Introduction
The landscape of clinical research is undergoing a transformative shift with the advent of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems, which are redefining how data is collected, managed, and analyzed. By moving away from traditional paper-based methods, these systems not only enhance data accuracy but also streamline the research process, making it more efficient and reliable.
As the demand for mobile EDC solutions continues to surge, understanding their architecture and functionality becomes essential for clinical researchers aiming to optimize their studies. This article delves into the numerous advantages of EDC systems, the challenges faced during their implementation, and best practices for maximizing their efficiency, while also exploring future trends that promise to further revolutionize clinical trials.
Through a detailed examination, it becomes evident that embracing EDC technology is not merely a trend, but a necessary evolution in the pursuit of improved patient outcomes and research integrity.
Understanding Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems in Clinical Research
EDC systems in clinical research have become vital instruments, facilitating efficient collection, management, and analysis of clinical trial information. By substituting traditional paper-based approaches, EDC systems in clinical research facilitate real-time data entry and significantly enhance data accuracy, which is critical for producing reliable research outcomes. With the market for mobile EDC systems in clinical research anticipated to expand by 16% each year, the demand for these innovative technologies continues to increase.
EDC systems in clinical research are designed with user-friendly interfaces, automated validation checks, and robust security features that safeguard sensitive patient information. For medical researchers, understanding the underlying architecture of these systems—including database structures and user permissions—is vital for optimizing their functionality. Familiarity with EDC systems in clinical research can lead to improved data quality and more streamlined research processes, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
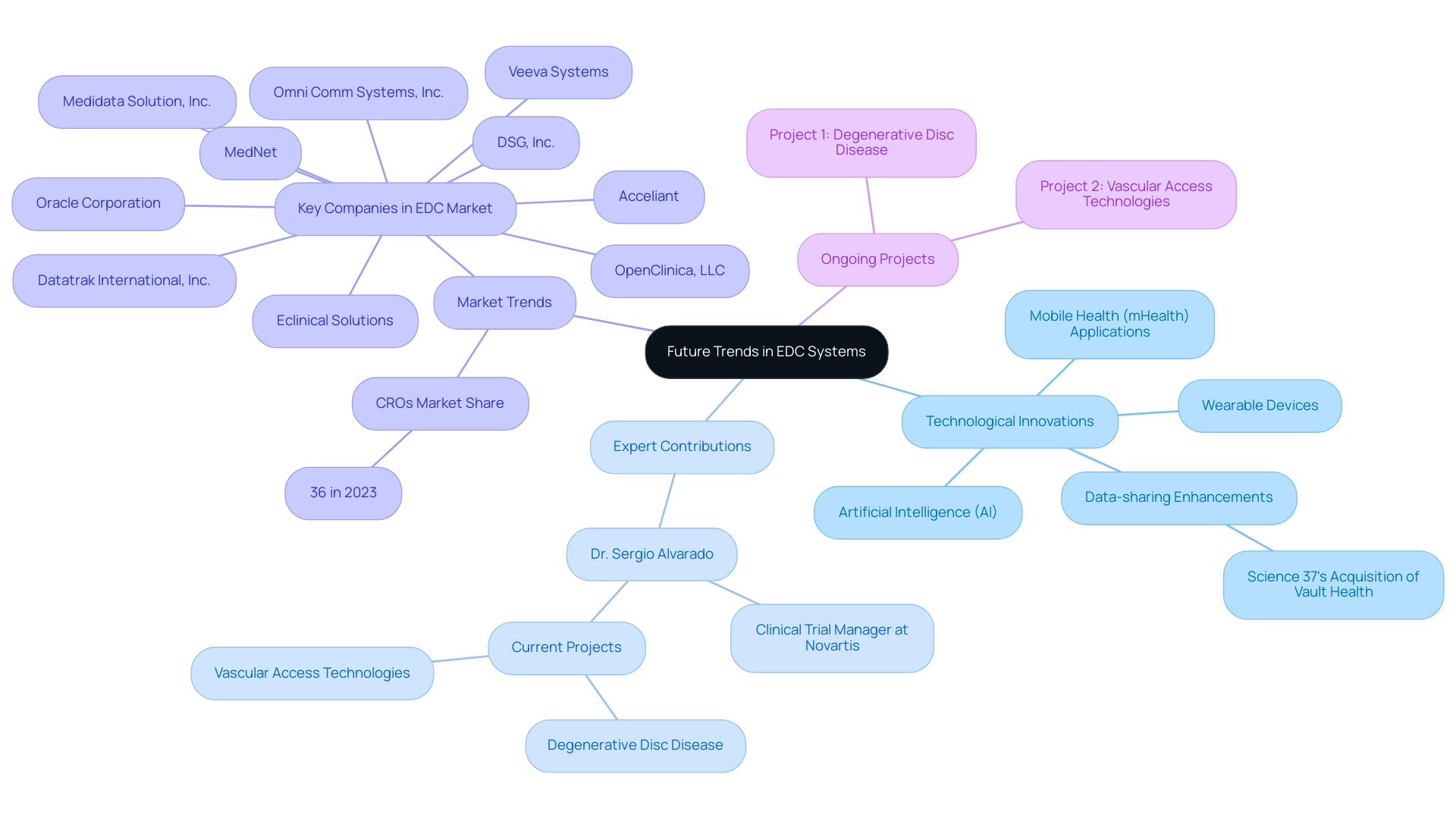
Prominent vendors like Medidata, acknowledged for enabling over 30,000 trials, and Veeva Systems, which has supported over 1,000 study initiations, illustrate the competitive environment of EDC systems in clinical research. Furthermore, Medrio's completion of a SOC 2 Type I Evaluation and the recent benchmarking report rating Rave EDC as the most preferred provider highlight the effectiveness of EDC systems in clinical research. As Steve Bennett, a Business Formation Expert, states, 'With LLCBuddy, you're not just getting a tutorial; you're gaining a trustworthy partner for your entrepreneurial journey.'
This sentiment resonates in the research sphere as well, where the right EDC systems in clinical research can significantly impact the success of studies. Moreover, the emergence of information agreements and the strategic application of generative AI in research reflect current trends in sharing and usage, emphasizing the need for contemporary solutions that enhance management and precision.
Key Advantages of Implementing EDC Systems in Clinical Trials
The introduction of EDC systems in clinical research offers substantial benefits, especially in the areas of information quality, security, and operational efficiency. Our comprehensive clinical trial management services encompass:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Nationalization of investigational devices
These services help streamline the trial setup process and ensure adherence to regulations. For instance, the use of EDC systems in clinical research enables real-time information entry, effectively mitigating the transcription errors that are often prevalent in traditional paper-based methods.
Built-in validation checks further ensure that only accurate and complete information is collected, which is paramount for maintaining regulatory compliance. As Jim Harris aptly states, 'Information accuracy is of utmost importance during a clinical trial, and you can’t afford to compromise on integrity and reliability as it may trigger an FDA inspection.' Significantly, the EDC systems in clinical research may yield from 49% to 62% of savings compared to the paper information capture (PDC) process, enhancing the credibility of claims regarding operational efficiency.
However, organizations must also navigate substantial upfront costs for software, infrastructure, and training, as highlighted in the case study titled 'Challenges in EDC Implementation.' This study emphasizes the potential resistance to new technologies and the necessity for comprehensive training and clear communication of benefits. Additionally, security attributes within EDC systems in clinical research protect sensitive information through encryption and user access controls, addressing the increasing worries regarding breaches of information.
Moreover, EDC systems in clinical research are designed to accelerate the data collection process, allowing for quicker analysis and expediting the overall research timeline. Recent news indicates that orthopedic surgeons are urged to participate in medical databases or registries, highlighting the importance of EDC systems in clinical research for improving evidence-based care alongside their medical practices. Collectively, these advantages not only enhance the reliability of study outcomes and significantly improve patient safety but also contribute to job creation, economic growth, and healthcare improvements in local economies, marking a pivotal advancement in clinical research methodologies.
Specifically, the efficient management of trials through EDC systems in clinical research fosters a more robust research environment that can lead to increased employment opportunities and better health outcomes in communities.
Navigating Challenges in EDC System Implementation
Despite the numerous advantages that EDC systems in clinical research present, their implementation can be fraught with challenges. Resistance to embracing new technologies is a common obstacle, especially among personnel who are used to conventional information collection methods. Research indicates that effective staff training is paramount; without it, the adoption of EDC systems in clinical research can lead to disruptions in workflow and an increased clerical burden, potentially exacerbating issues such as physician burnout, as highlighted by Shanafelt TD in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings, which discusses the relationship between clerical burden and characteristics of the electronic environment with physician burnout and professional satisfaction.
Significantly, the EDC systems in clinical research may yield from 49% to 62% in savings when contrasted with traditional data collection (PDC), highlighting the financial advantages of shifting to EDC approaches. Technical difficulties during integration can further complicate the process, alongside the necessity to comply with stringent regulatory requirements. To mitigate these challenges, it is essential to engage stakeholders early in the implementation process, ensuring all team members are adequately trained and supported.
Moreover, conducting thorough testing of the EDC setup prior to full-scale implementation allows for the identification of potential technical glitches. Collaborating closely with IT experts and EDC vendors not only facilitates smoother integration but also ensures that the EDC systems in clinical research are customized to meet the specific requirements of the study. In global trials, for example, utilizing EDC systems in clinical research that support multiple languages and comply with country-specific regulations is crucial for success.
The case study on global and multilingual support illustrates that providing training in the native language of the research team can significantly enhance the efficacy of the framework, ensuring all staff are equipped to utilize the technology effectively.
Best Practices for Maximizing EDC System Efficiency
To enhance the efficiency of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems, researchers must implement several best practices tailored to their operational needs. A primary focus should be on creating user-friendly and intuitive input forms. Such designs are essential in minimizing errors during information input, thereby safeguarding integrity.
Furthermore, conducting regular audits is crucial for identifying discrepancies and pinpointing areas ripe for improvement. The incorporation of automated alerts for inconsistencies can significantly streamline the validation process, facilitating timely corrective actions. Nurturing a culture of ongoing feedback among team members is equally vital; encouraging open communication between information managers and clinical personnel frequently results in valuable insights that can improve usability.
Additionally, it is important to consider that the cost of implementing an EDC solution can vary widely depending on licensing fees, setup costs, training, and maintenance. Utilizing integrated analytics tools within the EDC framework enables the tracking of trends and study progress, empowering researchers to make informed choices based on real-time insights. As mentioned by Stat One EDC, their server-based setup requires internet access, highlighting the importance of infrastructure in EDC implementation.
Moreover, EDC platforms facilitate multi-language functions for information gathering in worldwide trials, ensuring consistency and reliability of information across various languages, which is essential for usability.
Future Trends and Innovations in EDC Systems for Clinical Trials
The future of EDC systems in clinical research, particularly in Latin America, is set for remarkable advancements driven by innovative medical research and technological solutions. Under the guidance of experts such as Dr. Sergio Alvarado, a Clinical Trial Manager with a strong background in medical affairs at Novartis and a medical degree from Universidad de Los Andes, we are witnessing significant improvements in analytical capabilities. Dr. Alvarado's emphasis on incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) into medical practices is vital as AI and machine learning are not only streamlining information processing and reducing manual mistakes but also facilitating predictive analytics that can change patient outcomes.
A significant advancement in this area is Science 37's purchase of Vault Health’s life science platform in February 2023, which intends to improve data-sharing capabilities within EDC platforms. Furthermore, the growing adoption of mobile health (mHealth) applications and wearable devices in research studies is anticipated to transform information gathering techniques, resulting in more extensive datasets. Dr. Alvarado is currently working on six projects, including:
- Degenerative disc disease
- Vascular access technologies
These projects further illustrate his active contributions to the field.
As EDC frameworks evolve to accommodate these new data sources, seamless integration and real-time access to patient information will become crucial. The Contract Research Organizations (CROs) segment, which held a dominating share of around 36% in 2023, emphasizes the critical role of EDC systems in clinical research. Staying informed about these trends allows researchers to maximize the potential of EDC systems in clinical research and drive innovation in the field, particularly in the context of improving healthcare outcomes in Latin America.
Conclusion
The integration of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems into clinical research marks a pivotal advancement in the field, offering a multitude of benefits including enhanced data accuracy, operational efficiency, and improved patient outcomes. By transitioning from traditional paper-based methods, EDC systems facilitate real-time data entry and built-in validation checks, significantly reducing the risk of transcription errors and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. The substantial cost savings associated with EDC implementation further underscore its value, as organizations can expect a reduction in operational expenses while boosting the credibility of their research outcomes.
However, the journey towards effective EDC system implementation is not without challenges. Resistance to change, technical difficulties, and the need for comprehensive staff training can complicate the adoption process. Therefore, engaging stakeholders early on and ensuring that team members are well-equipped to navigate the new technology are essential steps in overcoming these hurdles. By prioritizing user-friendly design and fostering a culture of continuous feedback, researchers can maximize the efficiency of their EDC systems and enhance overall study performance.
Looking ahead, the future of EDC systems is bright, with innovations such as artificial intelligence and mobile health applications poised to further revolutionize data collection and analysis. As the landscape of clinical research continues to evolve, staying abreast of these trends will be crucial for researchers aiming to leverage EDC technology to its fullest potential. Ultimately, embracing these advancements is not merely a strategic choice, but a necessary evolution in the quest for improved research integrity and enhanced patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are EDC systems in clinical research?
EDC (Electronic Data Capture) systems are vital tools that facilitate the efficient collection, management, and analysis of clinical trial information, replacing traditional paper-based methods.
What are the benefits of using EDC systems?
EDC systems enhance data accuracy, allow real-time data entry, improve operational efficiency, and ensure the security of sensitive patient information through features like encryption and user access controls.
How do EDC systems impact data quality in clinical trials?
EDC systems incorporate automated validation checks that ensure only accurate and complete information is collected, mitigating transcription errors common in paper-based methods.
What is the expected market growth for mobile EDC systems?
The market for mobile EDC systems in clinical research is anticipated to expand by 16% each year.
Who are some prominent vendors of EDC systems?
Notable vendors include Medidata, which has enabled over 30,000 trials, and Veeva Systems, which has supported over 1,000 study initiations.
What challenges are associated with implementing EDC systems?
Organizations may face substantial upfront costs for software, infrastructure, and training, as well as potential resistance to new technologies that necessitate comprehensive training and clear communication of benefits.
How do EDC systems contribute to regulatory compliance?
The accuracy provided by EDC systems is crucial for maintaining regulatory compliance, as compromised data integrity could trigger inspections by regulatory bodies like the FDA.
What additional services do EDC systems support in clinical trials?
EDC systems support a variety of clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, and the nationalization of investigational devices.
What impact do EDC systems have on patient safety and research outcomes?
By improving the reliability of study outcomes and enhancing patient safety, EDC systems contribute to better healthcare practices and can lead to job creation and economic growth in local communities.
What recent trends are influencing EDC systems in clinical research?
Current trends include the emergence of information agreements and the strategic application of generative AI in research, emphasizing the need for contemporary solutions that enhance management and precision in clinical trials.

