Overview
The article highlights the significant innovations and challenges in clinical trials within Ecuador, specifically emphasizing advancements such as decentralized trials and adaptive study designs. It addresses critical regulatory hurdles and cultural barriers that impact the clinical research landscape.
By detailing how these innovations enhance patient participation and improve data collection, the article underscores the essential need for community engagement and enhanced infrastructure. These elements are vital for overcoming existing challenges and advancing the field of clinical research.
Introduction
In the realm of medical research, clinical trials are the cornerstone for evaluating the safety and effectiveness of new treatments. These meticulously structured studies unfold in distinct phases, each serving a critical function in the drug development process. Understanding the intricacies of these trials—from the initial safety assessments in Phase I to the expansive scrutiny of Phase III—is essential for stakeholders navigating the complexities of clinical research.
As innovations reshape methodologies, particularly in regions like Ecuador, the landscape of clinical trials is evolving, presenting both exciting advancements and formidable challenges. This exploration delves into the fundamentals of clinical trials, innovative practices emerging in Ecuador, the obstacles faced in conducting research, and the indispensable role of Contract Research Organizations (CROs) in advancing medical research.
Explore the Fundamentals of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are meticulously structured studies designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of medical interventions, progressing through distinct phases that each serve a critical purpose:
- Phase I: This initial phase primarily focuses on safety, determining the safe dosage range and identifying potential side effects. It typically involves a small group of healthy volunteers or patients.
- Phase II: In this phase, the efficacy of the intervention is evaluated, alongside further safety assessments in a larger participant group. This stage is crucial for understanding how the treatment works in a more diverse population.
- Phase III: This pivotal phase confirms the effectiveness of the intervention, closely monitoring side effects while comparing the new treatment to standard therapies in a large population. Roughly 30% of research studies reach this stage, highlighting its importance in the drug development process.
- Phase IV: Conducted post-approval, this phase observes long-term effects and effectiveness in the general population, often uncovering side effects not evident in earlier studies. Post-marketing surveillance is essential, as it can lead to drug withdrawals if serious issues arise.
Recent advancements in trial methodologies, such as the algorithmic approaches for data analysis presented in the article titled "Methodological Advances in Clinical Trial Data Analysis," have improved the accuracy of phase transition probabilities, enhancing our understanding of success rates in drug development. For instance, the probability of success for oncology treatments has notably increased from 1.7% in 2012 to 8.3% in 2015. However, it is important to interpret these success rates with caution due to potential biases, as emphasized in recent studies.
Real-world examples illustrate the importance of these phases. For instance, Flow-FX, a company dedicated to revolutionizing orthopedic surgery, has chosen Colombia and bioaccess™ as its contract development organization (CRO) for a first-in-human trial on its innovative Flow-Screw medical device for the administration of intraosseous antibiotics. This study, conducted at Clinical La Misericordia in Barranquilla, Colombia, exemplifies the critical nature of each phase in ensuring that medical interventions are both safe and effective.
Comprehending these phases is essential for stakeholders, as it enables better anticipation of requirements and challenges at each stage, facilitating enhanced planning and resource distribution in medical studies. As Andrew W. Lo highlights, understanding the complexities of research phases is crucial for progressing medical studies and guaranteeing the effective creation of new treatments. Moreover, the effect of Medtech research studies on local economies, including job creation and healthcare enhancement, highlights the greater importance of these examinations. In summary, a thorough understanding of research phases not only assists in navigating the complexities of drug development but also improves the likelihood of successful outcomes in medical interventions.
Examine Innovative Practices in Ecuadorian Clinical Trials
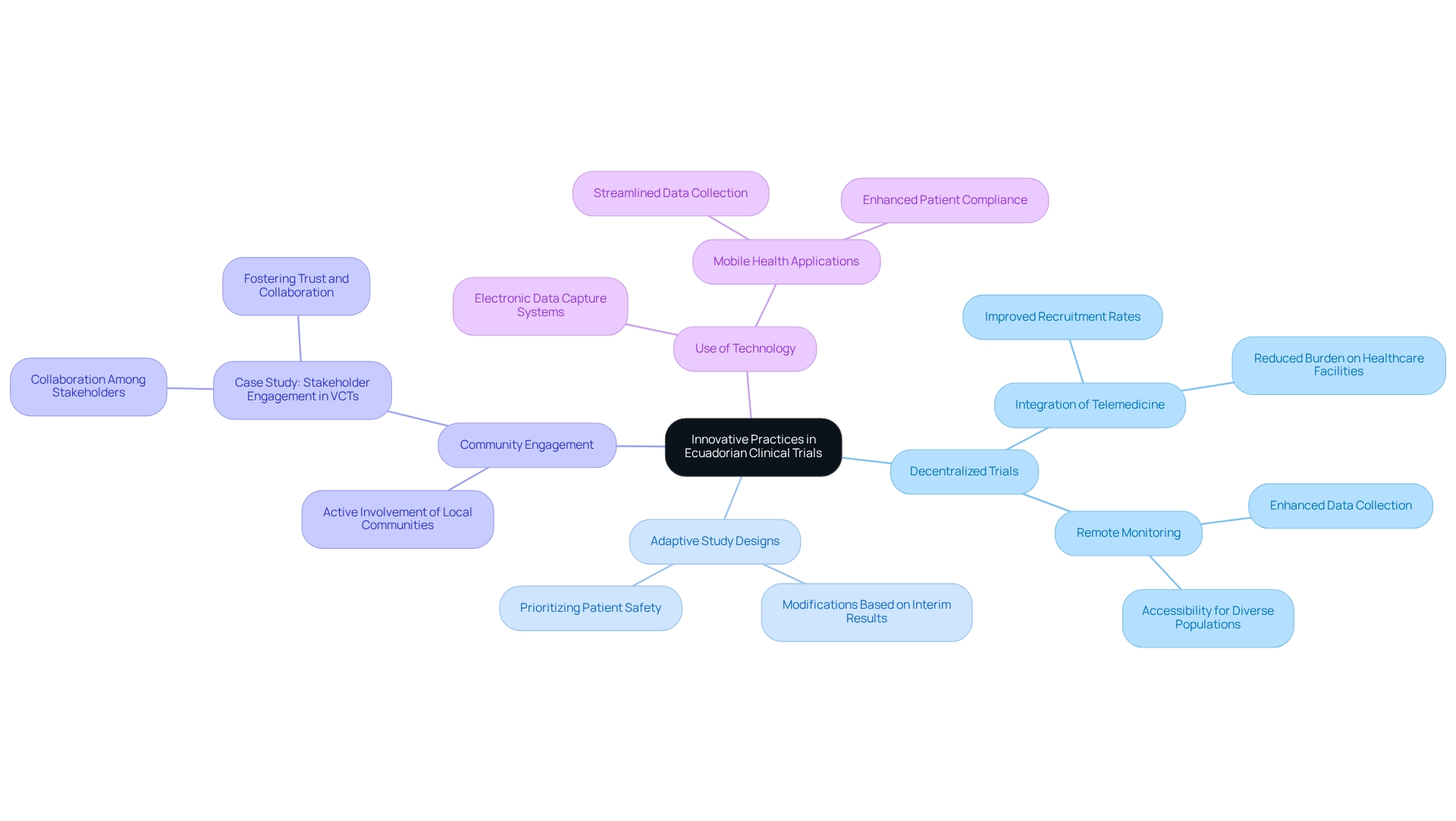
Ecuador is leading the way in clinical trial innovation in Ecuador, significantly enhancing the research environment. Key advancements include:
- Decentralized Trials: The integration of telemedicine and remote monitoring has revolutionized patient participation and data collection, making trials more accessible and efficient. Telemedicine alleviates the burden on healthcare facilities, optimizing resource use, which has been particularly effective in reaching diverse populations, thereby improving recruitment rates.
- Adaptive Study Designs: These designs allow for modifications to study protocols based on interim results, enhancing efficiency while prioritizing patient safety. This flexibility is crucial for responding to real-time data and optimizing trial outcomes.
- Community Engagement: Actively involving local communities in the research process has proven to enhance recruitment and retention rates. A case study titled "Stakeholder Engagement in VCTs" highlights successful collaboration among patients, researchers, technology providers, and regulators, demonstrating how fostering trust and collaboration can better align studies with community needs and expectations.
- Use of Technology: The implementation of electronic data capture systems and mobile health applications streamlines data collection and enhances patient compliance. These technological advancements enable real-time observation and elevate the overall quality of medical studies.
In Colombia, the partnership between bioaccess™ and Caribbean Health Group aims to establish Barranquilla as a leading location for medical studies in Latin America, supported by Colombia's Minister of Health. This initiative signifies a commitment to enhancing research study services, including comprehensive management services such as feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting. As Robert M. Califf, MD, the FDA Commissioner, emphasizes, virtual studies can enhance convenience for participants and broaden access to more diverse groups. Moreover, Karen Noonan, senior vice president of global regulatory policy at ACRO, underscores the necessity to shift the perspective of industry stakeholders regarding experiments and methodologies for execution. These groundbreaking methods not only elevate the standard of medical studies in Ecuador but also represent a significant aspect of clinical trial innovation in Ecuador, enriching patient experiences and outcomes while paving the way for more efficient medical investigations. Looking ahead, the future of virtual studies will involve navigating complexities while leveraging technological advancements, ensuring that measures are tailored to specific studies and patient needs.
Identify Challenges in Conducting Clinical Research in Ecuador
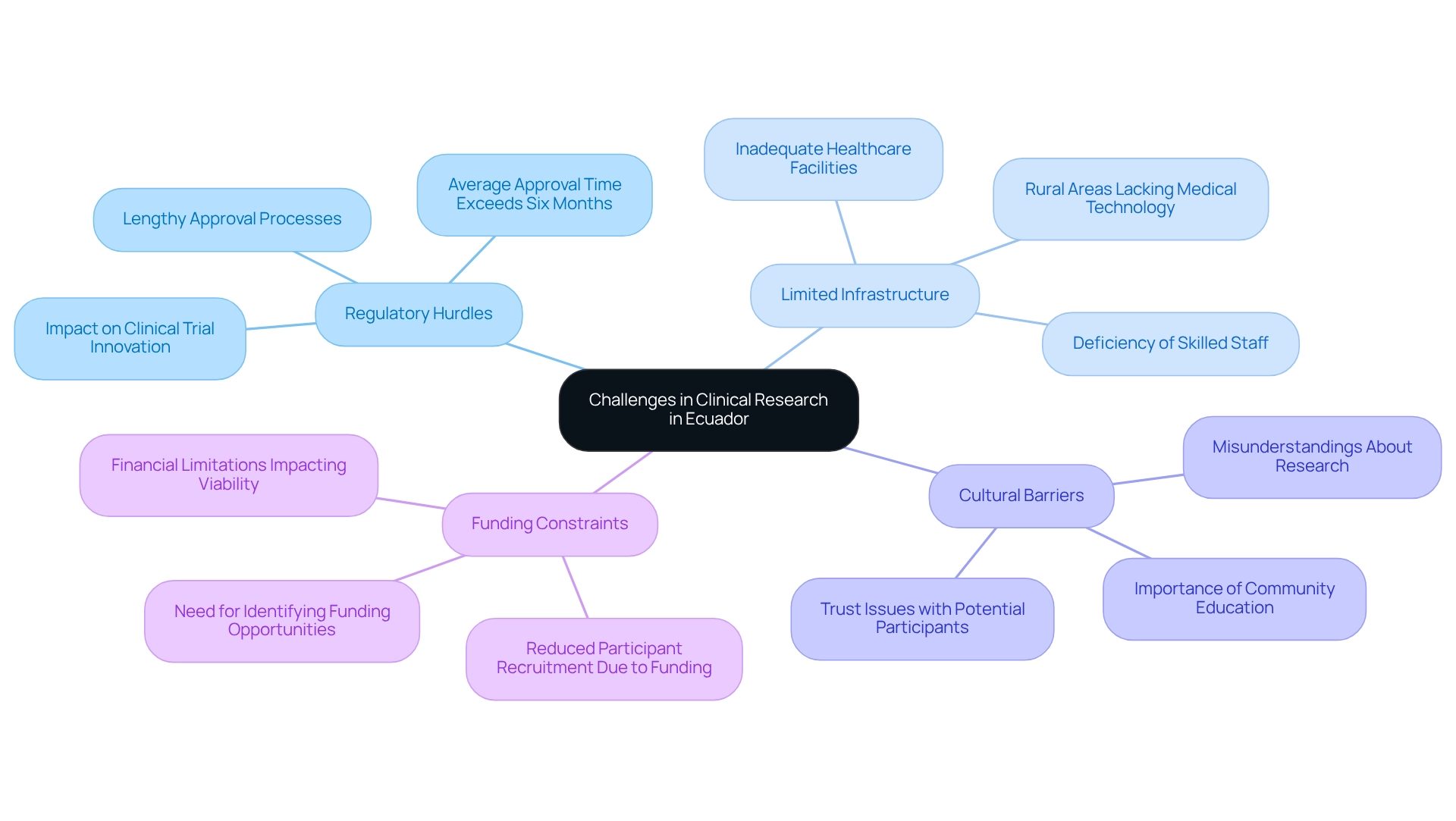
Conducting clinical research in Ecuador presents a landscape characterized by several significant challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The regulatory environment is complex, with lengthy approval processes that impede the timely initiation of clinical trials. In 2025, the average time for regulatory approval in Ecuador remains a critical concern, often extending beyond acceptable limits and hindering clinical trial innovation in Ecuador, thereby delaying access to innovative treatments. Recent statistics reveal that the average approval time can exceed six months, significantly impacting the research timeline. Leveraging the expertise of organizations like bioaccess®, which focuses on clinical trial innovation in Ecuador, Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, and other pivotal studies, can help streamline this process.
- Limited Infrastructure: Inadequate healthcare infrastructure in certain regions poses substantial obstacles to patient recruitment and data collection. This limitation is exacerbated by a deficiency of specialized facilities and skilled staff, which are crucial for conducting high-quality medical studies. For instance, numerous rural areas lack access to essential medical technology, further complicating the investigation process. Bioaccess® provides extensive management services for studies, specifically targeting clinical trial innovation in Ecuador, by offering customized solutions and assistance to address these infrastructure challenges.
- Cultural Barriers: Cultural barriers related to clinical trial innovation in Ecuador can significantly influence participant willingness and engagement. Misunderstandings regarding the aims and safety of research studies may deter potential volunteers. As highlighted by Dr. Maria Lopez, a researcher in Ecuador, "Community education is essential; without it, we risk losing the trust of potential participants who may fear the unfamiliar elements of research studies." Bioaccess® underscores the importance of community involvement and education in its strategy for clinical trial innovation in Ecuador, thereby promoting trust and participation.
- Funding Constraints: Financial limitations critically impact the scope and scale of clinical trials in Ecuador. Numerous investigative initiatives struggle to secure sufficient financing, which can restrict their viability and the capacity to conduct thorough examinations. For example, a recent study had to reduce its participant recruitment due to inadequate funding, illustrating the direct effect of financial limitations on study outcomes. Collaborating with experienced organizations like bioaccess®, which has over 20 years of experience in Medtech, can support clinical trial innovation in Ecuador by identifying funding opportunities and optimizing resource allocation.
Addressing these challenges necessitates strategic planning and collaboration with local stakeholders to promote clinical trial innovation in Ecuador. Innovative solutions tailored to the Ecuadorian context, such as leveraging eRegulatory software—which 77% of sites utilize—can contribute to clinical trial innovation in Ecuador by streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency. Furthermore, ongoing discussions regarding pending legislation, such as Brazil's PL 7082/2017, may serve as a model for improving medical study practices throughout Latin America. Drawing comparisons between Brazil's initiatives and Ecuador's challenges could inspire optimism for improved access to new treatments and elevated study standards.
Understand the Role of CROs in Advancing Clinical Research
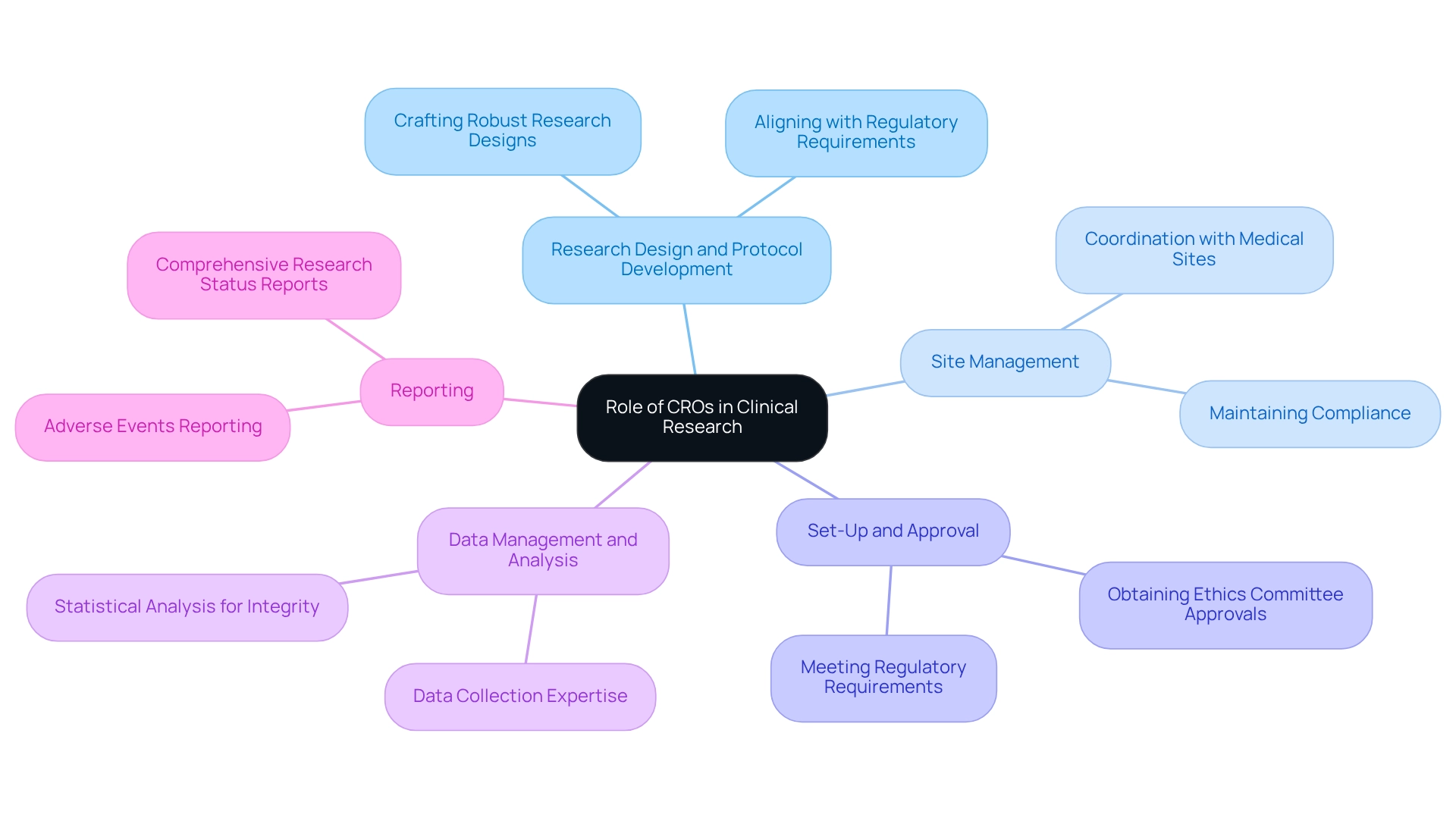
CROs play a pivotal role in the medical study environment, delivering a comprehensive range of services essential for the successful advancement of medical technologies. These services encompass:
- Research Design and Protocol Development: CROs assist sponsors in crafting robust research designs that align with regulatory requirements, ensuring that experiments are both effective and compliant.
- Site Management: They coordinate with medical sites to maintain compliance and facilitate seamless operations, which is crucial for the timely execution of research.
- Set-Up and Approval: This includes obtaining necessary approvals from ethics committees and health ministries, ensuring that all regulatory requirements are met before the experiment begins.
- Data Management and Analysis: With expertise in data collection and statistical analysis, CROs ensure the integrity and quality of results, which is vital for the credibility of findings.
- Reporting: CROs provide comprehensive reporting on research status, inventory, and serious and non-serious adverse events, which is essential for ongoing management and regulatory compliance.
In Ecuador, clinical trial innovation is instrumental in validating the advancements made through the collaboration of innovative medical technologies and research. This partnership enhances the effectiveness of medical studies and contributes to the overall progress of healthcare solutions in the region. As of 2024, the number of drugs in the R&D pipeline stands at 22,825, underscoring the growing demand for effective CRO services. Furthermore, with 77% of registered research being interventional, the role of CROs in supporting these experiments is more essential than ever.
bioaccess® provides expedited medical device research study services, leveraging over 20 years of expertise to oversee Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Research Follow-Up Studies. Their involvement is crucial for enhancing success rates of studies and ensuring diverse representation in investigations. Concerns such as the lack of Latino representation in certain studies highlight the necessity for CROs to address diversity in medical research. By fostering successful partnerships, CROs are advancing clinical trial innovation in Ecuador and driving overall innovation in the healthcare sector.
Conclusion
The exploration of clinical trials underscores their essential role in propelling medical research forward through meticulously structured phases aimed at ensuring both safety and efficacy. From the initial safety assessments in Phase I to the comprehensive evaluations in Phase III and beyond, each stage fulfills a critical function in the drug development continuum. Noteworthy innovations in methodologies, particularly in Ecuador, exemplify the substantial progress being made to bolster participant engagement and streamline operations, as evidenced by the implementation of decentralized trials and adaptive designs.
However, the path to conducting clinical research in Ecuador is fraught with challenges. Regulatory hurdles, limited infrastructure, cultural barriers, and funding constraints present significant obstacles that must be navigated with precision. Addressing these challenges necessitates strategic planning and collaboration with local stakeholders to cultivate a supportive environment for clinical trials. Insights from organizations like bioaccess® are invaluable in surmounting these difficulties and ensuring successful outcomes.
The pivotal role of Contract Research Organizations (CROs) in this landscape cannot be overstated. Their comprehensive services, ranging from study design to data management, are integral to facilitating the development of new treatments and ensuring rigorous adherence to regulatory standards. As the demand for effective CRO services continues to escalate, their contributions will be vital in enhancing the quality and success rates of clinical trials, ultimately leading to improved healthcare solutions.
In conclusion, grasping the intricacies of clinical trials, embracing innovative practices, overcoming inherent challenges, and leveraging the expertise of CROs are all crucial in advancing medical research. The future of clinical trials, particularly in emerging regions like Ecuador, holds immense promise, paving the way for more effective therapies and improved patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are clinical trials?
Clinical trials are meticulously structured studies designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of medical interventions, progressing through distinct phases that each serve a critical purpose.
What is the focus of Phase I in clinical trials?
Phase I primarily focuses on safety, determining the safe dosage range and identifying potential side effects, typically involving a small group of healthy volunteers or patients.
What is evaluated during Phase II of clinical trials?
Phase II evaluates the efficacy of the intervention alongside further safety assessments in a larger participant group, crucial for understanding how the treatment works in a more diverse population.
What occurs in Phase III of clinical trials?
Phase III confirms the effectiveness of the intervention, closely monitoring side effects while comparing the new treatment to standard therapies in a large population. Approximately 30% of research studies reach this stage.
What is the purpose of Phase IV in clinical trials?
Phase IV, conducted post-approval, observes long-term effects and effectiveness in the general population, often uncovering side effects not evident in earlier studies through post-marketing surveillance.
How have recent advancements impacted clinical trials?
Recent advancements in trial methodologies, such as algorithmic approaches for data analysis, have improved the accuracy of phase transition probabilities, enhancing the understanding of success rates in drug development.
Can you provide an example of a clinical trial?
An example is Flow-FX, which is conducting a first-in-human trial on its innovative Flow-Screw medical device for administering intraosseous antibiotics in Colombia, highlighting the critical nature of each phase in ensuring medical interventions are safe and effective.
Why is understanding the phases of clinical trials important for stakeholders?
Understanding these phases enables stakeholders to better anticipate requirements and challenges at each stage, facilitating enhanced planning and resource distribution in medical studies.
What impact do Medtech research studies have on local economies?
Medtech research studies can positively affect local economies through job creation and healthcare enhancement, underscoring the greater importance of these examinations in medical research.




