Introduction
Ophthalmology clinical trials play a crucial role in advancing eye care and combating eye-related conditions. With the prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and other ocular disorders on the rise, these trials are essential for evaluating new treatments and gaining insights into disease management. Innovative technologies like high-resolution scans and machine learning enhance the analysis of retinal images, leading to promising breakthroughs in eye health.
However, challenges such as trial attrition and the complexities of the eye require a comprehensive approach. Contract Research Organizations (CROs) contribute their expertise and streamlined processes to ensure the success of these trials. In collaboration with pharmaceutical companies, CROs have achieved significant progress in developing effective treatments for conditions like macular degeneration.
Technological advancements, such as AI and wearable devices, are transforming data collection and analysis in clinical trials, leading to improved patient outcomes. The regulatory landscape and patient-centric approaches are also vital considerations in the execution of ophthalmology trials. As the field continues to evolve, with emerging trends in gene therapy and telemedicine, the potential for advancing eye health is immense.
However, it is crucial to navigate the ethical, legal, and social dimensions to ensure the responsible and effective utilization of these innovations. Despite the complexities, the unwavering dedication of researchers, CROs, and patients brings hope for a future where vision care is accessible to all.
The Importance of Ophthalmology Clinical Trials
Ophthalmology clinical trials are instrumental in honing new treatments, therapies, and technologies to confront eye-related conditions. Amidst a growing market—where age-related macular degeneration alone is set to burgeon from a $9.2 billion industry to an estimated $30.2 billion by 2031, particularly in North America—these trials are critical for assessing the safety and efficacy of innovative treatments, as well as offering key insights into ophthalmic diseases' progression and management.
Breakthroughs in eye care, leveraging high-resolution scans like optical coherence tomography (OCT), offer a window into our systemic health with unprecedented detail, down to a thousandth of a millimeter. Modern computing and machine learning are then applied to these retinal images, enabling swift analysis that transcends human capability. Notably, a contact lens-related corneal infection study, the Orphan Drug for Acanthamoeba Keratitis (ODAK) Trial, has potentially set a precedent for effective new treatment protocols, sharing the same vision of advancing eye health through rigorous research.
The compelling narrative of clinical trials is echoed by specialists like Dr. Eric Santos, who underscores the uniqueness of each patient's response to therapy, whether within a trial or standard treatment. This personalized approach fosters a dynamic understanding of patient care.
Beyond individual patient impact, over two million people in the UK live with vision loss—a condition with dire socio-economic implications, costing the UK economy an estimated £25.2 billion annually. Fostering advancements through clinical studies has the potential to alleviate not only the personal burden of eye disorders but also the financial strain on economies.
Yet, the quest for effective treatments encounters challenges—the anterior segment of the eye, tasked with focusing an image onto the retina, is susceptible to a range of retinal disorders. With central serous chorioretinopathy, diabetic macular edema, and glaucoma collectively affecting millions globally, the search for answers continues through comprehensive research and rigorous testing of identified compounds.
Despite the optimism fostered by ongoing clinical trials, the industry acknowledges the harsh reality of clinical trial attrition, with efficacy and safety issues accounting for the majority of setbacks. Nevertheless, the adoption of new, evidence-based approaches across the industry aims to elevate success rates, as supported by the significant role that human genetic evidence plays in clinical trial progression and FDA approvals.
In essence, the realm of ophthalmology clinical trials is a complex yet vital terrain, where the diligent quest for groundbreaking treatments intertwines with the human element of care, capturing the full spectrum from molecular insights to patient-centric therapies and, ultimately, the real-world impact on communities and economies.
Role of CRO Companies in Ophthalmology Clinical Trials
Contract Research Organizations (CROs) are instrumental in realizing the potentials of ophthalmology clinical trials by providing specialized knowledge, streamlined processes, and rigorous adherence to regulatory guidelines. With their comprehensive services encompassing the development of protocols, identification and selection of appropriate sites, enrollment and management of study participants, meticulous data handling, and robust statistical analyses, CROss enhance the efficacy and success rate of the critical trials. Through partnerships, CROss enable advancements in eye care research, contributing immensely to the progress and approval of new treatments that can profoundly affect patient health outcomes.
CROs, noted for their agility and ability to offer personalized attention, are often preferred over larger one-stop-shop models, which may seem cost-effective at first glance but can suffer from inefficiency and service disruptions. Challenges such as inadequate patient recruitment and retention remain prevalent, with clinical trials frequently experiencing delays due to such logjams. Attending to these aspects, CROss play a pivotal role in expediting the clinical trial process by implementing innovative strategies and solutions tailored to the unique requirements of ophthalmology research, thus safeguarding the integrity and timely completion of these studies.
Case Study: Successful Ophthalmology Clinical Trials with CRO Companies
In a collaboration that exemplifies the synergy between pharmaceutical innovation and clinical research expertise, XYZ Pharma and ABC CRO Services joined forces to explore the treatment realm of age-related macular degeneration—an ailment affecting millions worldwide. The collaborative clinical trials harnessed ABC CRO Services' industry-renowned scientific accuracy and XYZ Pharma's therapeutics to test a novel ophthalmic drug, targeted at halting the progression and improving the visual acuity associated with this degenerative condition.
Grounded in a research approach that championed both the highest quality endpoints and the extensive use of AI to bolster imaging analysis, the trials yielded data that underscores the potential benefits of the investigational treatment. Safety and efficacy formed the twofold focus of the study, drawing parallels with a similar case where over 47 patients in the OASIS clinical trial experienced no adverse events, marking a triumph in patient safety.
Analyzing these results juxtaposed with the broader impact of vision loss, such as the substantial £25.2 billion annual economic cost to the UK economy, highlights the tremendous societal value of focusing clinical research on ophthalmological disorders. It is with cautious optimism and an eye toward future advancements in drug therapy and patient outcomes that such collaborations between clinical trial companies lead the way in the battle against debilitating diseases like macular degeneration.
Challenges and Solutions in Ophthalmology Clinical Trials
Ophthalmological trials necessitate a precise blend of specialized expertise and technology, given the intricacy of eye diseases. Recruitment and retention are central obstacles, alongside the requirement for certain patient demographics. To navigate these challenges, Clinical Research Organizations (CROs) have adopted strategies such as close collaboration with ophthalmologists and the use of patient registries.
Moreover, with advancements in imaging technology and telemedicine, data collection processes have been refined, lessening patient inconveniences significantly. For instance, real-world scenarios highlight that patient participation is not just about willingness but also about the practicality of studying logistics, such as a patient from rural Pennsylvania needing to travel to Turkey for a potentially life-saving trial. These situations illuminate the gravity of patient support through every stage of a trial.
The prevalent delays due to recruitment woes underscore a broader trend; nearly 80% of trials fail to meet their completion dates, with a third falling short of enrollment targets. As CROss strive to mitigate these delays, the industry is progressively evolving with new regulations and methodologies aimed at enhancing trial conduct within rare diseases and pediatric populations. The collective goal remains steadfast: to push the boundaries of medical research while addressing the patient-centric and logistical challenges head-on.
This dynamic field is continuously shaped not only by professionals and specialists but also by the invaluable participation of patients who help turn today's trials into tomorrow's treatments.
Technological Innovations in Ophthalmology Clinical Trials
Exploring the frontiers of technology, ophthalmology clinical trials are witnessing transformative advances that offer myriad benefits, from enhanced precision to improved patient outcomes. Sophisticated imaging techniques, notably optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus photography, have become key tools that enable accurate assessments of ocular structures and disease progression. Meanwhile, the deployment of remote monitoring devices and intuitive mobile applications has greatly improved the efficiency of data collection, significantly reducing the frequency of in-clinic visits and contributing to a more patient-centric approach.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms represents a leap forward in data analysis. These technologies are proven to be pivotal in managing and interpreting the vast datasets clinical trials produce, achieving faster and more reliable results. For instance, the advent of algorithms like HINT and SPOT can predict trial outcomes with impressive accuracy, considering not only the drug molecule and target disease but also patient eligibility criteria and historical trial data.
This predictive analysis can inform decisions to optimize trial designs or even reassess the investigated drug. The capacity to gather, manage, and analyze such complex data is monumental, with a Phase 3 trial now generating on average 3.6 million data points—three times more than a decade ago.
Contemporary trends further illustrate the expansive potential that digitalization holds for clinical trials. The global adoption of wearable technology—enjoying a user base of 1.1 billion as of 2022—underscores a growing inclination toward digital health solutions. Wearable devices and sensors, along with other off-the-shelf technologies like fitness trackers and smartphones, offer new avenues for patient engagement and seamless data transfer, crucially reducing errors and lag in reporting outcomes.
Moreover, such advancements promise to uphold rigorous healthcare standards, essential for delivering quality care and fostering clinical successes.
This digital transformation, while promising, does come with its set of challenges, particularly concerning ethical and privacy considerations, which must be meticulously addressed. Nonetheless, the convergence of technology and clinical research holds great promise for advancing medical knowledge and therapy development, cultivating an era of innovation while remaining vigilant of its implications.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
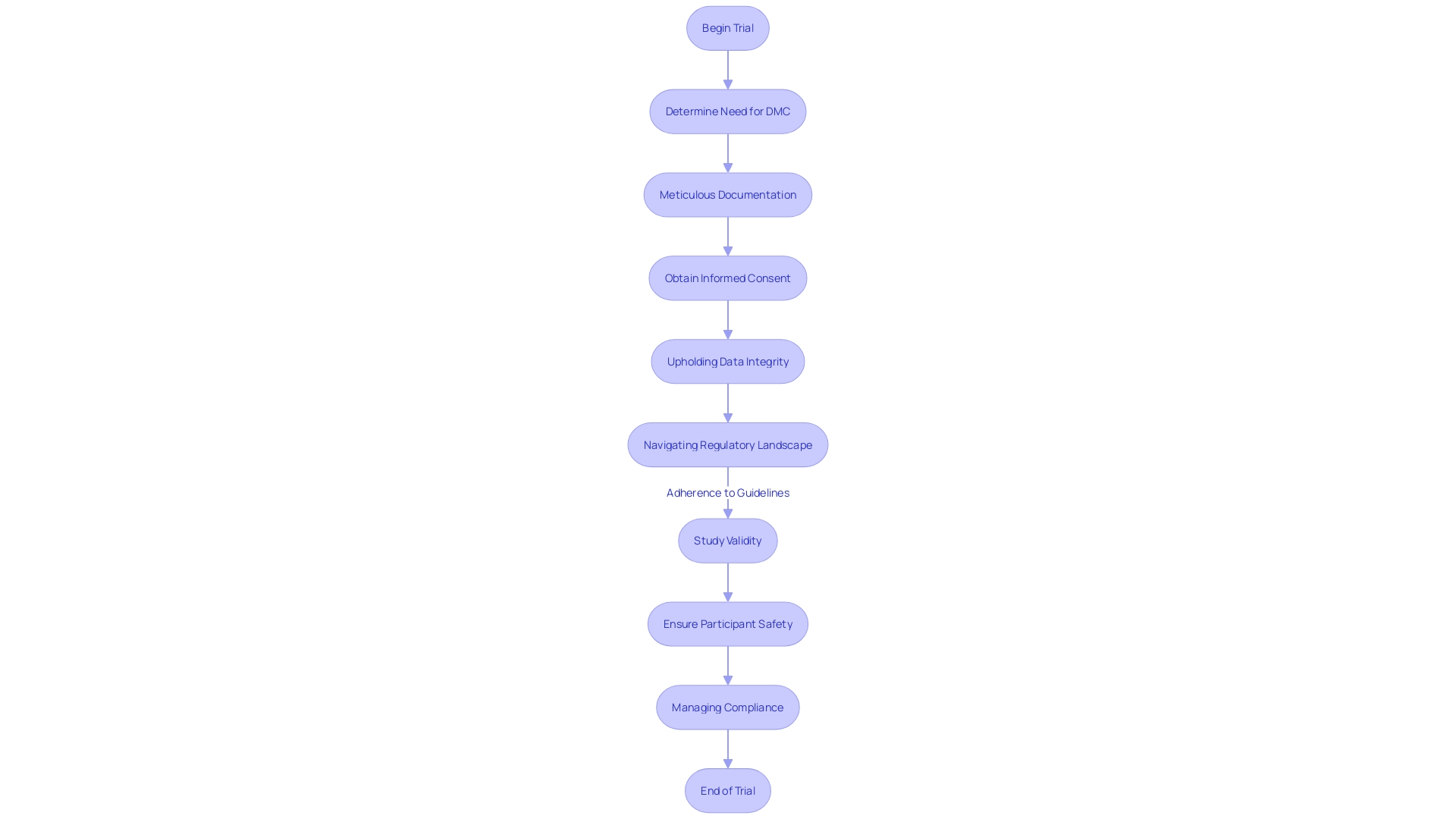
Ensuring participant safety and meeting regulatory standards are paramount in the execution of ophthalmology clinical trials. With regulatory authorities like the FDA setting rigorous guidelines to uphold ethical standards, it's essential for Contract Research Organizations (CROs) to meticulously manage compliance, covering aspects such as meticulous documentation, obtaining informed consent, and upholding data integrity. Their proficiency in maneuvering through the regulatory landscape is invaluable, as it promotes the efficiency of the trial process and adherence to the high standards required for study validity.
A key aspect of informed consent is the initial provision of critical information that is easily understandable, explaining the rationale behind an individual's participation, coupled with potential risks and advantages, the study's duration, and its procedures. Being cognizant of these elements is not only fundamental to the consent process but also serves as a resource for ongoing participant engagement with the trial.
Moreover, when developing optical systems within these trials, considerations extend beyond the primary domain, integrating interdisciplinary factors such as electrical or mechanical engineering, software development interfacing, and patient-device interaction. This holistic approach underscores that issues related to optics mesh into broader systems challenges, demanding comprehensive analytical processes or optical design software for successful resolution. Factors including light source variability—which encompasses wavelength, power, and coherence, among others—carry significant implications for both the function of optical devices and participant safety.
Awareness of these variances is crucial to optimizing trial success.
Additionally, public submissions of comments and feedback on regulatory matters exemplify the transparency and responsibility upheld within the sector. It is a shared responsibility to ascertain that any public commentary remains devoid of sensitive personal or confidential business information.
Data displays in promotional materials aimed at healthcare providers, often complex in nature, require careful design and interpretation. Evidence suggests that providers may struggle to accurately interpret intricate data displays, which highlights the need for clear and comprehensible conveyance of clinical trial data. As per completed studies, healthcare providers benefit from displays that incorporate comparator drugs, plain language summaries, and detailed study disclosures to facilitate understanding.
The ever-evolving nature of clinical trial regulation and execution emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary expertise, comprehensive understanding of key information, and meticulous consent processes within the realm of ophthalmology research, as reflected in the latest regulatory updates and scholarly analysis.
Patient-Centric Approaches in Ophthalmology Clinical Trials
Embedding the voices of patients and healthcare professionals into the framework of clinical trials has emerged as a critical factor in their success. Thorough patient engagement in ophthalmology clinical trials, for example, is not merely a box-ticking exercise but a thoughtful incorporation of patient feedback and support systems. Patient-friendly trial designs that are clear and considerate of the patient's experiences, alongside constant communication, have shown to cement trust—an essential component in boosting trial enrollment and retention rates.
Daniel J Herron, RWS Vice President, emphasizes the significance of this approach, highlighting that "actively involving patients in the planning and design so their perspectives and needs are considered" is the essence of patient-centricity.
Moreover, inclusion of diverse populations ensures a comprehensive understanding of varying experiences with a disease, leading to outcomes that are equitable and more widely applicable. This also extends to logistical considerations for participants, such as in the case of a patient from Pennsylvania needing to travel abroad for a trial, where every facet of the journey impacts their willingness and ability to participate. Integrating patient engagement within clinical trials not only improves study outcomes but also educates participants on their health, sometimes unearthing critical health issues—as was the case for Barbara, who discovered a serious heart condition through her participation and exemplifies the unexpected, lifesaving potential of clinical research.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
Ophthalmology clinical trials stand at the cusp of a revolution, propelled by swift advances in areas like gene therapy, which offers promise in addressing inherited retinal diseases (IRDs) that include varying onsets, affected cells, and progression rates. With gene therapy, research seeks to forestall photoreceptor degeneration or improve dysfunction, an approach heralded by the arrival of the first approved treatment for an IRD, amidst decades of rigorous study. The inherent complexity of Birds, particularly severe cases such as Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), which has over 20 molecular variations, illustrates the critical necessity for tailored treatments.
The field is not just about the biology; ethical, legal, and social considerations are intrinsically woven into these emerging technologies. They demand governance that keeps pace with healthcare's rapid evolution, echoing through each meticulously crafted case study and ethical vignette. For gene therapy, the eye's unique features, like immune privilege, enhance its suitability for targeted interventions, posing the possibility to tackle diseases at their genetic roots.
This research narrative gains momentum through integration with technologies like telemedicine, expanding patient reach, and pushing the boundaries of traditional trials. Such innovations are unfolding against a backdrop of substantial commercial interest, underscored by projections revealing a potential tripling of the age-related macular degeneration market to over $30 billion by 2031, with North America comprising nearly half of this market space.
It's a landscape of immense potential but also one brimming with caution. Statements by companies such as Oculis about emerging treatments like OCS-01 for ocular surgery inflammation and diseases like diabetic macular edema, remind us of the inherent uncertainties underlying the industry's forward-looking statements. Ongoing clinical trials and the collaboration between pharmaceutical entities and CROss are indeed a testament to the unwavering quest to improve vision care, yet they are also shrouded in the complexities of market forces, regulatory frameworks, and ethical conundrums challenging us to both envision and realize a future where eye health is within sight for all.
Conclusion
Ophthalmology clinical trials are essential for advancing eye care and combatting eye-related conditions. High-resolution scans and AI technology enhance the analysis of retinal images, leading to promising breakthroughs in eye health. Contract Research Organizations (CROs) contribute their expertise and streamlined processes to ensure the success of these trials.
Technological advancements like AI and wearable devices are transforming data collection and analysis, improving patient outcomes. Integrating AI and machine learning algorithms enables faster and more reliable data analysis, while wearable technology and digital health solutions facilitate seamless data transfer and reduce errors.
Navigating the regulatory landscape and complying with ethical, legal, and social considerations are crucial in executing ophthalmology trials. Informed consent and clear communication with participants are fundamental for patient-centric approaches.
The future of ophthalmology clinical trials holds promise with emerging trends in gene therapy and telemedicine. Gene therapy offers hope for addressing inherited retinal diseases, while telemedicine expands patient reach and pushes the boundaries of traditional trials. However, ethical considerations must be carefully addressed to ensure responsible utilization.
The dedication of researchers, CROs, and patients brings hope for a future where vision care is accessible to all. Ophthalmology clinical trials are complex yet vital, capturing insights from molecular research to patient-centric therapies. With meticulous efforts, responsible technology utilization, and a focus on patient needs, the potential for advancing eye health is incredible.
Join bioaccess™ and be part of the movement to make vision care accessible to all!




