Overview
Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) play a crucial role in medtech innovation by allowing developers to assess the viability, safety, and performance of new medical devices before extensive testing. The article highlights how EFS facilitates early data collection and real-world feedback, ultimately leading to faster innovation cycles and improved alignment of medical technologies with actual healthcare needs.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of medical technology, Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) have emerged as a critical component in the development of innovative devices. These preliminary investigations not only assess the viability and safety of new technologies but also bridge the gap between initial concepts and comprehensive clinical trials.
With the recent success of ReGelTec's EFS in Colombia, which utilized cutting-edge hydrogel technology to treat chronic pain, the potential of EFS to yield real-world benefits is becoming increasingly evident.
As the industry grapples with the challenges of digital transformation and the imperative for artificial intelligence integration, EFS offers a structured approach to gather essential data while refining product designs based on early feedback.
This article delves into the multifaceted role of EFS in driving innovation, navigating regulatory frameworks, and addressing the inherent challenges of conducting these studies, ultimately highlighting their significance in shaping the future of medtech.
Understanding Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech
In Medtech Innovation, the role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) is crucial as they serve as preliminary investigations that evaluate the viability and initial safety of new devices before their entry into comprehensive testing. Notably, ReGelTec's recent EFS in Barranquilla, Colombia, successfully treated eleven patients with chronic low back pain using their innovative HYDRAFIL™ hydrogel technology, showcasing the potential of EFS to deliver real-world benefits. The procedures were monitored from a distance through Zoom, showcasing a creative method for carrying out research studies.
The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation allows researchers and developers to collect crucial early data regarding the performance and potential risks of medical technologies within a limited patient population. The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation serves as a link between the conceptual stage of device development and subsequent larger-scale research studies, enabling the enhancement of the technology based on real-world feedback and observations. This proactive approach is particularly significant considering that only 13% of companies see digital transformation as a high priority for 2024, indicating a need for innovative practices in the sector.
Furthermore, with 71% of industry leaders believing that AI adoption is necessary for competitiveness, it underscores the urgency for innovation in medical technology. The role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech innovation can uncover potential issues early in the process, which can substantially reduce the time and costs associated with later-stage trials. High-performing companies, like bioaccess®, are increasingly focusing on robust data management practices, with 71% expressing high confidence in demonstrating traceability during unannounced audits.
Their expertise includes managing EFS through effective site selection, compliance reviews, and project management. The Accelerate EFS Toolkit created by MDIC offers vital resources and best practices for EFS sponsors and research professionals, ensuring that recommendations are based on extensive knowledge and practical experience. Ultimately, The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation contributes to faster innovation in the medtech sector, ensuring that emerging technologies are not only safe but also aligned with medical needs.
Furthermore, the role of early feasibility studies (EFS) in medtech innovation significantly affects trial timelines and expenses, as these investigations can enable prompt adjustments to protocols, thus improving overall efficiency in the medtech sector. Importantly, medtech clinical trials can stimulate local economies by creating jobs and enhancing healthcare, which further emphasizes The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation within the broader context.
The Role of EFS in Driving Medtech Innovation
The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation is crucial as it serves as a cornerstone for innovation within the medical technology sector, enabling developers to test hypotheses and gather essential preliminary data on new technologies. Conducted by experienced professionals at bioaccess®, who boast over 20 years of expertise in Medtech, this research enables investigators to explore critical elements such as:
- Usability
- Preliminary safety
- Potential efficacy of devices
Significantly, insights from EFS have indicated the necessity for modified and adaptive study designs, accommodating device-specific characteristics, with research showing a necessity range of 3–18.2%.
Such findings can lead to pivotal design modifications before the initiation of full-scale evaluations, ensuring the final product aligns closely with clinical requirements. Moreover, the engagement of healthcare professionals and patients throughout the EFS process allows developers to incorporate valuable user feedback into the design, significantly enhancing the likelihood of successful market adoption. This iterative approach accelerates the innovation cycle and ensures that newly developed devices meet the actual needs of end-users effectively.
According to Markiewicz et al., emphasizing device development prior to phase I trials is crucial, as it sets the foundation for successful outcomes in later stages of research. It is also essential to inform stakeholders about the various segments in which clinicians can contribute to EHTA, as their involvement is vital for integrating practical insights into the regulatory framework. The proposed innovation framework for clinician integration across various phases of EHTA underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in medical device development.
Furthermore, bioaccess® specializes in managing a comprehensive range of research, including:
- First-In-Human Trials (FIH)
- Pilot Trials
- Pivotal Trials
- Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Trials (PMCF)
Assessing the cost-effectiveness of the HEAT process itself, as emphasized in the case analysis 'Evaluation of Cost Effectiveness in EHTA,' is vital for justifying investments and enhancing implementation, thereby highlighting The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation within the overall development process while also aiding local economic growth and healthcare advancements.
Regulatory Framework for Early Feasibility Studies
The regulatory landscape for Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Latin America, particularly in Colombia, is influenced by the guidelines established by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States. Recognizing the role of early feasibility studies (EFS) in medtech innovation as a crucial phase in medical device development, the FDA facilitates the collection of vital safety and performance data in a controlled environment. Sponsors must submit a comprehensive Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) application, detailing the design, objectives, and proposed patient population, to ensure ethical conduct and prioritize patient safety.
Recent FDA guidance enhances flexibility during the research process by allowing timely modifications to device and trial protocols. With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) representing 90 to 95 percent of all diabetes cases, the FDA's announcements regarding the role of early feasibility studies (EFS) in medtech innovation for devices aimed at improving glycemic control are particularly pertinent. These innovations are designed to reduce glycated hemoglobin levels independently of medication delivery, marking significant progress in medical technology.
Adhering to these regulatory guidelines not only protects participants but also enhances the credibility of research findings, fostering trust among stakeholders in the development and approval of innovative medical technologies. Furthermore, the FDA accepts Pre-Submissions, allowing sponsors to seek guidance on non-clinical testing strategies and draft trial protocols. This proactive approach, exemplified by experts like Katherine Ruiz at bioaccess®, highlights The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation by emphasizing the importance of early engagement with regulatory bodies in the development process, ensuring compliance and excellence in Medtech research across Latin America.
Bioaccess® provides extensive trial management services, including:
- Feasibility assessments
- Site selection
- Compliance evaluations
- Trial organization
- Import permits
All while adapting to regulatory changes to maintain flexibility in trials.
Challenges and Considerations in Conducting EFS
Navigating a myriad of challenges is essential in conducting Early Feasibility Studies (EFS), highlighting The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation that researchers must effectively address to achieve favorable outcomes. A pivotal consideration is site selection; identifying healthcare sites that possess the appropriate patient demographics is essential for obtaining pertinent data. Logistical factors further complicate the execution of EFS, including recruitment timelines, patient consent procedures, and the allocation of resources.
The recent retirement of several grant mechanisms for pilot/feasibility projects by the National Institutes of Diabetes and Kidney Diseases, now replaced with a single mechanism that funds up to three initiatives annually, highlights the shifting landscape of funding that researchers must navigate. Additionally, leveraging a comprehensive clinical study management service like bioaccess® can significantly alleviate regulatory hurdles, streamline site selection, and ensure compliance, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the research process. This encompasses essential services such as trial set-up, start-up, and approval processes, along with comprehensive reporting on project status and adverse events.
The capacity to adjust to unforeseen challenges, such as patient dropouts or adverse events, is vital, as these elements can greatly affect timelines and outcomes. As noted by R.G. 'Weaver, 'Small investigations, big decisions: the role of pilot/feasibility assessments in incremental science and premature scale-up of behavioral interventions,' it is imperative to recognize the impact of these decisions on research outcomes.
Furthermore, a case analysis on bureaucratic challenges in clinical research illustrates significant delays in project start-up processes, particularly in the U.S., where administrative burdens can extend timelines to nearly a year, compared to 60-90 days in Europe. Therefore, fostering effective communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders is indispensable for proactively addressing these challenges. By maintaining open lines of dialogue, researchers can ensure that the project remains on course and fulfills its objectives, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency of the research process.
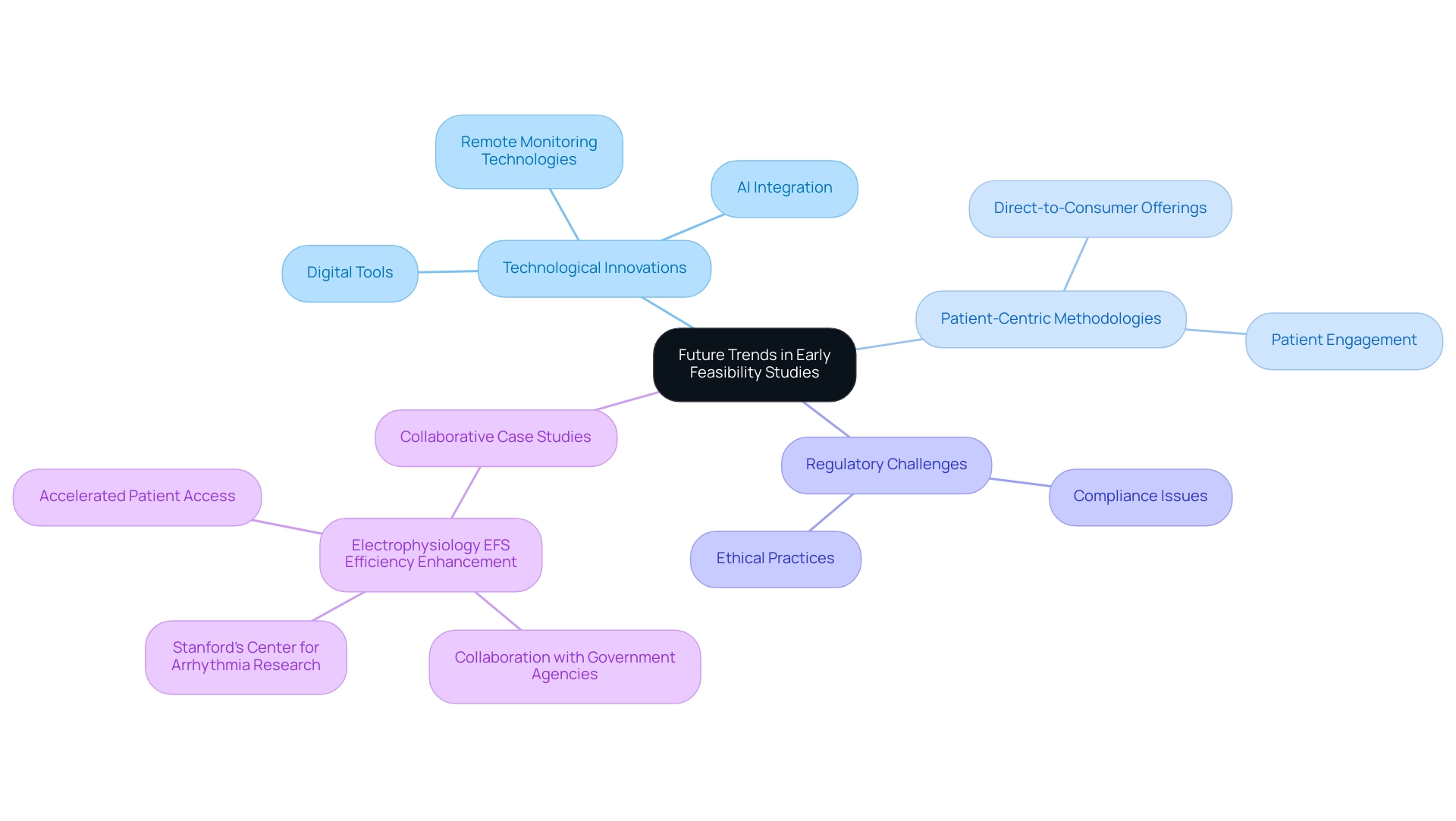
Future Trends and Innovations in Early Feasibility Studies
The outlook for The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation is marked by transformative advancements fueled by technological innovations and refined research methodologies. A pivotal trend is the growing incorporation of digital tools and remote monitoring technologies, which significantly enhance both data collection and patient engagement during EFS. For example, the case study on Electrophysiology EFS Efficiency Enhancement illustrates how collaboration with government agencies and Stanford’s Center for Arrhythmia Research has addressed challenges and broadened participation, ultimately accelerating patient access to innovative treatments.
Moreover, the knowledge of bioaccess®, supported by more than 20 years of experience in managing EFS, First-In-Human (FIH), Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies (PMCF), demonstrates its ability to handle the intricacies of research in Latin America. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into data analysis processes is poised to yield more efficient and insightful outcomes, further enhancing the overall clinical trial management services. As the medical technology landscape continues to evolve, The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation is expected to become increasingly streamlined and adaptive, facilitating quicker iterations and enhancements in device design.
This evolution is propelled by a rising emphasis on patient-centric methodologies, ensuring that patient needs and experiences are prioritized in the progression of medtech innovations. As Jim Welch, EY Global MedTech Leader, notes, 'For MedTech companies, which have typically sold to doctors and hospital systems, direct-to-consumer offerings hold the promise of a new revenue stream.' This shift in engagement strategies could significantly influence The Role of Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation.
Such trends underscore the necessity for adaptation and responsiveness in the evolving regulatory environments across Latin America, particularly as the medtech industry prepares for new opportunities in 2024. The recent $60 million settlement by Pfizer for claims that Biohaven paid kickbacks to doctors serves as a reminder of the regulatory challenges that the medtech sector must navigate, including issues related to compliance and ethical practices.
Conclusion
Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) are essential in advancing medical technology, bridging the gap between initial concepts and comprehensive clinical trials. The success of EFS, such as ReGelTec's study in Colombia, highlights their ability to provide significant real-world benefits, improving patient care while fostering innovation.
Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for effective EFS execution. Compliance with guidelines from organizations like the FDA ensures ethical standards and patient safety, enhancing the credibility of research findings. Proactive engagement with regulatory bodies is vital for the successful integration of new technologies into healthcare.
The challenges of conducting EFS—ranging from site selection to logistical complexities—emphasize the need for efficient clinical trial management. Collaborating with experienced organizations can streamline processes and maintain focus on achieving favorable outcomes.
Looking ahead, the future of EFS is promising, driven by technological advancements and a focus on patient-centric methodologies. The integration of digital tools and artificial intelligence is expected to improve the efficiency of these studies, leading to safer and more effective medical devices.
In summary, EFS is a foundational element in the evolution of medical technology, paving the way for innovations that address real-world healthcare needs. Continued investment in these studies holds the potential for transformative impacts on patient care and the broader medtech landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) in Medtech Innovation?
Early Feasibility Studies (EFS) are preliminary investigations that evaluate the viability and initial safety of new medical devices before they enter comprehensive testing. They collect crucial early data regarding performance and potential risks within a limited patient population.
How did ReGelTec utilize EFS in their recent study?
ReGelTec conducted a recent EFS in Barranquilla, Colombia, where they successfully treated eleven patients with chronic low back pain using their HYDRAFIL™ hydrogel technology. This study showcased the potential of EFS to deliver real-world benefits.
Why are EFS important for medical technology development?
EFS serve as a link between the conceptual stage of device development and larger-scale research studies, enabling enhancements based on real-world feedback. They help uncover potential issues early, which can reduce time and costs associated with later-stage trials.
What role does AI play in Medtech Innovation according to industry leaders?
Seventy-one percent of industry leaders believe that adopting AI is necessary for competitiveness in the medical technology sector, highlighting the urgency for innovation.
How do EFS contribute to the efficiency of clinical trials?
EFS can enable prompt adjustments to protocols, which significantly improves overall efficiency in the medtech sector, potentially reducing trial timelines and expenses.
What are the key elements explored during EFS?
EFS allow investigators to explore critical elements such as usability, preliminary safety, and potential efficacy of medical devices.
How does user feedback influence the EFS process?
Engaging healthcare professionals and patients throughout the EFS process allows developers to incorporate valuable user feedback into the design, enhancing the likelihood of successful market adoption.
What types of trials does bioaccess® manage?
Bioaccess® specializes in managing a range of research trials, including First-In-Human Trials (FIH), Pilot Trials, Pivotal Trials, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Trials (PMCF).
What is the significance of the Accelerate EFS Toolkit?
The Accelerate EFS Toolkit created by MDIC offers vital resources and best practices for EFS sponsors and research professionals, ensuring recommendations are based on extensive knowledge and practical experience.
How do EFS support local economies and healthcare?
Medtech clinical trials, including EFS, can stimulate local economies by creating jobs and enhancing healthcare, emphasizing their broader impact within the medical technology sector.




