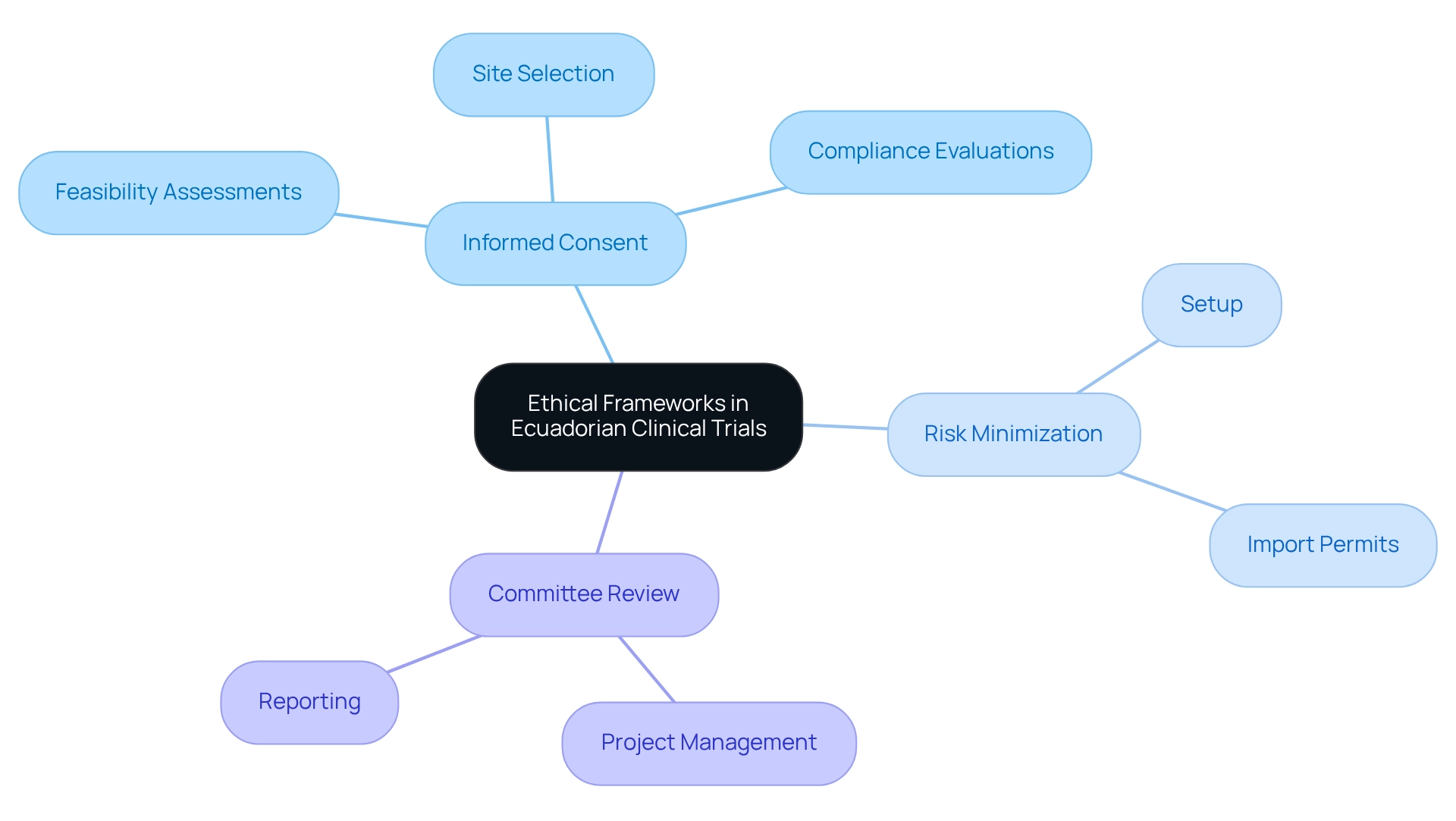
Ethical considerations for Ecuadorian trials are governed by a comprehensive moral framework that aligns with international standards, ensuring the safety of human subjects. Central to this framework is the Ministerial Agreement (MA) 0075-2017, which delineates essential moral principles and ethical considerations for Ecuadorian trials, such as:
- Informed consent
- Risk minimization
- The necessity for review by recognized committees
This agreement has significantly influenced the landscape of clinical studies in Ecuador, fostering a more structured approach to adherence to these standards.
To aid researchers in navigating these complexities, bioaccess® offers extensive clinical study management services, including:
- Feasibility assessments
- Site selection
- Compliance evaluations
- Setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
These services are designed to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of clinical trials while ensuring adherence to moral standards.
Recent statistics indicate that only 72 out of 137 identified COVID-19 publications in Ecuador were suitable for final analysis, representing 52.6%. This statistic underscores the challenges that investigators face in maintaining ethical considerations for Ecuadorian trials during health emergencies, as highlighted by authors advocating for a more effective and supportive investigative environment. Enrique Teran, a corresponding author, emphasized the adverse impact of committees for moral assessment, advocating for a more supportive investigative atmosphere, particularly in critical public health situations.
A notable case study involves the analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from a COVID-19 patient in Quito, utilizing Oxford Nanopore MinION technology. This study not only contributes to the understanding of the microbial environment in COVID-19 patients but also underscores the importance of moral adherence in clinical trials. The investigation upheld rigorous moral standards, ensuring that participant rights were respected throughout the research process.
As Ecuador approaches 2025, it is imperative for researchers to remain informed about ethical considerations for Ecuadorian trials, particularly the principles outlined in the Ministerial Agreement 0075-2017. By doing so, they can effectively navigate the complexities of moral compliance, safeguarding participant rights while advancing medical studies in the region. Furthermore, bioaccess® is dedicated to ensuring information security and client trust, addressing any concerns through established grievance and data protection procedures.
Identify Unique Ethical Challenges in Ecuador
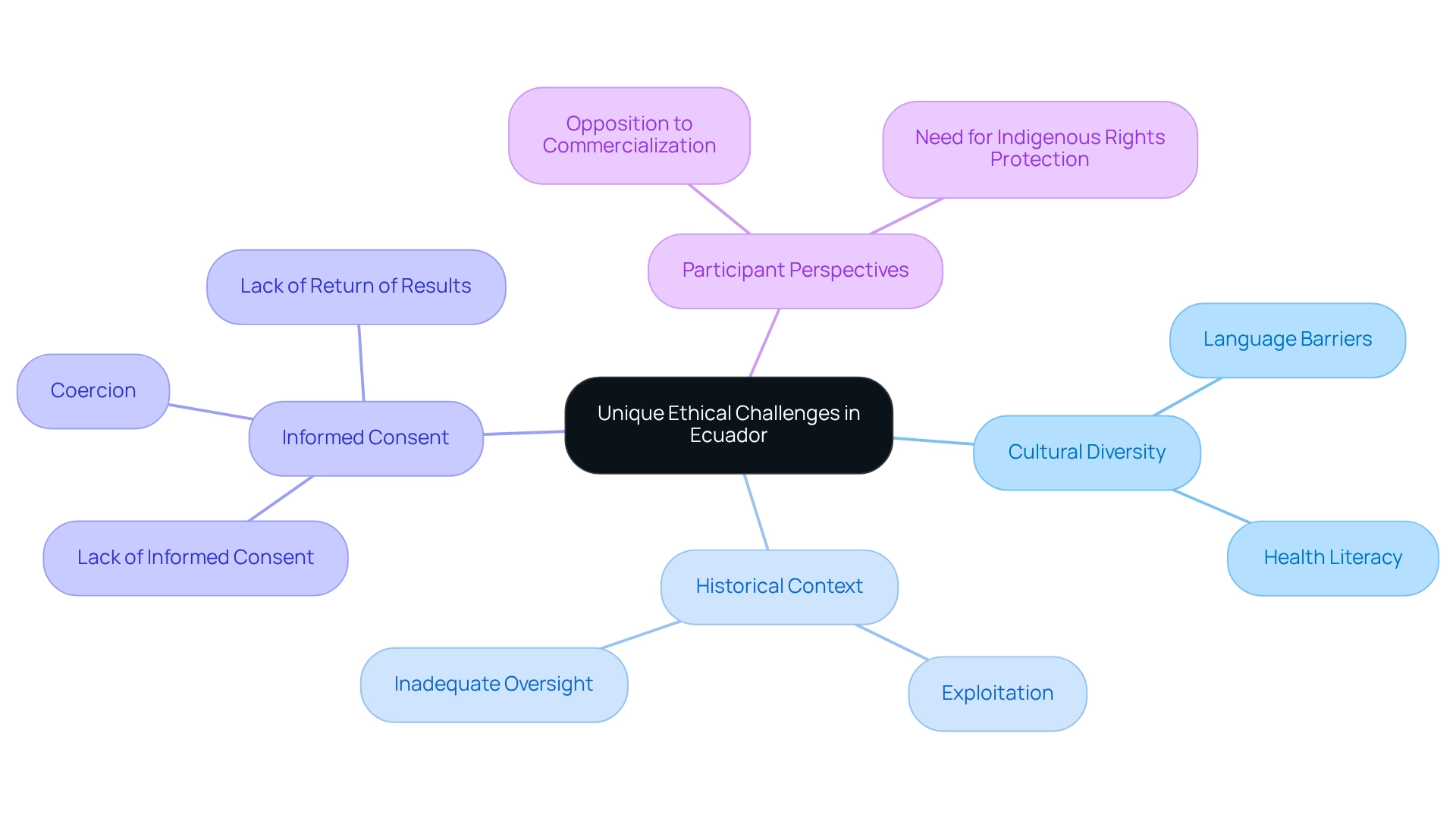
The unique moral challenges presented by Ecuador's clinical trials highlight the ethical considerations for Ecuadorian trials, primarily arising from its rich cultural diversity and a historical context of mistrust towards medical research, especially among indigenous populations. Engaging with local groups is essential for researchers to navigate these complexities effectively. Language barriers and varying levels of health literacy further complicate the informed consent process, highlighting the necessity for culturally sensitive approaches.
Previous research, particularly concerning the Waorani group, has revealed significant moral breaches, including a lack of informed consent, coercion, and a failure to return results. A historical examination titled "Historical Context of Blood Research in Waorani" underscores a troubling trend of exploitation and inadequate oversight since the late 1970s. Notably, a statistic from this community indicates that 97% of participants opposed the commercialization of their blood, underscoring the imperative for robust safeguards of indigenous rights in research studies.
As one Waorani participant poignantly articulated, "Ninety-seven percent of the subjects rejected the idea their blood could be shared or commercialized in any way, by any institution, in any country." Addressing these distinct moral challenges is crucial for upholding integrity and fostering trust in clinical research, as ethical considerations for Ecuadorian trials must be prioritized.
Implement Strategies for Ethical Compliance in Trials
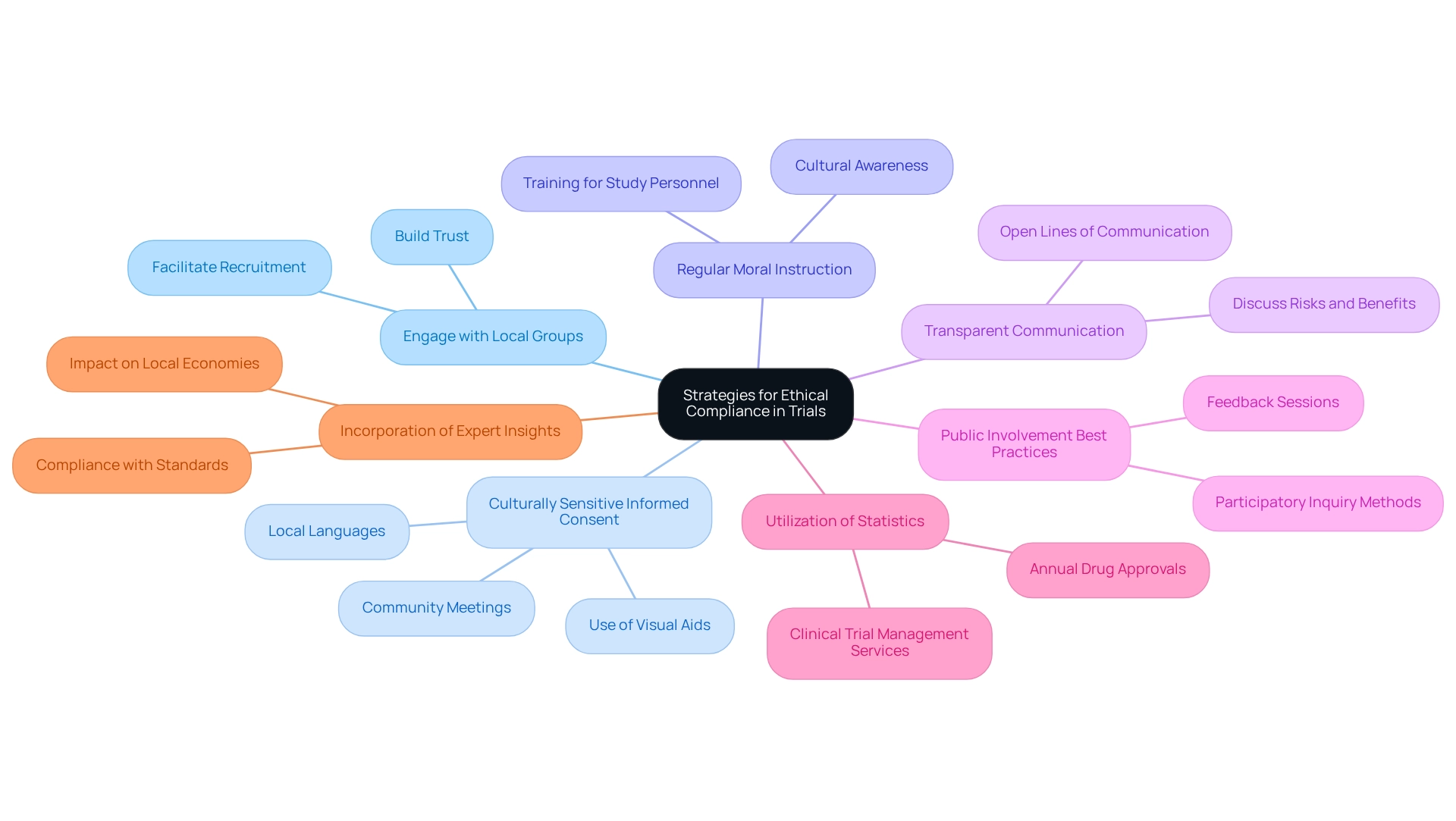
To address the ethical considerations for Ecuadorian trials, researchers must implement several essential strategies:
-
Engage with Local Groups: Establishing strong relationships with local leaders and stakeholders is crucial. This engagement fosters trust and facilitates smoother recruitment processes, enhancing participant willingness and retention. Insights from recent methodology evaluations highlight the significance of participatory strategies in studies, which can greatly enhance engagement outcomes.
-
Culturally Sensitive Informed Consent: Employ culturally appropriate methods for obtaining informed consent. Utilizing visual aids, community meetings, and local languages significantly improves participants' understanding of the study, ensuring they are fully informed before agreeing to participate.
-
Regular Moral Instruction: Continuous training for study personnel on moral standards and cultural awareness is essential. This training guarantees that all team members are aligned with moral practices and aware of the unique cultural contexts in which they operate, thereby minimizing breaches of conduct.
-
Transparent Communication: Maintaining open lines of communication with participants about the study's purpose, risks, and benefits is essential. This openness not only upholds moral standards but also fosters trust, encouraging participants to engage more completely in the study process.
-
Public Involvement Best Practices: Implementing public involvement strategies, such as feedback sessions and participatory inquiry methods, enhances the ethical landscape of clinical studies. A recent case study titled 'Thematic Analysis and Synthesis of Findings' highlights the effectiveness of these practices in ensuring that the voices of local communities are heard and respected, leading to more ethically sound results.
-
Utilization of Statistics: Grasping the broader context of clinical studies is essential. For instance, the count of new medications authorized each year by CDER from 2008 to 2024 underscores the importance of moral adherence in promoting successful study results. Furthermore, comprehensive clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies and site selection, play a critical role in ensuring that trials are conducted ethically and efficiently.
-
Incorporation of Expert Insights: As highlighted by Karen Daniels, an EPOC Associate Editor, compliance with standards is not merely a regulatory necessity but a crucial element of fostering trust and credibility in clinical studies. The effect of medtech clinical studies on local economies, including job creation and healthcare enhancement, further emphasizes the significance of principled practices and ethical considerations for Ecuadorian trials in promoting international collaboration and economic development. By embracing these strategies, researchers can navigate the ethical intricacies of clinical studies in Ecuador, ultimately aiding in more successful and reliable research initiatives.
Engage Communities and Ensure Informed Consent
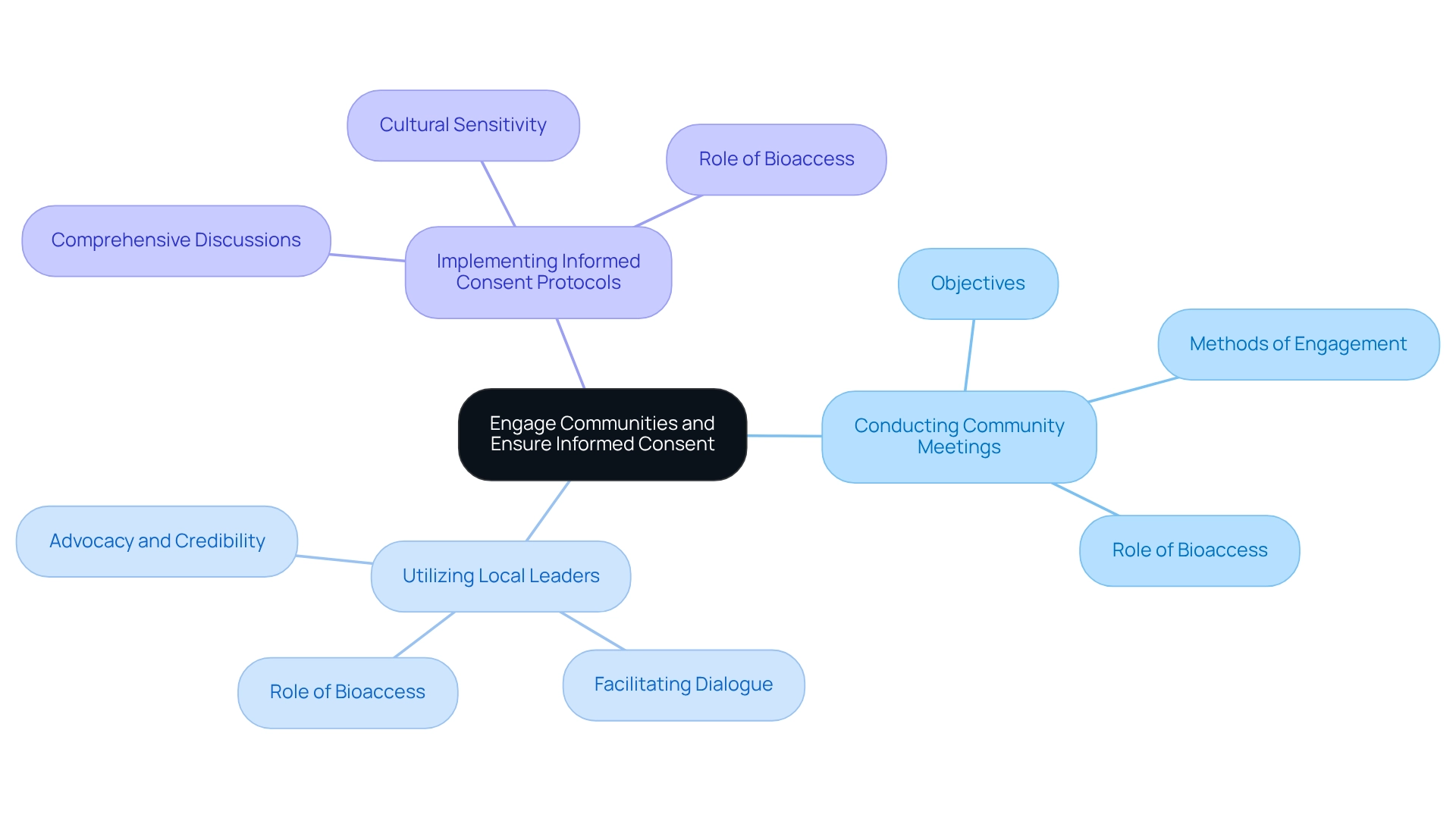
Involving groups in Ecuador is essential for the success of clinical studies. Researchers must prioritize community involvement through several key strategies, which Bioaccess facilitates via its comprehensive clinical trial management services.
- Conducting Community Meetings: Organizing informational sessions to discuss the initiative's objectives, procedures, and potential impacts is vital. These gatherings provide a platform for local members to express their concerns and pose questions, thereby promoting transparency and trust. Bioaccess plays a crucial role in planning and executing these meetings to ensure effective communication.
- Utilizing Local Leaders: Collaborating with respected local figures who can advocate for the trial enhances credibility and acceptance within the community. These leaders often hold significant influence over public opinion and can facilitate dialogue between researchers and participants. Bioaccess assists in identifying and engaging these local leaders to strengthen community ties.
- Implementing Informed Consent Protocols: It is imperative that informed consent is a thorough process rather than a mere formality. This entails comprehensive discussions about risks, benefits, and the right to withdraw from the study. Tailoring consent forms to reflect cultural contexts and varying literacy levels is essential for effective communication. Bioaccess provides guidance on developing culturally sensitive consent materials and training for staff involved in the consent process.
In Ecuador, 33% of Hispanics with physician-diagnosed arthritis reported severe joint pain, underscoring the urgent need for clinical studies that address such health concerns. By prioritizing these strategies, researchers can foster a more ethical and participatory approach to clinical trials, taking into account the ethical considerations for Ecuadorian trials. Public input has been shown to effectively influence study agendas, aligning investigations with local health beliefs and behaviors. The case study titled 'Advice for Future Research Projects' highlights the importance of public input in shaping research agendas, demonstrating that when researchers listen to the local population, studies can be better aligned with regional needs.
Additionally, a patient shared, "I’m just new here. So that’s why I came. Because I don’t have insurance and I didn’t have a job." This quote illustrates the real-world implications of collective involvement and informed consent, emphasizing the necessity for researchers to understand the challenges faced by potential participants. This collaborative approach not only enhances recruitment efforts but also ensures that trials are more attuned to societal needs, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes. Furthermore, the partnership model used in the study serves as a framework for future health research initiatives, highlighting the significance of building trust within the community.
Conclusion
Ecuador's clinical research landscape is defined by a robust ethical framework that prioritizes the protection of human subjects, as established by the Ministerial Agreement 0075-2017. This framework underscores the critical principles of informed consent and risk minimization, essential for fostering trust among participants, particularly in a nation characterized by cultural diversity and historical mistrust. Researchers are urged to adopt culturally sensitive strategies that engage local communities, ensuring that ethical standards are not only met but also respected.
The unique challenges faced in Ecuador, especially with indigenous populations, underscore the necessity for a proactive approach to ethical compliance. Engaging local communities through transparent communication, culturally appropriate informed consent processes, and ongoing ethical training for research staff is vital. By implementing these strategies, researchers can cultivate meaningful relationships with community members, thereby enhancing participation and trust in clinical trials.
As Ecuador navigates the complexities of clinical research, it is imperative for researchers to remain informed about ethical regulations and actively include community voices in the research process. This commitment to ethical integrity not only safeguards participant rights but also contributes to the overall success and credibility of clinical trials. The path forward lies in fostering collaboration, prioritizing ethical practices, and ensuring that research is responsive to the needs of the local population. By doing so, Ecuador can advance medical research while upholding the highest ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What governs the ethical considerations for clinical trials in Ecuador?
Ethical considerations for clinical trials in Ecuador are governed by a comprehensive moral framework that aligns with international standards, primarily through the Ministerial Agreement (MA) 0075-2017.
What are the key principles outlined in the Ministerial Agreement 0075-2017?
The key principles outlined in the Ministerial Agreement 0075-2017 include informed consent, risk minimization, and the necessity for review by recognized committees.
How has the Ministerial Agreement 0075-2017 impacted clinical studies in Ecuador?
The Ministerial Agreement 0075-2017 has significantly influenced the landscape of clinical studies in Ecuador by fostering a more structured approach to adherence to ethical standards.
What services does bioaccess® offer to assist researchers in clinical trials?
Bioaccess® offers extensive clinical study management services, including feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting.
What challenges do researchers face regarding ethical considerations during health emergencies in Ecuador?
Researchers face challenges in maintaining ethical considerations during health emergencies, as indicated by the statistic that only 72 out of 137 identified COVID-19 publications in Ecuador were suitable for final analysis, representing 52.6%.
What concerns did Enrique Teran raise regarding moral assessment committees?
Enrique Teran emphasized the adverse impact of committees for moral assessment and advocated for a more supportive investigative atmosphere, particularly in critical public health situations.
Can you provide an example of a clinical study that adhered to ethical standards in Ecuador?
A notable case study involved analyzing bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from a COVID-19 patient in Quito using Oxford Nanopore MinION technology, which upheld rigorous moral standards and respected participant rights throughout the research process.
Why is it important for researchers to stay informed about ethical considerations as Ecuador approaches 2025?
It is imperative for researchers to remain informed about ethical considerations, particularly the principles outlined in the Ministerial Agreement 0075-2017, to effectively navigate moral compliance and safeguard participant rights while advancing medical studies in the region.
How does bioaccess® ensure information security and client trust?
Bioaccess® is dedicated to ensuring information security and client trust by addressing concerns through established grievance and data protection procedures.




