Introduction
Factors Affecting Clinical Trial Costs
Clinical trials are crucial for advancing medical research and developing new treatments. However, conducting these trials can be a complex and costly endeavor.
In this article, we will explore the various factors that influence the costs of clinical trials. We will discuss the logistical challenges of conducting trials in different geographical locations and the impact it has on expenses.
Additionally, we will delve into patient recruitment and retention strategies, highlighting the importance of patient-centric approaches and diversity in trial demographics. Furthermore, we will examine the role of technology and data management in mitigating costs and improving research precision. Lastly, we will explore the significance of site selection and contract negotiation in optimizing budget allocation. By understanding these factors, we can gain insights into how clinical trial companies can establish cost-effective frameworks while ensuring the integrity and progression of critical clinical research endeavors.
Factors Affecting Clinical Trial Costs
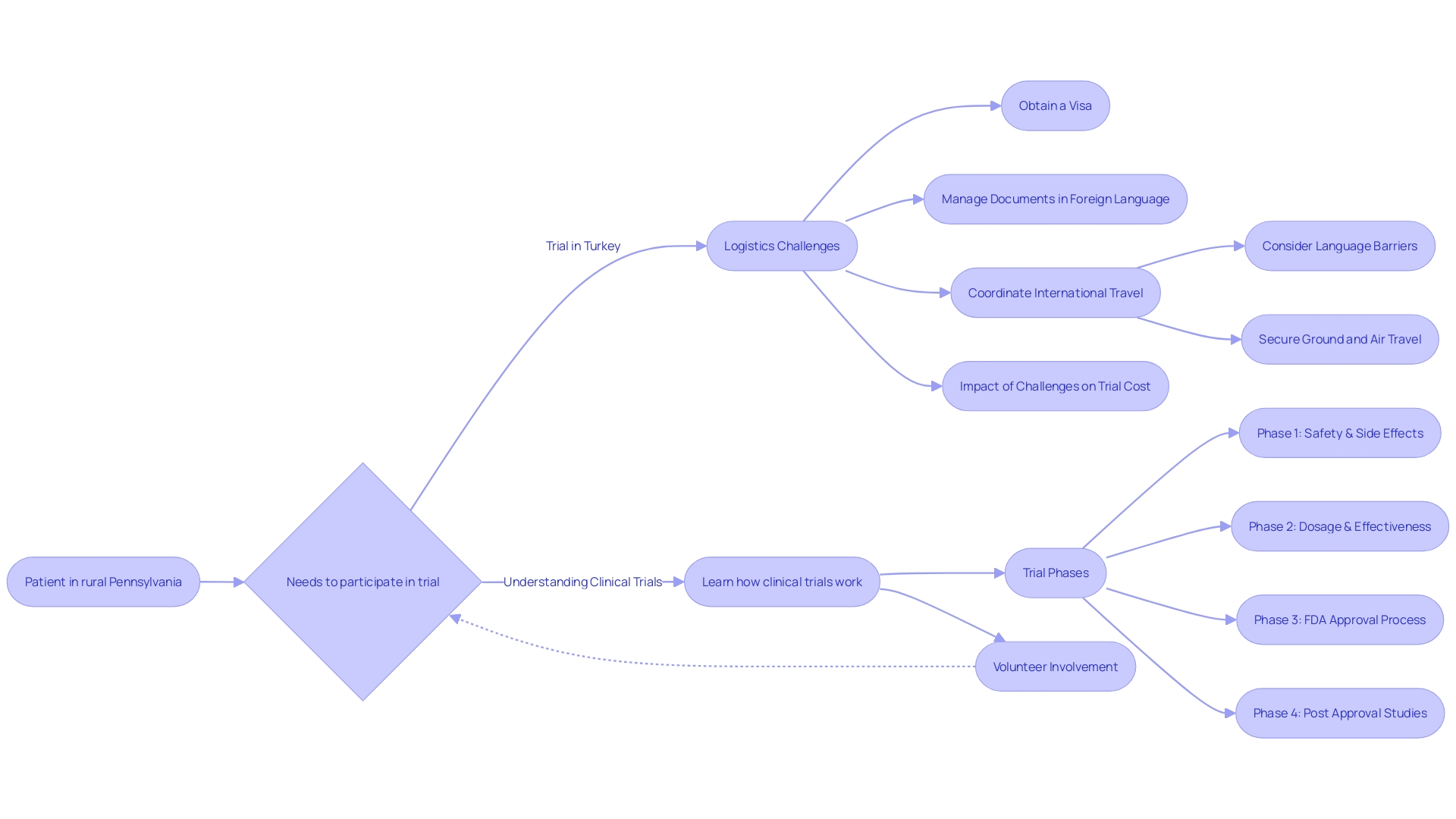
The logistics and geographical scope of a clinical trial are critical factors influencing the overall expenditure. For instance, a complex scenario may arise if a patient with a rare disease from a remote location is chosen to participate in a study conducted abroad.
In such cases, the participant faces not only the challenge of the disease itself but also the daunting task of navigating international travel. They might need to secure a visa, contend with language barriers while handling documents, and coordinate their flights and local transportation, all of which can contribute to the complexity—and thus the cost—of a trial. Clinical trials that necessitate far-reaching coordination, especially those spanning multiple countries, require an intricate framework that can escalate expenses considerably.
Patient Recruitment and Retention Strategies
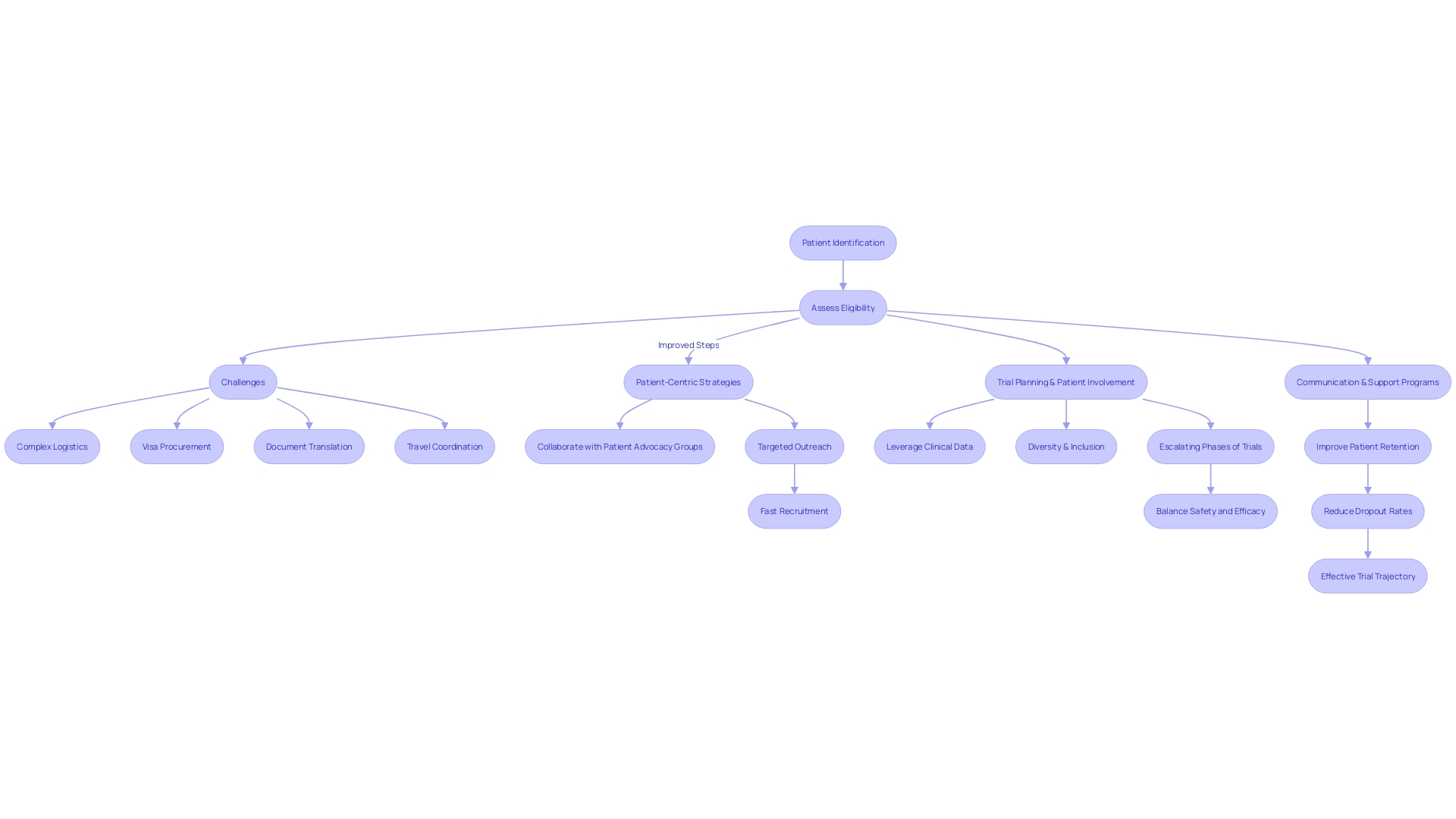
Enhancing patient enrollment and retention in clinical trials is paramount to optimizing both costs and trial outcomes. Specific challenges can arise when a patient with a rare condition, such as someone from rural Pennsylvania diagnosed with an ultra-rare disease requiring a trial based in Turkey, must navigate complex logistics like visa procurement, document translation, and travel coordination. The implementation of patient-centric strategies is thus vital.
Quickening recruitment efforts may involve collaborating with patient advocacy groups and targeted outreach. Herron emphasizes the importance of patient involvement in trial planning to honor their perspectives and needs. Recognized trials, such as EHR-sourced trials, leverage patient clinical data, allowing better operationalization of study goals.
Furthermore, the pursuit of diversity, equity, and inclusion in trial participant demographics is essential to ascertain varied experiences in responses to treatment. As established in clinical trial research, the phases of trials progressively escalate in participant numbers, intricately balancing safety and treatment efficacy evaluations. To improve patient retention, regular communication and support programs are instrumental to reduce dropout rates, maintaining a cost-efficient and effective trial trajectory.
Use of Technology and Data Management
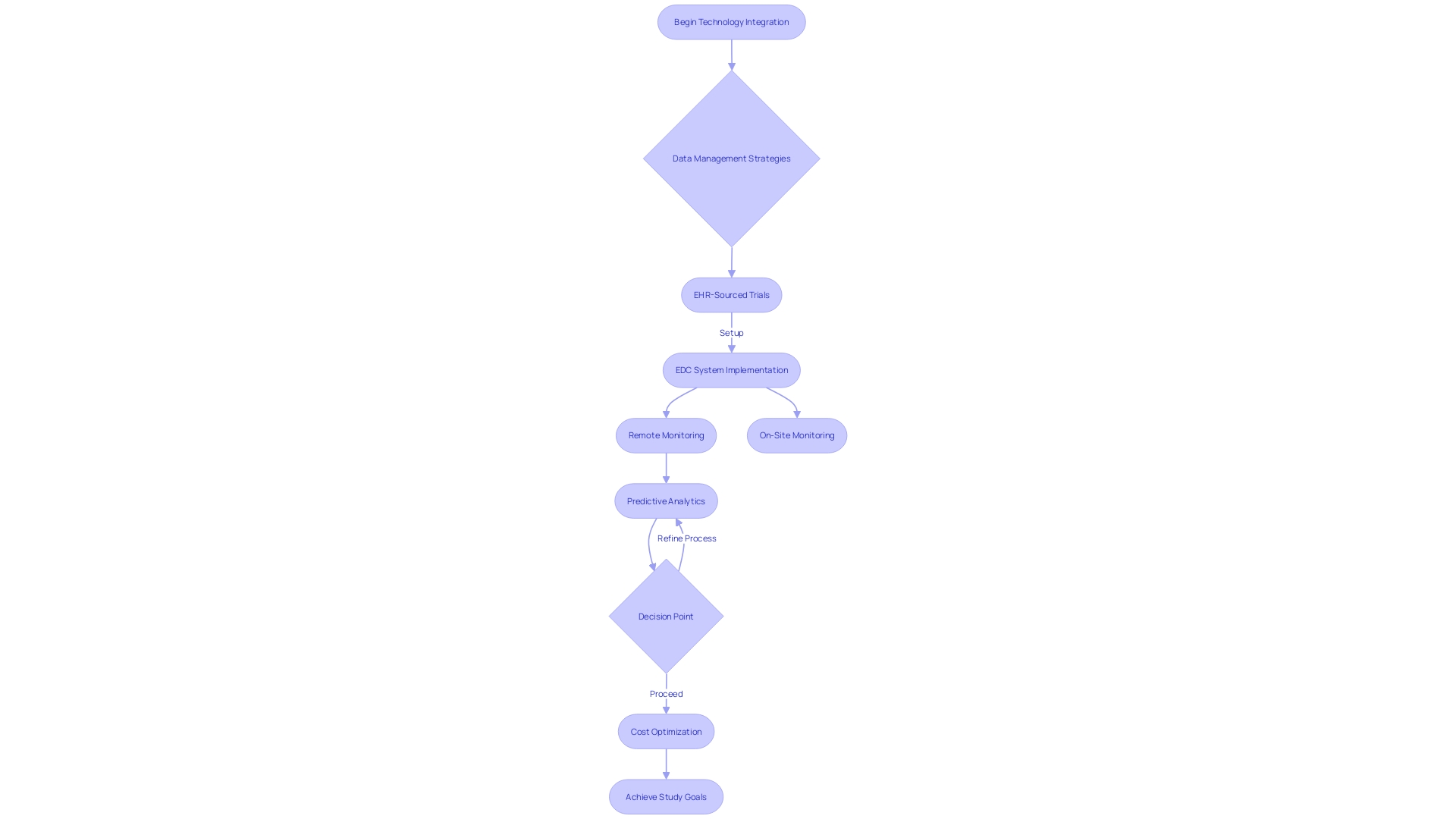
Modern clinical trial companies are increasingly turning to technology to mitigate costs and enhance the precision of their research. The utilization of electronic health records (EHR) is a prime example of the industry's shift towards more innovative and effective data management strategies. Within the scope of EHR-sourced trials, the integration of technology is demonstrating its capacity to not only streamline the operational aspects of the trials but also to improve the reliability of data by minimizing manual input errors.
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems are pivotal in this context, allowing for the efficient and accurate recording of patient information directly into digital repositories, thereby reducing the reliance on physical site visits and traditional monitoring methods. This not only aids in containing monitoring costs but also accelerates the data collection and analysis processes. The ongoing refinement of these technological solutions, including remote monitoring capabilities and predictive analytics, is revolutionizing the way clinical trial companies conduct research, prioritizing data quality and operational efficiency to achieve their study goals in a cost-optimized manner.
Site Selection and Contract Negotiation
Crafting the financial blueprint of clinical trials requires astute attention to the selection of study sites and adroit negotiations with investigators. Location decisions for trials should be driven by patient accessibility, as well as the site's clinical expertise and infrastructure—key factors that could significantly reduce costs linked to patient recruitment, monitoring, and data management.
For example, a case reported in Trials (2023) by Raman et al. illustrates the potential quandaries faced by a patient from rural Pennsylvania when contemplating participation in a clinical trial based in Turkey, emphasizing the complexity of cross-border trials for patients.
Additionally, a robust contract negotiation strategy with clinical sites can play a decisive role in managing study-related expenditures, ensuring that financial resources are judiciously utilized throughout the study conduct. As the Contract Research Organization (CRO) industry pioneer in Japan, CMIC Group underscores the need for tailored solutions at every phase of drug development to streamline processes and optimize budget allocation. This viewpoint is substantiated by insights from industry veterans, who highlight the significance of meticulously planned decisions, noting that careful preparation could improvise the outcomes on an operational and financial level in about 80% of cases, as per a discussion with Tree hill advisors. These strategies enable clinical trial companies to establish a sustainable and cost-effective framework, ensuring the integrity and progression of critical clinical research endeavors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, several factors significantly influence the costs of clinical trials. The logistical challenges and geographical scope of a trial can escalate expenses, especially when coordination across multiple countries is required. Patients from remote areas with rare diseases face additional complexities, such as visa procurement and language barriers, which further contribute to the cost of the trial.
Patient recruitment and retention strategies are vital in optimizing trial outcomes and reducing costs. Patient-centric approaches, collaboration with advocacy groups, and targeted outreach can help improve enrollment. Emphasizing diversity and inclusion in trial demographics is crucial to capture varied treatment responses.
Regular communication and support programs are instrumental in reducing dropout rates and maintaining cost efficiency. The use of technology and data management plays a significant role in mitigating costs and enhancing research precision. Electronic health records (EHR) and electronic data capture systems (EDC) streamline trial operations and improve data reliability.
These technological solutions not only reduce monitoring costs but also accelerate data collection and analysis processes, ensuring cost optimization. Selecting appropriate study sites and negotiating contracts with investigators are key factors in managing trial costs. Patient accessibility, clinical expertise, and infrastructure should guide site selection to minimize expenses related to recruitment, monitoring, and data management.
Robust contract negotiation strategies aid in optimizing budget allocation and ensuring judicious use of financial resources throughout the study. By understanding these factors, clinical trial companies can establish cost-effective frameworks while maintaining the integrity and progression of critical research endeavors. Implementing patient-centric approaches, leveraging technology, and making informed decisions regarding site selection and contract negotiation are essential for successful and cost-efficient clinical trials.




