Introduction
The International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF), developed by the World Health Organization, represents a transformative approach to understanding health and disability. By emphasizing the complex interplay between health conditions and the contextual factors influencing functioning, the ICF framework provides a structured means for healthcare professionals to articulate and address diverse patient needs. Its comprehensive nature extends beyond traditional medical diagnoses, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and enhancing patient care.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, the ICF's role in shaping research, policy, and clinical practice becomes increasingly vital, offering insights that can lead to improved health outcomes and a more inclusive understanding of disability. This article explores the multifaceted impact of the ICF across various domains, highlighting both its accomplishments and the challenges that lie ahead in its implementation.
Defining ICF: The International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health
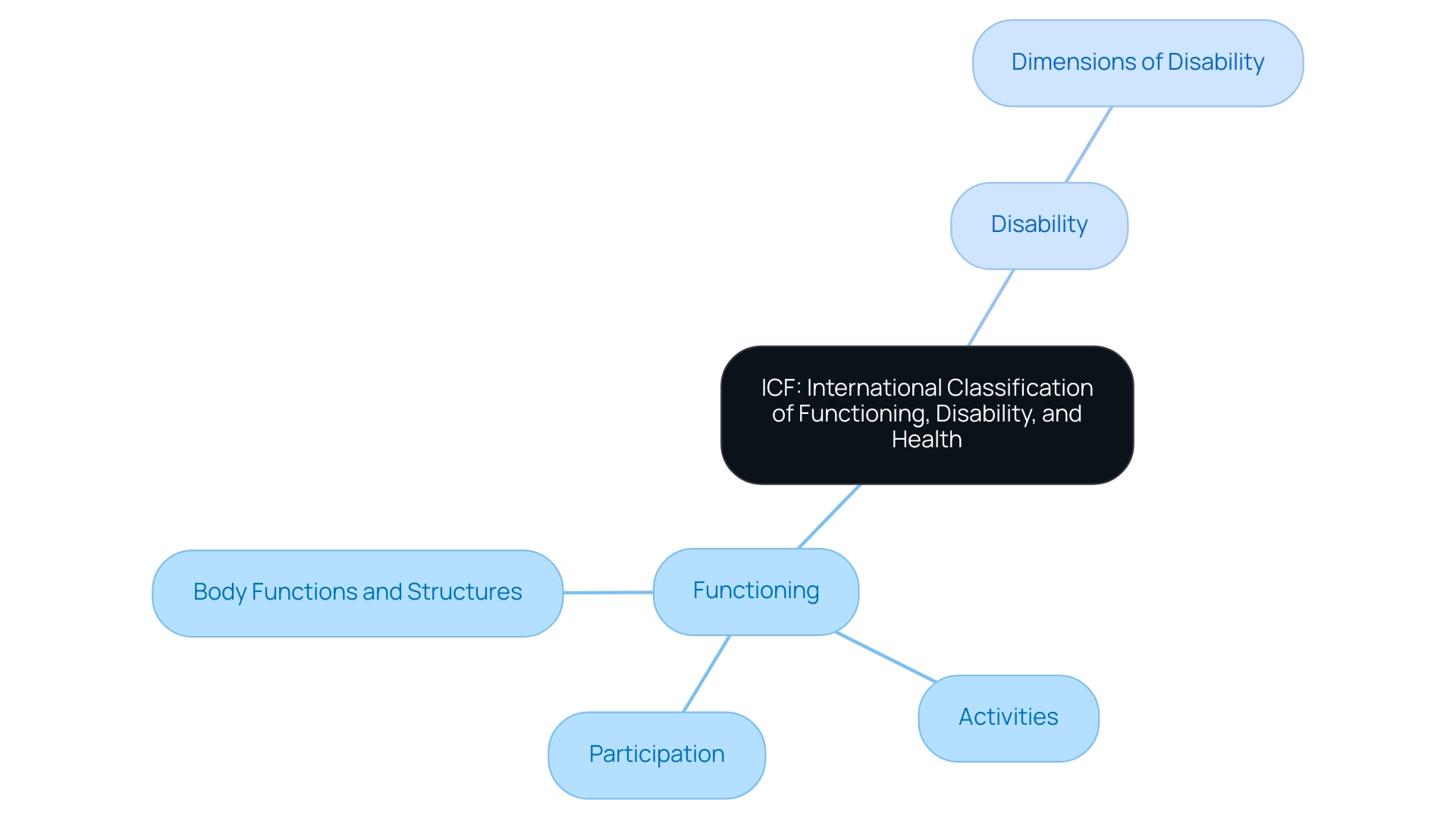
To understand the crucial structure for wellness and related areas, it is important to consider what does ICF stand for in healthcare, as it refers to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Wellness (ICF) created by the World Health Organization (WHO). This classification system highlights the intricate interplay between medical conditions and the contextual factors that shape functioning and disability. The ICF structure is organized into two primary components: functioning and disability, which are further delineated into body functions and structures, activities, and participation.
This organized method is invaluable for healthcare professionals, as it offers a standardized language for expressing wellness and disability, thereby enhancing effective communication and collaboration across diverse sectors within healthcare, which raises the question of what does ICF stand for in healthcare. Recent analyses highlight the system's essential role in fostering a cohesive understanding of disability, with a bibliometric study demonstrating two decades of its use in medical research. Significantly, a study indicated that 79% of respondents utilized the ICF for data registration, while 64% employed it for outcome evaluation, evidencing its integral role in research and practice.
As highlighted by Leonardi et al., 'the ICF has transformed the perception of disability over the past two decades,' emphasizing its significance in both clinical settings and social policies.
The Role of ICF in Enhancing Patient Care and Treatment Decisions
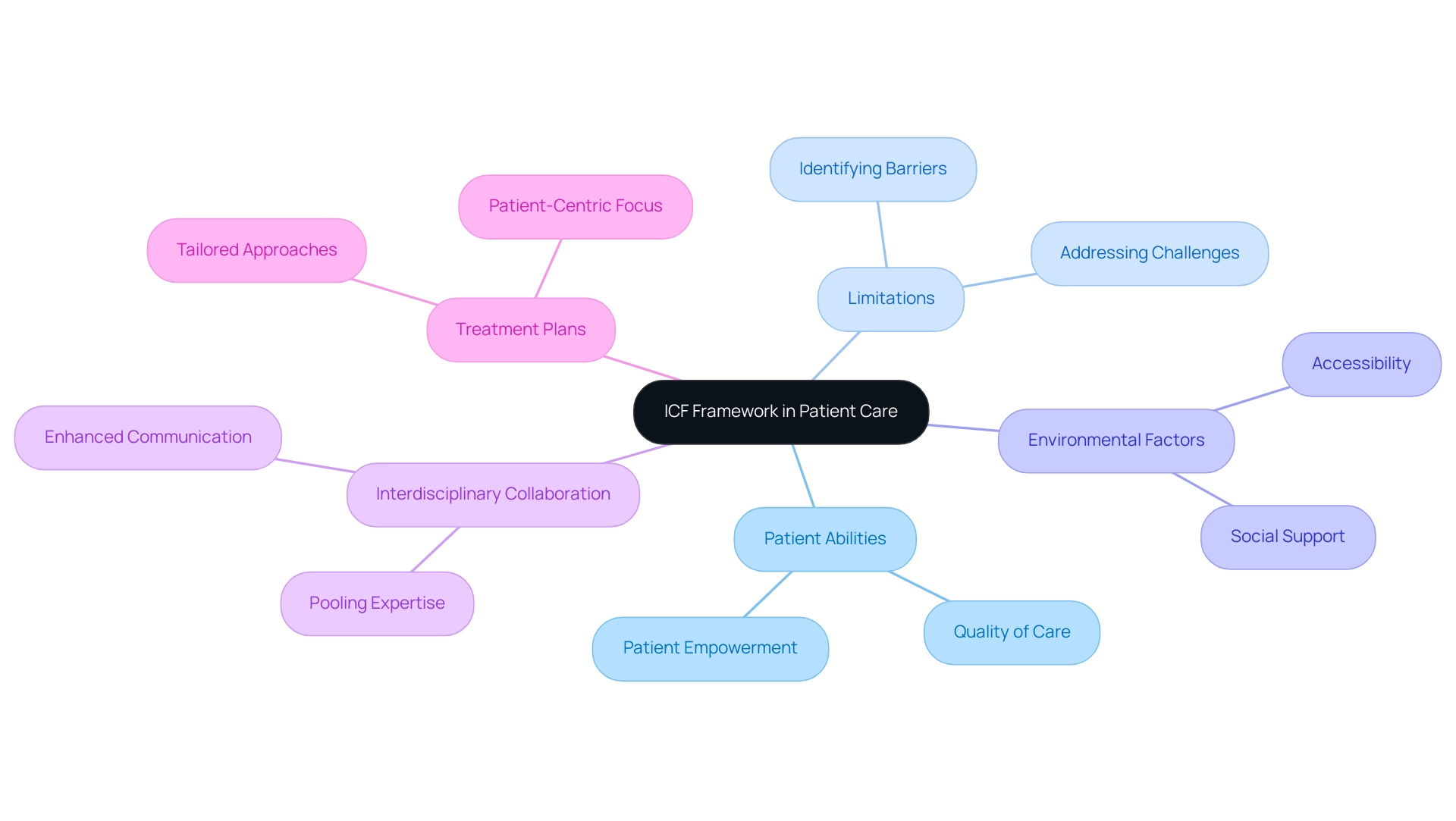
The framework of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) significantly enhances patient care by providing a comprehensive perspective on what ICF stands for in healthcare concerning an individual's health status. It goes beyond mere medical diagnoses to encompass the patient's abilities, limitations, and the surrounding environmental factors. This holistic approach enables providers to create tailored treatment plans that meet the unique needs of each patient.
Interdisciplinary collaboration is a key element fostered by the ICF, which raises the question of what ICF stands for in healthcare, enabling healthcare professionals from various disciplines to pool their expertise and address the multifaceted requirements of patients. A case study titled 'Evaluation of Structural Models' demonstrated the effectiveness of the ICF structure in ensuring unbiased regression results and validating research hypotheses, showcasing its practical implications in clinical settings. Furthermore, statistics indicate that 24.6% of pertinent documents were created by organizations including Ludwig Maximilian University Munich, Swiss Paraplegic Research, and McMaster University, further highlighting its influence on patient care.
This collaborative effort not only enhances the quality of care but also informs medical policies and practices. By emphasizing the significance of functioning and societal participation, the ICF model illustrates what ICF stands for in healthcare, ultimately resulting in better health outcomes and an enhanced quality of life for patients. Furthermore, its implementation in clinical settings has been associated with enhanced communication among medical teams, empowering patients to take an active role in their care processes.
As Ms. Melissa Selb pointed out in her contributions, 'the discussions surrounding what ICF stands for in healthcare are vital for refining treatment approaches and ensuring a patient-centric focus in clinical research,' emphasizing the structure's importance in modern medical practice.
ICF and Its Impact on Research and Policy Development
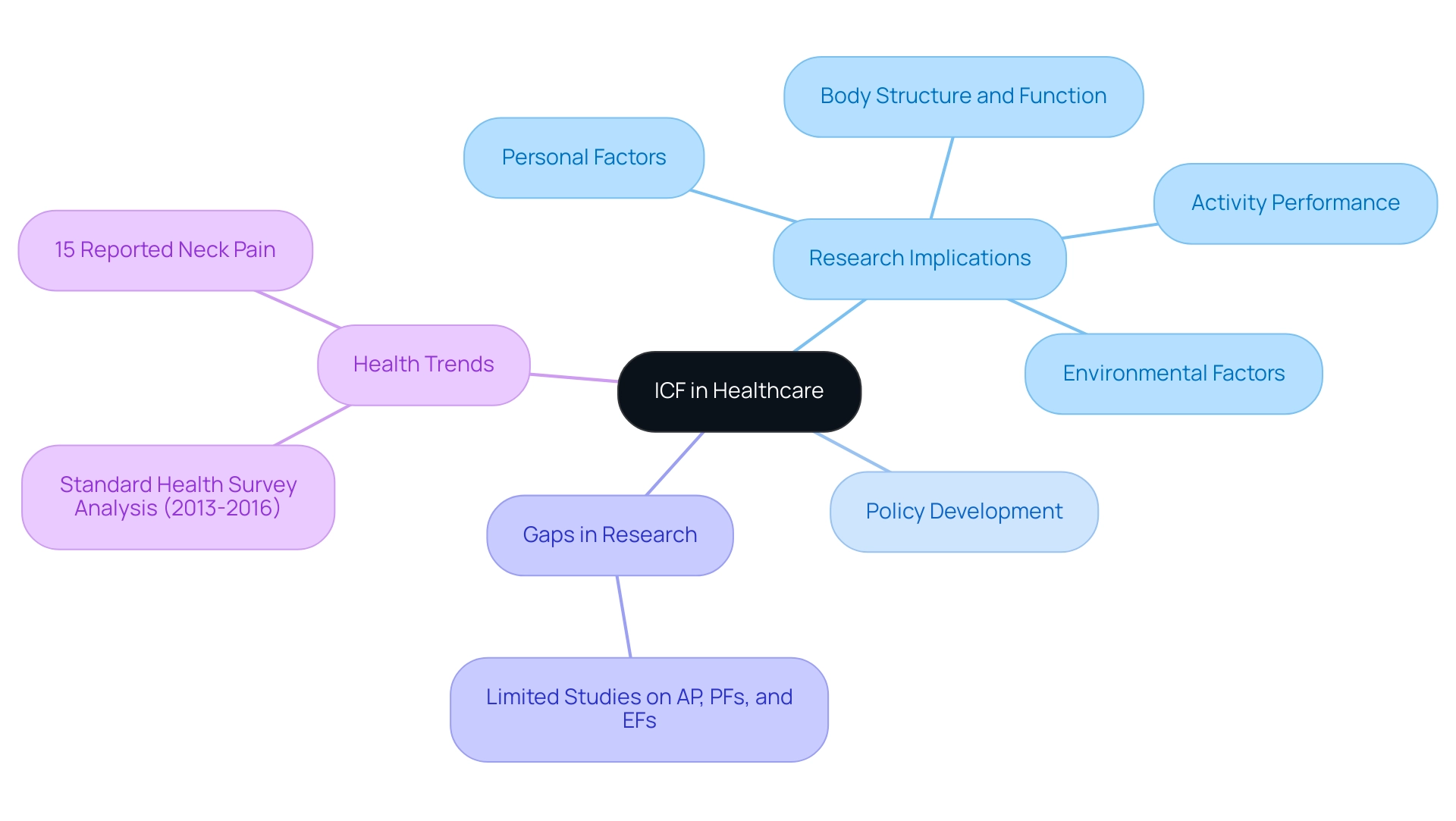
In the context of healthcare, understanding what does ICF stand for in healthcare is essential, as the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) plays a pivotal role in shaping both research and policy development. By offering an organized structure, ICF allows researchers to create studies that thoroughly evaluate the efficacy of different interventions across various aspects of well-being. For instance, a review of research focusing on young adults with cerebral palsy by Jacobson et al. highlighted the importance of social participation, revealing that while many studies assess Body Structure and Function (BSF), only a limited number consider Activity Performance (AP), Personal Factors (PFs), and Environmental Factors (EFs). This gap underscores the need for a more holistic approach to wellness research, which can be understood by exploring what does ICF stand for in healthcare. Furthermore, a statistic showing that 15% of participants reported pain and tension in the neck area further illustrates the significance of ICF in understanding wellness trends.
Policymakers also utilize the ICF to create inclusive wellness policies that address the diverse needs of populations, which raises the question of what does ICF stand for in healthcare, thereby ensuring fair access to medical services. The Institutional Review Board (IRB) emphasizes this by stating,
The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study,
highlighting the ethical considerations inherent in research guided by ICF principles. A case study titled 'ICF Components in Research on Young People with CP' analyzes the assessment methods used in studies focusing on adolescents and young adults with CP, categorizing them according to ICF components.
It reveals a significant gap in research that includes assessments of AP, PFs, and EFs, indicating the need for a comprehensive approach. By incorporating the ICF into both research and policy, stakeholders can effectively identify gaps in medical services and develop targeted strategies to improve wellness outcomes, addressing what does ICF stand for in healthcare. This alignment fosters a comprehensive approach to medical care that prioritizes functioning and participation, ultimately benefiting individuals and communities alike.
The ongoing analysis of the Standard Health Survey results from 2013 to 2016 further illustrates the relevance of ICF in understanding health trends and developing responsive health policies for the future.
Challenges and Limitations of Implementing ICF in Healthcare
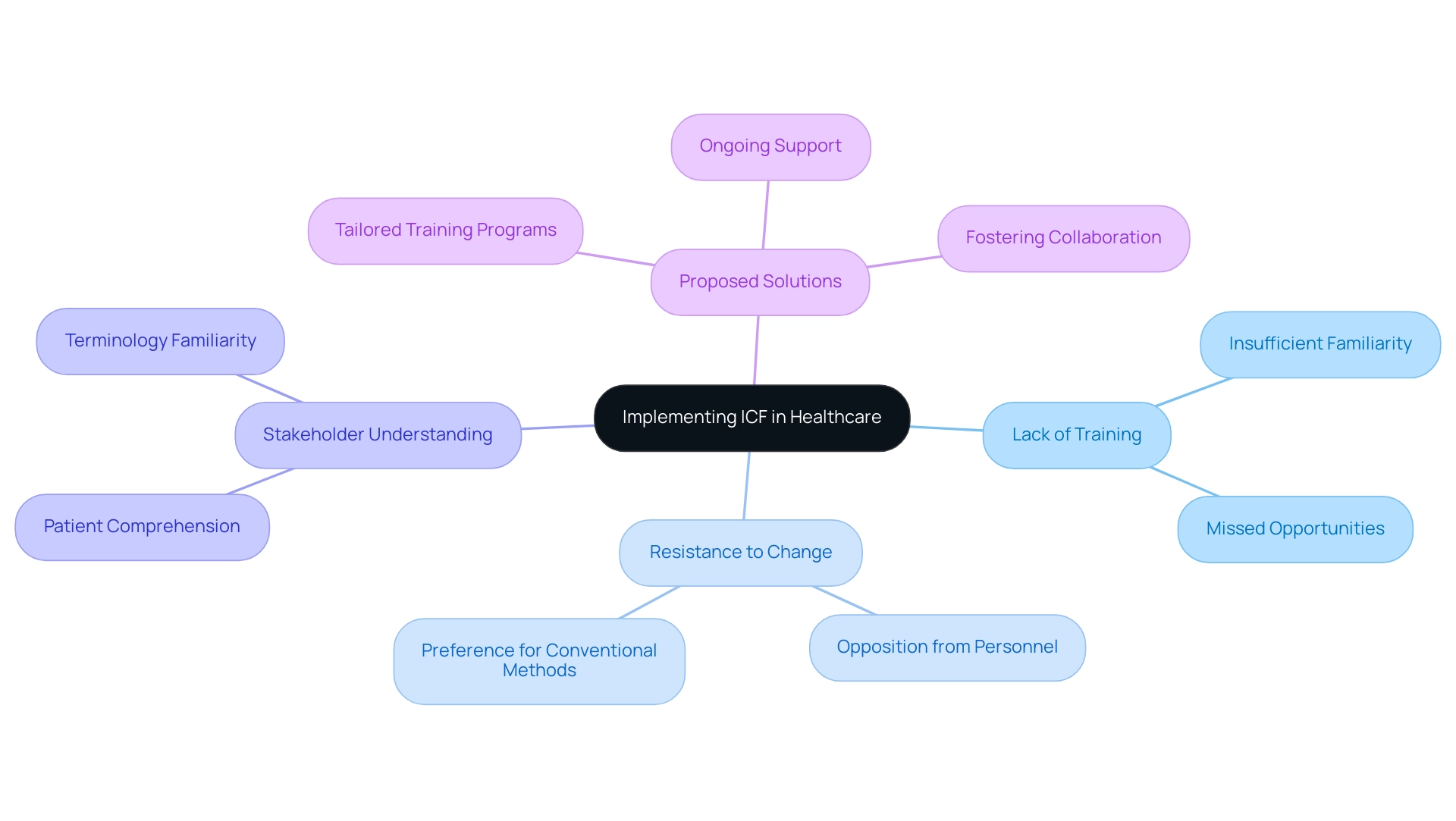
One of the notable challenges in medical environments is understanding what does ICF stand for in healthcare, as it pertains to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. A primary barrier is the lack of sufficient training and familiarity with what does ICF stand for in healthcare among healthcare professionals, which significantly hampers its effective application. Ms. Melissa Selb from Swiss Paraplegic Research emphasizes, "Without adequate training, the ICF framework cannot be fully utilized, leading to missed opportunities in patient care."
Incorporating ICF into current documentation practices and electronic medical records necessitates systemic adjustments that may face opposition from personnel familiar with conventional methods. Furthermore, ensuring that all stakeholders, including patients, comprehend what does ICF stand for in healthcare and the associated terminology and concepts presents an additional challenge. Statistics indicate that organizations investing in comprehensive training programs can expect an average ROI of seven times the cost of employing a coach, highlighting the financial benefits of such investments.
To effectively overcome these obstacles, medical organizations must invest in tailored ICF training programs, provide ongoing support, and foster a culture of collaboration. Such efforts are essential for maximizing the potential of ICF to enhance patient care and improve overall health outcomes, as evidenced by various case studies illustrating the challenges of implementing ICF in medical environments.
Future Directions for ICF in Healthcare
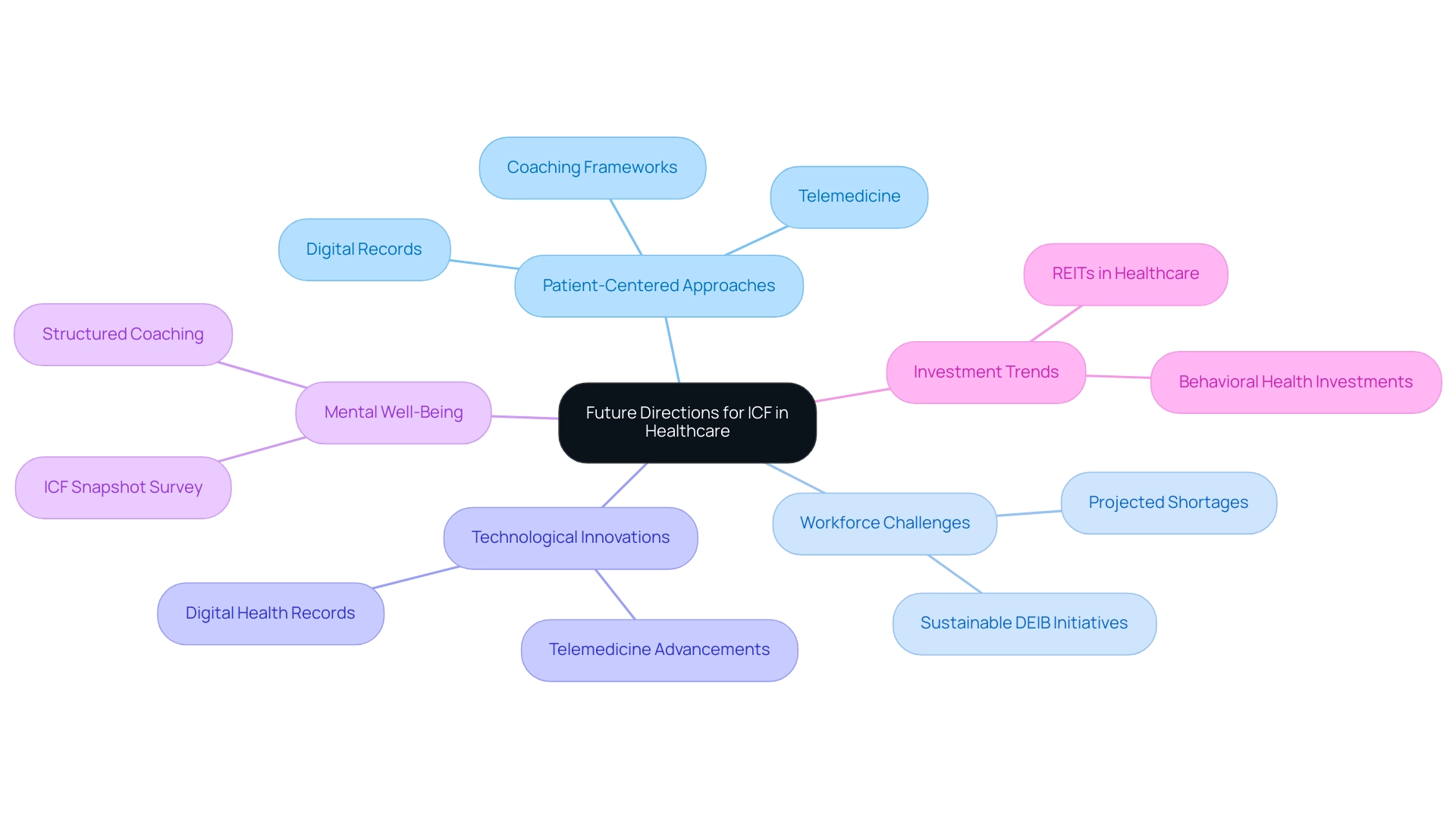
Understanding what does ICF stand for in healthcare reveals its immense promise for the future, particularly as patient-centered approaches become increasingly prioritized. The National Center for Health Workforce Analysis anticipates a substantial shortage of healthcare personnel, projecting thousands of vacancies in the upcoming 15 years, which increases the necessity for effective structures, specifically addressing what does ICF stand for in healthcare to enhance care delivery. Technological innovations, particularly in telemedicine and digital records, provide remarkable opportunities to incorporate principles of what does ICF stand for in healthcare more fluidly into clinical practice.
As noted by Krause,
The challenge is knowing how to root DEIB initiatives in sustainable and impactful ways with this worldview,
highlighting the critical need for a thoughtful approach to implementation. Furthermore, the '2024 ICF Snapshot Survey: Coaching and Mental Well-Being' underscores the growing relevance of what does ICF stand for in healthcare in current research, emphasizing its role in enhancing mental well-being through structured coaching frameworks. A noteworthy trend is the increasing investment in behavioral health by Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), driven by rising demand and favorable reimbursement changes.
This trend signals a shift in medical focus, with continued investment expected alongside challenges related to stigma and workforce needs. By promoting collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers, the ICF framework, which answers what does ICF stand for in healthcare, can continue to evolve, ensuring its vital role in enhancing healthcare systems globally.
Conclusion
The International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) represents a significant advancement in understanding health and disability through a comprehensive and structured framework. By emphasizing the interrelationship between health conditions and contextual factors, the ICF not only provides a standardized language for healthcare professionals but also fosters interdisciplinary collaboration, which is crucial for addressing the diverse needs of patients. Its implementation in clinical practice enhances patient care by allowing for tailored treatment plans and improving communication among healthcare teams.
Despite the substantial benefits, the adoption of the ICF framework is not without challenges. The lack of training and familiarity among healthcare professionals poses a barrier to its effective application. Organizations must prioritize comprehensive training and support to maximize the potential of the ICF in enhancing patient outcomes. Additionally, as the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the ICF's role in shaping research and policy development becomes increasingly vital, ensuring that health interventions are inclusive and responsive to the needs of various populations.
Looking ahead, the future of the ICF is promising, particularly as patient-centered approaches gain traction. The integration of technological innovations into healthcare practices presents an opportunity to embed ICF principles more seamlessly. As stakeholders collaborate and invest in the ICF framework, it is poised to play a critical role in transforming healthcare systems, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and a more inclusive understanding of disability. Embracing the ICF not only advances clinical practice but also contributes to a broader societal shift towards valuing functioning and participation in health and wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does ICF stand for in healthcare?
ICF stands for the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health, created by the World Health Organization (WHO).
What are the main components of the ICF framework?
The ICF framework is organized into two primary components: functioning and disability. These are further divided into body functions and structures, activities, and participation.
How does the ICF improve communication among healthcare professionals?
The ICF provides a standardized language for expressing wellness and disability, enhancing effective communication and collaboration across diverse sectors within healthcare.
What role does the ICF play in medical research?
The ICF has been used extensively in medical research, with studies indicating that 79% of respondents utilized it for data registration and 64% for outcome evaluation.
How has the perception of disability changed due to the ICF?
The ICF has transformed the perception of disability over the past two decades, emphasizing its significance in both clinical settings and social policies.
In what ways does the ICF enhance patient care?
The ICF enhances patient care by providing a comprehensive perspective on an individual’s health status, including abilities, limitations, and environmental factors, which helps create tailored treatment plans.
What benefits does interdisciplinary collaboration bring in the context of ICF?
Interdisciplinary collaboration fostered by the ICF enables healthcare professionals from various disciplines to pool their expertise, addressing the multifaceted requirements of patients and improving the quality of care.
How does the ICF influence medical policies and practices?
The ICF informs medical policies and practices by emphasizing the importance of functioning and societal participation, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and enhanced quality of life for patients.
What impact does the implementation of the ICF have on communication among medical teams?
The implementation of the ICF has been associated with enhanced communication among medical teams, empowering patients to take an active role in their care processes.
Why are discussions about the ICF important in clinical research?
Discussions surrounding the ICF are vital for refining treatment approaches and ensuring a patient-centric focus in clinical research, highlighting its importance in modern medical practice.




