Overview
Best practices for medical device testing standards focus on ensuring compliance and safety by adhering to established regulatory frameworks and methodologies. The article highlights the critical importance of compliance with standards like ISO 13485 and ISO 14971, which are essential for risk management and quality assurance in medical device development, thereby safeguarding patient health and enhancing product credibility.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of medical devices, compliance with stringent regulations is paramount to ensuring patient safety and product efficacy. These devices, ranging from simple bandages to advanced imaging systems, are subject to rigorous testing and oversight by regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States and INVIMA in Colombia.
As the landscape of medical device regulation evolves, stakeholders must navigate a complex web of standards and methodologies to avoid the pitfalls of non-compliance, which can lead to severe legal and financial repercussions.
This article delves into the critical aspects of medical device compliance, exploring the essential testing methodologies, international standards, and regulatory frameworks that govern the industry, while highlighting the increasing importance of biocompatibility testing in safeguarding public health.
Understanding Medical Devices and the Importance of Compliance
Medical instruments encompass a broad range of products, from basic bandages to sophisticated imaging systems, each with distinct characteristics and regulatory obligations. To navigate this landscape effectively, adherence to medical device testing standards is crucial for confirming that these products meet established safety and efficacy criteria before market entry. In the United States, the FDA and other regulatory authorities, such as Health Canada, enforce comprehensive guidelines aimed at protecting patients from potentially harmful products.
Likewise, in Colombia, the INVIMA (National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute) operates as a Level 4 health authority under PAHO/WHO, supervising regulation and classification of health products. The significance of these regulations is emphasized by recent events, such as the FDA's impending implementation of the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act (MoCRA) requirements beginning July 1, 2024, which may lead to increased inspections and enforcement actions in the healthcare equipment sector. Stakeholders engaged in the development and testing of healthcare products must possess a thorough understanding of the medical device testing standards compliance landscape; non-compliance can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions.
Challenges such as regulatory hurdles, competition, recruitment issues, and financial constraints continue to impact health technology startups during clinical trials. Our services include:
- Feasibility and selection of research sites and principal investigators
- Review and feedback on study documents to comply with country requirements
- Trial setup
- Project management
- Reporting on study status, inventory, and adverse events
Historical cases, like the $250,000 fine against Health Net Inc. in 2010 and the $100,000 penalty on Providence Health & Services in 2008, underscore the importance of adherence to these regulations, particularly concerning HIPAA compliance.
Furthermore, regulatory figures, including Doug Dziak, CPSC Commissioner, have emphasized the urgent need for stringent compliance measures, stating that limitations on the CPSC’s civil penalty authority hinder efforts to deter corporate violations of consumer protection laws. As the terrain of healthcare equipment regulation grows more intricate, it is crucial for stakeholders to stay alert and proactive in their compliance endeavors, particularly considering data suggesting an increase in compliance failures expected in 2024.
Key Testing Methodologies for Ensuring Medical Device Safety
Guaranteeing the security of medical instruments requires a comprehensive strategy incorporating multiple evaluation techniques, such as:
- Mechanical evaluation
- Electrical security assessment
- Biocompatibility analysis
Mechanical assessment is essential as it measures the strength and durability of instruments under expected conditions of use, offering crucial insights into their long-term reliability. For example, research shows that 85% of equipment that undergoes thorough mechanical evaluation comply with standards, greatly lowering the risk of failure in practical uses.
Electrical reliability assessments enhance this assurance by verifying that equipment functions securely without creating electrical risks for patients, an essential aspect in equipment design, particularly with the growing intricacy of contemporary technologies. Moreover, usability testing plays a crucial role by evaluating how easily healthcare professionals and patients can operate the equipment, identifying potential user errors that could jeopardize security. These methodologies must adhere to established medical device testing standards, including:
- ISO 14971 for effective risk management
- IEC 60601, which regulates electrical integrity
Such compliance is vital for a comprehensive evaluation of equipment safety and efficacy. Recent advancements in these testing methodologies have further refined practices, with data reflecting the need for manufacturers to proactively adapt to emerging trends while maintaining adherence to medical device testing standards. As Professor Inmaculada B. Aban notes, "the National Institute of Neurological Diseases calls for more rigorous reporting of these studies to raise awareness on the proper design and conduct of future preclinical studies as well as the proper interpretation of the results of completed studies."
This emphasizes the critical need for transparency and thoroughness in evaluations of equipment. Furthermore, improvements to Medical Equipment Reporting (MDR) tracking and the MAUDE database will enhance adverse medical equipment reporting, further ensuring that protocols are meticulously followed. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® specializes in comprehensive clinical trial management services, including:
- Early-Feasibility Studies
- First-In-Human Studies
- Pilot Studies
- Pivotal Studies
- Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies
These evaluation methodologies are essential to our clinical trials, ensuring that each study complies with the medical device testing standards for security and effectiveness. Case studies, like the Early Feasibility Study on HYDRAFIL™, illustrate how comprehensive clinical trial management services can confirm the efficacy of instruments while guaranteeing that protocols are carefully adhered to.
Navigating International Standards for Medical Device Testing
Navigating international medical device testing standards for healthcare product testing is essential for manufacturers seeking global market access, particularly in Colombia, where INVIMA (Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute) plays a pivotal role. Founded in 1992, INVIMA is tasked with overseeing health products, including therapeutic instruments, and ensuring adherence to standards of quality, effectiveness, and security as acknowledged by the Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization as a Level 4 health authority. The Directorate for Health Products and other Technologies within INVIMA manages the regulation of health products, monitoring their safety and effectiveness throughout their lifecycle.
ISO 13485 sets the quality management system criteria for organizations engaged in the design and production of healthcare products, ensuring that they consistently satisfy both regulatory and customer expectations. The term 'implantable health instrument' as used in ISO 13485 aligns with the definition of 'implant' defined in § 860.3, providing clarity on the terminology. The FDA recognizes ISO 13485 as a pivotal framework, providing access to this copyrighted document through the ANSI Standards Incorporated By Reference portal.
Furthermore, ISO 14971 outlines the risk management process, focusing on the identification and mitigation of risks related to product safety. As noted by the FDA, compliance with these standards not only ensures adherence to regulations but also significantly enhances product credibility with regulatory bodies and healthcare providers worldwide. The FDA has expressed concerns regarding the implementation of a phased-in effective date, stating that having two inspectional programs in operation simultaneously could lead to confusion.
Additionally, the FDA clarified that in cases of conflict between ISO 13485 clauses and the FD&C Act, the FD&C Act will control. The organized method of ISO 13485, which encompasses elements like risk management, document control, and product realization, helps manufacturers comply with medical device testing standards to ensure the provision of safe and effective healthcare products. This comprehensive framework is increasingly acknowledged worldwide, with widespread adoption expected in healthcare equipment production by 2024.
Authorities such as Katherine Ruiz highlight the significance of comprehending and adhering to INVIMA's regulations and the particular methodologies it uses to effectively manage the intricacies of the Colombian health product market.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing Medical Device Testing
Navigating the regulatory landscape for healthcare equipment testing requires an understanding of medical device testing standards, as different countries impose their own specific requirements. In the United States, the FDA supervises the approval procedure, requiring that manufacturers submit either a premarket notification (510(k)) or a premarket approval (PMA) application, depending on the classification of the product. In Colombia, INVIMA (Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos) plays a critical role as the national regulatory authority, established in 1992 under the Ministry of Health and Social Protection.
INVIMA is responsible for examining and overseeing the marketing and production of health products, ensuring adherence to health standards while granting approval for imports and exports. Its Directorate for Healthcare Instruments and other Technologies specifically oversees healthcare tools, tracks pre- and post-market programs, and establishes medical device testing standards for production, marketing, and quality assurance. This oversight is vital for producers, as it directly affects their capability to enter the market and ensures that their equipment complies with medical device testing standards for protection and effectiveness.
Recently classified as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO, INVIMA exemplifies competence in health regulation, guaranteeing safety, efficacy, and quality of healthcare instruments. Meanwhile, Health Canada enforces its own set of regulations that must be adhered to for approval, necessitating an understanding of both frameworks to ensure compliance. As regulatory expert Jennifer Hemmerdinger observes, 'the 18th annual Pulse of the MedTech Industry report reveals the health technology (MedTech) sector persistently advancing into new areas,' highlighting the significance of remaining updated on the newest regulatory structures for health product evaluation in 2024.
Additionally, the FDA intends to request any additional information needed for the Breakthrough Device designation decision within 30 days of receiving the request and will communicate its decision within 60 calendar days. Manufacturers must be vigilant in understanding these processes to avoid costly delays in bringing their products to market and to leverage the opportunities presented by evolving regulations.
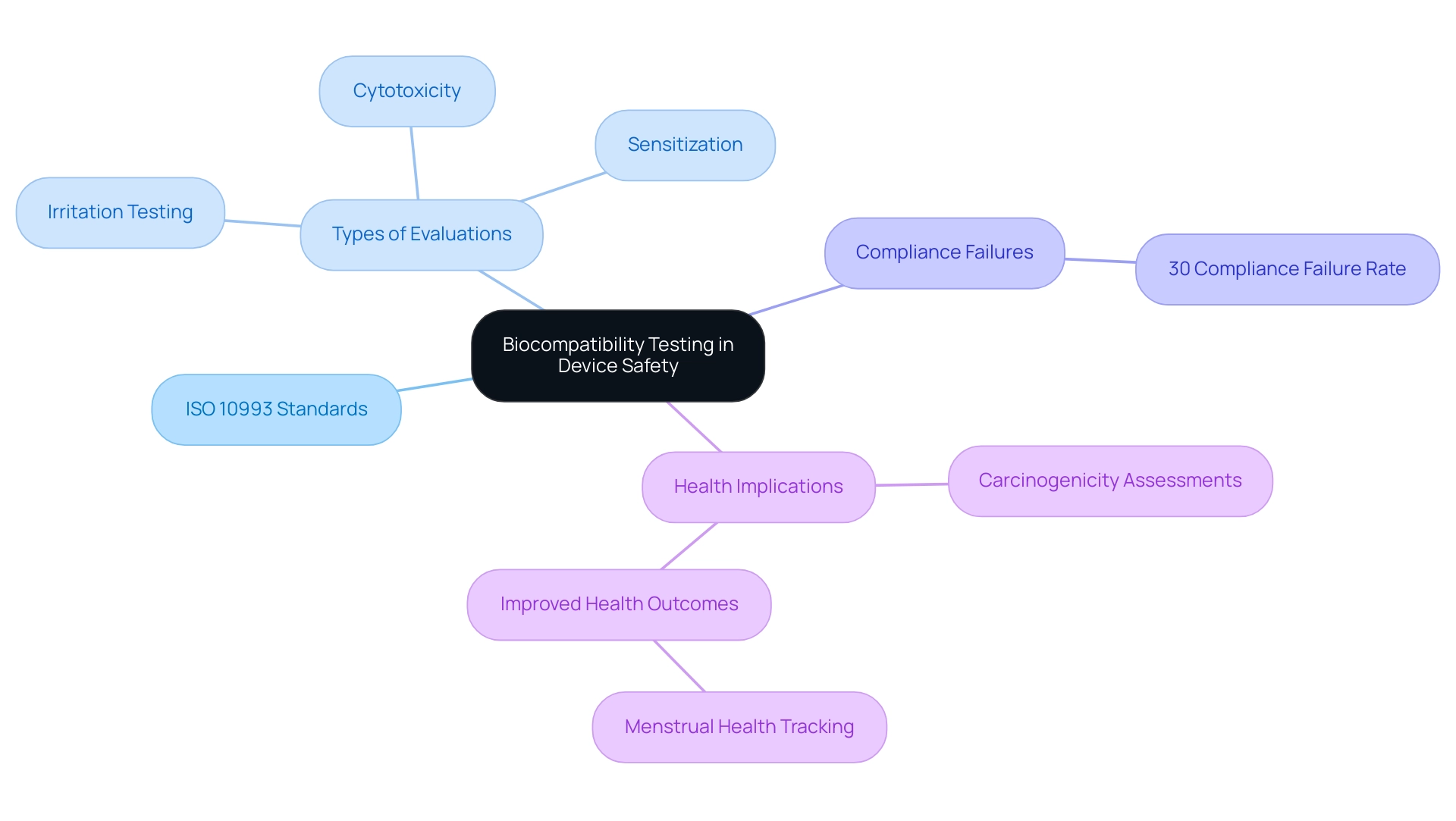
The Critical Role of Biocompatibility Testing in Device Safety
Biocompatibility evaluation is a fundamental aspect of health equipment assessments, focused on confirming that the materials utilized do not induce detrimental biological reactions. The ISO 10993 standards offer a comprehensive framework for assessing the biocompatibility of materials used in healthcare products, which aligns with medical device testing standards by incorporating essential evaluations such as cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation. For instance, the ISO 10993-10 recommends that human skin irritation tests should only be conducted if animal tests yield negative results.
This method guarantees that irritation evaluations are relevant to human biology, improving the protection characteristics of healthcare instruments. The stakes are high; inadequate assessment of biocompatibility can lead to significant adverse effects, including severe health complications. Statistics indicate that approximately 30% of medical instruments experience compliance failures related to biocompatibility, highlighting the critical need for rigorous medical device testing standards prior to approval and market release.
Additionally, distinct carcinogenicity assessments are conducted for implantable products believed to pose a risk of inducing cancer, emphasizing the comprehensive evaluation environment required for ensuring patient protection. As Rhiannon White, CEO of Clue, remarked,
Under my leadership, we are transforming menstrual health tracking into a powerful tool for research and improved reproductive health outcomes.
This emphasizes the broader implications of biocompatibility not just for effectiveness, but for improving health outcomes across various applications.
Furthermore, the case study on irritation testing reinforces the importance of biocompatibility testing, as it demonstrates that adherence to medical device testing standards ensures that irritation assessments are relevant to human biology and safety in medical devices, ultimately contributing to safer healthcare solutions.
Conclusion
In the realm of medical devices, regulatory compliance is essential for ensuring patient safety and product efficacy. This article highlights the critical role of regulatory bodies like the FDA and INVIMA in overseeing device development and testing. A comprehensive understanding of these regulations, alongside rigorous testing methodologies—such as mechanical, electrical safety, and biocompatibility testing—is vital for stakeholders navigating this complex landscape.
Biocompatibility testing is particularly crucial, as it assesses whether materials used in devices provoke harmful biological responses. With around 30% of medical devices facing compliance failures related to biocompatibility, thorough evaluations before market release are imperative to prevent serious health risks.
As regulatory frameworks evolve, manufacturers must remain proactive in their compliance efforts. Non-compliance can lead to significant legal and financial consequences, reinforcing the need to adhere to established guidelines. By prioritizing safety standards and investing in robust testing methodologies, stakeholders can enhance product credibility and protect public health.
Ultimately, a strong commitment to compliance not only safeguards patients but also builds trust in healthcare innovations. In an ever-evolving regulatory environment, proactive adherence to these standards will be crucial for the successful development and acceptance of medical devices in the market.




