Overview
This article examines best practices for designing clinical trials specifically for pediatric devices, highlighting the distinct challenges associated with:
- Ethical considerations
- Participant recruitment
- Data collection
It underscores the necessity of tailored methodologies and active stakeholder engagement, ensuring that trials are both scientifically robust and prioritize the safety and welfare of young participants. Innovative strategies and continuous monitoring throughout the research process are essential components that support this endeavor.
Introduction
Pediatric clinical trials pose a distinct array of challenges that necessitate a thorough examination of the physiological, psychological, and ethical dimensions involved in engaging with children. Researchers must adeptly navigate these complexities, addressing critical issues such as:
- Recruitment hurdles
- The imperative for parental consent
- The limited capacity of young participants to articulate their experiences
To ensure that trials are scientifically rigorous while prioritizing the welfare of child participants, innovative strategies are essential. By delving into tailored methodologies, ethical considerations, and the significance of stakeholder engagement, the landscape of pediatric clinical research is transforming, ultimately fostering improved outcomes and enhanced care for children. As the field progresses, comprehending and surmounting these challenges will be vital for the successful development of pediatric drugs and devices.
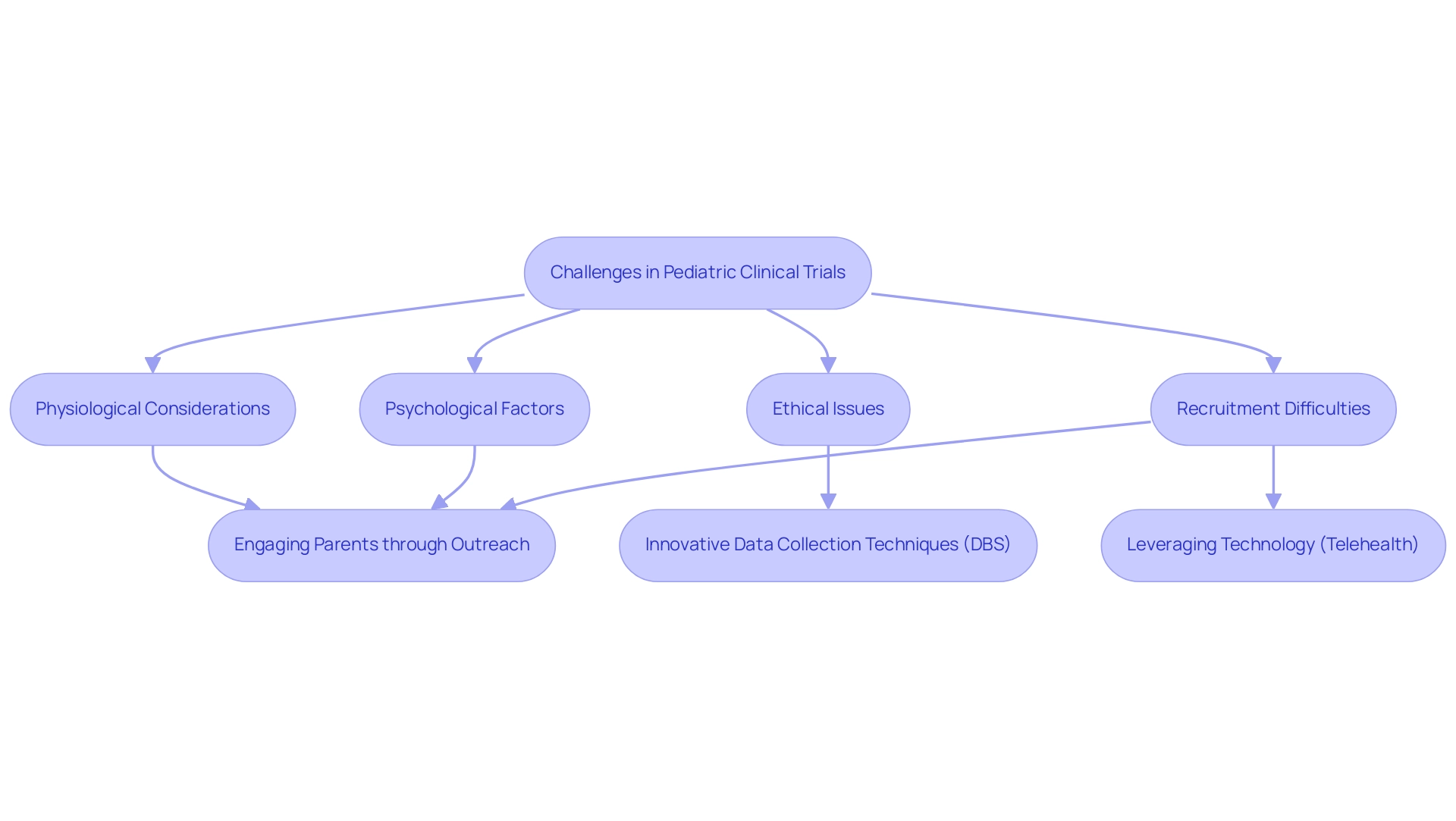
Understanding the Unique Challenges of Pediatric Clinical Trials
Pediatric clinical studies present a unique array of challenges stemming from physiological, psychological, and ethical considerations inherent in working with children. The limited patient population often leads to recruitment and retention difficulties, exacerbated by the diverse developmental stages of participants. Securing parental consent adds another layer of complexity, necessitating clear communication regarding study objectives and potential risks.
Moreover, children's restricted ability to articulate their experiences can significantly impede data collection and interpretation. This reality underscores the necessity for researchers to devise innovative strategies that capture meaningful insights.
To effectively tackle these challenges, recruitment strategies must be specifically tailored for child populations. Engaging with parents and guardians through educational outreach is essential, emphasizing the significance of clinical studies in enhancing medical care for children. Additionally, leveraging technology, such as telehealth consultations, can facilitate participation by minimizing logistical barriers.
Recent case studies highlight the critical role of trial design for pediatric devices that cater to the unique requirements of young patients. Innovative blood collection techniques, such as dried blood spots (DBS), have emerged as less invasive alternatives for immune monitoring. These methods not only alleviate ethical concerns associated with traditional blood draws but also enhance the feasibility of conducting immune profiling in young populations, thereby reducing discomfort and improving participant retention.
This consideration is particularly pertinent regarding the ethical factors related to dosage in trial design for pediatric devices. The US permits over 9.5 mL/kg body weight within any eight-week timeframe, necessitating meticulous preparation in study designs.
As we approach 2025, the landscape of children's medical studies continues to evolve, with ongoing discussions among researchers about the need for continuous evaluation and validation of study methodologies. As Steven E Kern articulates, "There must also be continual assessment and validation of simulation results with clinical outcomes as they emerge to assure that the models and gathered data converge." Addressing the distinct challenges encountered in children's studies is vital for ensuring that the safety and welfare of young participants remain a priority while achieving robust scientific results.
By fostering collaboration among scholars, medication creators, and health officials, the field can more effectively navigate the intricacies of drug development for children, ultimately enhancing the quality of care provided to this vulnerable population.
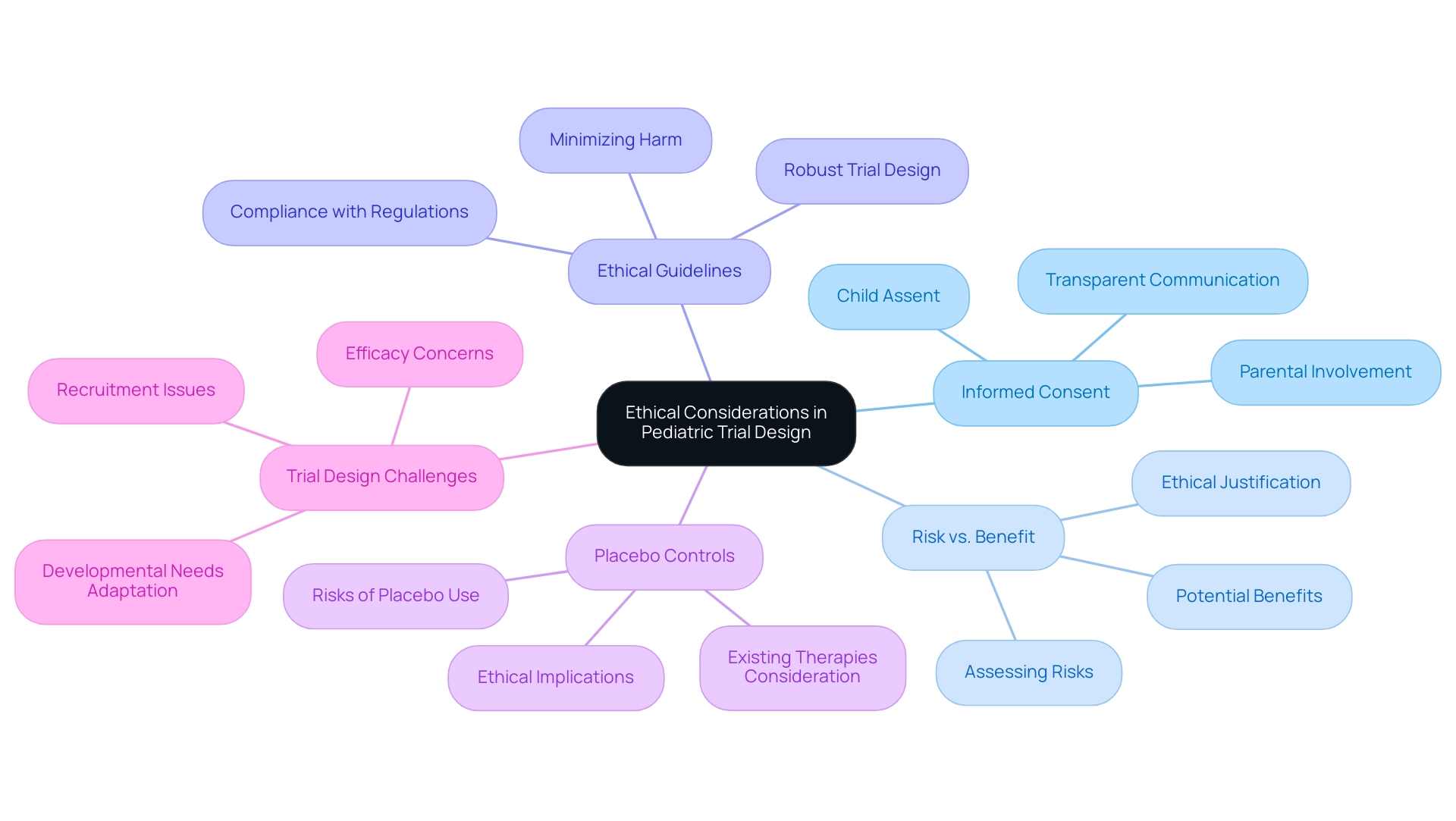
Ethical Considerations in Pediatric Trial Design
Ethical considerations in children's study design are paramount for safeguarding the welfare of young participants. Researchers encounter the complex challenge of obtaining informed consent from parents while simultaneously seeking assent from the children involved. This dual approach is crucial, as it respects the autonomy of young participants and acknowledges their capacity to comprehend the research to a certain extent. The significance of ensuring that the potential benefits of the research surpass the risks cannot be overstated.
Research indicates that approximately half of the randomized controlled trials published between 1982 and 1996 included fewer than 40 children, with median recruitment figures of 80 children for multicenter trials and 36 children for single-center investigations. This highlights the necessity for robust trial design for pediatric devices that can effectively address the unique challenges faced by young populations. Furthermore, ethical guidelines mandate that research must be structured to minimize discomfort or harm to participants, reinforcing the importance of meticulous planning and consideration.
Recent modifications in procedures and equipment tailored to children's developmental needs have shown that such adjustments can significantly alleviate stress during clinical research. This not only enhances the experience for young participants but also contributes to higher informed consent rates, which are essential for ethical compliance in research involving children.
A notable examination of the ethical implications surrounding the use of placebo controls in trials involving minors underscores the need for rigorous ethical justification, particularly when effective treatments are available. This case illustrates the delicate balance researchers must maintain between advancing medical knowledge and protecting vulnerable populations. Concerns persist regarding the value of multiple requests for child-focused research on medications within the same class, especially when previous investigations reveal a lack of efficacy, further complicating the ethical landscape.
Informed consent rates in research involving children remain a critical area of focus, with expert opinions underscoring the necessity of transparent communication about the associated risks and benefits. As Robert Nelson from the FDA emphasizes, discussions surrounding the ethical implications of children's drug studies encompass various aspects, including the selection of control groups and the evaluation of risk and benefit. Such insights are invaluable for ensuring that studies involving children are not only scientifically sound but also ethically responsible.
Ultimately, adhering to ethical guidelines in the trial design for pediatric devices not only protects young participants but also enhances the credibility and acceptance of the research within the broader community, paving the way for successful studies that prioritize ethical compliance.
Tailored Methodologies for Pediatric Device Trials
Customized approaches for children's device assessments must consider the unique physiological and psychological traits of young individuals. This involves:
- Utilizing age-appropriate language and materials
- Crafting protocols that cater to shorter attention spans
- Integrating innovative data collection techniques, such as interactive technologies that engage young participants effectively
Furthermore, flexible study designs demonstrate notable benefits, as they permit adjustments based on interim outcomes, guaranteeing that the study remains attuned to the changing requirements of the youth population.
As Sara K Pasquali, MD, MHS, from Duke Clinical Research Institute, states, "Clinical studies are the gold standard for generating evidence-based knowledge in medicine." By employing these tailored methods, researchers can greatly boost participant involvement and elevate the overall quality of data gathered, ultimately resulting in more dependable outcomes in children's medical studies. Additionally, the significance of transparency and reliability in clinical research methods cannot be overstated, as highlighted in recent initiatives aimed at enhancing evidence-based clinical decision-making.
The comparison of Bayesian adaptive designs with fixed designs and frequentist group-sequential design (GSD) further illustrates the evolving landscape of study design methodologies, emphasizing the need for innovative trial design for pediatric devices in pediatric research. By utilizing the expertise of bioaccess® in managing Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies, along with over 20 years of experience in Medtech, researchers can ensure that their studies are not only effective but also ethically sound and responsive to the needs of young participants. Bioaccess® provides the adaptability and expert knowledge required to maneuver through the intricacies of medical studies in Latin America, advancing global health enhancement through international cooperation and innovation in Medtech.
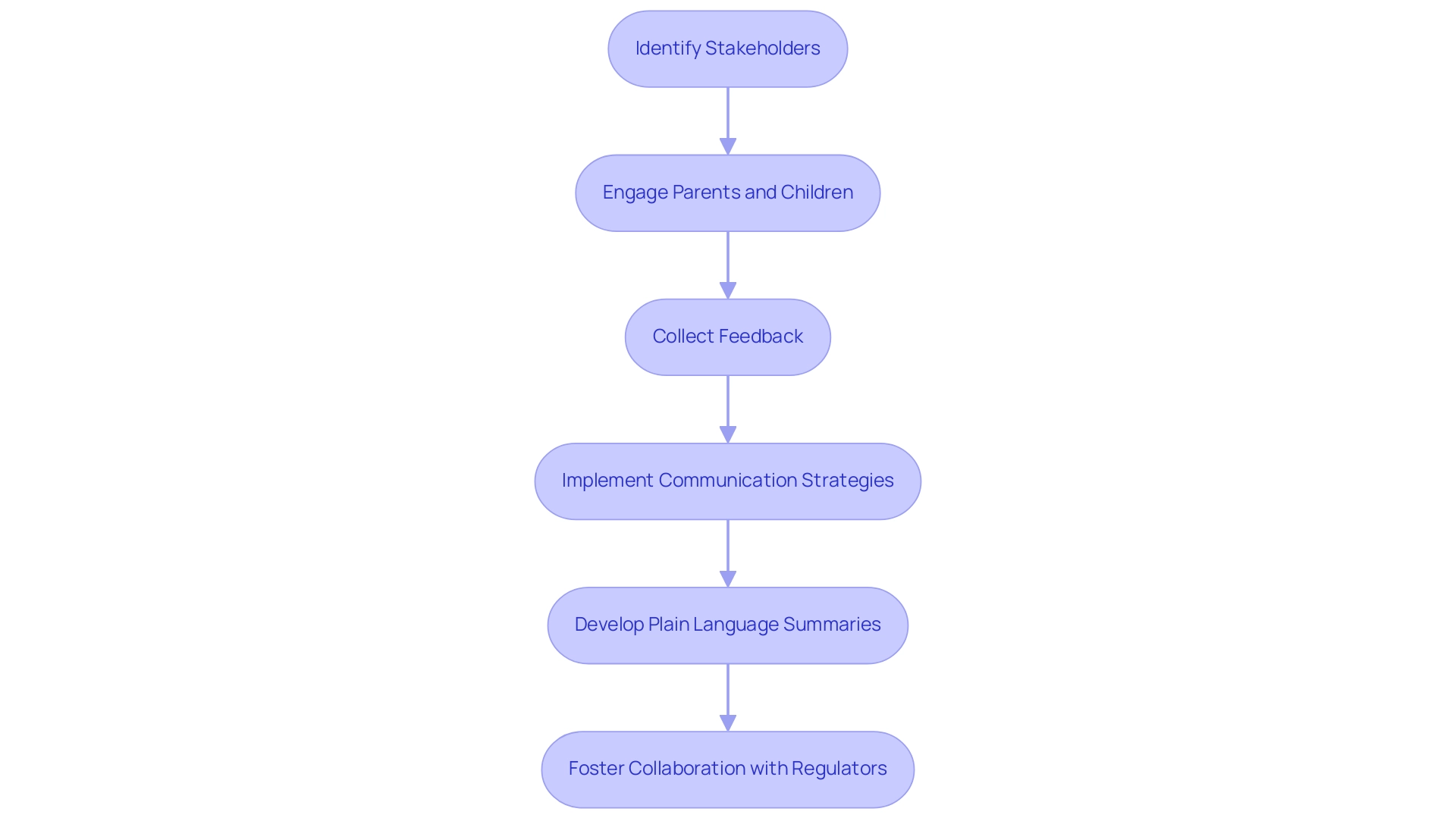
Engaging Stakeholders in Pediatric Clinical Trials
Involving stakeholders in pediatric clinical studies is essential for ensuring that research aligns with community needs and expectations. Actively engaging parents and children in the design process not only increases the relevance of the research but also cultivates a sense of ownership among participants. This can be accomplished by requesting their feedback on research protocols and addressing their concerns regarding safety and efficacy.
Effective communication strategies play a pivotal role in this engagement. Informational sessions provide parents with a clear understanding of the program's objectives and procedures, while feedback mechanisms allow them to voice their opinions and suggestions. Such initiatives help build trust and encourage participation, which is essential for successful recruitment and retention rates.
A significant case examination emphasizes the creation of Plain Language Summaries (PLS) for child clinical trials, as mandated by the EU Clinical Trials Regulation. This initiative underscores the importance of developing age-specific PLS formats to enhance understanding among various child groups. The study highlights that early involvement of child participants in protocol design is vital for ensuring the readability and value of the final summaries.
This early engagement not only aligns the research with community needs but also addresses the complexities involved in ensuring comprehension for all ages. Behtash Bahador noted, "Though multiple design formats may be complicated and costly, especially within six months of completion as the regulation requires, this should be considered a best practice if the end goal is to ensure comprehension for all ages included." While the current regulations mark progress, they also reveal the need for ongoing efforts to meet transparency goals for pediatric participants.
Statistics indicate that incorporating systems-level stakeholder perspectives significantly improves the adoption of evidence-based interventions into practice. Involving parents in the trial design for pediatric devices not only aligns the research with their expectations but also enhances the overall quality of the investigation. Insights from researchers suggest that successful strategies for involving parents in the trial design for pediatric devices include:
- Regular updates on progress
- Opportunities for them to contribute to discussions about the study design
Furthermore, the emphasis on early engagement with regulators and health technology assessment bodies is critical in fostering a collaborative environment that supports stakeholder involvement.
As we look towards 2025, the focus on stakeholder involvement in children's clinical studies continues to expand, reflecting a wider trend towards inclusivity in clinical research. By promoting a cooperative atmosphere, researchers can improve recruitment and retention rates, ultimately resulting in more successful studies and better outcomes for young patients.
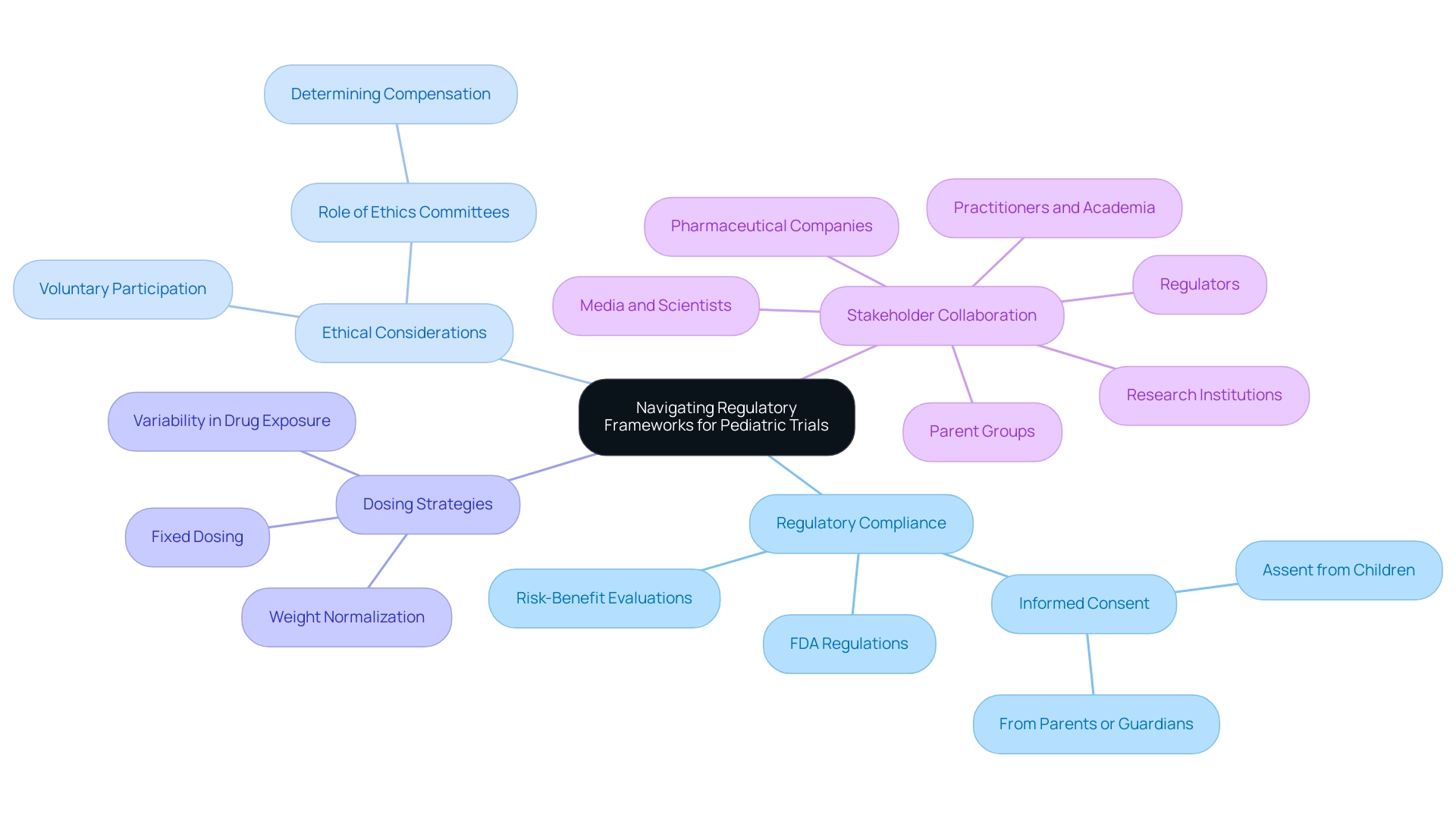
Navigating Regulatory Frameworks for Pediatric Trials
Navigating the regulatory frameworks for trial design in pediatric devices requires a comprehensive understanding of the specific guidelines governing research involving minors. Compliance with the FDA's regulations is paramount; these guidelines highlight the importance of ethical considerations and the protection of child participants. Key aspects include:
- Obtaining informed consent from parents or guardians
- Assent from the children themselves
- Ensuring that their participation is voluntary and free from undue influence
Ethics Committees play a crucial role in determining compensation amounts to uphold these ethical standards. As we look to 2025, the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, emphasizing the enhancement of ethical conduct in child research. The FDA has established clear guidelines mandating researchers to conduct thorough risk-benefit evaluations within the framework of trial design for pediatric devices tailored to the child population. This is essential, as variability in drug exposure among children can significantly affect study outcomes.
A notable case study on dosing strategies in trials involving children illustrates this point. It highlights how reliance on adult data can lead to inconsistencies in drug exposure, given the differences in body size and composition among young individuals. In the trial design for pediatric devices, researchers must consider various dosing approaches, such as:
- Weight normalization
- Fixed dosing
to address these challenges effectively and directly inform risk-benefit assessments.
Furthermore, successful compliance examples in child clinical research demonstrate the effectiveness of collaborative efforts among stakeholders, including regulators, ethics committees, and research institutions. As a children's doctor noted, "All the stakeholders: Regulators, Parent Groups, Ethics Committees, Research institutions, Practitioners, Academia, media, pharmaceutical companies, and scientists have to collaborate to ensure that ethical research involving children is promoted." By fostering communication and cooperation, these entities can ensure that ethical pediatric research is not only promoted but also effectively implemented.
In this context, bioaccess provides extensive clinical research management services encompassing:
- Feasibility assessments
- Site selection
- Compliance evaluations
- Setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
Additionally, bioaccess offers review and feedback on study documents to comply with country requirements and reporting on study status, inventory, and serious and non-serious adverse events. With specialists such as Katherine Ruiz, who focuses on regulatory matters for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, and Ana Criado, a director of Regulatory Affairs with significant expertise in biomedical engineering and health economics, bioaccess is well-prepared to manage the intricacies of studies involving children.
Understanding the distinctions between EU and U.S. regulations on child research provides important context regarding authorization and consent stipulations. Staying informed about regulatory changes and best practices is essential for researchers aiming to conduct compliant and ethically sound studies. Ultimately, this knowledge advances the trial design for pediatric devices, significantly improving children's health outcomes.
Effective Recruitment Strategies for Pediatric Trials
Recruitment strategies for pediatric studies must be meticulously crafted to navigate the distinct challenges of engaging children and their families. A multifaceted approach is essential, incorporating community outreach programs that resonate with local populations. Collaborating with pediatricians and healthcare providers enhances credibility and facilitates referrals, while targeted marketing strategies should appeal directly to parents' concerns and interests.
Clear communication about the study's objectives, potential benefits, and safety protocols is crucial in alleviating apprehensions and fostering trust. Providing comprehensive information not only empowers families but also encourages informed participation. Additionally, building strong connections with families and fostering a supportive atmosphere can greatly enhance recruitment efforts, ultimately resulting in more successful outcomes.
Recent statistics indicate that effective community outreach can increase recruitment rates by up to 30%, underscoring the importance of these initiatives in pediatric clinical research. As Paul M. Darden II, MD, noted, "To our knowledge, this is the first research to use a randomized method to test different methods of recruiting participants to an active trial," highlighting the innovative approaches necessary for effective recruitment.
Moreover, quality ratings of research averaged 68.7% based on the Newcastle–Ottawa scale, emphasizing the need for robust recruitment strategies to ensure high-quality research outcomes. With more than 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® plays a crucial role in facilitating research, connecting innovative Medtech companies with opportunities for studies in Latin America. The partnership between bioaccess™ and Caribbean Health Group seeks to establish Barranquilla as a premier location for clinical research, backed by Colombia's Minister of Health, which can greatly improve recruitment efforts and stimulate local economic development.
By prioritizing these strategies, researchers can enhance engagement and ensure that child-focused studies are both effective and ethically conducted.
Data Collection and Analysis in Pediatric Device Trials
In studies involving children's devices, the trial design for pediatric devices must be meticulously structured to ensure effective data gathering and evaluation that meets the specific requirements of young participants. The utilization of age-appropriate assessment tools is crucial, as these tools not only enhance the relevance of the data but also ensure that the process remains engaging and non-invasive for young subjects. The integration of technology, such as mobile applications and wearable devices, can significantly streamline real-time data collection, making it more efficient and less burdensome for participants and their families.
Moreover, employing robust statistical methods is essential for analyzing the collected data. This approach ensures that the findings are both dependable and relevant to future research and practice. For instance, a recent analysis involving 50,000 interactions across three research chains, following a burn-in of 10,000, demonstrated the effectiveness of advanced statistical techniques in maintaining power while controlling type I error rates, which is vital for the integrity of studies involving children. Additionally, methods for adjusting stopping boundaries are crucial in ensuring that studies maintain their statistical rigor.
As bioaccess® specializes in comprehensive clinical trial management services, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF), their expertise in trial design for pediatric devices is invaluable for navigating the complexities of trials involving devices for children. Case studies, such as those from the Boston Children's Research Biostatistics and Research Design Center (BARD), illustrate the successful application of tailored data collection methods. BARD's dedication to enhancing research design through biostatistical expertise has resulted in improved outcomes in both adult and child populations, showcasing the significance of collaboration and specialized support in achieving research excellence.
As Yu Wang noted, "All authors read and approved the final manuscript," emphasizing the collaborative nature of research. As we transition into 2025, the emphasis on innovative data gathering techniques in child device studies will continue to evolve, motivated by the necessity for age-appropriate evaluation tools and professional insights. By prioritizing these strategies, researchers can ensure that the trial design for pediatric devices yields significant outcomes that contribute to the advancement of medical devices intended for young patients. Moreover, research utilizing data from 16 RCTs comparing anti-sickness regimens for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in both adults and children underscores the importance of customized strategies in youth research.
The influence of these Medtech medical studies extends beyond individual experiments, fostering job creation, economic growth, and healthcare enhancement in local economies, while promoting international cooperation.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation of Trial Protocols
Ongoing oversight and the adjustment of research protocols are vital elements for the success of children's clinical studies. Establishing robust mechanisms for the ongoing assessment of participant safety, data integrity, and protocol adherence is crucial. This can include:
- Regular review meetings
- Interim analyses
- Soliciting feedback from all stakeholders involved
By fostering a culture of collaboration and transparency, researchers can enhance trust and accelerate feedback loops, allowing for quicker adaptations in the trial design for pediatric devices as challenges arise.
In pediatric research, the significance of continuous monitoring cannot be overstated. It not only ensures the safety of young participants but also enhances the reliability of the data collected. For instance, utilizing linear mixed-effects regressions to analyze secondary health outcomes, such as length of hospital stay and duration of oxygen supplementation, can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the intervention.
The research will utilize a two-group comparison of mean change in a repeated measures design for power calculations, which is essential for ensuring the robustness of the results.
Furthermore, extensive research study management services, like those provided by bioaccess, play a crucial role in enabling these processes. From viability assessments and site selection to compliance evaluations and test preparations, these services guarantee that tests are carried out effectively and in alignment with regulatory standards. The import permits and project management assistance offered by bioaccess further improve the operational aspects of clinical studies, enabling researchers to concentrate on participant safety and data integrity.
The experimental setup process involves thorough planning and coordination to ensure that all regulatory requirements are fulfilled, which is crucial for the success of the research. Additionally, the reporting services offered by bioaccess are essential for upholding transparency and accountability throughout the process, ensuring that all adverse events are documented and addressed promptly, thereby safeguarding participant safety.
Research examples have emphasized the constraints frequently encountered in medical experiments, such as dependence on protocol registration information and inadequate reporting of experiment outcomes. These challenges highlight the need for enhanced data quality and completeness in research registries, which are essential for precise evaluations of protocol modifications. As Jiabu Ye observed, "Statistical methods demonstrated for the case studies, along with the use of the user-friendly iSM tool, significantly improve the quantitative monitoring of safety events of interest in ongoing clinical investigations."
As researchers adapt trial protocols based on participant feedback, the trial design for pediatric devices can significantly improve the overall quality and outcomes of pediatric research, ultimately leading to better healthcare solutions for children and contributing to local economic growth through job creation and healthcare improvement.
Conclusion
Pediatric clinical trials are a critical domain of research, marked by distinct challenges that demand innovative solutions. The intricacies of recruitment, the imperative of obtaining informed consent, and the limited ability of young participants to articulate their experiences underscore the necessity for tailored methodologies that prioritize both ethical considerations and scientific rigor. Engaging stakeholders, including parents and children, in the trial design process ensures that studies are not only relevant but also respectful of the needs and rights of young participants.
The paramount importance of ethical compliance cannot be overstated, as it safeguards child participants while simultaneously enhancing the credibility of the research. Effective communication strategies and transparency regarding trial objectives are essential in fostering trust and encouraging participation. Furthermore, the integration of technology and adaptive trial designs can significantly enhance data collection and participant engagement, ultimately leading to more reliable outcomes.
As the landscape of pediatric clinical trials evolves, ongoing collaboration among researchers, regulators, and healthcare professionals becomes indispensable. This collective effort is vital for navigating the regulatory frameworks that govern pediatric research, ensuring that trials are conducted ethically and effectively. By prioritizing the welfare of child participants and embracing innovative approaches, the field can achieve significant advancements in health outcomes for children, thereby paving the way for progress in pediatric medicine and device development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the unique challenges faced in pediatric clinical studies?
Pediatric clinical studies face challenges related to physiological, psychological, and ethical considerations when working with children. These include difficulties in recruitment and retention due to a limited patient population and diverse developmental stages, as well as the complexity of obtaining parental consent and the children's limited ability to articulate their experiences.
How can researchers improve recruitment and retention in pediatric studies?
Researchers can improve recruitment and retention by tailoring strategies specifically for child populations, engaging parents and guardians through educational outreach, and utilizing technology such as telehealth consultations to minimize logistical barriers.
What innovative techniques are being used in pediatric clinical trials?
Innovative techniques such as dried blood spots (DBS) for blood collection are being used as less invasive alternatives for immune monitoring, which alleviate ethical concerns and enhance feasibility while reducing discomfort for young participants.
What ethical considerations are important in pediatric study design?
Ethical considerations include obtaining informed consent from parents and assent from children, ensuring that the benefits of research outweigh the risks, and minimizing discomfort or harm to participants. Researchers must also rigorously justify the use of placebo controls, especially when effective treatments are available.
What are the implications of sample sizes in pediatric research?
Research indicates that many randomized controlled trials have small sample sizes, often including fewer than 40 children. This highlights the necessity for robust trial designs that can effectively address the unique challenges faced by pediatric populations.
How do modifications in procedures impact pediatric clinical research?
Modifications in procedures and equipment tailored to children's developmental needs can significantly reduce stress during clinical research, enhancing the experience for young participants and contributing to higher informed consent rates.
What role does ethical communication play in pediatric studies?
Transparent communication about the risks and benefits of participation is crucial for informed consent in pediatric studies. This is essential for ethical compliance and helps ensure that studies are both scientifically sound and ethically responsible.
Why is continuous evaluation important in children's medical studies?
Continuous evaluation is important to ensure that study methodologies remain effective and relevant, as well as to validate simulation results against clinical outcomes, thereby prioritizing the safety and welfare of young participants while achieving robust scientific results.




