Overview
This article examines the unique challenges and effective strategies for patient recruitment in Ecuador for clinical trials. It underscores the necessity of addressing socio-economic disparities, cultural beliefs, and logistical obstacles. Engaging local stakeholders and leveraging technology are crucial for enhancing awareness and participation in medical research. Ultimately, these efforts lead to improved recruitment outcomes, making collaboration essential for success in this field.
Introduction
In Ecuador, the landscape of clinical trial recruitment is shaped by a distinctive set of challenges that intertwine socio-economic factors, cultural beliefs, and health literacy levels. Potential participants often grapple with mistrust stemming from historical medical abuses and encounter logistical hurdles. Consequently, the necessity for effective recruitment strategies becomes increasingly evident.
Engaging local communities and tailoring outreach efforts to resonate with cultural nuances are pivotal in building trust and enhancing participation rates. This article delves into innovative approaches that leverage community engagement, technology, and stakeholder collaboration to overcome these barriers.
Ultimately, it aims to foster a more inclusive environment for clinical research that reflects the diverse populations it seeks to serve.
Understand the Unique Challenges of Patient Recruitment in Ecuador
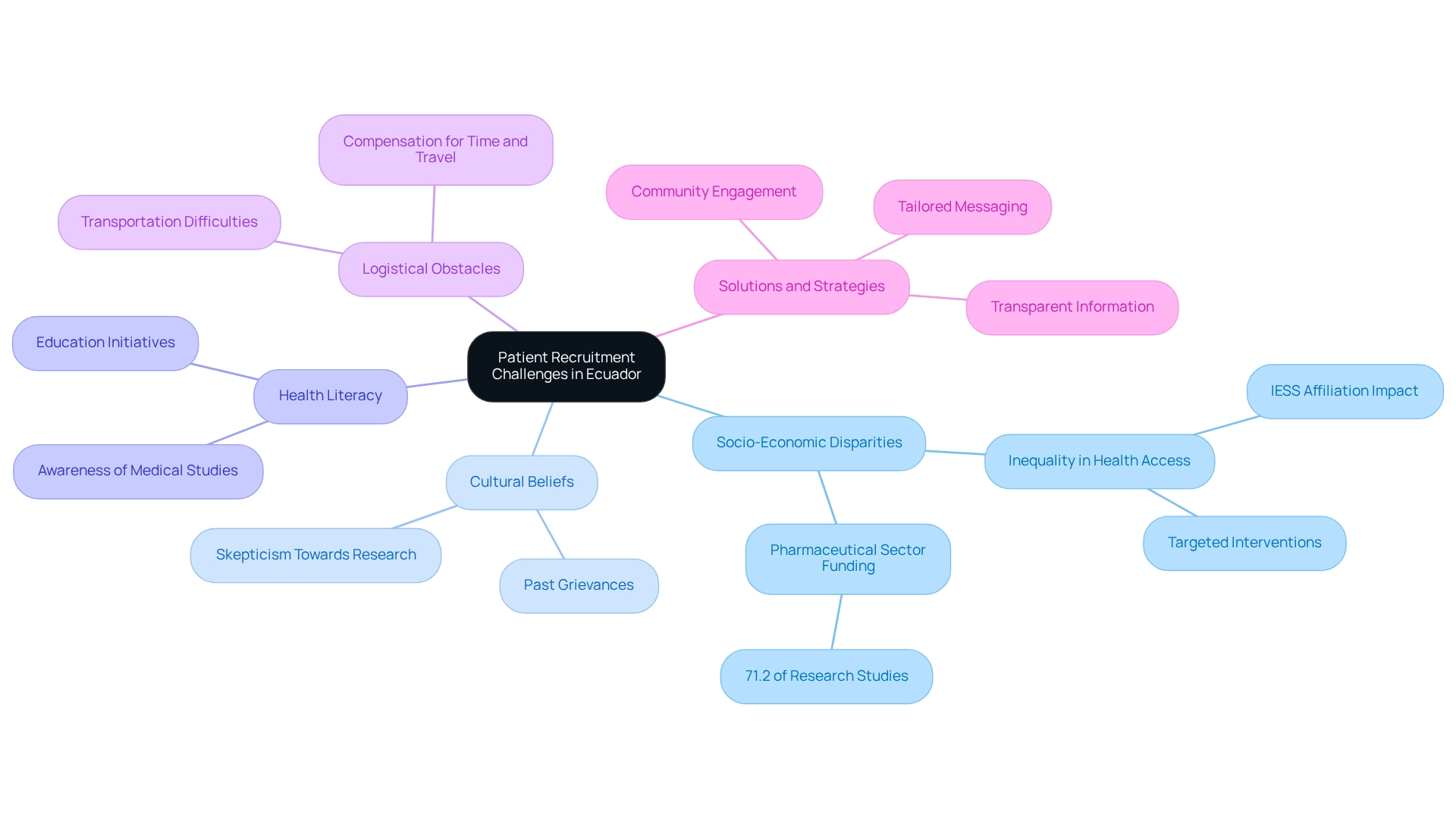
The distinct challenges faced by patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador are shaped by socio-economic disparities, cultural beliefs, and varying levels of health literacy. Many potential participants may be unaware of medical studies or harbor skepticism towards healthcare research, stemming from past grievances. Logistical obstacles, such as transportation difficulties and the need for compensation for time and travel, further complicate participation. Addressing these challenges is crucial for developing effective patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador that resonate with the local community, as a study focusing on rural Ecuador revealed that community engagement and education significantly enhanced these strategies. By cultivating an environment where potential participants feel informed and valued, trust in the process can be established. Additionally, tailoring hiring messages to align with local languages and cultural nuances has proven effective in increasing participation rates.
Statistics demonstrate that socio-economic inequalities profoundly impact participation in medical studies. For instance, the absolute contribution of IESS affiliation to the inequality of curative visits rose from 0.007 to 0.017 between 2006 and 2014, underscoring the necessity for targeted interventions to bridge the health access gap. Moreover, during the same period, the pharmaceutical sector financed 71.2% of research studies in Ecuador, highlighting the urgency of addressing these disparities. Expert insights underscore that confronting these socio-economic factors is vital for enhancing recruitment outcomes. Paulina Belén Rios-Quituizaca notes that these findings reflect a pre-pandemic perspective, offering valuable insights into the socio-economic landscape that continues to influence patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador for research study participation today. By implementing effective strategies that confront these specific challenges, such as community engagement and education, research studies can achieve higher enrollment and retention rates. Comprehensive medical study management services—encompassing feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, and project oversight—are essential for efficiently addressing these challenges. For example, forming partnerships with local organizations to bolster outreach and providing transparent information about the benefits and processes of research studies can enhance involvement. Ultimately, these efforts will propel medical research in the region and contribute to job creation, economic growth, and healthcare enhancement, fostering global health improvement through international collaboration and innovation in Medtech.
Implement Targeted Recruitment Strategies for Diverse Populations
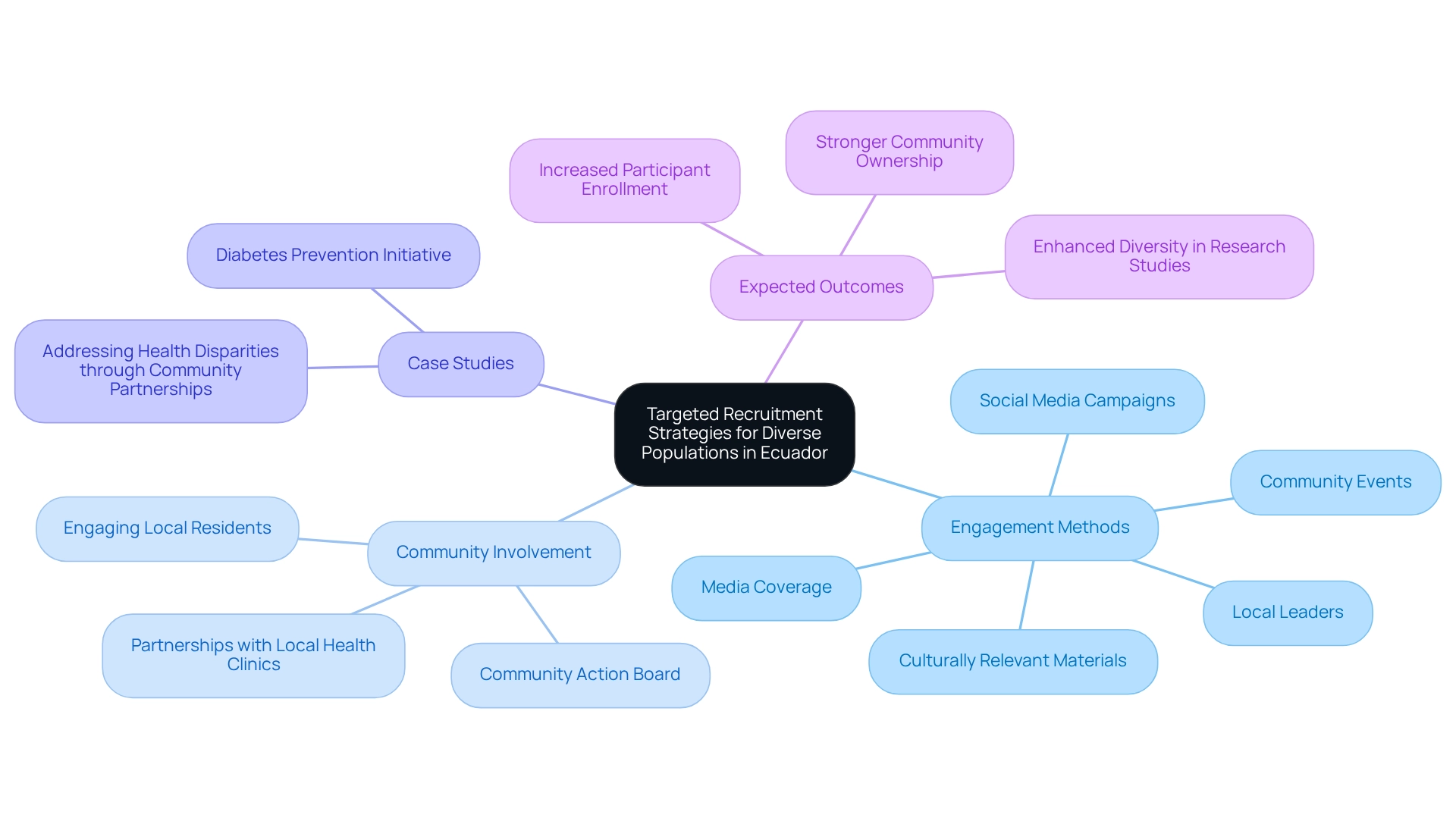
To effectively recruit diverse populations in Ecuador, it is essential to implement patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador that reflect the unique characteristics of various demographic groups. Involving local leaders to share information about research studies proves especially effective, as these figures often possess established trust within their communities. Utilizing culturally relevant materials and outreach methods—such as local radio announcements, community events, and social media campaigns—can significantly enhance visibility and participant engagement.
As of February 2025, numerous registered research studies in Ecuador underscore the necessity for patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador within this expanding environment. A notable example of this approach is a diabetes study that successfully partnered with local health clinics to host informational sessions. These sessions not only educated potential participants but also created a platform for addressing their concerns directly. This approach not only increased participant numbers but also fostered a sense of local engagement in the research process, highlighting the success of patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador for enhancing clinical trial participation.
The case study titled "Addressing Health Disparities through Community Partnerships" illustrates this point well, demonstrating how engaging local residents can lead to improved health outcomes. As Guedy Arniella, LCSW, from the Department of Community Outreach and Health Education, observed, "The Partnership developed an evidence-based intervention the locals actually wanted, and that was created for and by residents who know them well." Furthermore, the Action Board highlighted the significance of a partner-led hiring strategy, which can be crucial in accessing at-risk populations.
However, it is vital to be aware of common pitfalls in executing these targeted hiring strategies, such as failing to adequately address local concerns or neglecting to provide culturally sensitive information. By avoiding these missteps, researchers can enhance their efforts to attract participants.
Ultimately, the expected outcomes of these focused hiring strategies, particularly patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador, include increased participant enrollment, enhanced diversity in research studies, and a stronger sense of community ownership in the research process. Moreover, as emphasized by industry specialists, incorporating extensive research study management services—such as feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, study setup, import permits, project oversight, and reporting—can further enhance the participant enrollment process and ensure successful study results. Additionally, media coverage of clinical trials in Latin America and Colombia by Clinical Leader underscores the growing importance of these strategies in enhancing visibility and credibility within the region.
Engage Local Stakeholders to Enhance Recruitment Efforts
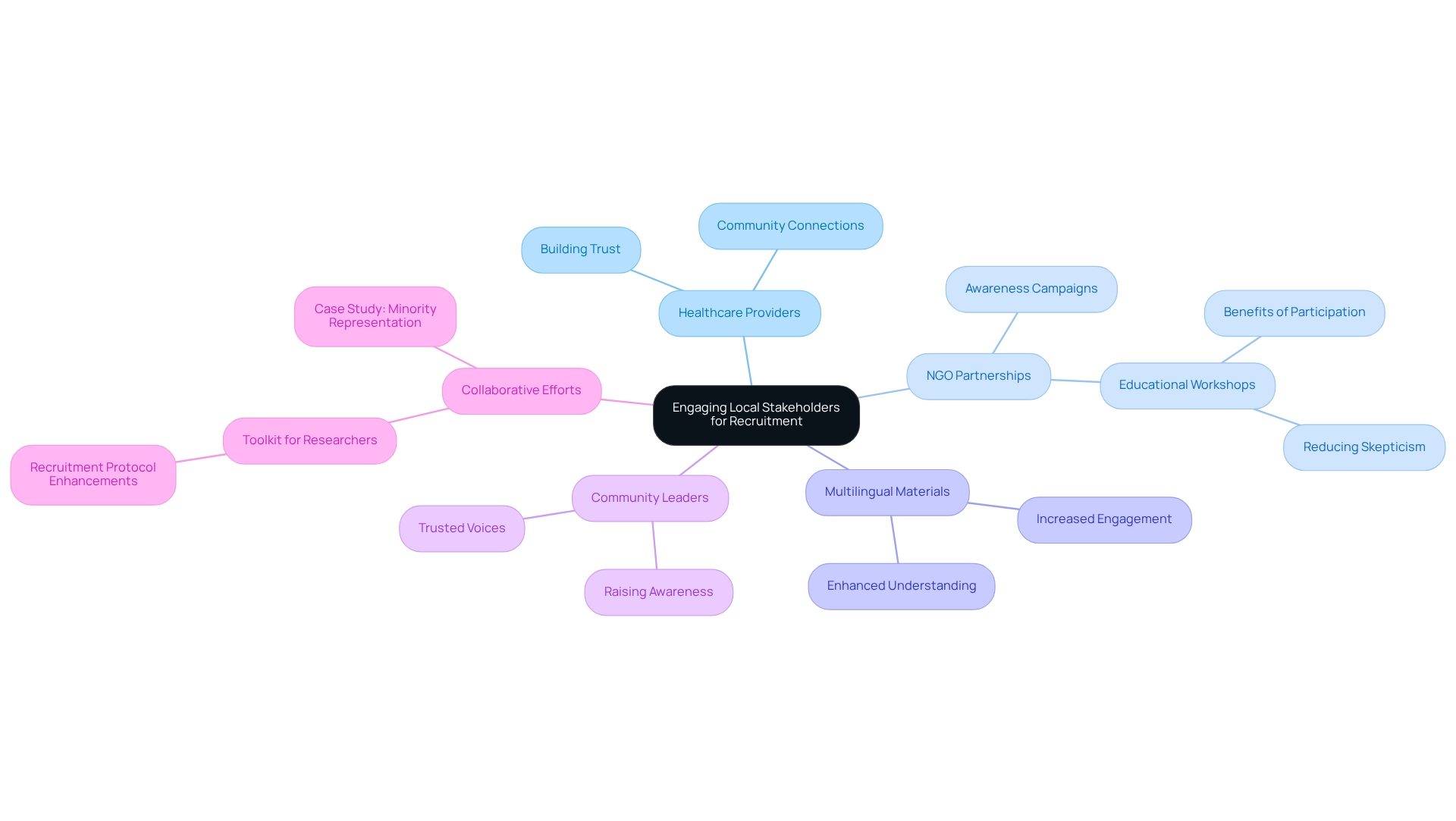
Involving local stakeholders—such as healthcare providers, organizations, and patient advocacy groups—is essential for improving patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador. These stakeholders serve as crucial links between researchers and potential participants, offering valuable insights into local needs and preferences. By utilizing reliable channels, they can efficiently disseminate information about research studies, significantly improving participation rates.
For instance, a partnership with a local health NGO during a cardiovascular study led to heightened awareness and increased enrollment among underserved populations. The NGO organized workshops that educated community members about the benefits of medical studies, effectively reducing skepticism and fostering a more favorable perspective on participation. This collaborative approach not only enhances patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador but also ensures that medical studies more accurately reflect the diverse communities they aim to serve.
Moreover, healthcare providers play a pivotal role in the patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador. Their established connections within the community can cultivate trust and inspire patients to consider involvement in research studies. The partnership between bioaccess™ and Caribbean Health Group in Barranquilla exemplifies how local healthcare organizations can come together to create a supportive environment for medical research, ultimately striving to position Barranquilla as a leading hub for research studies in Latin America. By actively engaging these local stakeholders, researchers can enhance patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador, promoting a more inclusive setting that encourages diversity and equity in clinical research, aligning with the broader goal of fairness in clinical study representation. As Marcella Nunez-Smith articulates, "Clinical trial diversity is an issue of fairness," highlighting the necessity of inclusive recruitment strategies.
Furthermore, providing research materials in multiple languages can enhance participant comprehension and involvement, further underscoring the significance of clear communication across diverse populations. The case study titled 'Collaborative Efforts to Enhance Minority Representation' illustrates how joint actions among various stakeholders can effectively boost minority participation in research studies. Additionally, EQBMED's approach of engaging trusted community leaders to raise awareness about research participation serves as a contemporary example of patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador. By integrating these elements—including the service features of bioaccess™ such as feasibility studies, site selection, and project management—researchers can significantly improve participant engagement and ensure that studies accurately represent the groups they intend to assist.
Leverage Technology to Optimize Recruitment Processes
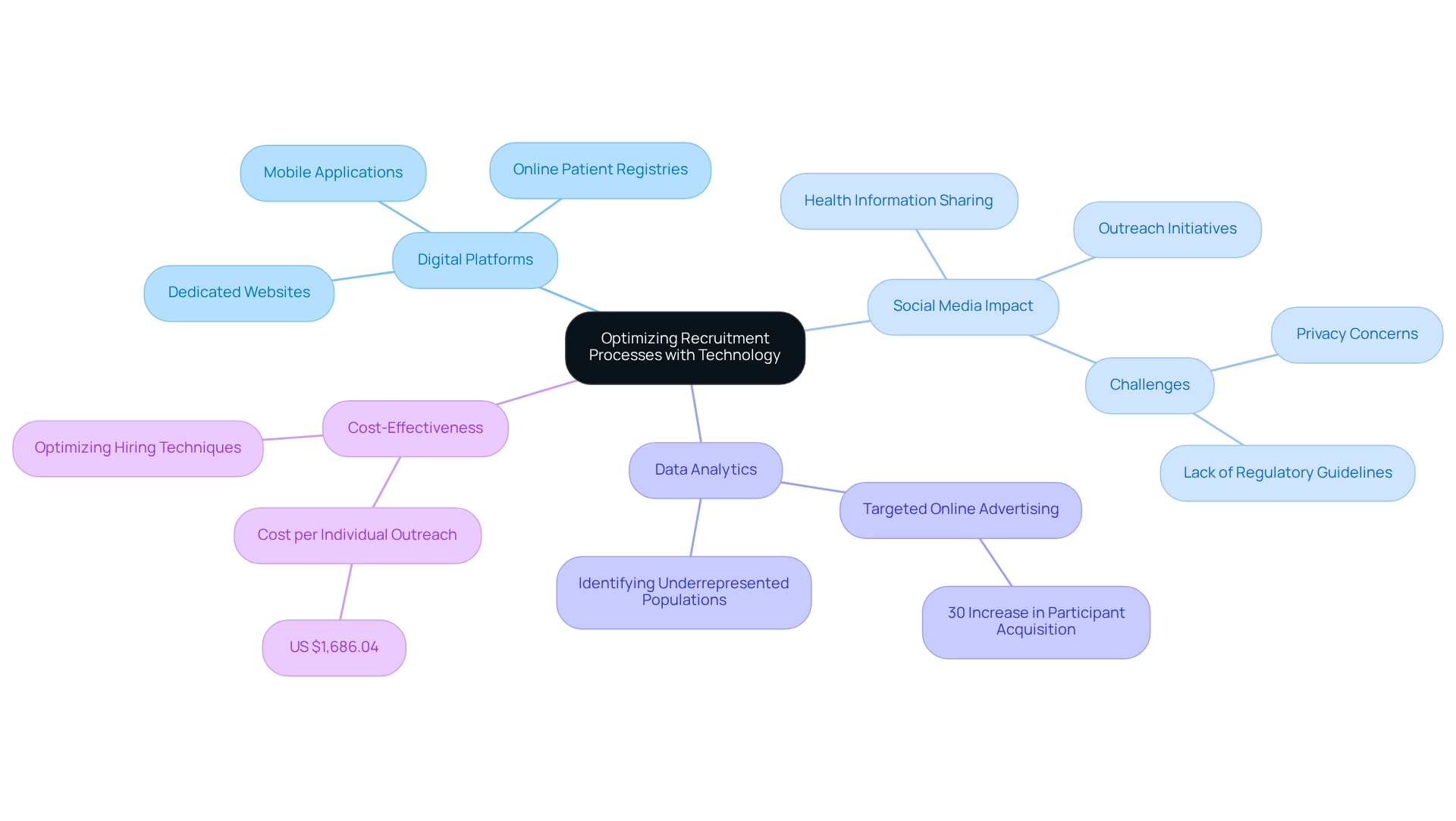
Utilizing technology is crucial for enhancing patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador. Digital platforms, such as social media, mobile applications, and online patient registries, enable researchers to connect with a broader audience and provide simpler access to information regarding medical studies. Establishing a dedicated website or app that offers detailed insights into ongoing studies, eligibility criteria, and the benefits of participation can effectively engage potential participants who prefer digital communication.
The impact of social media on clinical trial enrollment is particularly noteworthy. With a significant percentage of health information sharing occurring via digital media, it is essential to leverage these channels for outreach initiatives. As Ximena Gamboa states, "Social media have an important percentage that is higher than that of TV and newspapers. This shows the importance of digital media for the diffusion of health information in the 21st century." However, challenges such as privacy concerns and the absence of regulatory guidelines can hinder the effectiveness of social media. Addressing these barriers through proactive research and clear guidelines can enhance hiring outcomes, as highlighted in the case study 'Challenges and Barriers to Social Media Recruitment.'
Additionally, employing data analytics allows for the identification and targeting of specific populations that may be underrepresented in clinical trials. For instance, a recent initiative that utilized targeted online advertising based on demographic data achieved a remarkable 30% increase in participant acquisition for a mental health study, underscoring the potential of technology to enhance enrollment strategies. Furthermore, considering the cost per individual for personal outreach is US $1,686.04, it becomes evident that optimizing hiring techniques through digital strategies can be more cost-effective than traditional outreach methods. By embracing these digital tools and recognizing the importance of participant-driven dissemination of information, clinical researchers can significantly improve patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador, thereby enhancing awareness and participation in clinical trials. Moreover, integrating insights from media coverage, such as those reported by Clinical Leader, can further enhance the understanding of how awareness through media influences patient recruitment efforts.
Conclusion
Addressing the unique challenges of clinical trial recruitment in Ecuador is imperative for fostering an inclusive research environment. The socio-economic disparities, cultural beliefs, and historical mistrust towards medical research must be acknowledged and actively tackled. Engaging local communities and employing culturally relevant outreach methods enhances trust and participation rates. Successful case studies highlight the effectiveness of community partnerships and targeted strategies that resonate with the diverse populations in Ecuador.
Moreover, leveraging technology plays a crucial role in optimizing recruitment processes. Digital platforms, social media, and data analytics empower researchers to reach a broader audience and engage potential participants effectively. By combining traditional community engagement with modern technological tools, clinical trials can achieve higher enrollment rates and ensure that the research reflects the populations it aims to serve.
Ultimately, these efforts contribute to advancing medical research and improving healthcare outcomes in Ecuador. As stakeholders collaborate and innovate, they pave the way for a more equitable landscape in clinical research, benefiting both the scientific community and the diverse populations involved. Embracing these strategies will drive progress toward a more inclusive and representative future in clinical trials.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main challenges faced by patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador?
The main challenges include socio-economic disparities, cultural beliefs, varying levels of health literacy, skepticism towards healthcare research, logistical obstacles like transportation difficulties, and the need for compensation for time and travel.
How do socio-economic inequalities affect participation in medical studies in Ecuador?
Socio-economic inequalities significantly impact participation, as evidenced by an increase in the inequality of curative visits related to IESS affiliation from 2006 to 2014. This highlights the need for targeted interventions to improve health access.
What role does community engagement play in improving patient recruitment strategies?
Community engagement and education have been shown to significantly enhance patient recruitment strategies by creating an environment where potential participants feel informed, valued, and can build trust in the research process.
How can recruitment messages be tailored to increase participation rates?
Tailoring recruitment messages to align with local languages and cultural nuances has proven effective in increasing participation rates in medical studies.
What are some effective strategies for overcoming recruitment challenges in Ecuador?
Effective strategies include community engagement, education, forming partnerships with local organizations, providing transparent information about research studies, and implementing comprehensive medical study management services.
What is the significance of addressing socio-economic factors in patient recruitment?
Addressing socio-economic factors is vital for enhancing recruitment outcomes, as these factors continue to influence patient recruitment strategies and participation in research studies today.
How does the pharmaceutical sector impact research studies in Ecuador?
The pharmaceutical sector financed 71.2% of research studies in Ecuador between 2006 and 2014, underscoring the urgency of addressing socio-economic disparities to improve access and participation in medical research.
What potential benefits can arise from improving patient recruitment strategies in Ecuador?
Improved recruitment strategies can lead to higher enrollment and retention rates in research studies, contribute to job creation, economic growth, healthcare enhancement, and ultimately foster global health improvement through international collaboration and innovation in Medtech.




