Introduction
In the realm of clinical research, the advent of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems marks a significant evolution in how trial data is managed and analyzed. These digital platforms not only streamline the collection and storage of diverse data types but also enhance the overall efficiency of clinical trials. As organizations increasingly shift away from traditional paper-based methods, the advantages of EDC systems become evident—real-time data entry, improved compliance with regulatory standards, and the ability to generate insightful reports are just a few of the benefits that contribute to more effective trial management.
However, the transition to EDC is not without its challenges, including the need for comprehensive training and data security considerations. This article delves into the multifaceted world of EDC systems, exploring their key features, benefits, limitations, and best practices for successful implementation, ultimately highlighting their transformative potential in advancing clinical research.
Understanding Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems in Clinical Trials
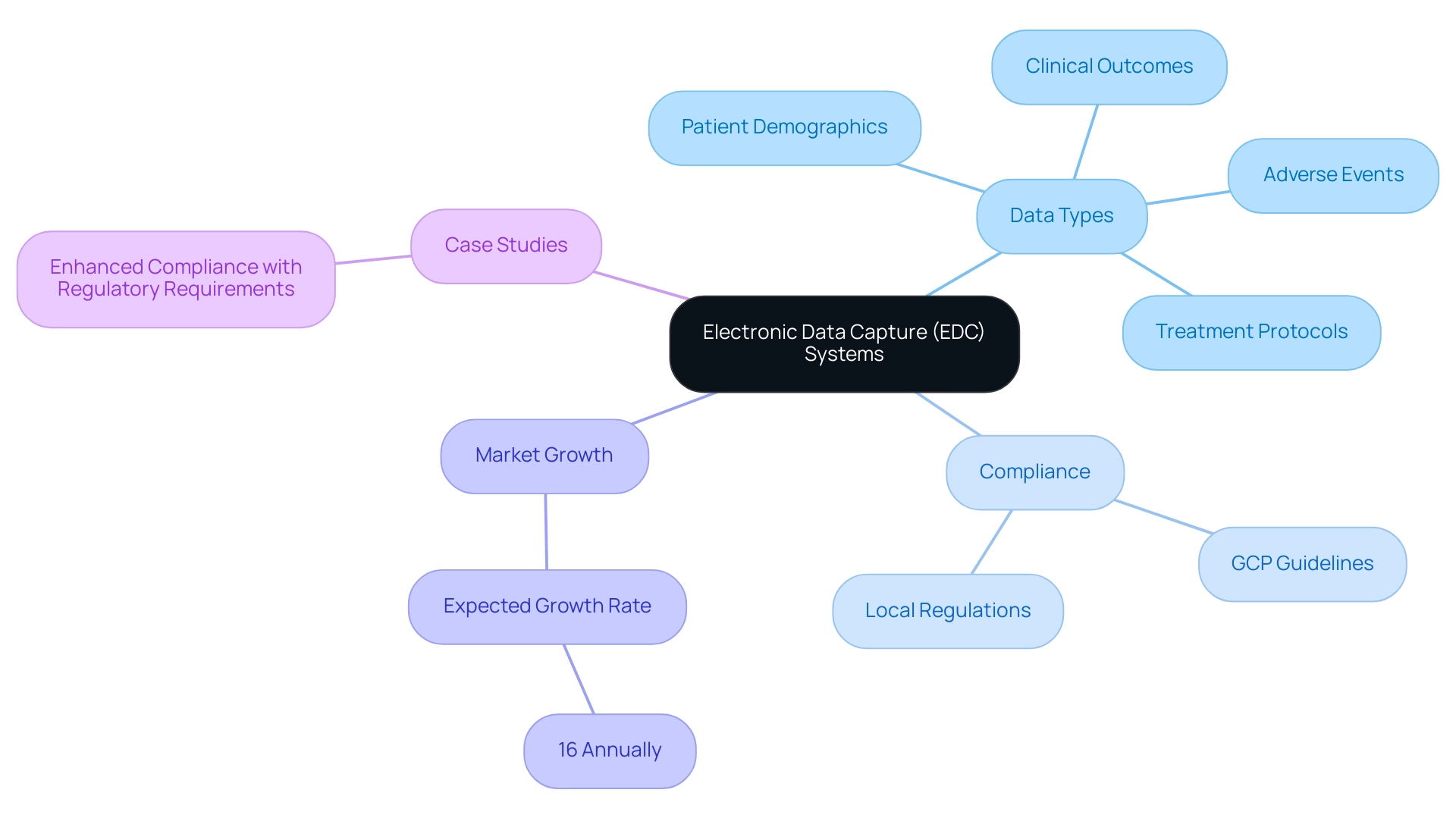
Electronic Information Capture (EIC) platforms signify a revolutionary method in the handling of clinical research information, providing digital platforms that enable the organized gathering, management, and storage of details. These frameworks offer considerable benefits compared to conventional paper-based techniques, especially in their capacity to facilitate immediate information entry and retrieval, which greatly enhances the effectiveness of EDC for clinical trials. The extensive functionalities of EDC platforms include the gathering of various information types, such as:
- Patient demographics
- Clinical outcomes
- Adverse events
- Treatment protocols
This multifaceted data collection is crucial for accurately assessing the efficacy and safety of treatments under investigation. Furthermore, EDC frameworks are vital for ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards, including Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, as well as adherence to country-specific requirements. This encompasses services such as:
- Review and feedback on study documents to ensure adherence to local regulations
- Setup, initiation, and approval from ethics committees and health ministries
The case study titled 'Enhanced Compliance with Regulatory Requirements' illustrates how EDC platforms provide a secure audit trail of information changes and safeguard sensitive details in accordance with privacy laws such as HIPAA and GDPR, ensuring the integrity of research information throughout the study. Significantly, the market for mobile EDC for clinical trials solutions is expected to increase by 16% each year, emphasizing a strong transition towards electronic information capture in clinical studies. This growth not only indicates the rising dependence on digital solutions but also highlights the potential of EDC for clinical trials to improve clinical study efficiency by optimizing information management processes.
As highlighted by Veeva Systems Inc., their Veeva Vault EDC has already powered over 1,000 study starts. By incorporating extensive clinical research management services—including feasibility studies, site selection, project management, and thorough reporting on study status and inventory—EDC platforms play a crucial role not only in enhancing compliance and efficiency but also in supporting local economies through job creation and healthcare advancements.
Key Benefits of Implementing EDC in Clinical Trials
The adoption of EDC for clinical trials provides a variety of significant advantages, especially regarding information precision and operational effectiveness. Research indicates that utilizing EDC can lead to cost savings between 49% and 62% when compared to traditional paper-based documentation (PDC). By reducing the risk of human mistakes linked to manual input, EDC for clinical trials solutions ensure that the information gathered is both trustworthy and legitimate.
Moreover, these frameworks greatly enhance the information gathering procedure, allowing faster access to essential insights that facilitate prompt decision-making. Adhering to regulatory standards is another vital benefit of EDC for clinical trials; these platforms promote compliance through features like audit trails and electronic signatures, which are necessary for preserving the integrity of clinical research data. Along with these advantages, EDC frameworks serve a crucial function in the setup and initiation phases, guaranteeing that all required documentation is prepared for ethics committee and health ministry authorizations.
Consequently, adopting EDC not only accelerates trial completion times but also contributes to overall cost reductions. Considering recent trends, like the encouragement for orthopedic surgeons to interact with clinical databases to improve evidence-based care, it is crucial to acknowledge how EDC for clinical trials can assist this initiative by providing accurate and easily accessible data. As James A. Welker aptly noted, 'All too frequently input is only obtained from a small user group that is technology oriented,' highlighting the need for broader user engagement in EDC platforms.
Moreover, understanding the comprehensive nature of clinical study management services—including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, and project management—is critical for directors of clinical research when selecting the most suitable EDC for clinical trials. The choice between commercial and open-source EDC solutions is also paramount; while commercial options offer user-friendly interfaces and robust support, open-source alternatives provide flexibility, making it essential to weigh these trade-offs carefully.
Essential Features of EDC Systems for Clinical Research
The functionality of EDC for clinical trials relies on several key attributes that greatly improve the conduct of clinical studies. Central to these systems are user-friendly interfaces, which simplify navigation for clinical research personnel, thereby enhancing overall usability. Real-time information entry capabilities enable instant updates, allowing for dynamic monitoring of progress and participant details.
Moreover, automated validation systems are essential; they confirm that the gathered information aligns with predefined criteria, thereby ensuring accurate entry and reducing mistakes that could jeopardize study integrity. As highlighted, the inclusion of validation fields is essential for maintaining data integrity. Customizable reporting tools are another essential feature, empowering researchers to generate tailored reports that yield valuable insights into performance and outcomes.
This includes systematic documentation of study status, inventory management, and reporting of both serious and non-serious adverse events, which are crucial for maintaining transparency and compliance. Additionally, as noted by Stat One EDC, their system includes a randomization functionality and is exploring further capabilities for the future. It is important to mention that Stat One EDC is server-based and requires internet access, which has implications for clinical study management.
Collectively, these functionalities not only streamline clinical study management but also foster a more efficient, patient-centric research environment. By incorporating comprehensive services such as feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, and adherence to country regulations, organizations can drive global health improvement and stimulate local economies through job creation and enhanced healthcare outcomes. As highlighted in the conclusion regarding the future of clinical trials, adopting advanced technologies like EDC for clinical trials is crucial for propelling medical innovation ahead.
Challenges and Limitations of EDC Systems in Clinical Trials
While electronic information collection (EDC) methods offer numerous benefits, they are not without their challenges and restrictions. A primary hurdle is the requirement for comprehensive training to equip staff with the necessary skills for effective system utilization. Resistance to change often arises among personnel who are accustomed to traditional information management methods, complicating the transition.
Furthermore, information security remains a critical concern; protecting sensitive patient details against breaches is paramount. Reports suggest that the risk of data security issues in EDC networks is a pressing topic, particularly as the industry evolves in 2024. Notably, a total of 259 Canadian trials were surveyed, highlighting the scale of challenges faced in this domain.
The substantial initial costs associated with implementing these solutions can also deter organizations, especially those with limited budgets. As emphasized by specialist Christine Bahls, experts assess initiatives to achieve gradual improvements in utilizing AI to alleviate systemic issues, such as accelerating study enrollment and minimizing the risk of unusable erroneous information. This underscores the necessity for systematic evaluation of EDC systems to inform adoption decisions, particularly as findings indicate a need for such evaluations.
Moreover, initiatives such as the Quality Accreditation Scheme for EHR2EDC Vendors show a dedication to ensuring adherence to best practices and protection standards, intending to alleviate some of these challenges. Importantly, these initiatives demonstrate that secure electronic transfer of information from EHR to EDC is feasible while keeping patient information on site. A comprehensive grasp of these obstacles is crucial for the effective execution of EDC frameworks in clinical studies.
Best Practices for Successful EDC Implementation in Clinical Trials
Successful execution of EDC for clinical trials relies on a series of best practices that can significantly enhance efficiency and data integrity. Significantly, almost 70% of biotech firms have faced challenges merging EDC technology with current software, highlighting the necessity of adequate training and integration. A crucial element is investing in thorough training for all users, as this not only maximizes the capabilities of the EDC platform but also ensures that team members are well-equipped to navigate its functionalities.
Engaging stakeholders early in the implementation process is equally essential; this approach helps address concerns, fosters buy-in, and aligns expectations across all parties involved. Moreover, conducting thorough testing of the EDC platform prior to full deployment is critical. This stage allows for the identification of potential issues, enabling necessary adjustments to be made before the system goes live.
Establishing clear protocols for information entry and management is another key practice that enhances quality and integrity, which is vital for regulatory compliance. As Páll Jóhannesson, Managing Director of Greenlight Guru Clinical, noted, 'Creating an EDC specifically for medical devices has shown that tailored solutions can effectively address unique challenges.' Maintaining open lines of communication among team members throughout the process further facilitates collaboration and ensures that challenges are swiftly addressed.
Furthermore, the case study titled 'Best Practices for EDC Implementation' illustrates that adhering to these best practices for EDC for clinical trials can improve study efficiency, data accuracy, and productivity. As Chris Rush emphasizes, effectively managing informed consent during these processes is crucial for regulatory compliance and participant rights. By incorporating these best practices, organizations can overcome common challenges associated with EDC for clinical trials, leading to successful implementation and improved outcomes in their trials.
Conclusion
The transition to Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems represents a pivotal advancement in the management of clinical trial data. By offering real-time data entry, improved compliance with regulatory standards, and enhanced operational efficiency, EDC systems significantly outperform traditional paper-based methods. The advantages of EDC include not only substantial cost savings and increased accuracy but also the ability to streamline trial processes, thereby facilitating quicker decision-making.
Despite these benefits, the implementation of EDC systems is not without its challenges. Organizations must navigate the complexities of staff training, data security concerns, and the initial costs associated with adopting these technologies. As highlighted, comprehensive training and stakeholder engagement are essential to overcoming resistance to change and ensuring a smooth transition to digital data management.
Ultimately, the successful integration of EDC systems into clinical trials can lead to transformative improvements in research efficiency and data integrity. By adhering to best practices and fostering a culture of collaboration, organizations can harness the full potential of EDC systems, driving innovation in clinical research and contributing to advancements in patient care. As the landscape of clinical trials continues to evolve, embracing these digital solutions will be critical for achieving future research goals and enhancing healthcare outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Electronic Information Capture (EIC) platforms?
EIC platforms are digital systems designed for the organized gathering, management, and storage of clinical research information, offering significant advantages over traditional paper-based methods.
What types of data can be collected using EDC platforms?
EDC platforms can gather various types of information, including patient demographics, clinical outcomes, adverse events, and treatment protocols.
How do EDC platforms enhance clinical trials?
EDC platforms facilitate immediate data entry and retrieval, improve information management processes, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of clinical trials.
What regulatory standards do EDC frameworks help to comply with?
EDC frameworks assist in adhering to stringent regulatory standards, including Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and country-specific requirements, such as document reviews and ethics committee approvals.
What is the significance of the case study titled 'Enhanced Compliance with Regulatory Requirements'?
This case study demonstrates how EDC platforms provide secure audit trails and protect sensitive information in compliance with privacy laws like HIPAA and GDPR, ensuring the integrity of research data.
What is the expected market growth for mobile EDC solutions in clinical trials?
The market for mobile EDC solutions is projected to grow by 16% each year, indicating a strong shift towards electronic information capture in clinical studies.
How does EDC contribute to cost savings in clinical trials?
Research indicates that using EDC can lead to cost savings of 49% to 62% compared to traditional paper-based documentation by minimizing human errors and streamlining data collection processes.
What features of EDC platforms promote compliance in clinical trials?
EDC platforms promote compliance through features such as audit trails and electronic signatures, which are essential for maintaining the integrity of clinical research data.
Why is user engagement important in EDC platforms?
Broader user engagement is crucial for obtaining comprehensive input, as reliance on a limited technology-oriented user group can skew data and insights, impacting the effectiveness of clinical research.
What should clinical research directors consider when selecting an EDC solution?
Directors should evaluate the comprehensive nature of clinical study management services, including feasibility studies and site selection, and consider the trade-offs between commercial and open-source EDC solutions based on user-friendliness and flexibility.




