Introduction
In the realm of clinical research, the integrity and efficiency of data management are paramount. Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems have emerged as essential tools, revolutionizing the way clinical trial data is collected and managed. These systems not only streamline the data entry process but also enhance data quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
As organizations increasingly adopt Direct Data Capture (DDC) methods, the focus shifts to real-time data collection, which mitigates common errors and improves participant engagement. With regulatory bodies continuously updating guidelines, understanding Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and implementing robust training programs are critical for research teams.
This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of EDC systems, exploring:
- Techniques for data validation
- Compliance measures
- The importance of training personnel
Ultimately, it highlights the transformative impact these advancements have on the clinical trial landscape.
Understanding Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems function as essential software applications that enable effective clinical data capture and management of research information. By simplifying the clinical data capture process, these systems significantly reduce the risk of mistakes and enhance information integrity, which is essential in medical research. Our comprehensive clinical study management services encompass:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Setup
- Project management
- Monitoring
ensuring that each study runs smoothly and effectively.
Notably, research indicates that the digital divide is shrinking across age, income, and race demographics, making EDC systems more accessible and relevant to diverse populations. The capability to access information in real-time empowers researchers with timely insights, essential for effective decision-making throughout the trial process. When evaluating EDC systems, it is crucial to assess factors such as:
- User-friendliness
- Regulatory compliance features
- Capacity for clinical data capture
- Integration with existing systems
Adhering to FDA 21 CFR Part 11 standards and local regulatory requirements is critical for ensuring the authenticity and security of clinical data capture. Furthermore, investing in comprehensive training for staff on the EDC system maximizes its functionality, ultimately leading to enhanced clinical data capture processes and contributing to the overall success of research studies. A pertinent example is the Motivational Enhancement System for Postpartum Women, a brief computer-assisted intervention aimed at increasing motivation to reduce drug use among postpartum women.
Created through randomized controlled studies, this system has demonstrated promise in encouraging individuals to pursue additional treatment services, emphasizing the potential of e-technologies in tackling substance use problems. As Abu Saleh Mohammad Mosa, Director of Research Informatics, observes, 'In recent years, the adoption of clinical data capture systems for trial research has greatly increased,' highlighting the growing acknowledgment of these systems in improving the research landscape. Moreover, the impact of Medtech research studies extends beyond investigation, contributing to job creation, economic growth, healthcare improvement, and fostering international collaboration.
Leveraging Direct Data Capture for Enhanced Data Quality
Direct Information Capture (DDC) is a revolutionary method that involves gathering information directly from primary sources, such as patients or medical instruments, via electronic devices or mobile applications. The application of clinical data capture can lead to significant improvements in information quality and operational efficiency within trial processes. For example, electronic patient-reported outcomes (ePRO) tools allow participants to submit their health information in real-time.
This immediacy significantly mitigates recall bias—an often overlooked source of error in clinical research—while simultaneously boosting compliance rates among participants. Furthermore, DDC systems are usually fitted with automated validation checks that quickly inform researchers of any inconsistencies or missing information during the entry process. To fully harness the potential of DDC, it is essential to invest in intuitive user interfaces and provide comprehensive training for participants.
By ensuring that users are comfortable with the technology, researchers can achieve higher quality information and ultimately enhance overall research results. The expanding collection of literature supports these findings, indicating that DDC not only enhances information quality but also positively influences clinical data capture and clinical trial compliance, reinforcing its status as a best practice in contemporary clinical investigations. Significantly, merely 15% of research at present employs standards like WHO ICD version 9 or 10, emphasizing a domain for enhancement in standardization.
As Andersen et al. pointed out, traditional 100% SDV monitoring only marginally reduced error rates (0.26%) compared to partial SDV, challenging the notion that a 0% error rate is an achievable goal. This highlights the need for robust data quality management procedures for clinical data capture, as demonstrated in the case analysis on data quality enhancement, which emphasizes the necessity for standardized approaches in DQ assessment.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulatory Standards
To achieve compliance with regulatory standards, it is imperative for research teams to thoroughly understand Good Practice (GCP) guidelines alongside the regulatory requirements set forth by agencies such as the FDA and EMA. Our extensive research management services include:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Setup
- Import permits
- Project oversight
- Reporting on study status and adverse events
All of which are crucial for upholding regulations and guaranteeing the success of studies. A pivotal aspect of this process involves the establishment of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for data management, which should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect current best practices.
Training sessions focusing on regulatory requirements and ethical considerations are essential, as a well-informed staff is key to upholding compliance standards. Moreover, accurate record-keeping and documentation of all research activities support compliance and are essential for effective clinical data capture, streamlining the audit and inspection processes. Recent statistics indicate that negative percent agreement increases to 99.2% in the new scenario, underscoring the importance of rigorous compliance measures and the effectiveness of our services in achieving these standards.
The Accelerating Clinical Trials EU (ACT EU) initiative offers valuable insights by publishing monthly statistics on research authorization in the EU and EEA, illustrating the ongoing transformation within the research landscape, including the number of applications submitted and their outcomes. In addition to these practices, organizations can benefit from implementing compliance monitoring tools capable of tracking adherence to protocols and identifying potential non-compliance issues at an early stage. As observed by Agata Higgerson, who participated in this work while working for the European Medicines Agency (EMA), staying informed about regulatory advancements is essential in managing the intricacies of research, especially considering the difficulties encountered in upholding adherence to changing standards.
This proactive method guarantees that medical studies not only fulfill regulatory compliance but also enhance the integrity and validity of research outcomes.
Implementing Data Validation Techniques
Implementing robust validation techniques in electronic capture (EDC) systems is essential to ensure the integrity and quality of clinical data capture in clinical trial information. This process encompasses several strategies, notably:
- Automated checks
- Manual reviews
- Consistency checks
Automated validation rules can be effortlessly incorporated into EDC systems, enabling the real-time detection of out-of-range values, missing information, and inconsistencies.
These automated checks significantly reduce the risk of human error and enhance overall efficiency. However, the role of trained personnel in conducting manual reviews remains essential, particularly for high-stakes entries where accuracy is paramount. Furthermore, consistency checks—such as cross-referencing information from various sources or time points—are invaluable in revealing discrepancies that may otherwise go unnoticed.
Regular audits of information quality and validation processes should be incorporated into the research protocol. This practice not only facilitates the prompt resolution of issues but also upholds the overall integrity of the research. As Dr. Akanksha Goyal aptly noted, tools like the DVP provide critical metrics on aging queries, which are essential for Clinical Data Managers to effectively manage timelines associated with clinical data capture and improve the validation process.
In a setting where artificial intelligence is transforming research studies, as emphasized in the case study 'Revolutionizing Research Studies: The Role of AI in Accelerating Medical Breakthroughs,' these automated validation methods are crucial in optimizing processes, ultimately speeding up the pace of medical advancements. Moreover, statistics on information quality problems discovered through validation procedures highlight the necessity of these techniques, emphasizing their significance in research related to healthcare.
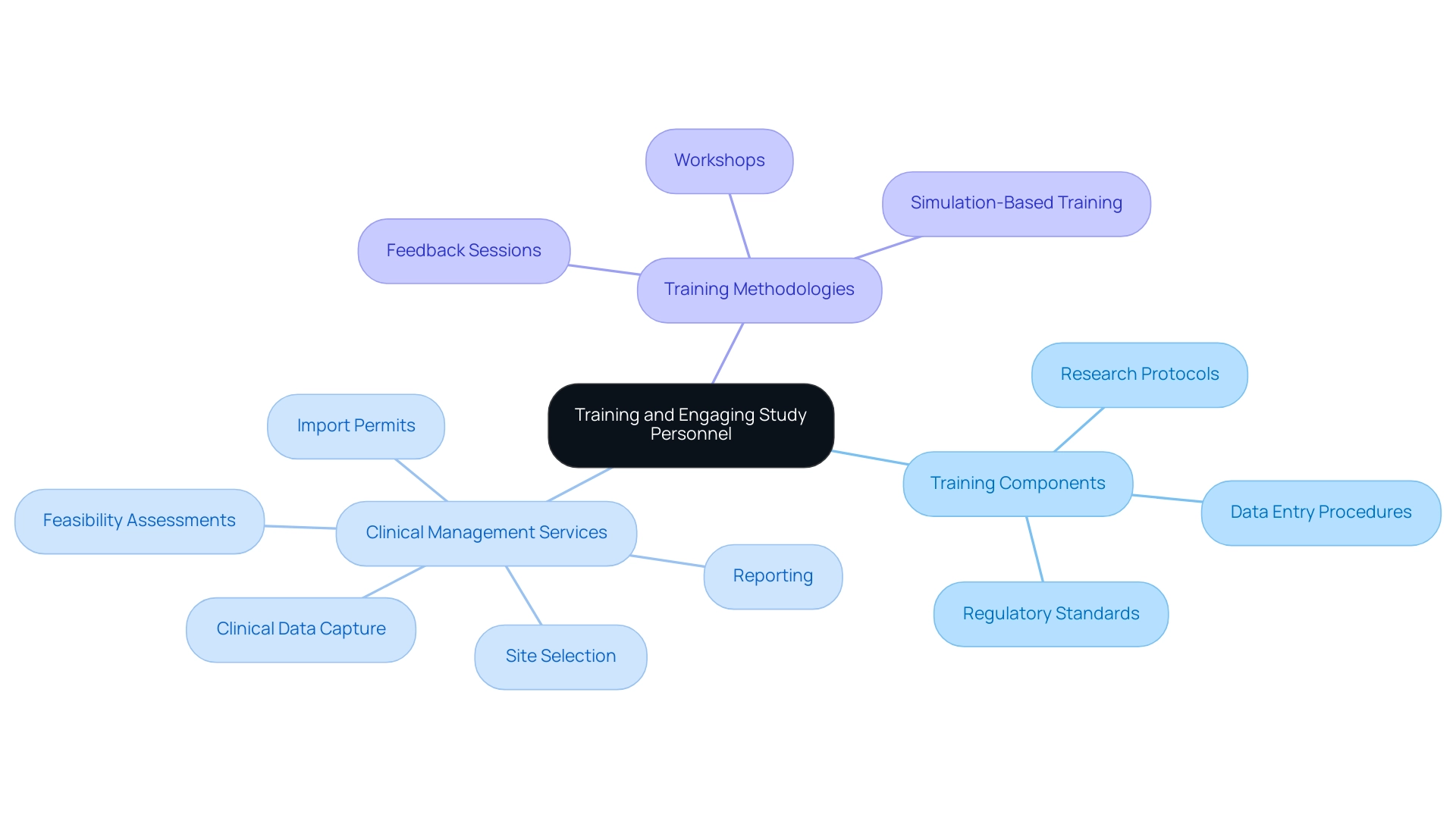
Training and Engaging Study Personnel
Creating efficient training programs for all staff engaged in research studies is vital for success. These programs should thoroughly address:
- Research protocols
- Data entry procedures
- Adherence to regulatory standards
These elements are essential to our extensive clinical management services, including:
- Clinical data capture
- Feasibility assessments
- Site selection
- Import permits
- Reporting
Regular workshops and refresher courses are essential to keep teams abreast of emerging technologies and best practices in the field, enabling us to meet compliance reviews and trial setup requirements efficiently.
Engaging study teams through discussions and feedback sessions fosters a collaborative environment that promotes knowledge sharing and problem-solving. Simulation-based training has been shown to significantly enhance understanding and retention of complex processes, ultimately resulting in improved practices for clinical data capture and management. In fact, the evaluation of training effectiveness emphasizes that suitably trained monitors and CRAs are becoming more essential as the research landscape grows more intricate.
Evidence suggests that these professionals are better prepared to navigate this complexity. As Maria Luisa Garcia Perez, a Project Management Technician at the Aragonese Institute of Health Sciences, states,
Learning by doing is an interesting training strategy for health care professionals because of its emphasis on the <.
This approach aligns with findings from an analysis of training strategies in low and middle-income countries, which revealed that educational outreach visits were the most effective method, achieving significant improvements in healthcare provider performance, followed by in-service training and peer-to-peer learning.
By implementing carefully developed, theory-based, and piloted training programs focused on clinical data capture, organizations can ensure long-term success and enhance the overall performance of clinical trial personnel, ultimately contributing to the positive impact of Medtech clinical studies on local economies and aligning with the regulatory functions of INVIMA and the innovative landscape led by bioaccess®.
Conclusion
The exploration of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems reveals their critical role in enhancing the efficiency and integrity of clinical trial data management. By streamlining data entry and minimizing errors, EDC systems not only uphold data quality but also ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards. The integration of Direct Data Capture (DDC) methods further amplifies these benefits, allowing for real-time data collection that boosts participant engagement and reduces recall bias.
Moreover, adherence to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and the implementation of robust training programs are essential for fostering a well-informed research team capable of navigating the complexities of clinical trials. The importance of data validation techniques cannot be overstated, as they are vital for maintaining the accuracy and reliability of the data collected. Regular audits and automated checks serve to bolster data integrity, ensuring that clinical findings are both valid and actionable.
In conclusion, the advancements in EDC systems, combined with a strong emphasis on training and compliance, are transforming the clinical trial landscape. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise not only to enhance the quality of research but also to contribute to broader economic and healthcare improvements. Embracing these innovations is imperative for organizations aiming to stay at the forefront of clinical research and deliver impactful results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems?
EDC systems are essential software applications that facilitate effective clinical data capture and management of research information, improving accuracy and integrity in medical research.
What services are included in comprehensive clinical study management?
Comprehensive clinical study management services include feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, project management, and monitoring.
How do EDC systems enhance research accessibility?
Research indicates that the digital divide is shrinking across various demographics, making EDC systems more accessible and relevant to diverse populations, allowing for real-time information access.
What factors should be assessed when evaluating EDC systems?
Important factors to consider include user-friendliness, regulatory compliance features, capacity for clinical data capture, and integration with existing systems.
Why is compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11 standards important?
Adhering to FDA 21 CFR Part 11 standards and local regulatory requirements is critical for ensuring the authenticity and security of clinical data capture.
What is Direct Information Capture (DDC)?
DDC is a method of gathering information directly from primary sources, such as patients or medical instruments, using electronic devices or mobile applications.
How does DDC improve clinical trial processes?
DDC enhances information quality and operational efficiency by allowing real-time health information submission, reducing recall bias, and increasing participant compliance rates.
What role do automated validation checks play in DDC systems?
Automated validation checks in DDC systems quickly inform researchers of inconsistencies or missing information during data entry, improving data quality.
What is the significance of training participants in DDC systems?
Providing comprehensive training for participants ensures they are comfortable with the technology, leading to higher quality information and improved research results.
What challenges exist in the standardization of clinical research data?
Currently, only 15% of research employs standards like WHO ICD version 9 or 10, indicating a need for enhanced standardization in clinical data capture practices.
What does the case analysis on data quality enhancement emphasize?
The case analysis emphasizes the necessity for standardized approaches in data quality assessment to improve clinical data capture processes.




