Overview
The article focuses on the top ten good clinical practices (GCP) that researchers should adhere to in order to ensure ethical and scientifically valid medical studies. It emphasizes that following GCP principles, such as ethical conduct, informed consent, and data integrity, is essential for safeguarding participant rights and enhancing the reliability of research findings, particularly in the context of the unique challenges faced by Medtech companies in Latin America.
Introduction
In the realm of clinical research, adherence to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a cornerstone of ethical and scientific integrity. As the international quality standard established by the International Conference on Harmonisation, GCP outlines the essential principles that govern the design, conduct, and reporting of trials involving human subjects.
This framework is particularly pertinent in regions like Latin America, where Medtech companies encounter unique regulatory challenges and communication barriers. Understanding GCP is crucial for fostering innovation and collaboration in this evolving landscape.
The implications of GCP extend beyond compliance; they encompass the protection of participant rights, the credibility of data, and ultimately, the advancement of medical science. As the demand for rigorous clinical trials increases, the importance of comprehensive training and effective implementation of GCP principles becomes ever more apparent, paving the way for improved healthcare outcomes and ethical research practices.
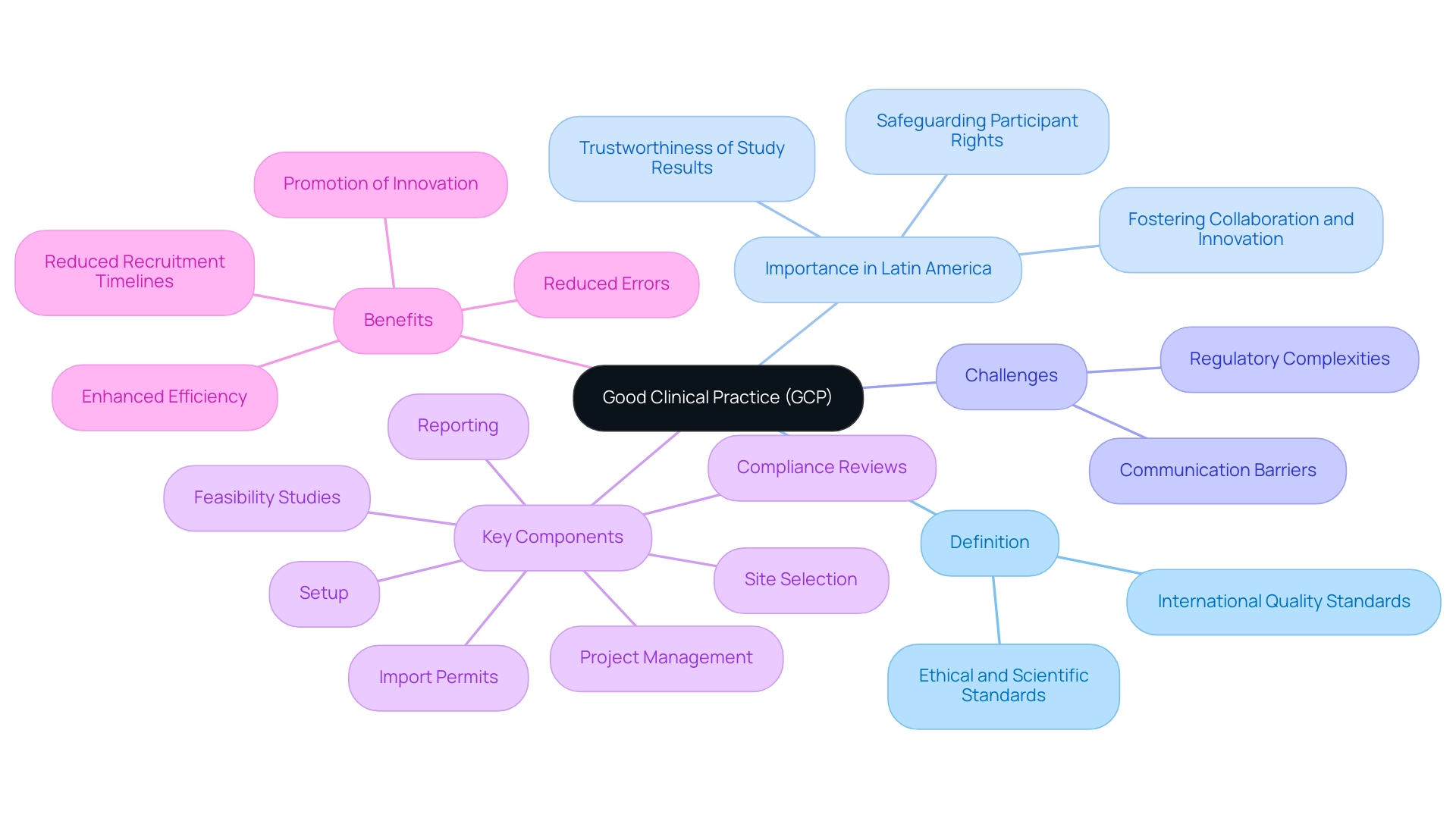
Understanding Good Clinical Practice (GCP)
Good clinical practices (GCP) are defined as the international quality standards established by the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) for the design, conduct, recording, and reporting of studies involving human subjects. This framework encompasses ethical and scientific quality standards that are crucial for safeguarding the rights, safety, and well-being of participants. Moreover, GCP guarantees the trustworthiness of the information gathered during medical studies, crucial for dependable results.
In the context of Latin America, where Medtech companies face challenges such as regulatory complexities and communication barriers, understanding good clinical practices (GCP) is imperative for fostering collaboration and innovation. Recent guidelines, including the WMA Declaration of Helsinki, emphasize that every precaution must be taken to protect the privacy of study participants and the confidentiality of their personal information, underscoring the ethical standards integral to good clinical practices (GCP). For Medtech startups aiming to navigate these challenges effectively, comprehensive research management services—including:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
can play a pivotal role.
For instance, case studies have shown that implementing structured feasibility studies can reduce recruitment timelines by up to 30%, demonstrating the tangible benefits of adhering to good clinical practices (GCP). As noted by Stocken DD, 'GCP but not as you know it,' reflects the evolving nature of these standards, particularly as they adapt to the unique challenges in Latin America. The continuous improvement in good clinical practices (GCP) compliance within pharmaceutical organizations underscores the need for a culture of learning and adaptation, as illustrated by case studies demonstrating that regular training and quality audits enhance efficiency and reduce errors.
Upholding good clinical practices (GCP) is crucial, as it directly influences the validity of study outcomes and the overall progression of medical science, especially in the evolving environment of Latin American health investigations.
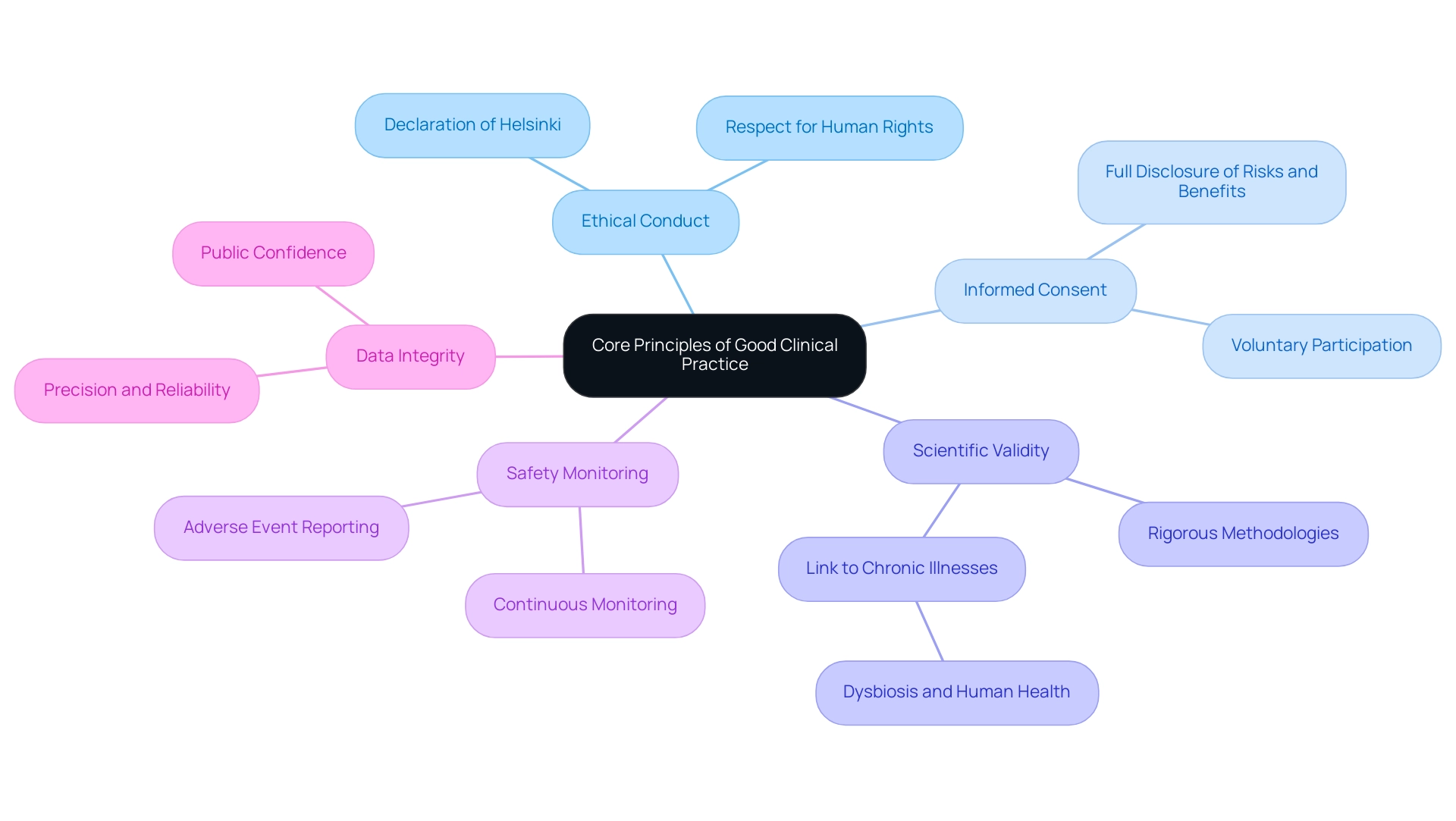
Core Principles of Good Clinical Practice
The core principles of good clinical practices (GCP) are essential to ensuring the integrity and ethical conduct of medical studies, particularly in emerging markets like Colombia, where media coverage emphasizes the increasing significance of trials. These principles include:
- Ethical Conduct: Investigations must adhere to the ethical guidelines set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki, emphasizing respect for human rights and the welfare of participants.
- Informed Consent: It is imperative that participants are fully informed about the study's purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits, allowing them to provide voluntary consent without coercion.
- Scientific Validity: Research must be designed with rigorous scientific methodologies to ensure findings are credible and contribute meaningful knowledge to the field.
- Safety Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of participant safety and well-being is essential throughout the study, ensuring that any adverse events are promptly addressed.
- Data Integrity: The gathering and presentation of information must be precise, dependable, and confirmable, as data integrity is essential for upholding public confidence in scientific studies.
These principles not only guide researchers but also play a vital role in addressing current challenges in the pharmaceutical sector, particularly in ensuring equitable access to medicines. Notably, only 8% of products are registered in low-income countries, highlighting significant barriers to access. As Sebastian E. Winter observes, 'Few recent advances in human medicine have been as influential as the finding that an imbalance (dysbiosis) of our resident microbial communities in the colon is linked to many chronic human illnesses,' highlighting the significance of ethical conduct and scientific validity in studies. Furthermore, the case study titled 'Access to Medicines in LMIC' illustrates the ongoing challenges pharmaceutical companies face in making products available in these regions.
Upholding good clinical practices (GCP), alongside comprehensive trial management services—including feasibility studies, site selection, trial setup, compliance reviews, import permits, project management, and reporting on serious and non-serious adverse events—is crucial for advancing ethical conduct in medical studies and fostering international collaboration in the Medtech field.
The Importance of GCP Training for Researchers
Training in good clinical practices (GCP) is essential for all personnel involved in clinical trials, including investigators, study coordinators, and clinical research associates. This comprehensive training equips individuals with a robust understanding of good clinical practices (GCP), regulatory requirements, and the ethical considerations essential for conducting studies. Among the numerous advantages of good clinical practices (GCP) training are improved compliance with regulations, enhanced quality of studies, and increased confidence among staff.
Significantly, as emphasized by Maria Nyåkern, Ph.D., a Medical Device Executive:
It is crucial to possess robust experimental background and medical expertise when participating in trials because it can assist in ensuring that the studies are carried out in a safe and ethical manner.
Furthermore, comparing the ISO 14155 Standard with FDA Medical Device Regulations underscores the necessity of good clinical practices (GCP) training to ensure compliance with international standards. The implementation of good clinical practices (GCP) principles in a practical, skills-oriented setting is essential, as it enhances the perceived importance of good clinical practices (GCP) training, making it more relevant to everyday activities.
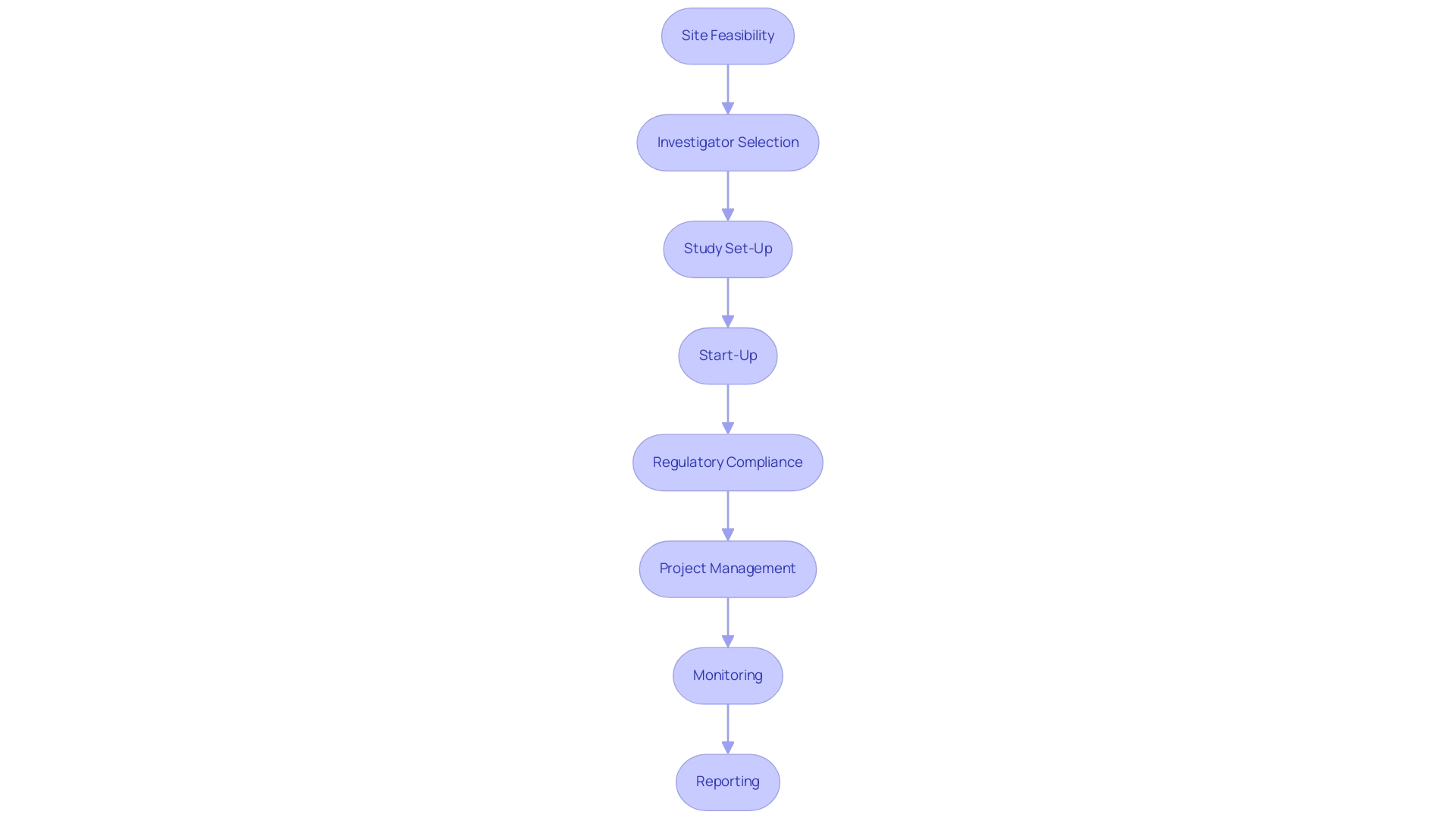
Various training formats, including online courses, workshops, and certification programs, are available, allowing researchers to select the option that best aligns with their learning preferences. This flexibility is essential in addressing the demands of today's varied scientific environment, particularly as recent reports highlight the increasing significance of good clinical practices (GCP) in improving the quality of medical device studies. Furthermore, the comprehensive process for advancing medical device studies—encompassing site feasibility, investigator selection, study set-up, start-up, regulatory compliance, project management, monitoring, and reporting—plays a pivotal role in addressing the challenges faced by medical device startups, such as regulatory hurdles and recruitment issues.
Training in good clinical practices (GCP) directly supports these service capabilities by ensuring that all personnel are equipped to manage each phase effectively and ethically. This comprehensive method not only promotes effective and ethical medical studies but also aids in job creation, economic development, and healthcare enhancement within local economies.
Implementing GCP in Clinical Trials
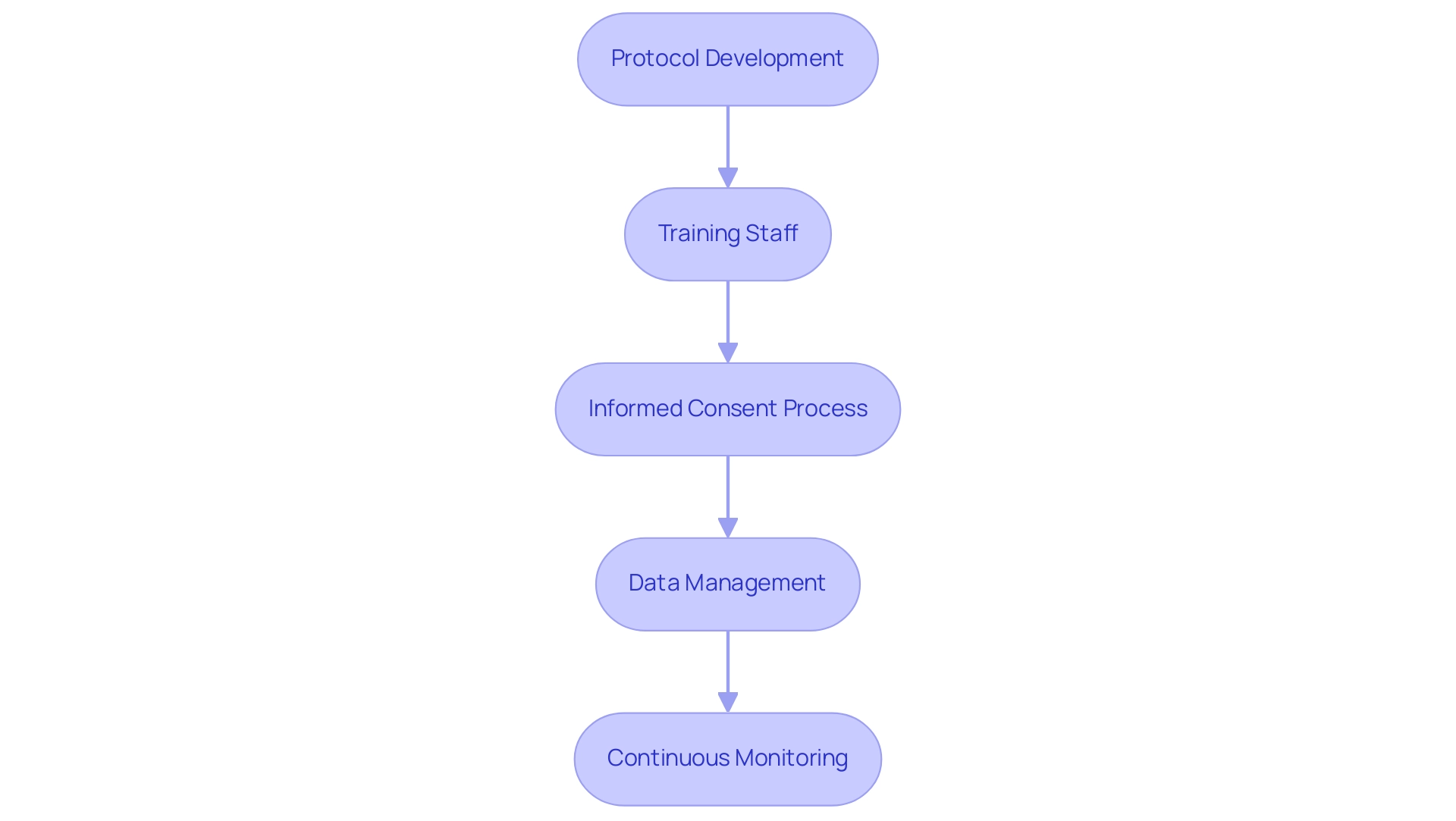
Applying good clinical practices (GCP) in research studies involves several vital steps that are necessary for ensuring compliance and preserving the integrity of the research process. Here are the key components:
-
Protocol Development: Crafting a comprehensive study protocol is the foundation of any medical trial.
This document should clearly outline the objectives, design, methodology, and statistical considerations, adhering to the stringent requirements set forth by ISO 14155, which mandates a Clinical Investigation Plan (CIP) prior to commencing any research study. This plan is vital for ensuring strict accountability and control over documentation and recording, thereby maintaining participant privacy and confidentiality.
-
Training Staff: It is imperative that all team members receive thorough training in good clinical practices (GCP) principles.
Comprehending their specific roles and responsibilities ensures that everyone is aligned with the ethical standards required in research. Helen Mossop from the Biostatistics Research Group underscores this by stating,
Good Statistical Practice—development of tailored Good Clinical Practice training for statisticians,
highlighting the necessity for specialized training.
-
Informed Consent Process: Establishing a transparent and thorough process for obtaining informed consent from participants is fundamental.
ISO 14155 prohibits the use of vulnerable populations in clinical investigations, except where necessary, which emphasizes the importance of ethical considerations in protecting participants.
-
Data Management: Implementing robust data collection and management systems is critical for safeguarding data integrity throughout the study.
Proper data handling ensures accuracy and reliability in results.
-
Continuous monitoring of the experiment's progress is vital.
This includes timely reporting of any adverse events or protocol deviations, ensuring that the study remains compliant with good clinical practices (GCP).
Furthermore, our service capabilities include feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup for testing, import permits, project management, and extensive reporting, which encompasses review and feedback on study documents and nationalization of investigational devices.
The successful implementation of good clinical practices (GCP) not only ensures ethical conduct and high-quality data but also fosters job creation, economic growth, and healthcare improvements in local economies, thereby enabling better international collaboration and advancing the field of medical technology.
A practical example of successful GCP implementation can be seen in the international study conducted by GUSTO investigators, which compared thrombolytic strategies for myocardial infarction.
By meticulously following these steps, researchers can effectively integrate good clinical practices (GCP) into their studies, thereby upholding ethical conduct and generating high-quality, reliable data.
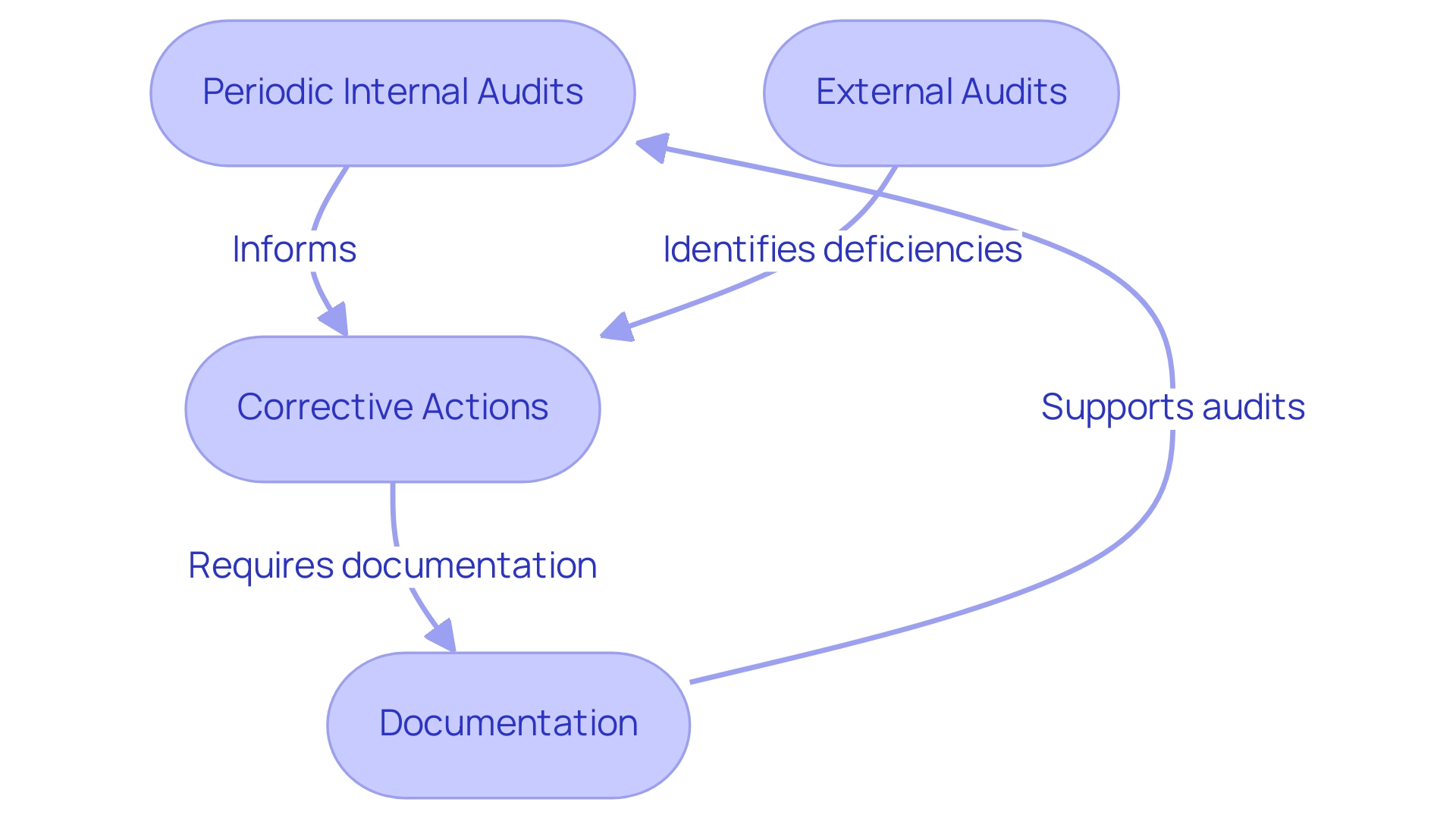
Ensuring Compliance and Auditing in GCP
Ensuring adherence to good clinical practices (GCP) is crucial in the field of research studies and requires a systematic method for auditing and monitoring. Key components integral to this process include:
-
Periodic internal audits are essential for evaluating adherence to good clinical practices (GCP) guidelines.
These audits allow researchers to pinpoint areas for enhancement and elevate overall study quality, underscoring the significance of meticulous compliance evaluations as a component of our extensive management services.
-
External Audits: Institutions must be well-prepared for inspections by regulatory bodies, which typically involve comprehensive reviews of documentation, data integrity, and participant consent processes. Such inspections are essential for ensuring that clinical studies meet established standards of conduct, and our service includes support for study setup, including obtaining import permits and ensuring compliance with country requirements.
-
Corrective Actions: Upon identifying any deficiencies, it is critical to implement corrective actions swiftly. This commitment to continuous improvement not only addresses immediate concerns but also fosters a culture of compliance within study teams, supported by good clinical practices (GCP) and effective project management practices.
-
Documentation: Maintaining meticulous records of all trial activities—including training, participant consent, data collection, and monitoring activities—is essential.
Thorough documentation supports transparency and accountability, facilitating a robust audit trail, which is a key focus of our reporting services. This includes detailed reporting on study status, inventory, and serious and non-serious adverse events.
By prioritizing compliance and auditing, researchers uphold the integrity of their studies, align with regulatory expectations, and actively contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge. The importance of these practices is further underscored by recent discussions in the field.
Dr. Khin, currently working at Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., highlights the essential role of compliance in ensuring ethical and effective research. Moreover, the insights from the case study on Investigation Planning and Conduct illustrate the necessity of an Investigation Plan (CIP), which mandates strict accountability and control over documentation, ensuring ethical conduct in investigations. This aligns with our commitment to comprehensive clinical trial management services, including the review and feedback on study documents to comply with country requirements.
Conclusion
Adherence to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is critical for maintaining the integrity and ethical conduct of clinical research, especially in regions like Latin America. The core principles of GCP—ethical conduct, informed consent, scientific validity, safety monitoring, and data integrity—are essential for protecting research participants and ensuring credible findings. As the clinical trial landscape evolves, the significance of these principles in achieving reliable outcomes and equitable access to medical advancements becomes increasingly evident.
GCP training is vital for all research personnel, providing them with the necessary skills to navigate regulatory requirements and ethical considerations. This training enhances compliance and improves research quality. The availability of various training formats ensures that researchers can select options that fit their needs, promoting a culture of continuous improvement.
Implementing GCP in clinical trials involves meticulous planning, robust data management, and ongoing compliance monitoring. By emphasizing these components, researchers can elevate study quality and contribute to medical innovation. Regular audits and corrective actions further strengthen the commitment to high standards, ensuring ethical conduct and reliable data generation.
In conclusion, the importance of Good Clinical Practice is profound. As the demand for rigorous clinical trials increases, understanding and adhering to GCP is essential for fostering innovation, protecting participant rights, and advancing medical science. A focused approach to implementing GCP principles, supported by comprehensive training and effective management practices, will lead to successful clinical trials that ultimately benefit society.




