Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of clinical research, Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems have emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing the way data is collected, managed, and analyzed. As organizations transition from traditional paper-based methods to sophisticated digital platforms, the implications for data accuracy, efficiency, and regulatory compliance become increasingly profound. This article delves into the multifaceted world of EDC systems, exploring their key features, benefits, challenges, and future trends that are shaping the future of clinical trials.
By examining the innovative solutions provided by industry leaders and the essential components that define effective EDC systems, the discussion aims to highlight the critical role these technologies play in enhancing research capabilities and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems in Clinical Trials
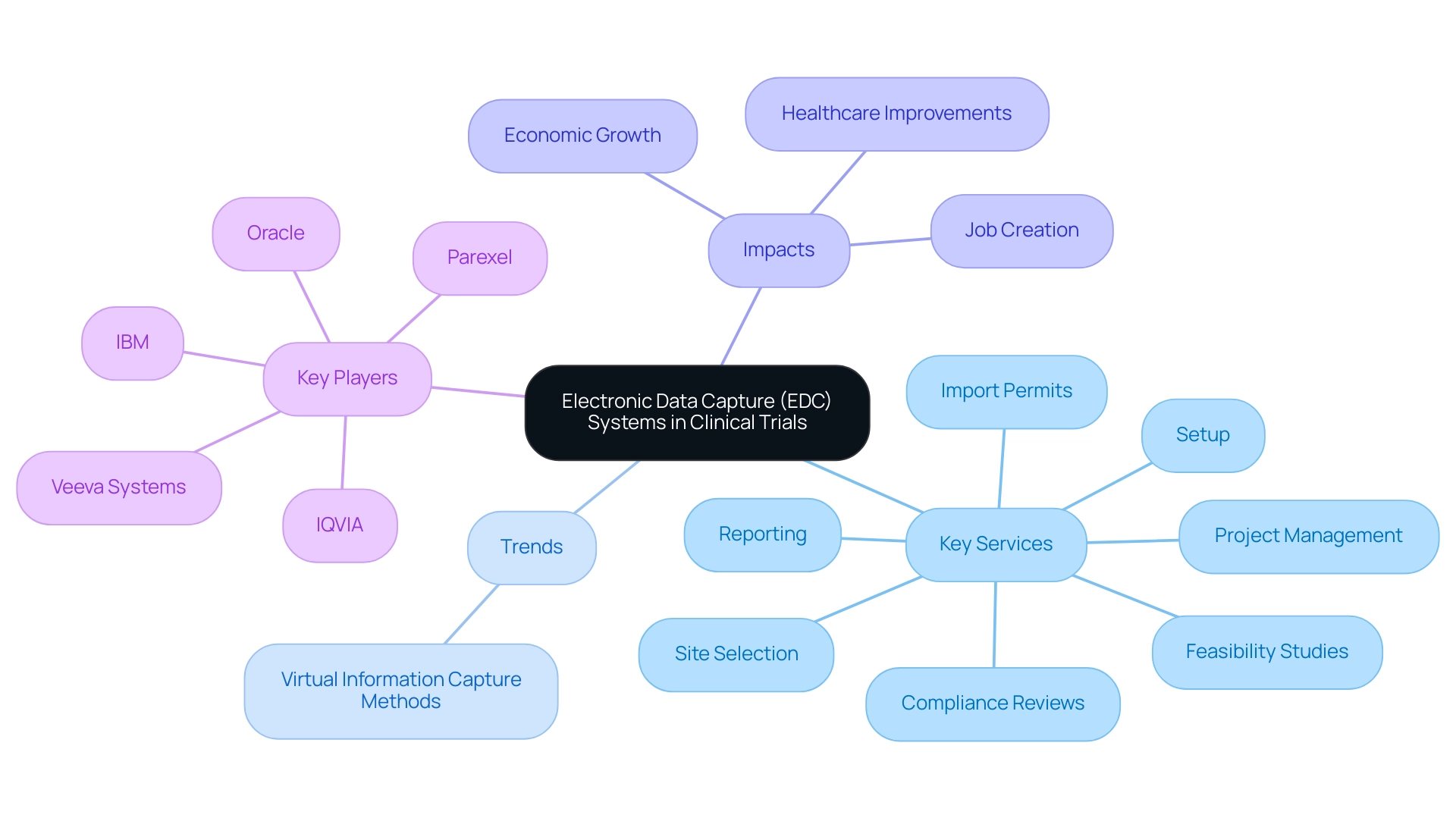
Clinical trial EDC systems represent a significant advancement in the gathering, management, and storage of clinical research information. Over the past several years, particularly from 2018 to 2023, these software solutions have undergone substantial improvements, transitioning from traditional paper-based methodologies to highly efficient digital platforms. EDC frameworks enable real-time data entry, enhancing data accuracy and streamlining the entire data management process.
Their significance in clinical studies, particularly with clinical trial EDC systems, is profound; they facilitate adherence to stringent regulatory standards, thereby optimizing efficiency and contributing to improved patient outcomes. Comprehensive services for managing clinical trial EDC systems—including:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
further bolster their effectiveness. For instance, feasibility studies involve assessing potential research sites and principal investigators (PIs) to ensure alignment with study objectives and regulatory requirements.
A significant trend has been the emergence of virtual information capture methods in clinical studies, demonstrating the adaptability and innovative trajectory of clinical trial EDC systems. Key players such as IBM, Oracle, IQVIA, Parexel, and Veeva Systems are at the forefront of this competitive landscape, driving innovation in electronic information capture solutions. Veeva Systems Inc., for example, has demonstrated strong financial performance, reflecting the growing demand and investment in EDC technologies.
This evolution not only enhances clinical research capabilities and improves study efficiency but also positively impacts local economies through job creation, economic growth, and healthcare improvements, reinforcing the importance of international collaboration in the field. Feedback from clients has demonstrated that the adoption of these frameworks has resulted in a 30% improvement in information precision and a 25% decrease in testing durations, highlighting the concrete advantages of utilizing clinical trial EDC systems.
Key Features of Leading EDC Systems: What to Look For
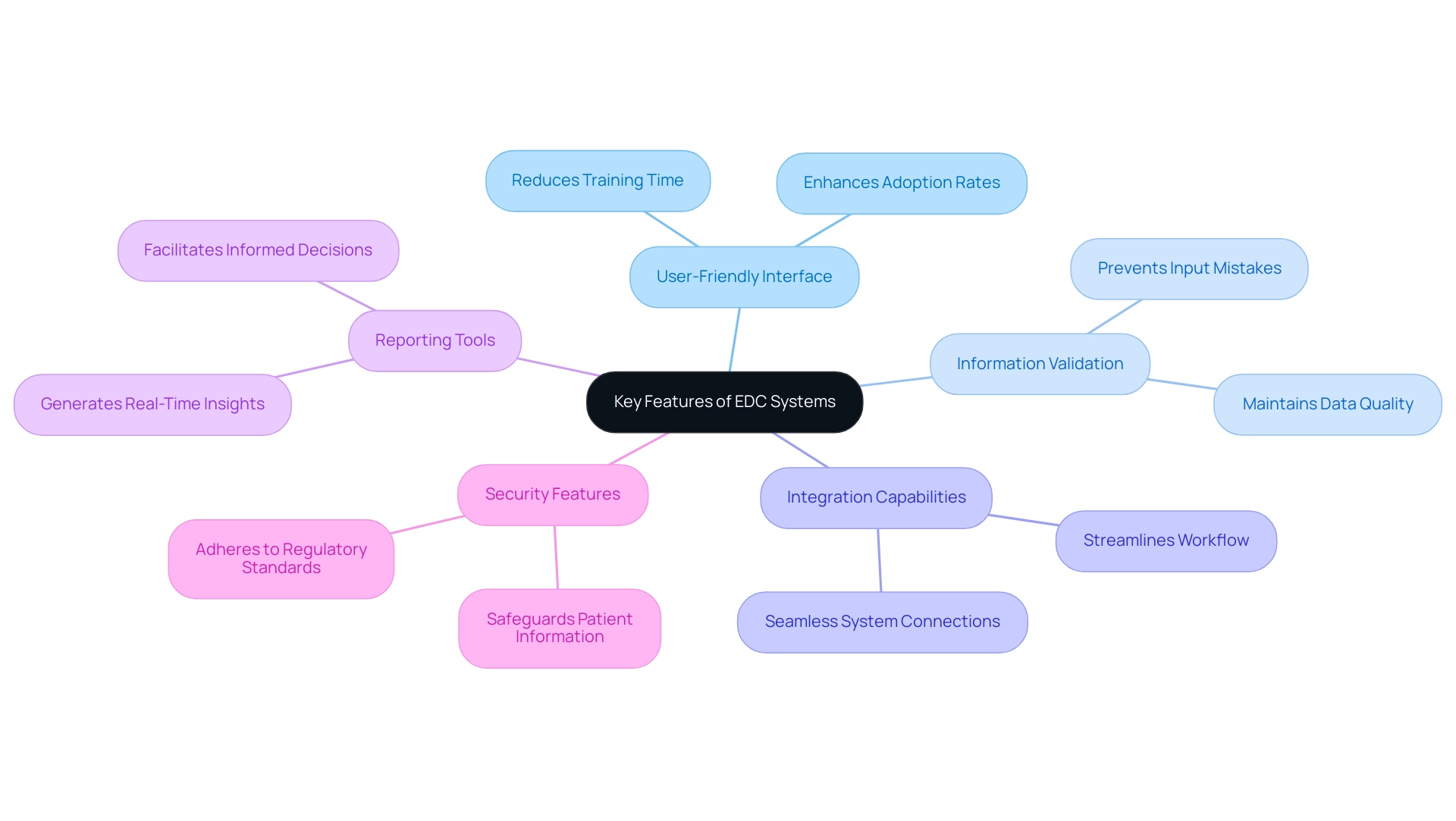
When assessing Electronic Data Capture (EDC) platforms, several key features stand out as essential for effective clinical trials:
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive design significantly enhances user adoption rates, reducing the time required for training. Industry specialists stress that a user-friendly interface is essential for enabling all team members to effectively navigate the platform, thus enhancing overall productivity.
- Information Validation: Integrated validation checks are crucial as they guarantee accuracy and integrity of the information. For example, the introduction of validation mechanisms aids in preventing frequent input mistakes, thereby maintaining the quality of the gathered information.
- Integration Capabilities: The ability to seamlessly connect with other systems, such as laboratory information management systems or electronic health records, is crucial for creating a cohesive workflow. Systems that support these integrations can significantly streamline processes and enhance information accessibility.
- Reporting Tools: Robust reporting functionalities are necessary for generating real-time insights and facilitating thorough analysis. Effective reporting capabilities enable researchers to make informed decisions swiftly, which is particularly crucial in dynamic clinical environments.
- Security Features: Given the sensitive nature of clinical trial information, implementing strong security measures is essential for safeguarding patient details. Adhering to regulations like FDA 21 CFR Part 11 further emphasizes the need for strong security protocols in any EDC framework. As mentioned, clinical trial EDC systems support adherence to these regulatory standards, ensuring that information integrity is maintained.
Moreover, Stat One EDC is server-based and requires internet access, which is a significant practical consideration for users. Furthermore, the importance of audit trails in EDC platforms cannot be overstated; they record every information alteration, including who made the modification and when, which is crucial for preserving integrity and adhering to regulatory requirements.
These features not only improve the usability and efficiency of EDC platforms but also align with the latest trends towards user-friendly design and compliance in electronic information capture for 2024.
Benefits of Implementing EDC Systems in Clinical Trials
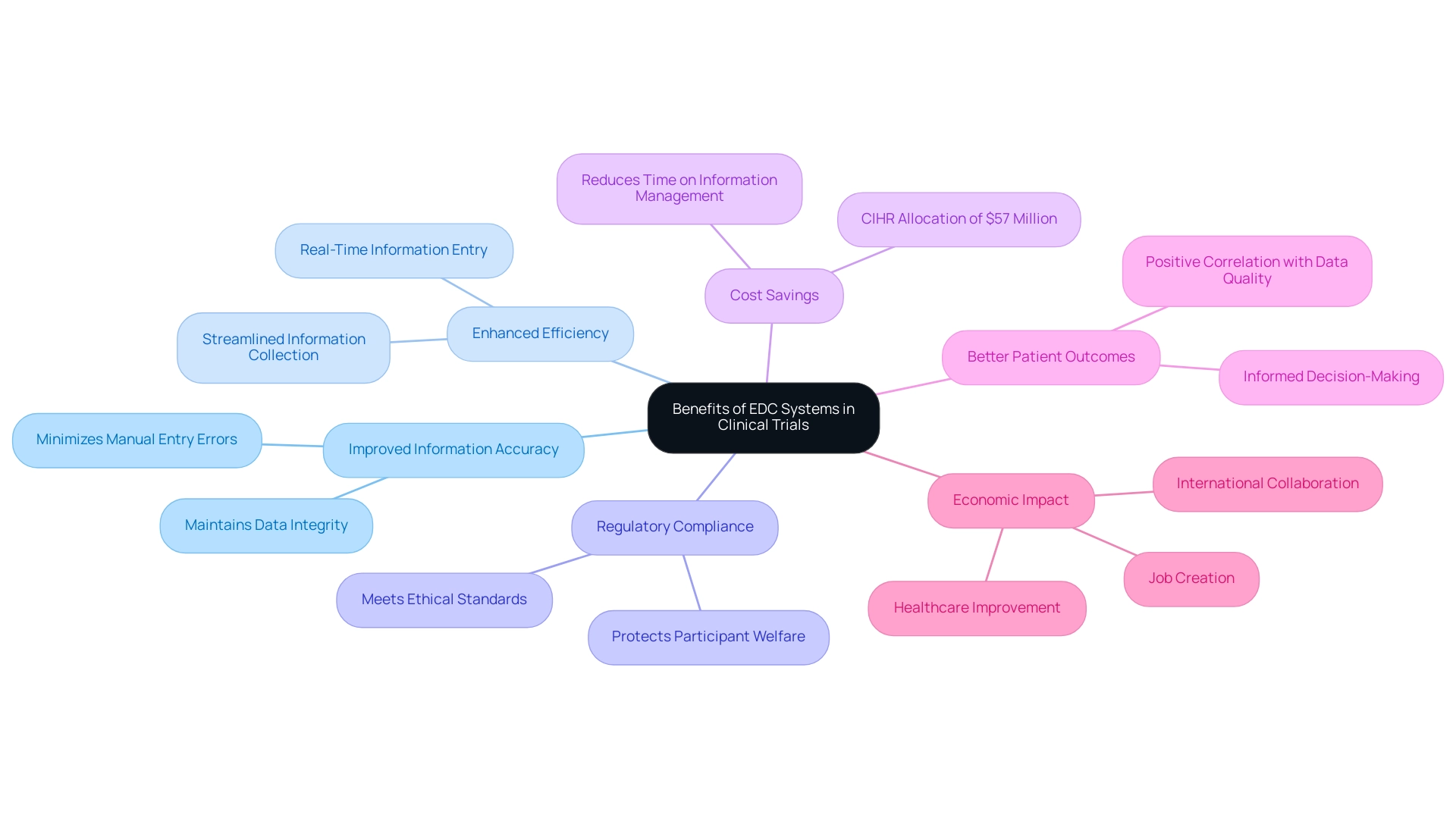
Implementing Electronic Information Capture (EDC) platforms in clinical trials offers a multitude of advantages that can significantly enhance the research process, particularly when integrated with comprehensive clinical trial management services such as feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, including review and feedback on study documents and reporting on serious and non-serious adverse events:
- Improved Information Accuracy: EDC platforms effectively minimize the risk of errors commonly associated with manual information entry. By automating information gathering, these mechanisms ensure that the integrity of the information is maintained throughout the study.
- Enhanced Efficiency: The ability for real-time information entry and automated processes streamlines the information collection phase, resulting in quicker study completion. This efficiency is critical in today's fast-paced research environment, where timely results are essential.
- Regulatory Compliance: Designed to meet stringent regulatory requirements, clinical trial EDC systems help ensure that clinical studies align with ethical standards and guidelines. This adherence is crucial for preserving the trustworthiness of the research and protecting participant welfare.
- Cost Savings: EDC frameworks lead to significant cost reductions by decreasing the time spent on information management and minimizing mistakes. A recent analysis indicated that the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) allocated only $57 million to clinical studies research during a specific period. This statistic highlights the necessity for more effective funding usage through clinical trial EDC systems, which can optimize resource distribution and improve overall study efficiency.
- Better Patient Outcomes: With improved information quality and accelerated analysis, EDC systems play a vital role in enabling informed decision-making, ultimately resulting in enhanced patient care. Various studies illustrate the positive correlation between data quality and patient outcomes. As mentioned, "Better yet, they can grow alongside Castor as they step into the future of fully integrated studies," highlighting the adaptability and future potential of EDC systems.
Furthermore, the impact of Medtech clinical studies extends beyond the immediate research environment, contributing to local economies through job creation, economic growth, healthcare improvement, and international collaboration. A case study titled "Analysis of Trial Characteristics" examined 947 registered studies, revealing that while academic and industry-funded examinations had a relatively equal split, industry studies were larger in scale. This difference highlights how EDC frameworks can influence participant recruitment and site allocation, ultimately improving study characteristics.
In summary, the adoption of clinical trial EDC systems not only strengthens data precision and operational effectiveness but also provides a framework for cost-efficient and ethically compliant clinical evaluations, thereby enhancing overall patient results and positively impacting local economies.
Challenges and Drawbacks of EDC Systems: What You Need to Know
While clinical trial EDC systems offer numerous benefits, they also present specific challenges that clinical trial organizations must navigate.
-
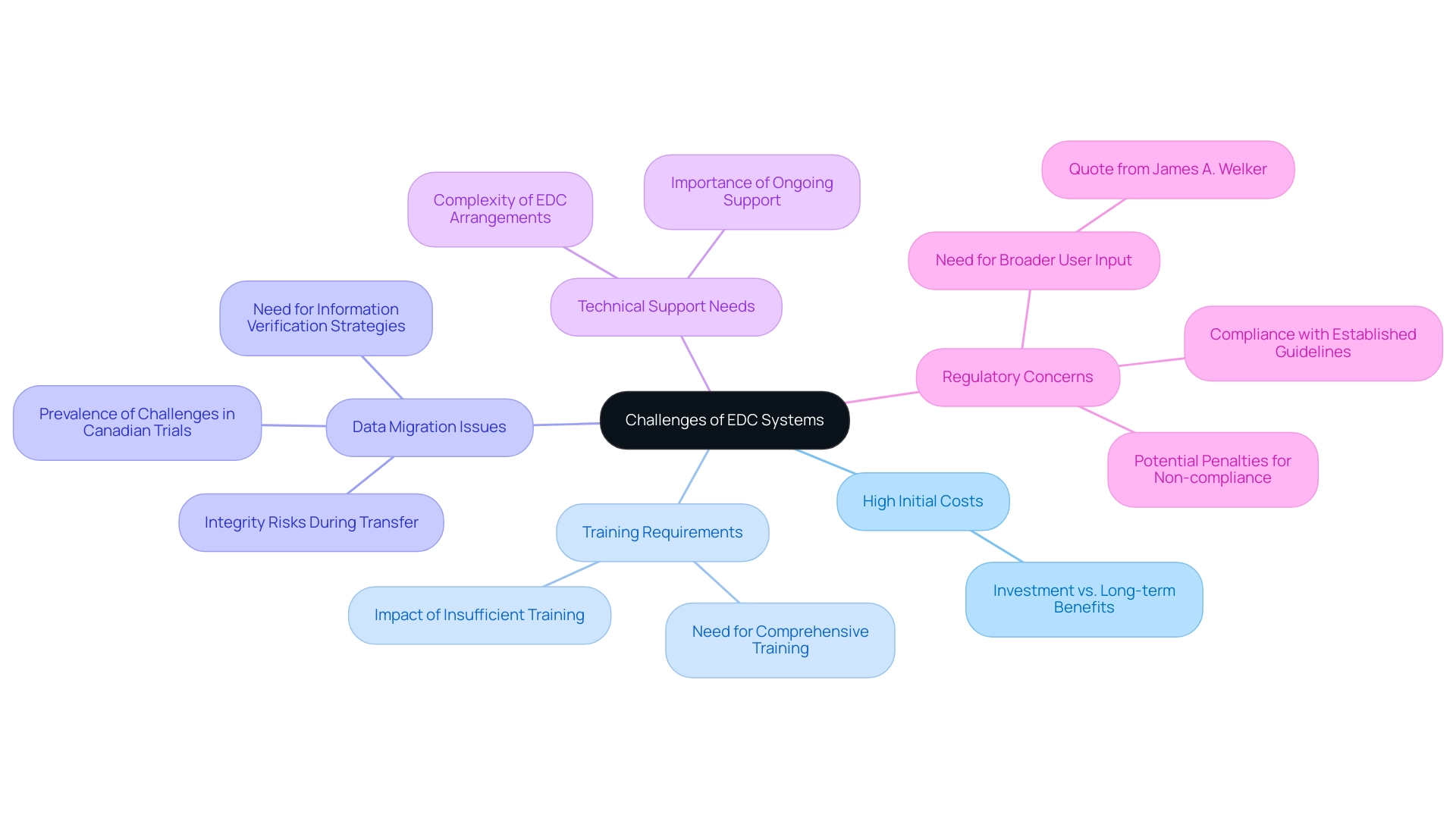
High Initial Costs: The upfront investment required for EDC solutions can be substantial, particularly for smaller organizations with limited budgets. It's essential for these entities to weigh the long-term benefits against the immediate financial burden.
-
Training Requirements: Effective utilization of EDC tools necessitates comprehensive training. Users often require extensive instruction to become proficient, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Recent reports suggest that insufficient training can result in inefficiencies and reduced information quality, highlighting the necessity for well-organized training programs.
-
Data Migration Issues: Transitioning from traditional paper-based systems or other electronic platforms presents significant challenges. Data migration can result in integrity risks, as discrepancies may arise during the transfer process. Case studies have indicated that organizations must implement robust information verification strategies to safeguard against these issues. Additionally, a recent web-survey involving 259 Canadian trials highlighted the prevalence of data migration challenges across various organizations.
-
Technical Support Needs: To maintain operational efficiency, organizations may require ongoing technical support. The complexity of EDC arrangements means that technical issues can arise unexpectedly, necessitating reliable support to ensure smooth functioning.
-
Regulatory Concerns: Despite being designed for compliance, EDC solutions are not immune to regulatory scrutiny. Any lapses in adherence to established guidelines can lead to severe penalties, emphasizing the importance of staying vigilant regarding regulatory requirements. James A. Welker aptly remarked,
All too frequently input is only obtained from a small user group that is technology oriented,
highlighting the need for broader input when developing EDC solutions to ensure they meet the diverse needs of all users.
Furthermore, the case study titled "Practical Implications of EDC Adoption" examines the rapid increase in EDC adoption and its effects on information quality and efficiency in experiments, emphasizing the significance of tackling these challenges. Furthermore, De Vries's analysis on EDC's function in adaptive clinical studies in 2007 highlights the development of these frameworks and their growing importance in modern clinical research. Tackling these challenges is essential for optimizing the capabilities of EDC frameworks in improving information quality and effectiveness in clinical studies.
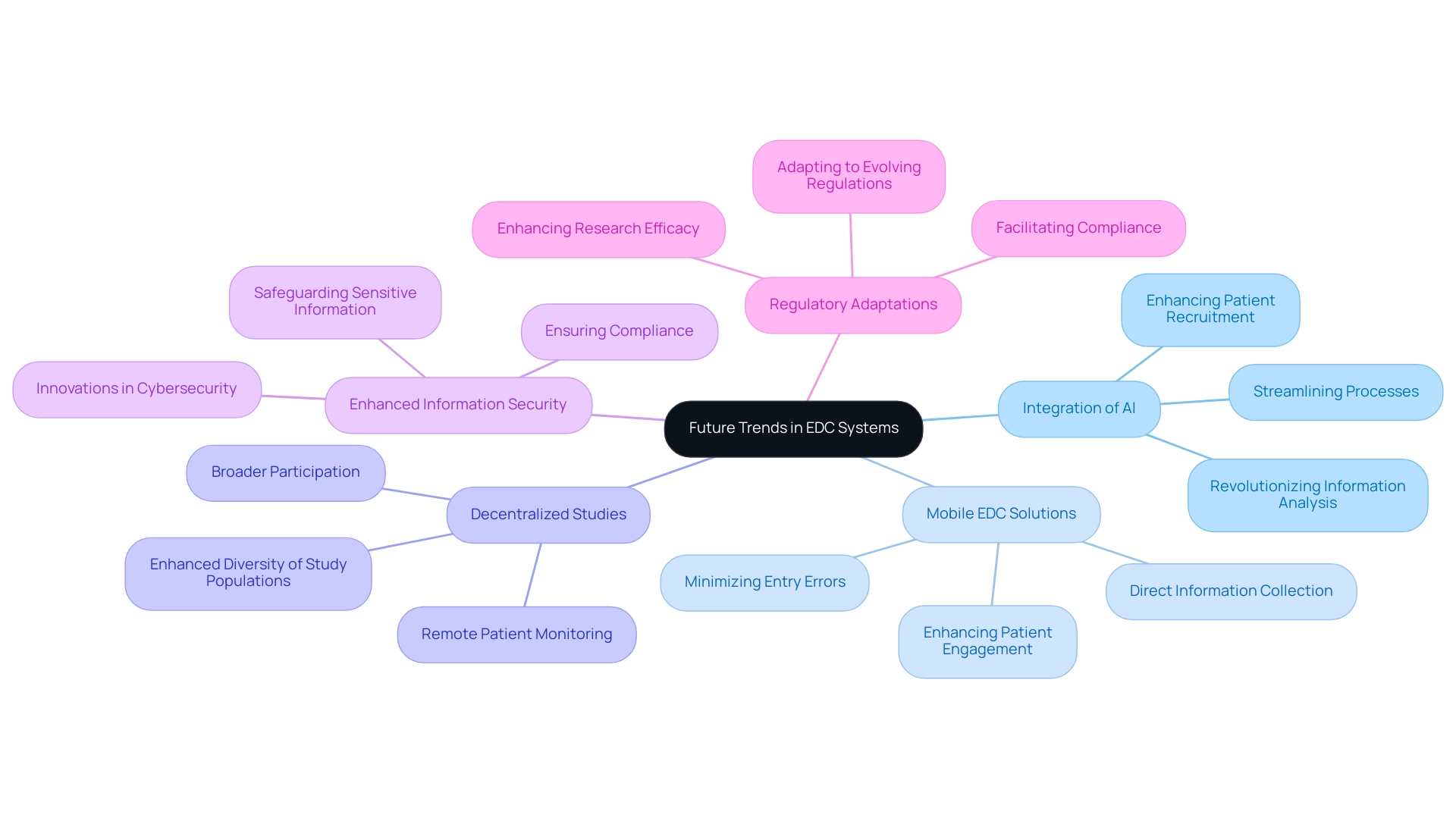
Future Trends in EDC Systems: Innovations Shaping Clinical Trials
The future of clinical trial EDC systems is set for substantial evolution in clinical studies, driven by several key trends.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence: The incorporation of AI technologies is revolutionizing information analysis, streamlining processes, and enhancing patient recruitment strategies. The emergence of clinical trial EDC systems for virtual information capture in clinical studies, a major trend observed in the industry, reflects this shift towards more efficient methodologies and is expected to significantly impact the effectiveness of clinical research.
- Mobile EDC Solutions: The increasing prevalence of mobile technology empowers researchers to collect information directly from patients, significantly enhancing engagement while minimizing entry errors. This advancement is crucial for enhancing the overall quality of clinical information.
- Decentralized Studies: Clinical trial EDC systems are increasingly facilitating decentralized clinical studies, allowing for remote patient monitoring and information collection. This trend not only broadens participation but also enhances the diversity of study populations, which is essential for generalizability.
- Enhanced Information Security: In light of rising breaches, innovations in cybersecurity are becoming essential to safeguard sensitive clinical trial information. EDC frameworks must evolve to incorporate robust security measures, ensuring compliance and protecting participant data.
- Regulatory Adaptations: As regulations continue to evolve, EDC solutions will need to adapt accordingly. This adaptability ensures that frameworks align with the changing landscape of clinical research, facilitating compliance and enhancing research efficacy. Additionally, insights from Table 79: Veeva Systems Inc. Financial Performance highlight the financial robustness of clinical trial EDC systems, underscoring their significance in the clinical research landscape.
With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.8% projected for Electronic Data Capture Systems from 2024 to 2033, the integration of these trends will be pivotal in shaping the future of clinical trials.
Conclusion
The evolution of Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems marks a significant turning point in the realm of clinical research. By transitioning from traditional paper-based methods to advanced digital platforms, EDC systems enhance data accuracy, improve operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards. Key features such as:
- User-friendly interfaces
- Robust data validation
- Seamless integration capabilities
are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of these systems. Moreover, the benefits of implementing EDC systems extend beyond improved data management, leading to better patient outcomes and substantial cost savings.
However, the adoption of EDC systems is not without its challenges. Organizations must navigate:
- High initial costs
- Training requirements
- Potential data migration issues
The importance of ongoing technical support and vigilance regarding regulatory compliance cannot be overstated. Addressing these challenges is crucial to fully harnessing the advantages that EDC systems offer in enhancing data quality and efficiency in clinical trials.
Looking ahead, the future of EDC systems is poised for transformative innovations, driven by trends such as:
- The integration of artificial intelligence
- Mobile solutions
- Decentralized trials
These advancements will not only streamline processes but also expand participation and enhance the diversity of trial populations. As the clinical research landscape continues to evolve, the role of EDC systems will become increasingly vital in ensuring that trials are conducted effectively, ethically, and in alignment with regulatory requirements. The commitment to innovation and adaptation will ultimately shape the future of clinical trials, reinforcing the critical impact of EDC systems on research capabilities and patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are clinical trial EDC systems?
Clinical trial EDC (Electronic Data Capture) systems are advanced software solutions designed for the gathering, management, and storage of clinical research information, transitioning from traditional paper-based methods to efficient digital platforms.
How have EDC systems improved from 2018 to 2023?
From 2018 to 2023, EDC systems have undergone substantial improvements, enabling real-time data entry, enhancing data accuracy, and streamlining the entire data management process.
What services are included in managing clinical trial EDC systems?
Services for managing clinical trial EDC systems include feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting.
What is the purpose of feasibility studies in clinical trials?
Feasibility studies assess potential research sites and principal investigators (PIs) to ensure alignment with study objectives and regulatory requirements.
What recent trend has emerged in clinical studies regarding data capture?
The emergence of virtual information capture methods has been a significant trend in clinical studies, showcasing the adaptability and innovation of clinical trial EDC systems.
Who are the key players in the EDC market?
Key players in the EDC market include IBM, Oracle, IQVIA, Parexel, and Veeva Systems, which are driving innovation in electronic information capture solutions.
What benefits have clients reported from using clinical trial EDC systems?
Clients have reported a 30% improvement in information precision and a 25% decrease in testing durations after adopting clinical trial EDC systems.
What are the essential features to assess in EDC platforms?
Essential features of EDC platforms include a user-friendly interface, information validation, integration capabilities, reporting tools, and strong security features.
Why is a user-friendly interface important in EDC systems?
A user-friendly interface enhances user adoption rates and reduces training time, enabling all team members to navigate the platform effectively and improve overall productivity.
How do validation checks contribute to EDC systems?
Integrated validation checks ensure the accuracy and integrity of information, helping to prevent input mistakes and maintain the quality of gathered data.
What role do reporting tools play in EDC platforms?
Robust reporting tools provide real-time insights and facilitate thorough analysis, enabling researchers to make informed decisions quickly in dynamic clinical environments.
Why are security features critical in EDC systems?
Security features are essential for safeguarding sensitive clinical trial information and ensuring compliance with regulations like FDA 21 CFR Part 11.
What is the significance of audit trails in EDC platforms?
Audit trails record every information alteration, including who made the modification and when, which is crucial for maintaining integrity and adhering to regulatory requirements.

