Introduction
The landscape of clinical trials is undergoing a significant transformation with the rise of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems. These innovative platforms replace traditional paper-based methods, streamlining the data collection process and enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of clinical research. As the demand for reliable and real-time data access grows, EDC systems have become indispensable in maintaining data integrity and regulatory compliance.
This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of EDC implementation, the pivotal role it plays in data management, and the challenges organizations face during its adoption. Furthermore, it explores future trends that promise to reshape the EDC landscape, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence and the evolving needs of decentralized clinical trials.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders aiming to navigate the complexities of modern clinical research effectively.
Defining Electronic Data Capture (EDC) in Clinical Trials
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) signifies a crucial improvement in the organized gathering of trial information, employing electronic techniques instead of conventional paper-based approaches. These advanced EDC solutions are intended to optimize the information gathering process, thereby improving precision and enabling real-time access to essential details. In the context of clinical trials, clinical EDC is essential for maintaining information integrity and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
As Krunal Bhatt, Scrum Master and Technical Team Manager at Octalsoft, observes, 'The adoption of clinical EDC systems not only enhances the efficiency of information collection but also guarantees that the integrity is maintained throughout the trial process.' By adopting clinical EDC, researchers can effectively manage substantial volumes of information, which leads to better management of patient records, resulting in higher retention rates and more accurate trial results. Moreover, the integration of comprehensive trial management services—including:
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Meticulous compliance reviews
enhances the overall effectiveness of trials.
These services ensure that all regulatory requirements are met and that the trials are conducted efficiently. The emergence of information contracts also highlights a modern approach to sharing, emphasizing the importance of structured agreements in the evolving landscape. As of May 2023, a remarkable 94% of interventional research studies have successfully posted their results, highlighting the effectiveness of clinical EDC in promoting transparency and accountability in research.
This clinical EDC technology has fundamentally altered the environment of medical information capture, storage, and analysis, making it an essential component of modern trials and contributing to local economies through job creation, economic growth, and enhanced healthcare results.
Key Benefits of Implementing EDC Systems in Clinical Research
The adoption of clinical EDC frameworks in clinical research provides numerous benefits that greatly influence information quality and overall study efficiency. Digitally powered trials are quicker, more efficient, and less expensive than traditional trials, emphasizing the significance of clinical EDC in contemporary research. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Information Quality: EDC frameworks reduce manual input mistakes and improve precision through automated verification checks, ensuring the integrity of gathered information.
- Streamlined Processes: With EDC, real-time information entry and monitoring capabilities enable researchers to promptly identify and address issues, facilitating quicker decision-making during trials.
- Enhanced Security: EDC frameworks typically incorporate advanced security measures, including encryption and strict access controls, which protect sensitive patient information and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- Cost Efficiency: By greatly minimizing the time and resources needed for data oversight, EDC solutions can result in considerable cost reductions throughout the trial lifecycle.
- Regulatory Compliance: Designed with industry regulations in mind, such as Good Clinical Practice (GCP), EDC systems help ensure that studies adhere to necessary compliance standards.
These advantages underscore the growing preference for clinical EDC systems in trials, as they enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the research process while also contributing to improved patient outcomes. According to a recent analysis of 947 registered clinical trials in Canada, the integration of clinical EDC within both academic and industry-funded trials reflects its critical role in adapting to the evolving needs of clinical research. Notably, industry trials, which tend to be larger in scale, have demonstrated a marked increase in the adoption of clinical EDC, indicating its value in managing complex data environments effectively.
Dimple Rajgor succinctly summarizes this shift, stating,
Our purposes are (1) to provide a brief overview of EDC platforms, their types, and related pros and cons, as well as to describe commonly used EDC tools and their features; and (2) to describe simple steps involved in designing a registry/clinical study in DADOS P, an open-source EDC application.
Moreover, the historical viewpoint offered by De Vries in 2007 concerning the role of clinical EDC in adaptive trials further highlights the development and significance of these frameworks. This changing environment illustrates how clinical EDC frameworks are becoming essential instruments for enhancing information quality in research.
The Role of EDC in Data Management
Clinical EDC platforms are vital for efficient information management in research trials, serving as a centralized hub for collection, storage, and analysis. These frameworks simplify the amalgamation of information from various origins, including medical facilities and laboratories, ensuring that thorough and pertinent details are easily available in one place. This centralized method not only enhances accessibility of information but also enables real-time monitoring of quality and completeness, which is essential for preserving the integrity of research in healthcare.
Recent statistics suggest that 33% of survey participants regard AI-driven information inconsistency detection as a crucial factor for choosing healthcare analytics platforms, highlighting the significance of advanced features in clinical EDC systems. Additionally, clinical EDC solutions often incorporate functionalities for information cleaning and validation, which are pivotal in preserving dataset integrity throughout the clinical trial process. As Steve Bennett, a Business Formation Expert, states, 'This article aims to illuminate the key trends and statistics of EDC software in 2024, providing stakeholders with the insights needed to navigate and excel in the ever-evolving realm of information capture.'
Moreover, tackling skill deficiencies in cloud computing teams is vital for the successful execution of clinical EDC frameworks, as these frameworks require efficient information management that necessitates teams equipped with the appropriate tools and expertise. A pertinent case analysis on handling risk in business administration illustrates how clinical EDC frameworks can effectively oversee information integrity and adherence, ultimately enhancing the overall effectiveness of research in healthcare. By enhancing data management processes, clinical EDC solutions significantly align with the latest trends and expert insights that highlight their role in optimizing data management practices in 2024.
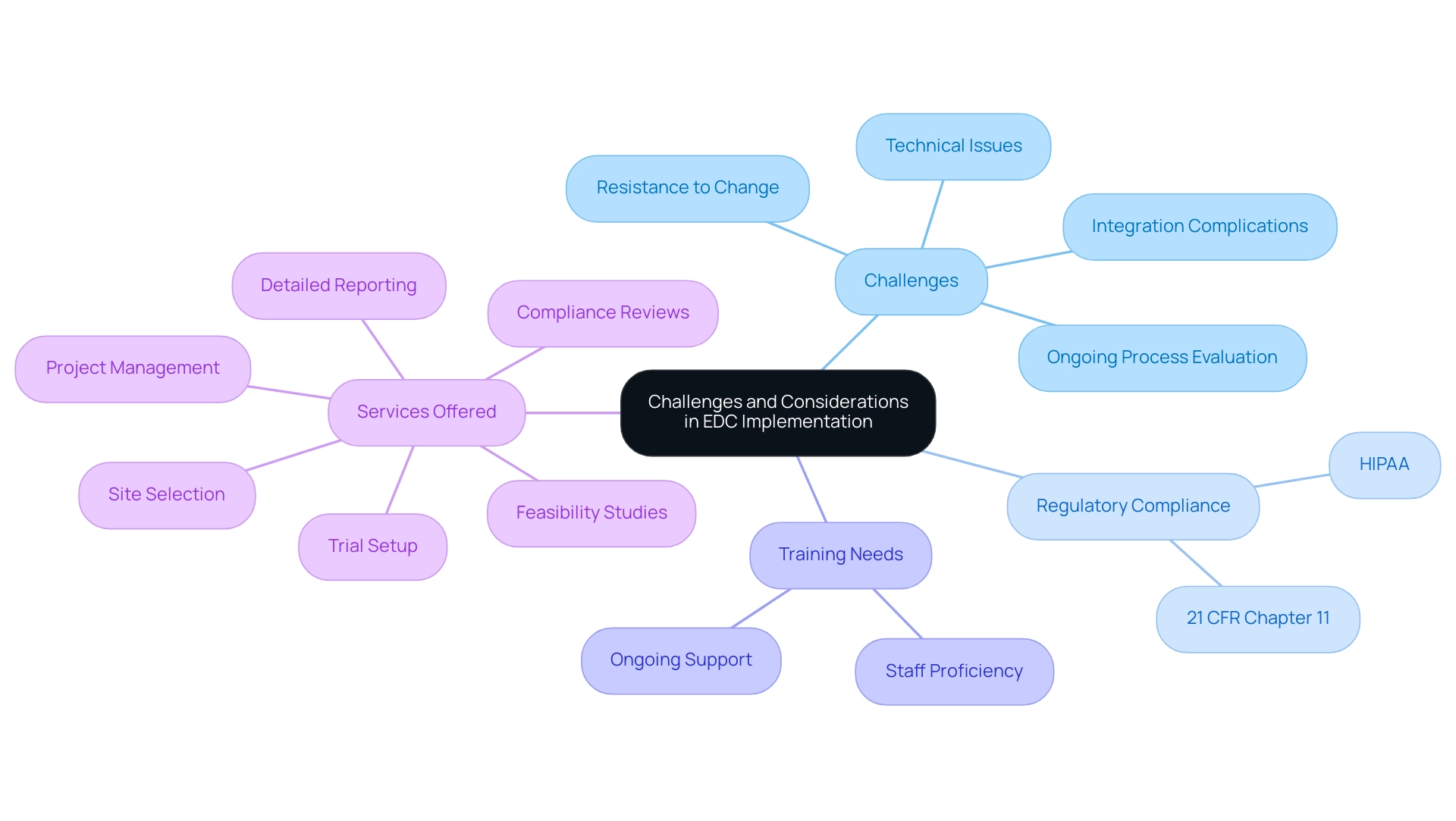
Challenges and Considerations in EDC Implementation
Although clinical EDC platforms provide considerable benefits in research studies, their deployment is frequently accompanied by difficulties. Resistance to change from clinical staff, who may be more comfortable with traditional paper-based methods, is a common hurdle. Additionally, the incorporation of EDC networks with existing infrastructures can introduce complications that require careful planning.
Thorough training on new technologies is vital to guarantee that staff members are proficient and confident in using these tools. Compliance with regulatory standards, including those outlined in 21 CFR chapter 11 and HIPAA, adds another layer of complexity, necessitating a deep understanding of these requirements and ongoing reassessments as processes evolve. Engaging stakeholders early in the transition, coupled with robust training and support, can significantly mitigate these issues.
Our comprehensive trial management services, which are essential for successful clinical EDC implementation, include:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Detailed reporting on study status and adverse events
Specifically, our project management and monitoring services are designed to address integration complications by ensuring that all components function seamlessly together. Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, underscores the importance of navigating these regulatory landscapes effectively.
Our services also focus on ensuring compliance with critical regulatory standards, providing the necessary support for EDC implementation. As highlighted by Litchfield J et al., the future of clinical trials may increasingly be internet-based, which poses additional considerations for clinical EDC adoption. The case study on the advantages and difficulties of clinical EDC technologies versus paper forms illustrates that while clinical EDC solutions can enhance efficiency and accuracy—such as reducing data entry errors—they also present challenges like the need for ongoing process evaluation and the potential for technical issues.
Dimple Rajgor highlights the significance of these factors, pointing out the dual emphasis on offering an overview of EDC frameworks and the steps involved in designing studies within them. By addressing resistance and fostering an environment conducive to change, organizations can optimize the transition to clinical EDC frameworks and fully harness their potential benefits.
Future Trends in Electronic Data Capture
The future of clinical EDC technology is poised for transformative advancements, largely propelled by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into clinical EDC frameworks. These technologies are anticipated to significantly improve analysis capabilities, allowing researchers to extract more sophisticated insights and implement predictive analytics effectively. As research trials progressively transition to decentralized approaches, the clinical EDC solutions will need to adjust by providing features that support remote information gathering and enhance patient involvement.
Moreover, the evolution of data security measures, including the potential use of blockchain technology, is likely to provide robust protections for sensitive health information. As these trends develop, the efficiency of clinical EDC solutions will not only increase but also play a crucial role in optimizing clinical trial processes and enhancing patient outcomes. Current discussions in the industry highlight the necessity of fostering open dialogue about conflicting opinions on account plans, focusing on shared goals, and seeking compromise, as emphasized in a recent quote:
- 'Address conflicting opinions on account plans by encouraging open dialogue, focusing on shared goals, and seeking compromise.'
Additionally, recent contributions underscore the importance of salvaging customer loyalty in the face of dissatisfaction, with two contributions made just 9 hours ago emphasizing this critical nature of stakeholder engagement. Key players in the Electronic Data Capture market, such as Castor EDC, Medidata Solutions, and Oracle, are leading advancements in clinical EDC systems, further illustrating the dynamic nature of this field.
Conclusion
The integration of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems into clinical trials represents a pivotal advancement that has transformed the landscape of clinical research. By replacing traditional paper-based methods with electronic systems, EDC enhances the accuracy and efficiency of data collection, ensuring that researchers can access real-time, reliable data while maintaining regulatory compliance and data integrity. The numerous benefits of EDC systems, including:
- Improved data quality
- Streamlined processes
- Enhanced security
- Cost efficiency
highlight their essential role in modern clinical trials.
Despite the clear advantages, organizations must navigate various challenges during EDC implementation. These challenges include:
- Resistance to change
- Integration complexities
- The need for comprehensive training
These significant hurdles require careful management. Engaging stakeholders early and providing robust support can facilitate a smoother transition to EDC systems, allowing organizations to fully leverage their potential.
Looking forward, the future of EDC is poised for significant innovation driven by advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies promise to enhance data analysis capabilities and support the growing trend of decentralized clinical trials. As EDC systems continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly critical role in optimizing clinical trial processes, improving patient outcomes, and fostering a more efficient research environment. The ongoing commitment to embracing these technologies will be vital for stakeholders aiming to succeed in the rapidly changing landscape of clinical research.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Electronic Data Capture (EDC)?
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) is a method for organizing and collecting trial information using electronic techniques instead of traditional paper-based methods, aimed at improving the accuracy and efficiency of data gathering in clinical trials.
Why is clinical EDC important in clinical trials?
Clinical EDC is essential for maintaining data integrity and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, which enhances the overall effectiveness and reliability of clinical trials.
What are some benefits of adopting clinical EDC systems?
Key benefits of clinical EDC systems include enhanced information quality, streamlined processes, enhanced security, cost efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
How does clinical EDC improve information quality?
Clinical EDC frameworks reduce manual input errors and improve precision through automated verification checks, ensuring the integrity of the collected information.
In what ways does clinical EDC streamline trial processes?
EDC allows for real-time information entry and monitoring, enabling researchers to quickly identify and address issues, which facilitates faster decision-making during trials.
What security measures are typically included in EDC frameworks?
EDC frameworks often incorporate advanced security measures such as encryption and strict access controls to protect sensitive patient information and ensure compliance with regulations.
How does clinical EDC contribute to cost efficiency in trials?
By minimizing the time and resources needed for data oversight, EDC solutions can lead to significant cost reductions throughout the trial lifecycle.
What regulatory standards do EDC systems help to comply with?
EDC systems are designed with industry regulations in mind, including Good Clinical Practice (GCP), helping to ensure that clinical studies adhere to necessary compliance standards.
What impact has the integration of clinical EDC had on clinical trials in Canada?
A recent analysis indicated that the integration of clinical EDC in both academic and industry-funded trials reflects its critical role in adapting to the evolving needs of clinical research, particularly in managing complex data environments.
What are the goals outlined by Dimple Rajgor regarding EDC platforms?
Dimple Rajgor aims to provide an overview of EDC platforms, their types, pros and cons, commonly used tools and their features, and to describe the steps involved in designing a registry or clinical study using the open-source EDC application DADOS P.




