Overview
To ensure patient safety in clinical trials, researchers must implement comprehensive protocols that include risk assessments, safety monitoring, and effective informed consent processes. The article outlines specific steps such as establishing a safety oversight committee, continuous monitoring, and fostering a culture of open communication, all of which are crucial for protecting participants and enhancing the integrity of clinical research.
Introduction
In the realm of clinical trials, patient safety stands as a paramount concern that demands meticulous attention and strategic planning. As research teams navigate the complexities of trial design and execution, establishing a robust framework for safety is essential to protect participants and uphold ethical standards.
This article delves into the critical components necessary for fostering a culture of safety, including:
- The development of comprehensive safety protocols
- The imperative of informed consent
- Effective monitoring systems
- Ongoing staff training
By exploring these foundational elements, researchers can enhance their commitment to patient welfare, ensuring that clinical trials not only advance medical knowledge but also prioritize the health and safety of all participants involved.
Establishing a Strong Foundation for Patient Safety in Clinical Trials
To establish a robust framework for clinical trials, it is crucial to develop comprehensive protocols that address how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials tailored to the specific study. Key steps in this process include:
-
Conduct a Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks to participants through a thorough analysis of the study design, intervention, and participant population.
This evaluation should include both physical and psychological risks to learn how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials.
-
Develop Safety Protocols: Formulate detailed protocols that delineate procedures for monitoring and managing adverse events. It is essential to incorporate clear definitions of adverse events and serious adverse events (SAEs) as part of how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials and to guide the research team effectively.
-
Train the Research Team: Ensure that all team members receive thorough training on precautionary protocols, including the proper procedures for reporting and responding to adverse events. Conducting regular training sessions emphasizes how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials across the team.
-
Create a Safety Oversight Committee: Establish a dedicated committee responsible for reviewing security data throughout the trial.
This committee must possess the authority to halt the study if significant concerns regarding well-being are identified, which is essential in understanding how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials.
-
Implement Continuous Monitoring: Utilize Data Monitoring Committees (DMCs) to analyze risk data at regular intervals. This continuous assessment allows prompt decision-making concerning participant well-being, which is essential in learning how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials within the ever-changing research environment.
-
Foster a Culture of Protection: Encourage open communication among team members regarding concerns about well-being. Creating an environment where employees can confidently raise concerns without fear of repercussions is essential for understanding how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials.
By methodically tackling these elements, researchers can establish a strong base that emphasizes well-being throughout the study process. As indicated by Dr. Rudi Eggers, Director of the Integrated Health Services Department at WHO,
The Global report on care quality is a vital milestone in our efforts to improve security for individuals worldwide... urging coordinated action to safeguard individuals from harm.
This emphasizes the significance of prioritizing protective protocols in research studies as a fundamental aspect of how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials.
Furthermore, recent statistics from an analysis of 715 general, acute care hospitals over 18 quarters indicate a significant enhancement in care measures, emphasizing how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials through rigorous protocols. Moreover, the case study on preventive health screenings illustrates hospitals' dedication to client well-being and preventive care, with screenings returning to pre-pandemic levels, reflecting a proactive approach to healthcare. It's also essential to recognize how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials by including community hospitals in the discussion of patient safety protocols, as their unique challenges and needs can impact the overall effectiveness of safety measures.
The Role of Informed Consent and Ethics in Safeguarding Patients
Informed consent serves as a cornerstone of ethical practice in research studies, acting as a protective measure for participants. To ensure that informed consent is effective, researchers should adhere to the following best practices:
-
Provide Clear Information: Craft consent forms that are not only clear but also concise, articulating the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits in layman’s terms.
Avoiding medical jargon ensures participants can grasp the essential elements of the study without confusion.
-
Engage in a Dialogue: The informed consent process must be interactive. Researchers should foster an environment of open dialogue, encouraging participants to ask questions and providing thorough answers to guarantee comprehension of what they are consenting to.
-
Assess Competency: It is crucial to evaluate a participant’s capacity to provide informed consent, particularly among vulnerable populations such as minors or individuals with cognitive impairments. This assessment safeguards the ethical integrity of the consent process.
-
Ensure Voluntariness: Involvement in research studies should always be voluntary. Researchers must clearly communicate that participants retain the right to withdraw from the study at any point without any negative consequences.
-
Document the Process: Maintaining meticulous records of the informed consent process is essential. This documentation should include any questions raised and information shared, serving as a protective measure for both participants and researchers.
-
Regularly Update Participants: If new information arises that could affect a participant’s choice to continue in the study, it is essential for researchers to convey this and secure re-consent when necessary.
Prioritizing informed consent not only ensures compliance with regulatory standards but also fosters trust and transparency with participants. This method ultimately improves how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials within research studies, a concern highlighted in a recent analysis of 117 investigations involving 22,118 participants, which emphasizes the necessity for better informed consent processes. As noted by ethicist Dr. Christine Grady, 'informed consent is fundamental to ethical research practices,' reinforcing the responsibility researchers have to their participants.
Furthermore, the case study named 'Limitations and Future Directions of Informed Consent Research' demonstrates the difficulties in informed consent processes and proposes areas for future investigation, emphasizing the continuous need for enhancement in this essential aspect of research.
Implementing Effective Monitoring and Reporting Systems
To establish robust monitoring and reporting systems in clinical trials, follow these essential steps:
-
Develop a Monitoring Plan: Design a comprehensive plan that details the methodologies for collecting, analyzing, and reporting data. This plan should clarify the monitoring frequency and the specific metrics that will be evaluated, supported by feasibility studies and site selection processes, including the selection of research sites and principal investigators (PIs).
-
Utilize Technology: Implement electronic data capture (EDC) systems to optimize data collection processes and improve accuracy. These systems enable real-time monitoring of safety data, significantly enhancing responsiveness to any emerging concerns. With the global remote health monitoring market projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 20% from 2023 to 2028, integrating such technology is increasingly vital.
Furthermore, by 2027, the total number of individuals using RPM solutions is expected to reach 115.5 million globally, underscoring the growing importance of remote monitoring in clinical trials.
-
Establish Reporting Protocols: Create well-defined protocols for the timely reporting of adverse events, specifying timelines and the individuals responsible for reporting. Making sure that all team members are knowledgeable about these protocols aids in timely incident reporting, which is essential for well-being.
Significantly, 80% of Americans endorse the use of remote health monitoring, reflecting public sentiment that highlights its importance in oversight.
-
Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Schedule routine evaluations of data by a dedicated oversight committee. These reviews are essential for identifying trends and potential issues early, allowing for proactive management of patient well-being, which in turn can foster healthcare improvement and economic growth in local communities.
Additionally, ensure compliance reviews are integrated into these assessments to meet regulatory requirements.
-
Engage Participants: Actively encourage participants to report any health changes or side effects they experience. Their feedback is invaluable for ongoing risk monitoring and can aid in identifying unforeseen hazards.
-
Implement Corrective Actions: Formulate a clear process for addressing security concerns, including corrective measures and communication strategies to keep stakeholders informed about any modifications to the study protocol. This responsiveness not only helps in overseeing participant well-being but also enhances the integrity of the study.
The recent acquisition of a contract research organization by a pharmaceutical company in September 2023 exemplifies the industry's trend towards consolidation, highlighting the necessity for strong oversight systems in research studies.
Furthermore, confirm that the import permit and nationalization of investigational devices are considered as part of the trial setup process.
By implementing these effective monitoring and reporting systems, researchers can proactively protect participant well-being and enhance the overall integrity of clinical trials, which is crucial for understanding how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials, ultimately contributing to job creation and international collaboration in the Medtech sector.

Training and Education for Research Staff
To ensure that research staff are thoroughly equipped to uphold patient safety protocols, it's essential to implement the following strategies:
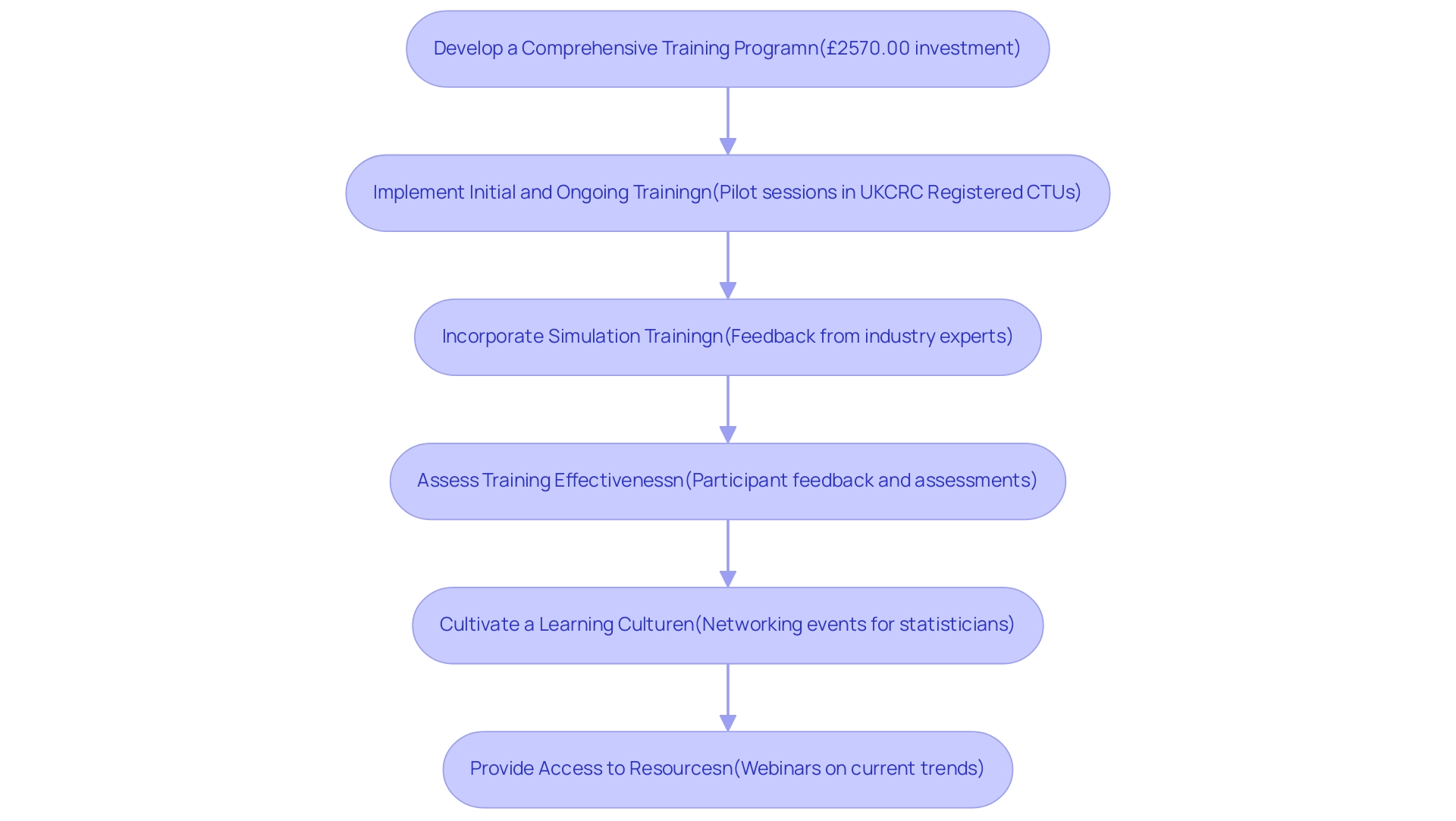
- Develop a Comprehensive Training Program: Establish a training curriculum that thoroughly addresses all aspects of care quality, including ethical considerations, informed consent, and the reporting of adverse events. The investment in such training is significant; for instance, students enrolled in the MSc in Evidence-Based Health Care (EBHC) pay £2570.00, highlighting the financial commitment to education in this field.
- Implement Initial and Ongoing Training: Initiate training for all new personnel, supplemented by regular refresher courses to keep the team informed of the latest protection protocols and regulatory updates. Pilot training sessions conducted in five UKCRC Registered CTUs and with NIHR statisticians have proven effective in ensuring relevance and effectiveness in training approaches.
- Incorporate Simulation Training: Engage staff with simulation training, allowing them to practice their responses to adverse events in a controlled setting, thereby enhancing their preparedness for real-world scenarios. This method aligns with the feedback from industry experts, such as a PhD Candidate at Columbia University, who stated, "This was a thorough short course of the theory behind missing data analysis and practical code implementation. I feel more prepared to approach this problem in my datasets and look forward to investigating."
- Assess Training Effectiveness: Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of training programs through participant feedback and assessments. Use this data to refine the curriculum, addressing any identified knowledge gaps.
- Cultivate a Learning Culture: Promote an environment that encourages staff to seek clarification and pursue further training on safety-related topics, fostering ongoing professional development. Networking events, like the one aimed at new statisticians in the pharmaceutical industry, provide valuable opportunities for staff to connect and share insights, ultimately enhancing their training experience.
- Provide Access to Resources: Ensure that staff members have easy access to the latest guidelines, research, and resources relevant to patient well-being, empowering them to remain informed and compliant. Upcoming webinars, including the one concentrating on the dissolution of oral solid dosage forms, reflect current trends and discussions in the field, highlighting the significance of continuous education for research personnel.
By emphasizing strong training and educational programs, research groups can greatly improve their ability to safeguard participants and comply with standards, which is crucial for understanding how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials and ultimately aids the integrity of studies.
Engaging Stakeholders and Building Trust
Involving stakeholders efficiently and building trust in research studies are essential elements for success. Here are several key approaches to consider:
- Communicate Transparently: Establish open lines of communication with all stakeholders, ensuring they receive regular updates on progress, security data, and any modifications to protocols. This practice not only builds trust but also enhances participant engagement, particularly in the context of clinical studies managed under the oversight of regulatory bodies like INVIMA, which serves as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
- Engage Individuals in Decision-Making: Actively involve individuals in conversations about study design and precautionary measures. Their insights are invaluable and can lead to more patient-centric approaches, fostering a deeper sense of trust among participants. As one PPI contributor noted, "Without the upheaval of having to attend an appointment," patient-centric approaches can significantly improve engagement and trust.
- Foster Collaboration with Sponsors: Work closely with sponsors to ensure that protocols meet both their expectations and regulatory requirements. This cohesive method can greatly improve well-being and simplify research processes, especially in intricate settings such as Latin America.
- Build Relationships with Regulatory Bodies: Cultivating strong relationships with regulatory agencies, such as INVIMA, is essential for compliance and can facilitate smoother approvals and oversight. Such relationships emphasize the dedication to upholding high security standards, as emphasized by the recent FDA guidance on decentralized studies in 2023, which illustrates how regulatory frameworks can improve stakeholder involvement and study design.
- Conduct Community Outreach: Connect with the community to inform prospective participants about the research process and the importance of patient well-being. This outreach can demystify the research process, making it more accessible and trustworthy while contributing to local economic growth and healthcare improvement.
- Solicit Feedback: Regularly seek input from stakeholders regarding safety measures and overall conduct. Utilizing this information to make necessary improvements demonstrates a commitment to continuous enhancement and participant welfare.
Furthermore, it is crucial to emphasize the extensive service capabilities associated with research management, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting. These services are essential for guaranteeing the success of medical studies and building trust among stakeholders.
Furthermore, media attention on research studies in Latin America, especially from outlets like Clinical Leader, has a substantial impact on shaping public perception and confidence in the research process. By actively involving stakeholders and prioritizing transparent communication, researchers can significantly enhance how to ensure patient safety in clinical trials, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. The recent success noted in the composite success rate for drug development, which rose to 10.8% in 2023, further exemplifies the positive impact of such strategies on trial efficacy and stakeholder satisfaction.
Conclusion
A commitment to patient safety is essential in the conduct of clinical trials, ensuring that the welfare of participants is prioritized throughout the research process. Establishing comprehensive safety protocols, conducting thorough risk assessments, and implementing effective monitoring systems are foundational steps that researchers must undertake. These measures not only safeguard participants but also enhance the integrity of the trial itself.
Informed consent serves as another critical aspect of ethical research, requiring clear communication and active engagement with participants. By fostering an environment where questions are encouraged and ensuring that participants understand the risks and benefits of their involvement, researchers can build trust and transparency. This commitment to ethical practices not only meets regulatory standards but also reinforces the overall safety of clinical trials.
Ongoing training and education for research staff are equally vital. Through comprehensive training programs and simulation exercises, team members can be adequately prepared to respond to adverse events, thus reinforcing the culture of safety. Moreover, engaging stakeholders—including patients, sponsors, and regulatory bodies—further enhances trust and collaboration, which are essential for the successful execution of clinical trials.
Ultimately, prioritizing patient safety in clinical trials is not merely a regulatory requirement but a moral imperative that defines the quality and credibility of research. By systematically addressing safety protocols, informed consent, monitoring systems, and staff training, researchers can create a robust framework that promotes not only patient welfare but also the advancement of medical knowledge. The commitment to safety will resonate throughout the medical community, leading to improved outcomes for all participants involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of developing comprehensive protocols in clinical trials?
Comprehensive protocols are crucial for ensuring patient safety in clinical trials by addressing specific study needs and outlining procedures to manage risks effectively.
What are the key steps to ensure patient safety in clinical trials?
The key steps include conducting a risk assessment, developing safety protocols, training the research team, creating a safety oversight committee, implementing continuous monitoring, and fostering a culture of protection.
How can researchers identify potential risks to participants?
Researchers can identify potential risks through a thorough analysis of the study design, intervention, and participant population, evaluating both physical and psychological risks.
What should safety protocols include?
Safety protocols should include detailed procedures for monitoring and managing adverse events, along with clear definitions of adverse events and serious adverse events (SAEs).
Why is training the research team important?
Training ensures that all team members understand precautionary protocols and know the proper procedures for reporting and responding to adverse events, promoting patient safety.
What is the role of a safety oversight committee?
A safety oversight committee reviews security data throughout the trial and has the authority to halt the study if significant concerns about participant well-being arise.
How does continuous monitoring contribute to patient safety?
Continuous monitoring, often through Data Monitoring Committees (DMCs), allows for regular analysis of risk data and enables prompt decision-making regarding participant well-being.
Why is fostering a culture of protection essential in clinical trials?
Encouraging open communication among team members about well-being concerns creates an environment where issues can be raised without fear, enhancing patient safety.
What is the significance of informed consent in research studies?
Informed consent is a cornerstone of ethical practice, protecting participants by ensuring they are fully aware of the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits.
What best practices should researchers follow for effective informed consent?
Best practices include providing clear information, engaging in dialogue, assessing competency, ensuring voluntariness, documenting the process, and regularly updating participants.
How should researchers assess a participant's capacity to provide informed consent?
Researchers should evaluate a participant’s ability to understand the study and its implications, particularly among vulnerable populations such as minors or individuals with cognitive impairments.
What should be documented during the informed consent process?
Researchers should maintain meticulous records of the consent process, including questions raised and information shared, to protect both participants and researchers.
Why is it important to update participants about new information?
If new information arises that could affect a participant’s decision to continue in the study, researchers must communicate this and secure re-consent when necessary.
What recent analysis emphasizes the need for better informed consent processes?
An analysis of 117 investigations involving 22,118 participants highlights the necessity for improvement in informed consent processes to enhance patient safety in clinical trials.




