Overview
Effective user testing of medical devices involves a structured process that includes defining objectives, developing test protocols, and analyzing results to enhance usability and compliance with regulatory standards. The article outlines specific steps and principles, such as user-centered design and human factors engineering, which are crucial for identifying usability issues and improving overall user experience, thereby ensuring that devices are safe and effective for end-users.
Introduction
In the realm of medical device development, usability testing stands as a cornerstone for ensuring that products are not only safe and effective but also user-friendly. This systematic evaluation process delves into the intricacies of user interaction, aiming to uncover potential errors and align device design with the actual needs of users.
By embracing principles such as user-centered design and human factors engineering, developers can create devices that resonate with end-users, ultimately enhancing satisfaction and safety. As the industry faces increasing regulatory scrutiny, understanding the nuances of usability testing becomes paramount.
This article explores the fundamental aspects of usability testing in medical devices, offering a comprehensive guide to best practices, participant recruitment, and effective result analysis, all aimed at fostering innovation while prioritizing user experience.
Understanding Usability Testing in Medical Devices
Usability assessment in medical equipment functions as a structured evaluation procedure focused on analyzing interaction with products. This essential practice centers on recognizing possible mistakes, comprehending needs, and guaranteeing that the design fosters both safety and effectiveness. Several key principles underpin effective usability testing:
- User-Centered Design: This principle prioritizes the needs and capabilities of end-users, ensuring that usability is enhanced through thoughtful design. By concentrating on practical experiences of individuals, developers can create products that connect with the intended audience.
- Human Factors Engineering: This aspect involves integrating insights about human behavior, capabilities, and limitations throughout the design process. Incorporating these factors results in more intuitive tools that align with natural interactions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to established standards such as ISO 62366 is crucial. This standard outlines the requirements for user testing of medical devices, ensuring that safety and effectiveness are consistently evaluated in compliance with regulatory expectations.
Comprehending these principles is crucial not only for fulfilling regulatory requirements but also for improving satisfaction and safety. A recent assessment emphasized the difficulties encountered by individuals in identifying the purpose of essential buttons in alarm systems, especially with the 'Audio Alarm Pause' button, suggesting a need for improved design for ease of use. This corresponds with the significance of managing project modifications seamlessly; as mentioned, effective stress management techniques such as prioritizing and communicating can assist teams in concentrating on enhancing user experience.
Additionally, the study titled "Evaluation of Visual Cues in Patient Monitoring Systems" proposed evaluating the effectiveness of visual signals, such as color changes and flashing notifications, in directing clinicians' attention to critical patient-related information. By integrating effective visual cues and adhering to user-centered design strategies, developers can significantly improve clinical effectiveness and patient safety in real-world settings.
Step-by-Step Procedures for Effective User Testing
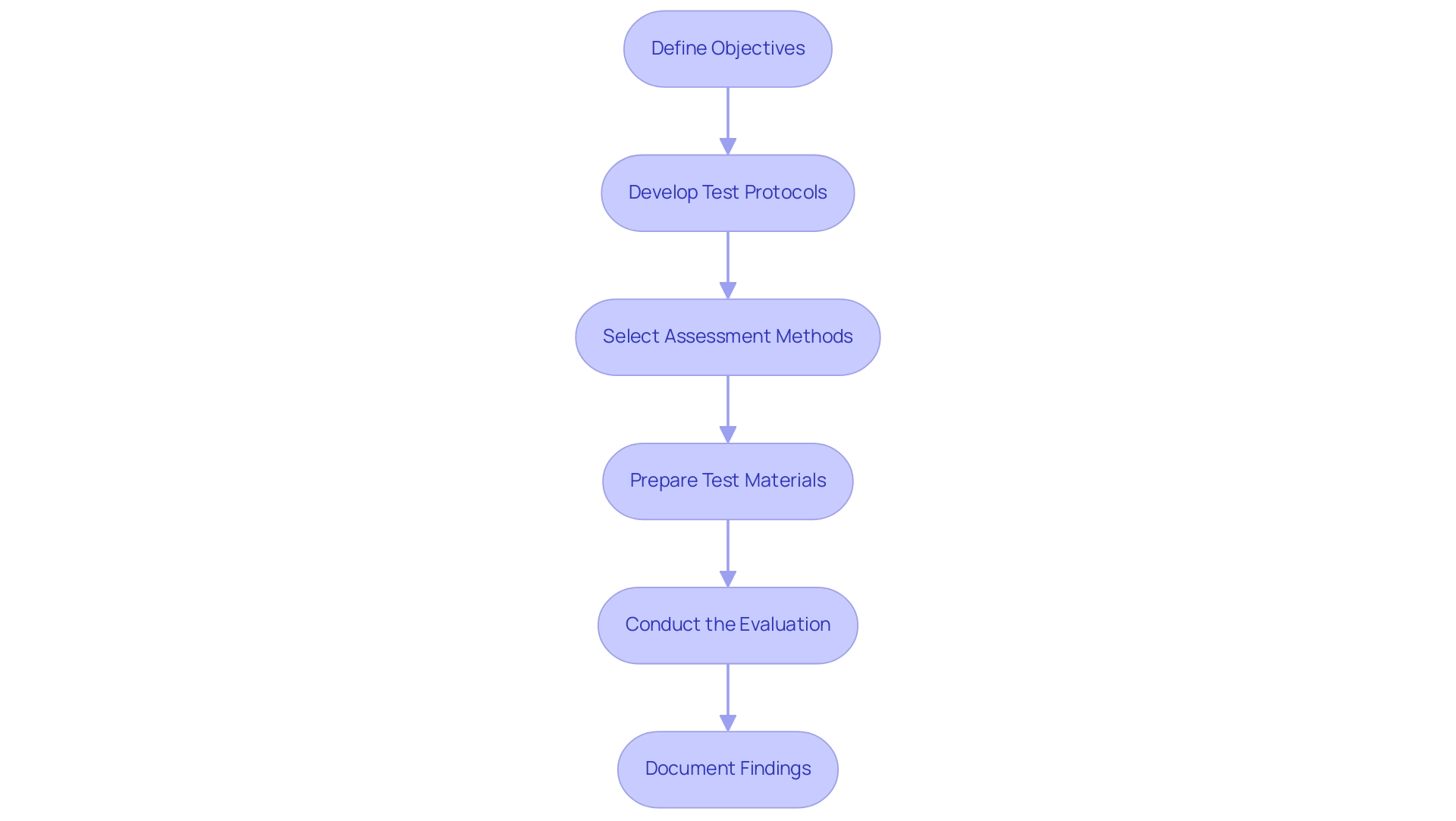
To conduct effective user testing of medical devices, adhere to the following structured steps:
- Define Objectives: Clearly articulate the goals of the usability evaluation. This may involve identifying specific individual errors, measuring task completion times, and enhancing overall satisfaction. Setting clear objectives is essential for aligning results with both client needs and regulatory compliance.
- Develop Test Protocols: Create a comprehensive plan that details the assessment methodologies, specifies tasks for users to complete, and outlines success criteria. Protocols should be adaptable to accommodate various evaluation scenarios, ensuring thorough assessment of device usability.
- Select Assessment Methods: Decide on the most suitable assessment methods, whether moderated or unmoderated, and whether sessions will be conducted remotely or in-person. The choice should reflect the objectives and available resources, allowing for optimal data collection.
- Prepare Test Materials: Gather and organize all necessary materials, including prototypes, questionnaires, and consent forms. Ensuring accessibility and clarity of these materials promotes a smooth evaluation experience for participants.
- Conduct the Evaluation: Facilitate the assessment sessions by observing participant interactions meticulously. Collect both qualitative and quantitative data during these sessions to capture a comprehensive view of the experience. As emphasized by MakroCare, "By adhering to best practices and collaborating with skilled evaluation services professionals, manufacturers can mitigate risks, improve user satisfaction, and attain regulatory compliance."
- Document Findings: Systematically record observations and participant feedback throughout the evaluation process. This documentation is essential for subsequent analysis and helps in identifying areas for improvement.
To demonstrate the significance of addressing issues during user evaluations, consider a case study where a team resisted necessary upgrades. By listening to their concerns and demonstrating the value of the upgrades, the transition was eased, highlighting the significance of user-centered approaches in evaluation.
By adhering to these procedures, you will enable a comprehensive and efficient evaluation process for user testing of medical devices, ultimately improving satisfaction, minimizing risks, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Thorough evaluation demonstrates enhanced experience for individuals through human-centered design, emphasizing the significance of the specified steps.
Creating Realistic Testing Environments
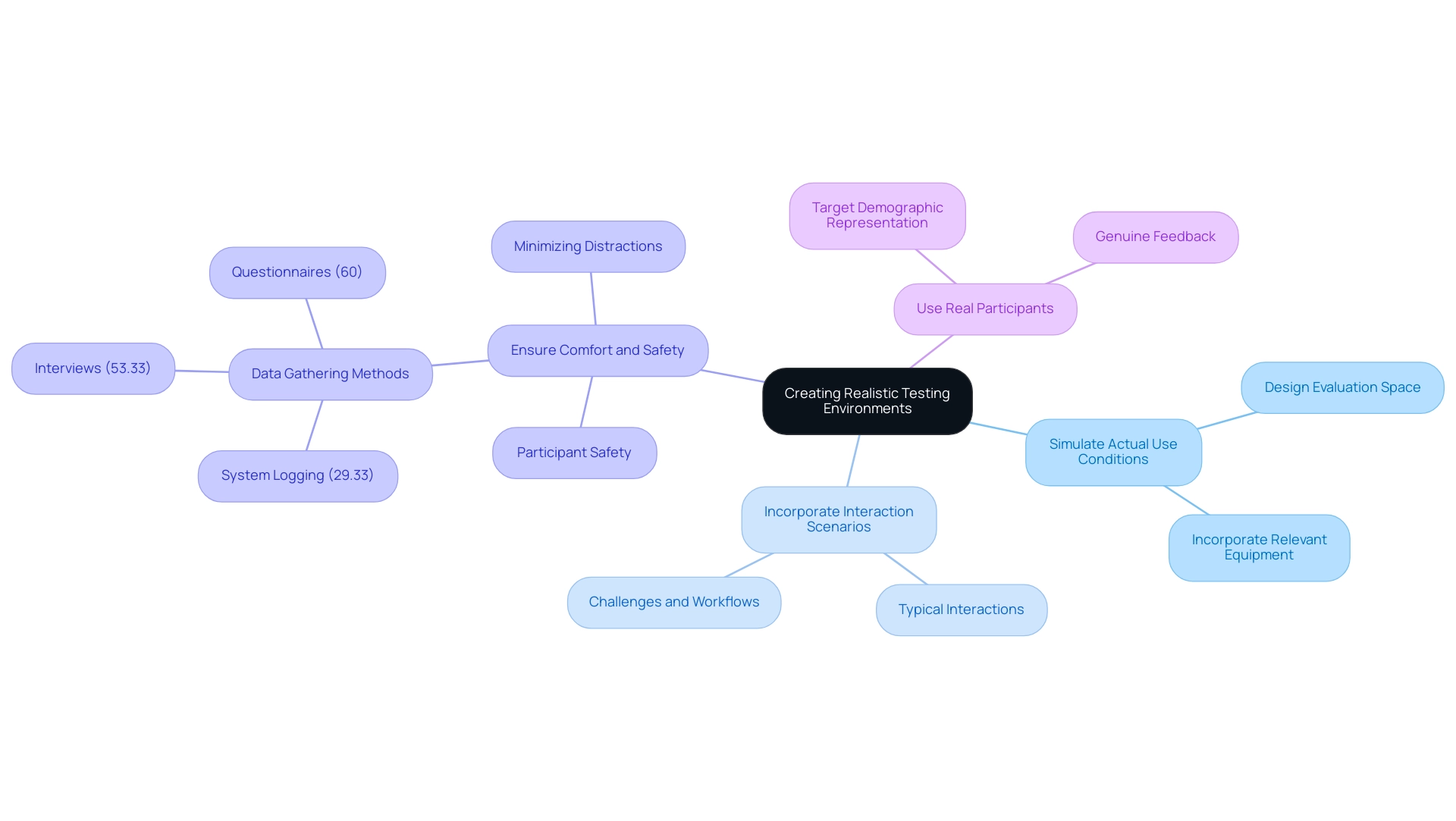
Creating a practical evaluation setting is essential for user testing of medical devices to achieve credible usability results. This entails reproducing the genuine circumstances under which the device will be employed, which can be accomplished through several essential strategies:
- Simulate Actual Use Conditions: Design the evaluation space to closely resemble a clinical or home environment, incorporating relevant equipment and materials that individuals will encounter in real scenarios.
- Incorporate Interaction Scenarios: Create situations that accurately represent typical interactions, challenges, and workflows associated with the medical device. This guarantees that the assessment is based on practical application through user testing of medical devices.
- Ensure Comfort and Safety: The assessment environment must prioritize participant safety and comfort, allowing them to concentrate on the tasks without unnecessary distractions. Statistics indicate that 60% of data gathering methods utilized were questionnaires, 53.33% were interviews, and 29.33% were system logging, emphasizing the importance of comfort in obtaining valid feedback.
- Use Real Participants: Whenever feasible, involve actual participants who represent the target demographic. Involving genuine individuals generates feedback that is both pertinent and practical, greatly improving the testing process.
By promoting a realistic setting, the credibility of user testing of medical devices results is significantly improved. Additionally, research indicates that numerous proposed experience evaluation frameworks remain conceptual and lack concrete assessment methods and metrics. This underscores the necessity of grounding user testing of medical devices in reality.
As noted by Bargas-Avila & Hornbæk, emotions, enjoyment, and aesthetics are crucial dimensions of experience that must be assessed within the proper context. Moreover, with recent insights revealing that only 1% of individuals engage with content sliders, the need for realistic scenarios becomes even more apparent. Applying these strategies not only enhances the evaluation process but also results in more precise and impartial user insights, especially when moderators uphold neutrality and refrain from leading questions during assessments.
Recruiting the Right Participants for Usability Tests
Enlisting suitable participants is crucial for obtaining valuable insights during the evaluation of medical instruments, particularly for startups facing intricate regulatory challenges and fierce competition. A study examining publicly available documents for all 22 medical instruments designated as 'highest risk' or 'novel' from 2014 to 2017 emphasizes the importance of effective recruitment in user testing of medical devices. To ensure successful recruitment in the face of these challenges, consider the following strategies:
- Define Target Demographics: Clearly identify the characteristics of the final consumers for the apparatus, which should include factors such as age, specific medical conditions, and levels of technical proficiency. Comprehending these demographics is essential, as it enables a customized strategy for recruitment that aligns with the needs of the target audience.
- Utilize Multiple Recruitment Channels: Employ a variety of methods to reach potential participants. This can include using social media platforms, collaborating with local clinics, and engaging patient advocacy groups. By diversifying recruitment avenues, you enhance the likelihood of reaching a broader audience that reflects the device’s intended demographic.
- Screen Participants: Implement a thorough screening process to ensure that candidates not only meet the defined criteria but also accurately represent the target demographic. This step is essential for acquiring pertinent feedback through user testing of medical devices, which can guide design enhancements and adjustments, especially important for startups with restricted resources.
- Incentivize Participation: Offering incentives, such as gift cards or free trials, can significantly boost participation rates. This approach not only encourages individuals to participate but also helps to ensure a diverse group of participants, which is critical for robust user testing of medical devices.
- Engage Clinical Research Sites: Address the challenge of disinterested clinical research sites by building relationships with these institutions. Offering clear benefits for participation and demonstrating the potential impact of the medical device can help in securing their involvement in trials.
- Maintain Ethical Standards: Adhere to ethical guidelines throughout the recruitment process. This includes obtaining informed consent from participants and safeguarding their confidentiality. Ethical considerations are paramount in maintaining trust and integrity in clinical research, especially when seeking collaboration from disinterested clinical research sites.
As James Lewis noted, "Lastly, we thank Simone Borsci, James Lewis, and Martin Schmettow for their valuable comments on an early version of this manuscript, which helped us to significantly improve the content." By strategically selecting participants in accordance with these guidelines, the chances of gathering relevant and actionable feedback are significantly increased, ultimately leading to better-informed design choices and enhanced user experiences. Furthermore, considering the constraints posed by limited financial resources, startups should prioritize cost-effective recruitment methods while ensuring a representative sample.
Furthermore, citing the case study on Bayesian Estimation in User Experience Evaluation can be integrated more effectively by demonstrating how utilizing prior knowledge can enhance recruitment strategies, thereby improving the overall effectiveness of user experience assessment.
Analyzing Results and Reporting Findings
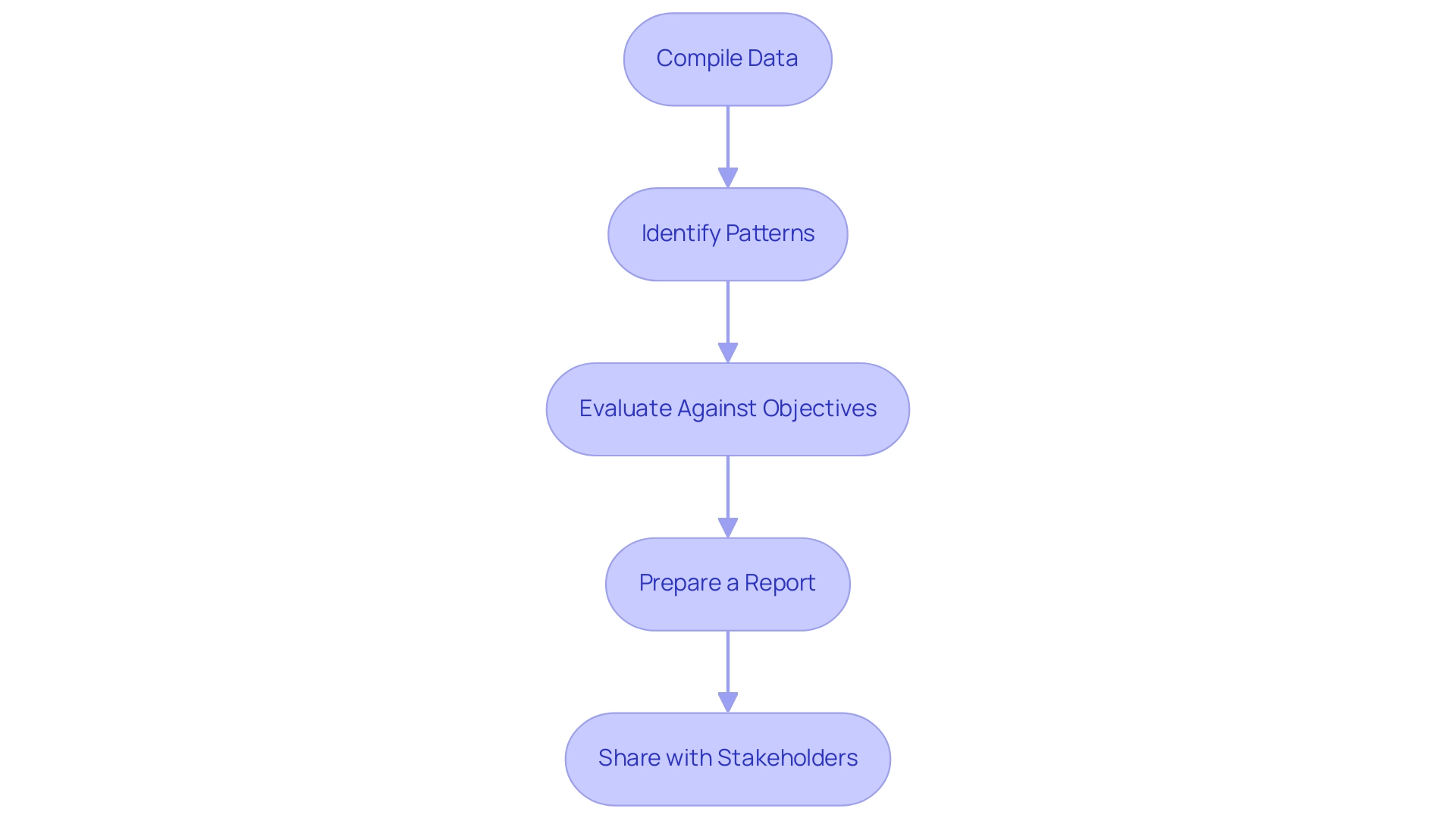
Upon completing user testing of medical devices, a thorough analysis of the results is crucial for effective reporting.
- Compile Data: Begin by gathering all qualitative and quantitative data collected during the evaluation sessions. This data serves as the foundation for your analysis.
- Identify Patterns: Examine the data for recurring themes, issues, and behaviors that surfaced during testing. Contextual inquiry techniques, which combine observation with participant interviews, can enhance your understanding of these patterns in their natural environment. This approach is vital, as it allows you to capture tasks as they occur naturally, providing deeper insights.
- Evaluate Against Objectives: Assess the findings against the initial evaluation objectives to pinpoint areas of success and identify opportunities for improvement. This evaluation is essential for ensuring that the user testing of medical devices aligns with user needs and design goals.
- Prepare a Report: Develop a comprehensive report that details your findings, recommendations, and implications for design changes. Utilize visual aids, such as charts and graphs, to improve clarity and facilitate understanding among stakeholders.
- Share with Stakeholders: Present your findings to relevant stakeholders, including design teams, regulatory bodies, and project sponsors. This joint method promotes clarity and guarantees that all stakeholders are aware and involved in the decision-making process.
By methodically examining outcomes and efficiently presenting results from user testing of medical devices, you not only boost the practicality of these instruments but also aid in their overall enhancement, tackling frequent functionality challenges recognized in the field. Significantly, recent findings suggest that moderated studies frequently encounter a standard no-show rate of approximately 8%, which highlights the necessity of comprehensive participant engagement strategies in evaluation. This is especially pertinent given that merely 1% of individuals interact with content sliders, emphasizing a wider concern of engagement that may reflect difficulties in functionality assessment for medical devices.
As usability testing continues to evolve, incorporating current methodologies for analyzing results will be critical for addressing emerging challenges and improving user experience.
Conclusion
Usability testing in medical device development is an essential practice that directly influences user safety, satisfaction, and overall efficacy. By focusing on user-centered design and human factors engineering, developers can create devices that not only meet regulatory standards but also resonate with end-users. The article outlined crucial principles, including:
- The importance of realistic testing environments
- Effective participant recruitment
- Systematic result analysis
All of which contribute to a more intuitive user experience.
Following structured procedures for user testing ensures that objectives are met and that the insights gathered lead to meaningful improvements in device design. Engaging real users in realistic scenarios enhances the validity of the testing outcomes, while diligent analysis and reporting of findings foster collaboration among stakeholders, paving the way for informed decision-making.
In an era of increasing regulatory scrutiny, prioritizing usability testing is not merely a compliance measure; it is a commitment to innovation that places user experience at the forefront. As the medical device industry continues to evolve, embracing these best practices will be vital for developing products that not only fulfill their intended purpose but also enhance the quality of care provided to patients. Ultimately, the integration of effective usability testing into the development process will lead to safer, more effective medical devices that truly meet the needs of users.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is usability assessment in medical equipment?
Usability assessment in medical equipment is a structured evaluation procedure focused on analyzing interaction with products to recognize potential mistakes, understand user needs, and ensure that the design promotes safety and effectiveness.
What are the key principles of effective usability testing?
The key principles include User-Centered Design, which prioritizes end-user needs; Human Factors Engineering, which integrates insights about human behavior into the design process; and Regulatory Compliance, which involves adhering to standards like ISO 62366 for user testing of medical devices.
Why is understanding usability principles important?
Understanding these principles is crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and improving user satisfaction and safety in medical device usage.
What challenges have been identified in usability assessments of medical devices?
A recent assessment highlighted difficulties individuals face in identifying the purpose of essential buttons in alarm systems, particularly the 'Audio Alarm Pause' button, indicating a need for improved design for ease of use.
How can visual cues enhance usability in medical devices?
Effective visual cues, such as color changes and flashing notifications, can direct clinicians' attention to critical patient-related information, thereby improving clinical effectiveness and patient safety.
What are the structured steps to conduct effective user testing of medical devices?
The steps include: 1. Define Objectives: Articulate the goals of the evaluation. 2. Develop Test Protocols: Create a detailed plan for assessment methodologies and tasks. 3. Select Assessment Methods: Choose the most suitable methods for data collection. 4. Prepare Test Materials: Organize necessary materials for the evaluation. 5. Conduct the Evaluation: Facilitate assessment sessions and collect data. 6. Document Findings: Systematically record observations and participant feedback.
How can manufacturers improve user satisfaction and regulatory compliance during evaluations?
By adhering to best practices in user testing and collaborating with skilled evaluation service professionals, manufacturers can mitigate risks, enhance user satisfaction, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
What is the significance of addressing issues during user evaluations?
Addressing user concerns and demonstrating the value of necessary upgrades can ease transitions and highlight the importance of user-centered approaches in the evaluation process.




