Introduction
The concept of patient engagement in clinical trials has taken center stage, bringing about significant implications for patient outcomes. This article explores the multifaceted nature of patient engagement, from gathering patient insights to empowering patients to manage their health.
It delves into how digital health technologies, such as mobile apps and wearables, are revolutionizing patient interactions with clinical research. Additionally, the article discusses how these technologies enhance trial design and execution, improving data collection and participant experience.
Regulatory frameworks for digital health in clinical trials, as well as the benefits and challenges of implementing digital health technologies, are also examined. Finally, the article looks to the future, exploring the potential of digital therapeutics and the role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in advancing clinical trials. The integration of stakeholders across the healthcare ecosystem is highlighted as crucial for the successful incorporation of digital health technologies into clinical trial frameworks.
Enhanced Patient Engagement
The concept of patient engagement has become central to clinical trials, wielding profound implications for patient outcomes. Rather than a mere buzzword, patient engagement reflects a rich tapestry of meanings.
It encapsulates a spectrum from gathering patient insights for research decision-making to forging partnerships in which patients influence the course of trials. Moreover, it includes the diverse actions patients take to manage their health, like seeking information and adhering to treatments.
Recognizing this multifaceted nature informs the deployment of digital health technologies that revolutionize how patients interact with clinical research. Companies are harnessing mobile apps, wearables, and digital platforms to transcend traditional tribal boundaries, a transformation underscored by one company's aim for 90% of its new studies in 2021 to adopt digital health strategies. Notably, the integration of Unify, a clinical study support platform, epitomizes innovation in patient engagement, enabling participants to provide vital data remotely. This approach not only satisfies patients' involvement in managing their health but also enriches data quality, reducing the frequency of in-clinic visits and in some cases, eliminating them entirely, thereby heralding a new era in clinical trial effectiveness and patient-centricity.
Enhanced Trial Design and Execution
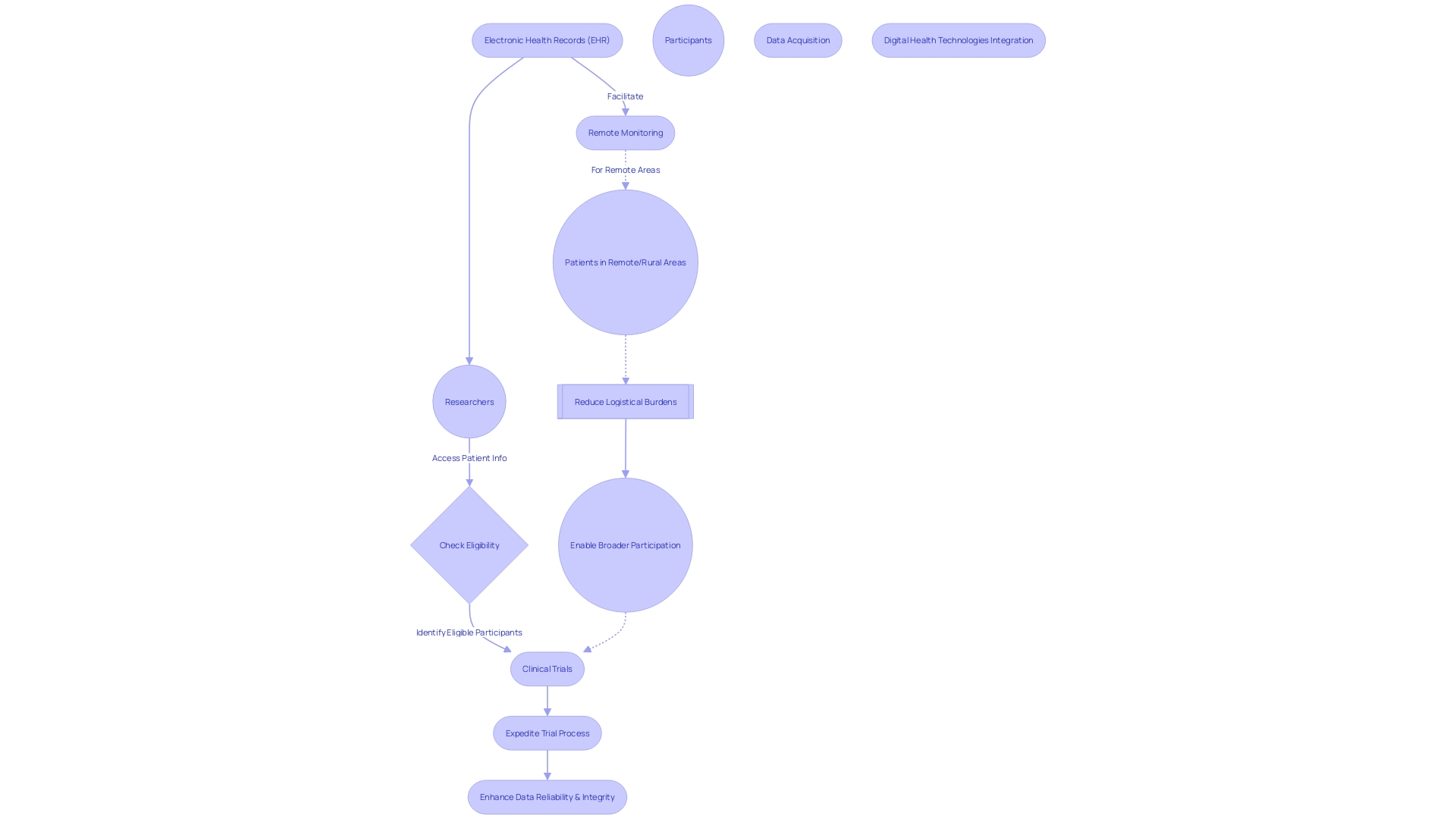
Clinical trial companies are increasingly employing digital health technologies to enhance trial design and patient engagement. The integration of electronic health records (EHRs) exemplifies this shift, as it provides researchers with direct access to extensive, up-to-date patient information.
This access is invaluable for identifying potential trial participants who meet the study's eligibility criteria, particularly for those with rare conditions who otherwise might be overlooked. Moreover, digital tools enable remote monitoring and data acquisition, which is especially pivotal for patients in remote or rural areas.
Such patients, who might otherwise face the daunting prospect of traveling internationally for a trial, can now participate without the added stress of navigating complex travel logistics or understanding unfamiliar languages. By diminishing the need for in-person visits, these pioneering approaches not only minimize the logistical burden on participants but also pave the way for broader participation in clinical trials. Importantly, these digital advancements serve to both expedite the clinical trial process and bolster the reliability and integrity of the data collected.
Regulatory Framework for Digital Health in Clinical Trials
As the landscape of healthcare continues to evolve, the integration of Digital Health Technologies (DHTs) into clinical trials represents a significant shift in the healthcare delivery model. Recognizing the need to navigate these changes with precision and care, regulatory agencies such as the FDA have taken proactive steps in issuing guiding principles. A refined example of this regulatory engagement is the updated FDA guidance on the use of DHTs in clinical investigations, which elaborates on the proper selection of a DHT, the rationale for its use, and the retention and protection of data it collects.
At the heart of these regulations are the imperatives to protect patient privacy and to guarantee the ethical and secure handling of data. This ensures that stakeholders can trust in the clinical trial data's integrity and validity. The robust process begins with a request form, meticulously evaluated by a Digital Service Team, to assess whether the digital technology proposed is secure, compliant, and cohesive with the existing technological solutions.
Furthermore, the industry has witnessed the advent of a new era where smartphones and consumer digital apps have become pivotal in health access, stirring significant interest among life science firms to integrate digital health strategies into their offerings. This paradigm shift not only reflects today's healthcare delivery challenges but also encompasses verification and validation efforts, with an emphasis on achieving consumer-level usability while maintaining the high-quality data expected in clinical trials. The goal is to ensure these tools meet similar standards for clinical care and clinical trials, advocating for a harmonized approach across the spectrum of healthcare technology.
Benefits and Challenges of Digital Health in Clinical Trials
Digital Health Technologies (DHTs) are transforming clinical trials by enhancing data collection accuracy and patient participation, while also tackling challenges such as diverse patient inclusion. Take the example of a patient in rural Pennsylvania with a rare disease.
Offered a clinical trial in Turkey, they face daunting challenges from visa procurement to language barriers. By employing DHTs in such situations, researchers can potentially reduce the need for such travel, opening trial participation to a wider demographic and minimizing the logistical burden on patients.
Evaluating DHTs requires an understanding of each technology's specific contribution to health outcomes, which can be complex due to the variance in terms such as eHealth and telehealth. Validating these tools is key, as expressed at FDA's public meeting, where stakeholders emphasized the necessity for rigorous development and verification of DHTs for clinical trials.
Furthermore, the healthcare delivery model involving patients, providers, plans, and pharmaceutical companies is evolving. A 'fifth P'—phones and digital apps—is entering the picture, enabling patients to access healthcare in new ways while life sciences companies keenly explore digital health strategies. This dynamic underscores the need for careful validation to ensure DHTs' data quality meets the high standards set for medical devices. With respect to the digital therapeutics market, significant trends such as personalized treatments, value-based care, and the COVID-19 pandemic are shaping the future, according to industry reports. For stakeholders in the pharmaceutical sector, understanding these trends is vital for recognizing opportunities and addressing the accompanying risks as DHTs continue to influence the healthcare landscape.
Future Directions for Digital Health in Clinical Trials
Digital therapeutics, an emerging facet of digital health, is revolutionizing how we approach clinical trials. These software-driven treatments span across multiple platforms such as mobile devices, virtual reality, and sensor technology. Particularly noteworthy is their potential in chronic and neurological disease management.
Digital therapeutics, which may be prescribed as standalone treatments or alongside pharmaceuticals, are becoming pivotal in optimizing trial designs and enhancing patient outcomes. However, despite their ability to reduce patient costs, factors like their relative newness and inadequate insurance coverage limit widespread adoption. Furthermore, the healthcare sector's data is expanding at an unprecedented rate, with medical information now doubling every 70 days.
This data surge offers immense possibilities to refine clinical trials. Notably, a modern Phase 3 trial can produce about 3.6 million data points, indicating a tripling of data volume over the past decade. Riding this wave of digitalization, artificial intelligence and machine learning are set to play an indispensable role in processing vast data sets and revealing critical insights that could lead to more effective patient selection and trial outcomes.
The collaboration of stakeholders—including patients, biopharmaceutical firms, digital health technology companies, clinicians, and academic scholars—is fundamental. Thorough development, rigorous validation, and consensus on standards are crucial for incorporating digital health technologies into clinical trial frameworks. As per recent dialogues, such as an FDA-hosted public meeting, there's a strong call for the shared criteria akin to those for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) to ensure data quality and comparability across clinical research and care settings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, patient engagement in clinical trials has significant implications for patient outcomes. Digital health technologies have revolutionized patient interactions, improving data collection and participant experience. The integration of these technologies enhances trial design, reduces logistical burdens, and enables broader trial participation.
Regulatory frameworks ensure patient privacy and data integrity when incorporating digital health technologies. The future of digital health in clinical trials looks promising, with the emergence of digital therapeutics and the use of artificial intelligence. These advancements optimize trial designs, enhance patient outcomes, and handle the increasing volume of medical data.
Collaboration among stakeholders is crucial for successful incorporation of digital health technologies. Shared standards address challenges such as validating efficacy and ensuring data quality. The integration of digital health technologies into clinical trials transforms the healthcare delivery model, benefiting patient engagement, trial effectiveness, and overall outcomes.




