Overview
Designing safe medical device trials necessitates a structured approach that encompasses multiple phases, including:
- Preclinical testing
- Various clinical trial phases
- Post-market surveillance
This comprehensive strategy is essential for ensuring both safety and effectiveness. The article underscores the critical importance of adhering to regulatory guidelines and strategic planning. Furthermore, it highlights the incorporation of innovations such as decentralized studies and artificial intelligence to enhance trial efficiency and patient engagement. Ultimately, these elements contribute to successful regulatory approvals and improved patient outcomes.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of medical technology, clinical trials represent a critical pathway for evaluating the safety and efficacy of innovative medical devices. These meticulously structured studies unfold through various phases, each designed to gather essential data that informs regulatory decisions and ultimately ensures patient safety. As stakeholders navigate this complex terrain, understanding the intricacies of trial design, regulatory requirements, and data management becomes paramount. Recent trends indicate a shift towards greater data ownership and transparency, alongside the adoption of decentralized and adaptive trial designs that enhance engagement and efficiency. This article delves into the multifaceted world of clinical trials for medical devices, exploring strategic planning, design considerations, and the future trends shaping this vital sector.
Understanding Clinical Trials for Medical Devices
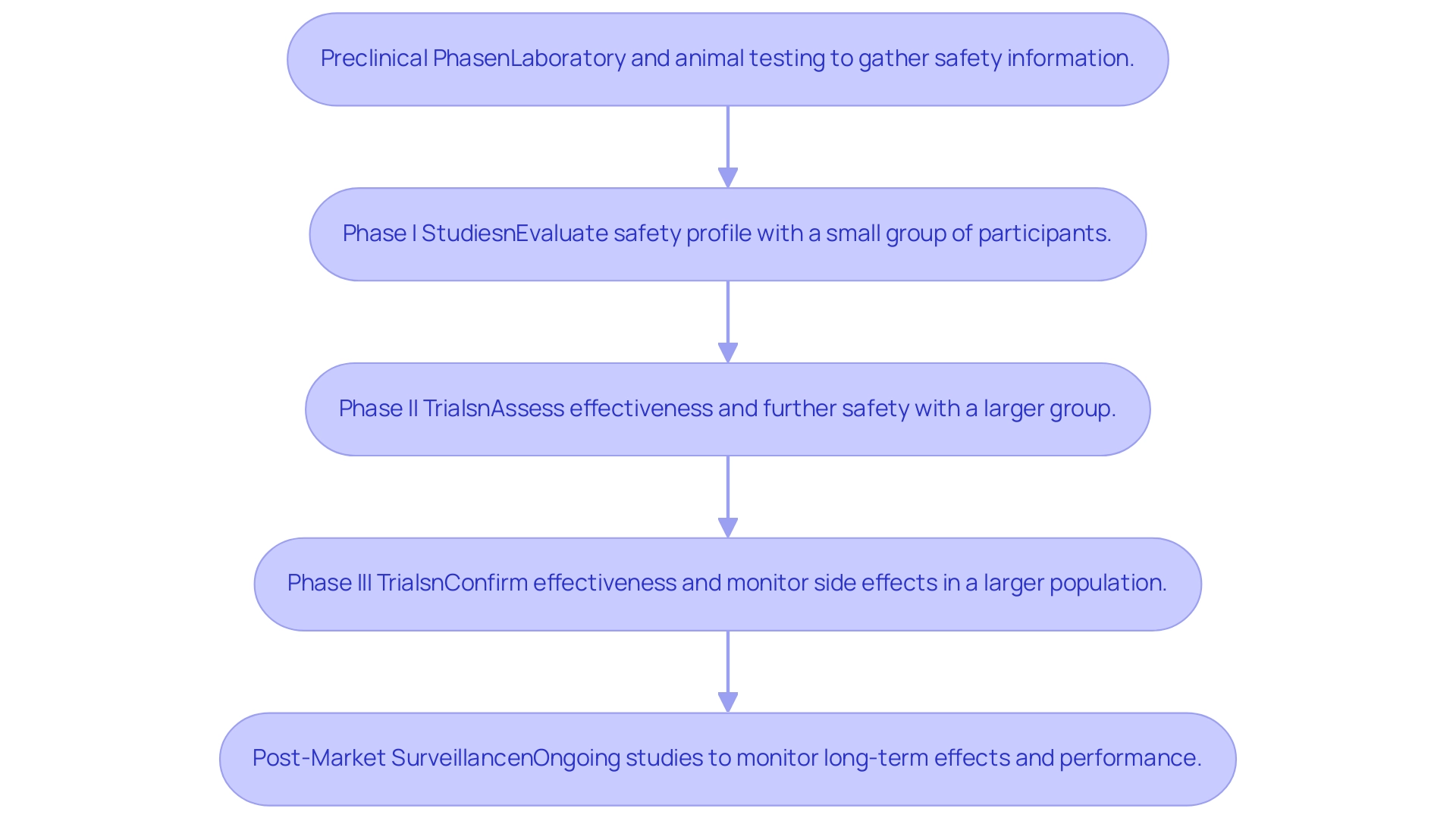
Designing safe medical device trials necessitates meticulously structured clinical studies aimed at evaluating both the safety and effectiveness of innovative devices. These trials typically progress through several critical phases:
- Preclinical Phase: This initial stage involves laboratory and animal testing to gather essential safety information, laying the groundwork for subsequent human studies.
- Phase I Studies: Concentrated on safety, these studies involve a small group of participants to evaluate the safety profile of the apparatus and identify any possible adverse effects.
- Phase II Trials: In this phase, the effectiveness of the apparatus is evaluated alongside further safety assessments, involving a larger group of participants to provide more comprehensive data.
- Phase III Trials: Conducted on an even larger population, Phase III trials aim to confirm the product's effectiveness, monitor side effects, and compare results with standard treatments, ensuring robust evidence for regulatory submissions.
- Post-Market Surveillance: After the product is marketed, ongoing studies are conducted to monitor long-term effects and performance, ensuring continued safety and effectiveness in real-world settings.
Understanding these phases is vital for stakeholders, as it enables them to navigate the complexities of medical device development and the regulatory approval processes effectively while designing safe medical device trials. Recent trends indicate a growing demand for increased information ownership and transparency among sponsors, with many moving towards fully insourced models. This shift is influenced by the ICH E6 R2 guidelines, which emphasize the importance of operational control and quality outcomes for patients.
A case analysis titled 'Increased Data Ownership and Transparency Among Sponsors' highlights this trend, illustrating how sponsors are seeking greater ownership and transparency of their data.
In 2025, the environment of clinical studies for medical instruments in Latin America is transforming, with a significant rise in the quantity of studies conducted. For instance, Avantec Vascular has chosen bioaccess® to support its first-in-human clinical study of an innovative vascular device in Latin America, showcasing the company's expertise in managing complex studies. bioaccess® offers vital services like regulatory dossier submission and principal investigator selection, which are essential for the success of clinical studies.
Innovations aimed at simplifying site experiences are also emerging, focusing on reducing the burden of technology and enhancing information entry processes for clinical research associates. As regulatory requirements become more complex, designing safe medical device trials is essential for maintaining regulatory preparedness and ensuring a smooth commercialization process. As Dipanwita Das, CEO & co-founder of bioaccess®, emphasizes, "Last, but certainly not the least is regulatory preparedness. Regulations are becoming increasingly intricate and prescriptive and more challenging, but keeping track of FDA guidance on innovative study designs and DCT methods, remaining updated with global regulations, ensures a seamless commercialization process, along with privacy." This highlights the significance of remaining updated with international regulations and FDA guidance on novel study designs to ensure successful outcomes. With over 15 years of experience in the Medtech sector, bioaccess® is well-positioned to support stakeholders in navigating these challenges, particularly in addressing the growing demand for data ownership and transparency through its tailored services.
Strategic Planning: From Concept to Execution in Clinical Trials
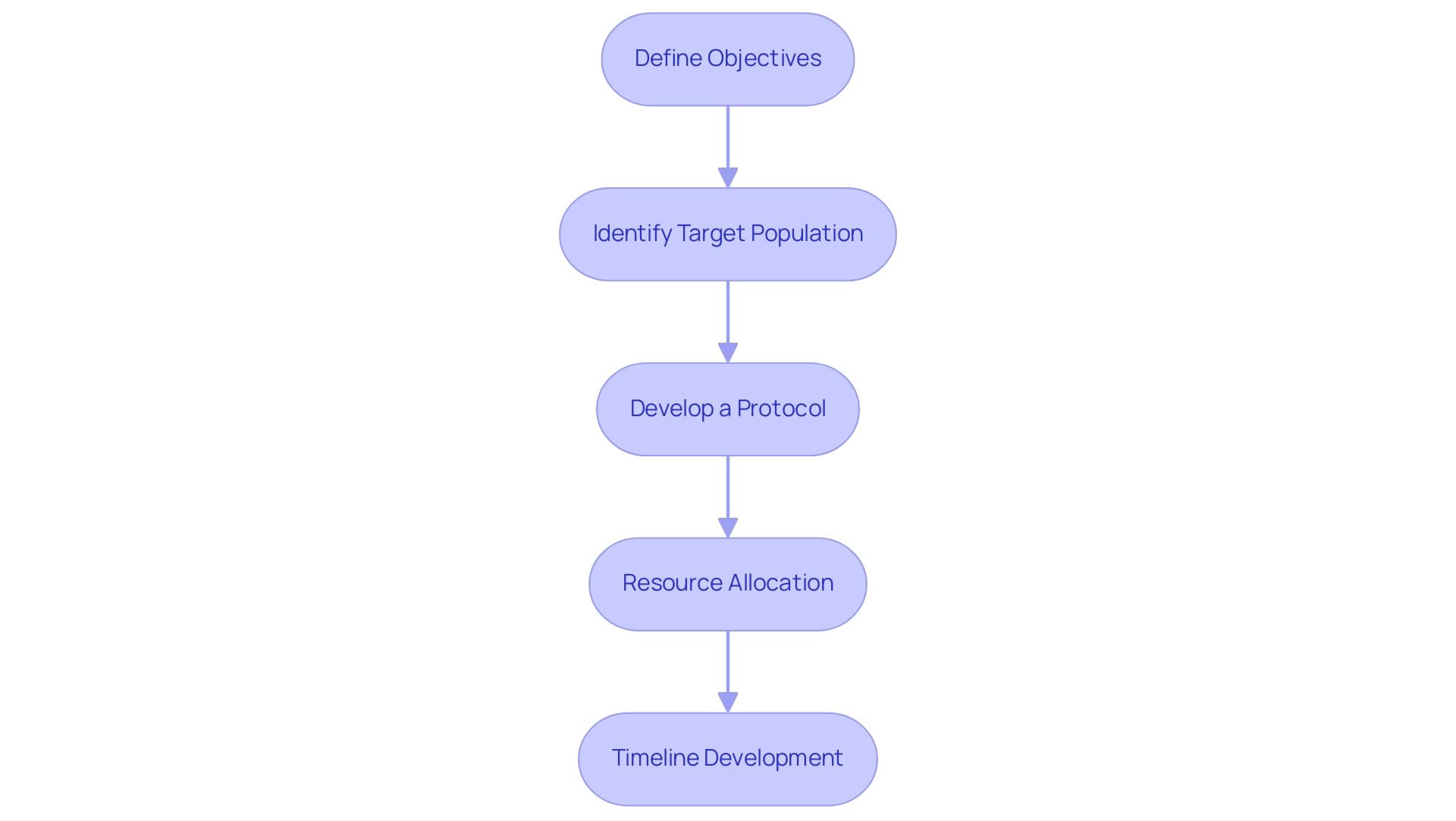
Effective strategic planning in medical device clinical trials encompasses several critical steps that ensure a well-structured approach to research, particularly in the dynamic Latin American Medtech landscape:
- Define Objectives: Establishing clear and measurable objectives is paramount. This includes delineating primary and secondary endpoints that align with regulatory requirements and clinical relevance. Recent statistics indicate that a significant portion of clinical studies struggle with endpoint clarity, underscoring the need for precise definitions to enhance outcomes.
- Identify Target Population: Understanding the characteristics of the target population is essential for gathering relevant data. This involves analyzing demographic factors, health conditions, and other variables that may affect outcomes. In 2025, the focus on diverse populations is increasingly recognized as vital for ensuring the generalizability of findings across different patient groups, especially in the context of Latin America where cultural and health disparities exist.
- Develop a Protocol: A comprehensive protocol serves as the backbone of the trial. It should outline the research design, methodology, and statistical analysis plans. Successful case studies, such as those from Alcon, emphasize the significance of monitoring site experiences and information entry processes to refine protocols and enhance patient care. Notably, 45% of Alcon's data is entered on the same day as the visit date, illustrating the importance of timely data entry in developing a comprehensive protocol.
- Resource Allocation: Effective resource management is crucial. This step involves assessing and allocating necessary resources, including budget, personnel, and technology. Leveraging AI technologies can significantly improve patient recruitment, retention, and endpoint tracking, thereby optimizing resource utilization. As Max Baumann states, "We expect continued focus on optimizing the development journeys of assets to achieve not only an approval-enabling endpoint but to qualify for commercial success." Furthermore, collaborating with a vetted CRO such as bioaccess can improve the management of clinical studies in Latin America, ensuring adherence to local regulations and efficient execution. Bioaccess specializes in managing Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF).
- Timeline Development: Establishing a realistic timeline for each phase of the study is essential. This ensures that all stakeholders are aligned and aware of their responsibilities. Strategic planning steps should include contingency measures to address potential delays, which are common in the crowded clinical end-markets of today.
By meticulously following these steps and leveraging the expertise of bioaccess in designing safe medical device trials, researchers can create a robust framework that guides the process from concept through execution, ultimately increasing the likelihood of achieving both regulatory approval and commercial success. Furthermore, understanding the regulatory environment, including the role of INVIMA in Colombia, is crucial for navigating the complexities of medical product oversight in Latin America. For customized assistance in your clinical research requirements, consider collaborating with bioaccess to ensure a successful and compliant project.
Key Design Considerations for Medical Device Trials
Creating a clinical examination for a medical instrument necessitates meticulous attention to various essential components to guarantee the research's integrity and the credibility of its outcomes. Partnering with a leading Contract Research Organization (CRO) like bioaccess® can significantly enhance this process, particularly in the Latin American context.
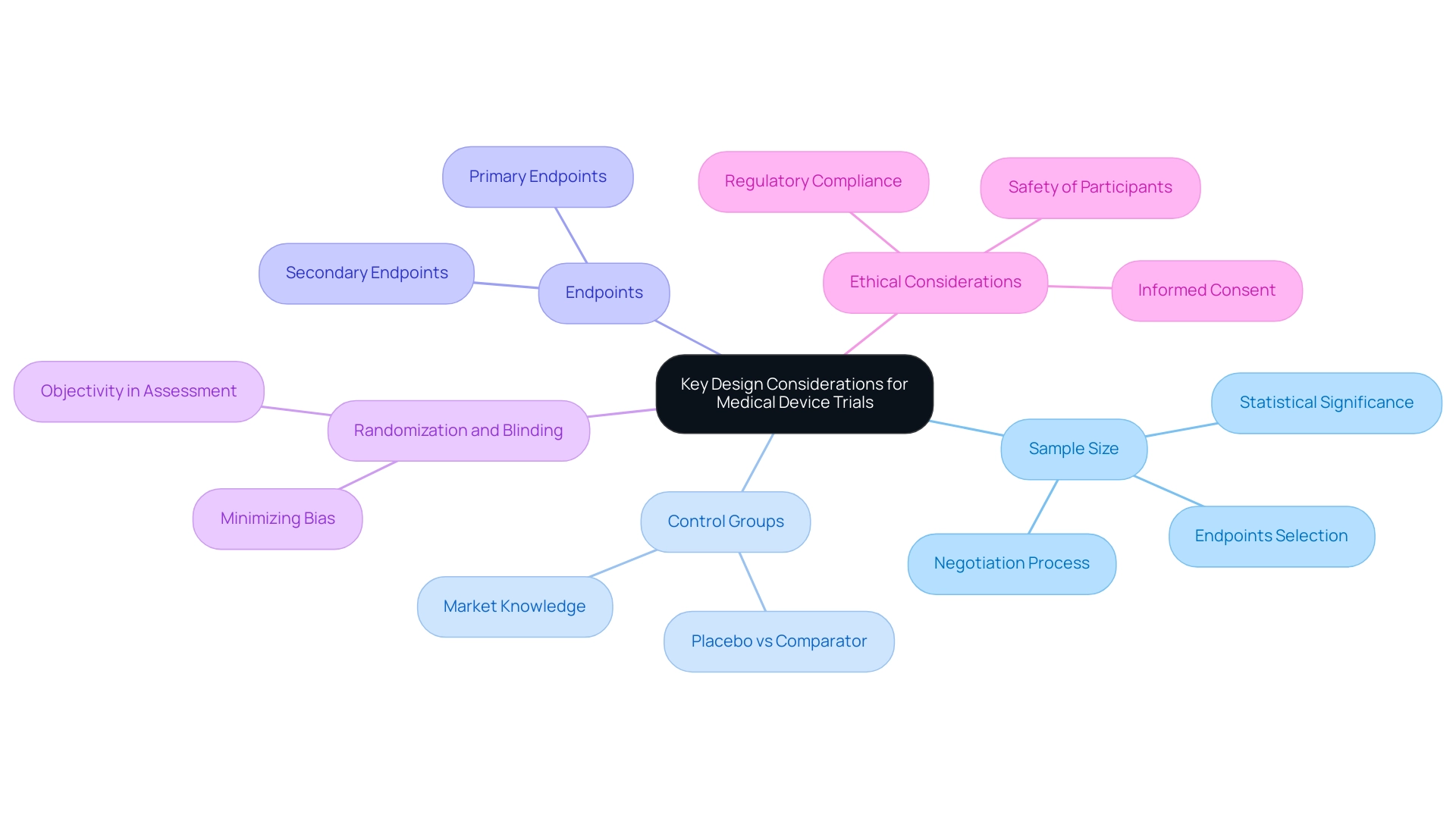
- Sample Size: Accurately calculating the number of participants is essential for achieving statistically significant outcomes. Contrary to common belief, clinical trials for significant risk devices often do not necessitate large participant pools, which can be particularly encouraging for small startups. This flexibility permits more manageable research while still yielding reliable data. Manufacturers should consider six key questions when calculating sample sizes, including the selection of suitable endpoints for the research objective. bioaccess® provides extensive clinical study management services, including feasibility assessments that assist in determining optimal sample sizes customized to particular study requirements.
- Control Groups: The selection of the control group is crucial in evaluating the new instrument's effectiveness. Researchers must determine whether to use a placebo or a comparator instrument, as this choice directly affects the experiment's capacity to showcase the instrument's advantages over current options. bioaccess® provides expertise in selecting appropriate control groups based on extensive market knowledge and regulatory requirements in Latin America.
- Endpoints: Clearly defined primary and secondary endpoints are crucial for aligning the study with its objectives. These endpoints should be measurable and relevant to the device's intended use, ensuring that the study can effectively evaluate its performance. bioaccess® assists in establishing these endpoints, ensuring they meet both clinical and regulatory standards.
- Randomization and Blinding: Implementing randomization helps minimize bias, while blinding ensures objectivity in outcome assessment. These methodologies are fundamental in maintaining the study's credibility and in producing trustworthy results. bioaccess® employs rigorous methodologies to uphold the integrity of the research process.
- Ethical Considerations: Adhering to ethical standards is paramount. This involves acquiring informed consent from participants and prioritizing their safety throughout the research process. Ethical compliance not only safeguards participants but also improves acceptance by regulatory bodies. bioaccess® is well-versed in navigating the ethical landscape of clinical trials in Latin America, ensuring compliance with local regulations, including those set forth by INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute.
In addition to these design elements, it is important to recognize that sample size determination often involves negotiation between manufacturers and statisticians. This collaborative method permits the assessment of various scenarios, aiding in balancing feasibility with the reliability of data. For instance, the case analysis titled "Negotiation of Sample Size within Acceptance Limits" illustrates how this negotiation process can lead to a well-defined and justified sample size based on quantifiable criteria.
By addressing these considerations, researchers can engage in designing safe medical device trials that meet regulatory requirements and contribute valuable insights into the efficacy of medical devices. As Jan Bogaerts observed, the future of clinical study design is evolving, and adopting these best practices, particularly with the support of bioaccess®, which specializes in Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), and other pivotal studies, will be essential for success. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® is your reliable partner in navigating the clinical study process.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements in Medical Device Trials
Navigating regulatory requirements is a critical aspect of designing safe medical device trials. Understanding these requirements is essential for researchers aiming to ensure compliance and facilitate the approval process.
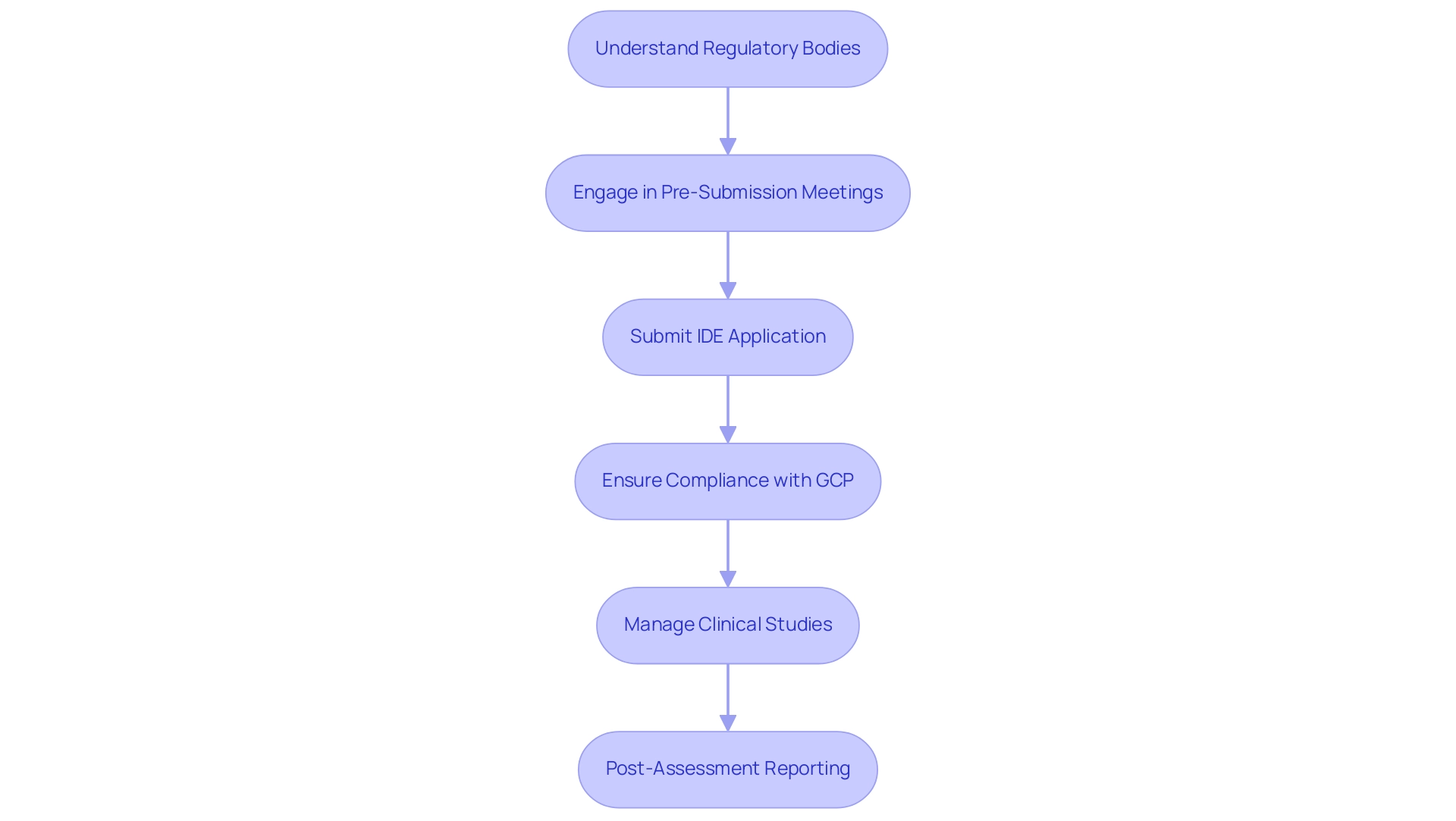
- Understanding Regulatory Bodies: Familiarizing yourself with the relevant authorities, such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe, is crucial. Each agency has distinct guidelines and expectations that must be understood to navigate the approval landscape effectively.
- Pre-Submission Meetings: Engaging with regulatory agencies early in the process is vital. These pre-submission meetings allow researchers to discuss project design, clarify expectations, and obtain valuable feedback that can influence the research's direction and improve its chances of approval.
- Submission of Investigational Device Exemption (IDE): Preparing and submitting an IDE application is a pivotal step in gaining approval for conducting trials. This application must demonstrate that the device is safe for use in human subjects and that the proposed study design is scientifically sound.
- Compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP): Adhering to GCP guidelines is imperative to protect participants and ensure the integrity of the data collected. This adherence not only safeguards patient welfare but also enhances the credibility of the study results.
- Comprehensive Clinical Study Management Services: At bioaccess, we provide a complete range of services to support your clinical studies. This includes feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, study setup, import permits, project management, and reporting. Our expertise ensures that all elements of your assessment are meticulously handled, increasing the chances of successful product approval.
- Post-Assessment Reporting: After the assessment, researchers must be prepared to submit results and report any adverse events to regulatory bodies as required. This transparency is essential for ongoing safety monitoring and regulatory compliance.
By understanding and adhering to these regulatory requirements, researchers can streamline trial processes and improve their approach to designing safe medical device trials, significantly enhancing the likelihood of successful product approval. As we approach 2025, the FDA and EMA continue to emphasize rigorous testing and information quality, particularly in light of the EU MDR's focus on connected device security throughout the product lifecycle. Successful navigation of these requirements is supported by insights from Regulatory Affairs specialists, who highlight the importance of thorough preparation and proactive communication with regulatory bodies.
As noted by the Head of Clinical Data Engineering, "Traditionally, information management was outsourced to our CRO vendor partners." This initiative aims to bring all our research in-house, allowing internal teams to work more practically. By implementing research internally, we can manage our information effectively and provide high-quality care for our patients.
Furthermore, challenges in adverse event reporting, including quality, interoperability, and timeliness, remain significant obstacles for researchers. Case studies illustrate that effective adverse event reporting systems are essential for pharmacovigilance, facilitating international collaboration and prompt regulatory actions despite ongoing challenges in information quality and interoperability.
Data Management and Statistical Planning for Valid Results
Efficient information management and statistical preparation are crucial in designing safe medical device trials. Key aspects include:
- Information Gathering Techniques: Choosing suitable information gathering techniques is vital to align with trial objectives. Utilizing electronic information capture (EDC) systems can streamline this process, although challenges in scaling metadata management have been noted, particularly for organizations still relying on spreadsheets. The growing complexity of regulations, including privacy requirements, necessitates a robust approach to information management. At bioaccess®, we leverage our over 20 years of experience in Medtech to implement efficient information gathering strategies tailored to the unique requirements of each study.
- Information Integrity: Ensuring accuracy and reliability is essential throughout the trial. Implementing robust information management systems helps maintain integrity, allowing for real-time monitoring and proactive issue management. For instance, some sponsors have successfully leveraged historical trend information to identify anomalies and enhance quality, leading to faster approvals and more efficient resource use. A centralized group at bioaccess® can oversee information and spot irregularities, ensuring effective risk management throughout the study.
- Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP): A well-organized SAP is essential for detailing the statistical methods that will be utilized to evaluate study results. This plan should detail the statistical techniques, sample size calculations, and the rationale behind chosen methodologies, ensuring clarity and transparency in the analysis process. Christina Yap, with over 20 years of experience in the statistical design and analysis of clinical studies, emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive SAP in achieving reliable results, a principle we uphold at bioaccess®.
- Interim Analysis: Planning for interim evaluations allows researchers to assess data at various stages of the study. This flexibility enables prompt modifications based on initial findings, which can significantly influence the overall results and regulatory strategy. Our expertise in overseeing Early-Feasibility and First-In-Human investigations ensures that interim analyses are effectively incorporated into the design.
- Final Reporting: Comprehensive reporting is essential for summarizing findings, methodologies, and statistical analyses for regulatory submission. Clear and detailed reports not only enhance the credibility of test results but also facilitate smoother interactions with regulatory bodies. As noted by the Head of Clinical Data Engineering, the transition to in-house information management empowers teams to take charge of their information, operationalizing research with higher quality results. At bioaccess®, we prioritize thorough final reporting to support successful regulatory submissions.
By concentrating on these critical elements, researchers can significantly bolster the credibility of their study results, ultimately supporting successful regulatory submissions and advancing the development of innovative medical devices through designing safe medical device trials. The proactive management of data, as illustrated in the case study "Proactive Issue Management Using Historical Trend Data," showcases how defining thresholds and sharing data across departments can enhance data quality and lead to greater resource efficiency.

Overcoming Challenges in Clinical Trial Execution
Common challenges in clinical trial execution encompass several key areas that require strategic attention:
- Recruitment Issues: Effective participant recruitment is paramount. Developing targeted strategies that leverage social media and online communities can significantly enhance enrollment rates. Research indicates that while only 5% of participants learn about studies through traditional advertising, younger demographics are increasingly discovering opportunities via social platforms. A nuanced approach to communication that considers patient preferences based on demographics is essential for successful recruitment. Furthermore, utilizing technology to reduce site visits may enhance enrollment for hard-to-reach patient populations, addressing some of the inherent challenges in recruitment. The partnership between bioaccess™ and Caribbean Health Group seeks to establish Barranquilla as a premier location for clinical studies in Latin America, further improving recruitment efforts.
- Budget Constraints: With budget overruns being a prevalent concern, it is crucial to monitor expenses meticulously. Utilizing advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, can lead to cost reductions of up to 20%. Bree Burks, Vice President of Site Strategy at Veeva, emphasizes that "Sponsors will step up to solve site capacity issues," highlighting the importance of financial planning and resource allocation. Exploring diverse funding opportunities can also provide the necessary financial support to keep experiments on track. John Myklusch's expertise in financial strategy can play a pivotal role in ensuring effective budget management throughout the evaluation process.
- Regulatory Delays: The complexity of regulatory requirements necessitates proactive engagement with regulatory bodies. Regulatory readiness is crucial because of the growing intricacy and expectations of regulations, including overseeing FDA guidance and privacy requirements. Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, emphasizes the significance of keeping open channels of communication to accelerate approvals and address any issues promptly, ensuring that studies progress without unnecessary delays.
- Information Management Issues: Strong information management systems are essential to avoid loss and guarantee precision throughout the study. Implementing comprehensive information governance frameworks can enhance integrity and facilitate smoother operations.
- Participant Retention: Engaging participants throughout the study is critical to minimizing dropouts and ensuring data completeness. Consistent communication and support can nurture a feeling of engagement and dedication among participants, ultimately aiding in the initiative's success. Notably, GlobalCare Clinical Trials' partnership with bioaccess™ has achieved over a 50% reduction in recruitment time and 95% retention rates, showcasing effective strategies in participant engagement.
By proactively addressing these challenges, researchers can significantly enhance the likelihood of success and uphold the integrity of their research. bioaccess™ provides extensive clinical study management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, to support these efforts.
Future Trends in Medical Device Clinical Trial Design
Emerging trends in medical device clinical trial design are reshaping the landscape of clinical research, with several key developments gaining traction in 2025:
-
Decentralized Studies: The transition towards decentralized studies is characterized by a growing dependence on remote monitoring and telehealth solutions. This approach not only enhances participant engagement but also facilitates more efficient information collection. Statistics indicate that decentralized studies can reduce patient dropout rates by up to 30%, significantly improving the overall quality of data collected.
-
Adaptive Designs: The implementation of adaptive study designs is becoming more prevalent, allowing researchers to make real-time modifications based on interim results. This flexibility can result in more effective evaluations, with studies employing adaptive designs indicating a 20% quicker time to completion compared to traditional methods. Such designs are particularly beneficial in the medical device sector, especially in the context of designing safe medical device trials, where rapid iteration is often necessary.
-
Artificial Intelligence: The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) in clinical studies is transforming data analysis and patient recruitment processes. AI tools can analyze extensive datasets to identify appropriate candidates for studies, thereby streamlining recruitment efforts. Recent advancements suggest that AI can enhance recruitment efficiency by up to 50%, allowing for quicker patient enrollment and faster study progression.
-
Patient-Centric Approaches: A growing emphasis on patient-centric strategies is transforming how studies are designed and executed. By prioritizing participant experience and outcomes, researchers can improve retention rates and overall satisfaction. This trend is backed by discoveries that suggest patient-focused studies can result in a 25% rise in participant retention, ultimately enhancing more reliable information.
-
Regulatory Innovations: As regulatory landscapes evolve, staying ahead of anticipated changes is crucial for study design and execution. The growing complexity of regulations, including those concerning privacy and cybersecurity, necessitates a proactive approach to compliance. For instance, the introduction of the NIS2 Directive and the Cyber Resilience Act in the EU underscores the importance of resilience and oversight in clinical research, influencing how studies are structured and monitored. Furthermore, regulatory readiness is growing more significant because of the complexity and requirements of regulations, including monitoring FDA guidance and ensuring privacy.
-
Information Management Advancements: Companies like GSK are adopting rule-based automation for information cleansing to accelerate the time to database lock, illustrating advancements in information management that enhance study efficiency. The Head of Clinical Data Engineering noted, "Traditionally, data management was outsourced to our CRO vendor partners. Part of the initiative is to bring all our research in-house so that our internal teams can start working on it. They can be more practical, and we implement research internally and we are able to manage our information, and we provide for our patients with high quality."
By adopting these trends, researchers can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their clinical studies, resulting in quicker approvals and better patient outcomes. The future of medical equipment clinical studies is not only about innovation in technology but also about creating a more responsive and patient-centered research environment. At bioaccess®, our expertise and customized approach aim to help advance medical devices sooner for companies in the Medtech industry, particularly through our comprehensive clinical trial management services in Latin America, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF).
Furthermore, these clinical studies contribute to local economies by creating jobs, fostering economic growth, and improving healthcare outcomes.
Conclusion
The multifaceted landscape of clinical trials for medical devices is essential for ensuring the safety and efficacy of innovative technologies. By understanding the structured phases of these trials—from preclinical testing to post-market surveillance—stakeholders can navigate the complexities of medical device development and regulatory approval. Embracing recent trends, such as increased data ownership and transparency, decentralized trial designs, and adaptive methodologies, enhances trial engagement and efficiency.
Strategic planning and meticulous design considerations are crucial for successful trials. Clear objectives, well-defined target populations, robust protocols, and effective resource allocation significantly impact trial outcomes. Additionally, navigating regulatory requirements and employing effective data management practices are vital to achieving successful approvals and maintaining data integrity.
As the field evolves, embracing future trends such as decentralized trials, AI integration, and patient-centric approaches will further enhance trial efficiency and effectiveness. These innovations streamline processes and improve patient experiences and outcomes. The commitment to regulatory preparedness and proactive communication with authorities remains pivotal in overcoming challenges and ensuring compliance.
In conclusion, the journey of medical device clinical trials is intricate yet rewarding, ultimately leading to advancements in healthcare and improved patient outcomes. By leveraging expertise and adhering to best practices, stakeholders can successfully navigate this landscape, paving the way for innovative medical solutions that benefit society as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main phases of medical device trials?
The main phases of medical device trials include: 1. Preclinical Phase: Laboratory and animal testing for safety information. 2. Phase I Studies: Small participant group focused on safety and identifying adverse effects. 3. Phase II Trials: Larger group evaluating effectiveness and further safety assessments. 4. Phase III Trials: Conducted on a larger population to confirm effectiveness and monitor side effects. 5. Post-Market Surveillance: Ongoing studies after marketing to monitor long-term effects and performance.
Why is understanding these phases important for stakeholders?
Understanding these phases helps stakeholders navigate the complexities of medical device development and regulatory approval processes effectively.
What recent trends are influencing medical device trials?
There is a growing demand for increased data ownership and transparency among sponsors, influenced by ICH E6 R2 guidelines emphasizing operational control and quality outcomes.
What is the significance of the case analysis titled 'Increased Data Ownership and Transparency Among Sponsors'?
This case analysis highlights how sponsors are seeking greater ownership and transparency of their data in the context of clinical trials.
How is the environment for clinical studies in Latin America changing in 2025?
There is a significant rise in the number of studies conducted, with companies like Avantec Vascular utilizing services like bioaccess® for managing complex studies.
What services does bioaccess® provide for clinical studies?
Bioaccess® offers services such as regulatory dossier submission and principal investigator selection, which are essential for the success of clinical studies.
What are the critical steps in effective strategic planning for medical device clinical trials?
The critical steps include: 1. Defining clear objectives. 2. Identifying the target population. 3. Developing a comprehensive protocol. 4. Allocating necessary resources. 5. Developing a realistic timeline.
Why is defining objectives important in clinical trials?
Clear and measurable objectives help enhance outcomes and ensure alignment with regulatory requirements.
How does understanding the target population benefit clinical studies?
Analyzing the characteristics of the target population ensures relevant data collection and enhances the generalizability of findings across diverse patient groups.
What role does bioaccess play in managing clinical studies in Latin America?
Bioaccess specializes in managing various types of studies, ensuring adherence to local regulations and efficient execution, particularly in Early-Feasibility Studies and First-In-Human Studies.
Why is timeline development essential in clinical trials?
Establishing a realistic timeline ensures all stakeholders are aligned and aware of their responsibilities, with contingency measures in place for potential delays.

