Overview
The article presents a comprehensive step-by-step guide for executing successful pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil. It underscores the critical nature of regulatory compliance, effective methodologies, and stakeholder collaboration. Adhering to ANVISA regulations is paramount, as is the implementation of robust recruitment and data collection strategies. These elements are essential for overcoming challenges and ensuring the reliability of pilot studies, which ultimately contributes to the advancement of innovative medical technologies.
Introduction
In the dynamic realm of medical device development, pilot studies play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of innovation. These preliminary investigations, often referred to as feasibility studies, serve as essential checkpoints that assess the viability of new technologies prior to their entry into the rigorous phase of extensive clinical trials. By evaluating critical aspects such as safety, usability, and initial efficacy, pilot studies not only assist researchers in identifying potential pitfalls but also refine study protocols and gather crucial data for larger trials.
In Brazil, where navigating complex regulatory landscapes can be particularly challenging, the significance of these studies is magnified, ensuring compliance while paving the way for advancements in healthcare. As the landscape of medical device research evolves, understanding the intricacies of pilot studies becomes indispensable for stakeholders who aim to enhance patient care and drive successful outcomes in this vital industry.
Understanding Pilot Studies: A Foundation for Medical Device Development
Pilot investigations, also known as feasibility assessments, are vital preliminary evaluations that scrutinize the viability of medical devices prior to extensive clinical trials. These analyses typically involve a limited sample size and concentrate on assessing crucial elements such as safety, usability, and initial effectiveness. By conducting a preliminary investigation, researchers can pinpoint potential design issues, refine protocols, and collect initial data that will inform larger-scale trials.
In Brazil, where regulatory frameworks can be complex, pilot studies for medical devices become even more critical. They not only aid in compliance with local regulations but also improve the overall development process of medical devices. Notably, recent statistics indicate that only one trial has specifically addressed the issue of over-optimistic effect sizes in interventions for cancer fatigue, underscoring the need for more comprehensive preliminary investigations in this domain to ensure accurate and reliable results.
As Nancy Mayo from the Division of Clinical Epidemiology at McGill University emphasizes, "The recently released reporting guidelines for initial and feasibility research must be adhered to by researchers, reviewers, and journals alike." This statement highlights the importance of following these guidelines to uphold the integrity and reliability of results.
Furthermore, the findings suggest that employing feasibility progression criteria in preliminary trials can significantly enhance the likelihood of effective screening in full-scale trials. An evaluation of preliminary research in rehabilitation identified seven evidence-based goals for conducting initial research, including assessing protocol integrity and estimating recruitment rates. However, the degree to which these objectives are met remains uncertain, indicating a gap in the literature that necessitates further investigation.
In 2025, Brazil has witnessed a surge in pilot studies for medical devices, reflecting an increasing recognition of their significance in the development process. Successful preliminary investigations, such as ReGelTec's Early Feasibility Assessment on HYDRAFIL™ aimed at addressing chronic low back pain in Colombia, not only lay the groundwork for more extensive trials but also contribute to the advancement of innovative medical technologies that can enhance patient care. Moreover, opportunities to improve the utilization of real-world data (RWD) involve expanding unique equipment identification (UDI) capture and enhancing connections between electronic health records (EHR) and other data sources, which can substantially bolster the quality and compliance of research trials.
As the landscape of medical equipment advancement continues to evolve, the importance of preliminary trials in ensuring efficient and compliant clinical examinations cannot be overstated.
Navigating Brazil's Regulatory Framework for Medical Devices
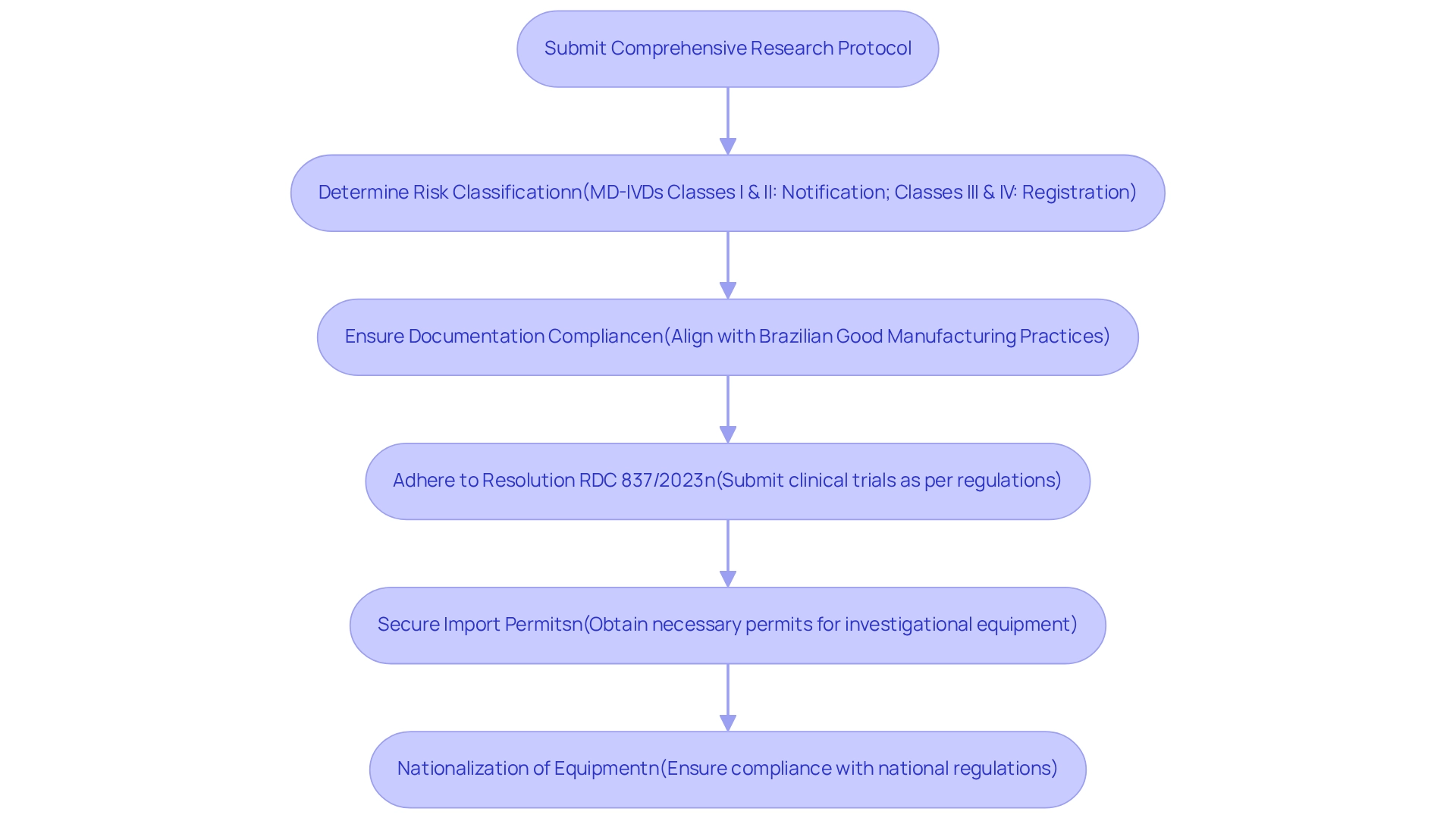
In Brazil, the regulatory authority overseeing medical devices is ANVISA (Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária). Before launching pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil, researchers must ensure that their protocols comply with ANVISA regulations, which involve obtaining essential approvals and certifications. The process begins with the submission of a comprehensive research protocol, meticulously designed to meet ANVISA's stringent requirements.
Furthermore, acquiring ethical clearance from an Institutional Review Board (IRB) is essential, as it guarantees that the research adheres to ethical standards and protects participant rights.
Key steps to ensure compliance with ANVISA for pilot studies include:
- Understanding Risk Classification: Manufacturers must first determine the risk class of their medical device, as this classification influences the regulatory pathway. As noted by expert Margret Seidenfaden, "Manufacturers intending to market a medical product in Brazil must first determine the risk class of the product." For instance, MD-IVDs Classes I and II are subject to notification, while Classes III and IV require registration.
- Documentation Compliance: All documentation submitted must align with Brazilian Good Manufacturing Practices, which are critical for the approval process. This includes appointing a Brazilian Registration Holder to facilitate communication with ANVISA.
- Adhering to Resolution RDC 837/2023: This regulation governs the submission of clinical trials for medical instruments, outlining specific requirements that must be met to avoid delays in the approval process. Notably, obtaining an INMETRO certificate can take between 3 to 12 months, underscoring the timeline involved in regulatory compliance.
- Import Permits and Nationalization: Securing import permits and nationalizing investigational equipment are crucial steps in the process, ensuring that all regulatory requirements are fulfilled before the research can commence.
Acquaintance with these regulations not only simplifies the implementation of pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil but also enhances the reliability of the research outcomes. An analysis of the requirements for the authorization of medical equipment in Brazil illustrates that compliance with these guidelines significantly reduces potential delays in introducing medical products to the market. As emphasized by specialists in the field, successfully navigating Brazil's medical regulations is vital for manufacturers aiming to leverage the expanding opportunities within the Latin American market.
By leveraging the expertise of bioaccess®, which focuses on comprehensive trial management services—including feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting—researchers can effectively navigate these regulatory challenges and enhance their likelihood of success.
Choosing the Right Methodology for Effective Pilot Studies
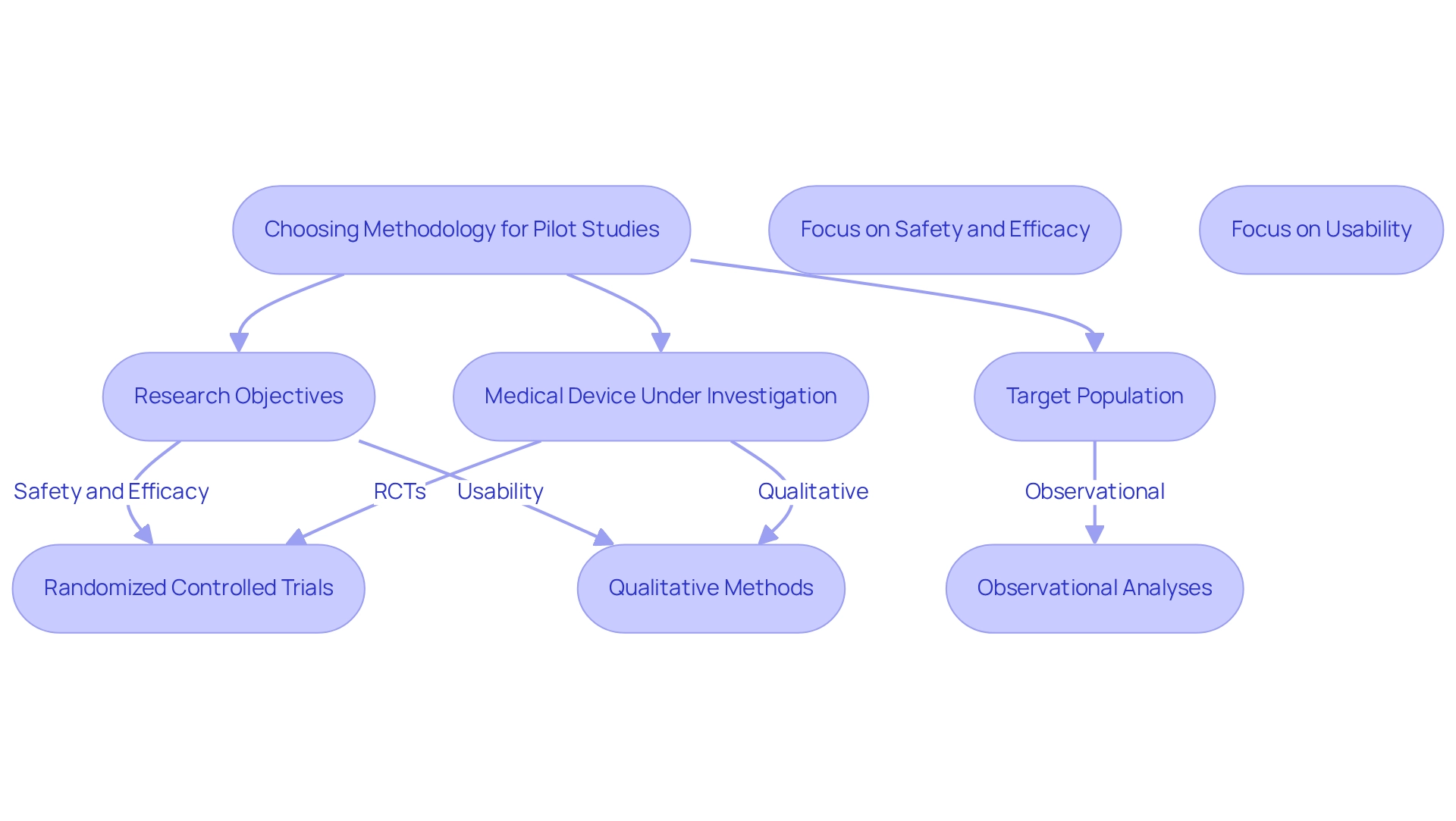
Selecting the appropriate approach for a preliminary research project is crucial for producing dependable and practical data, particularly in the context of pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil. Researchers must assess various factors, including the research objectives, the target population, and the specific medical device under investigation. Common methodologies employed in trial experiments include randomized controlled trials (RCTs), observational analyses, and qualitative methods, each offering unique benefits and drawbacks.
For instance, if the primary goal is to evaluate usability, qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups can provide in-depth insights into user experiences and preferences. Conversely, when the focus shifts to assessing safety and efficacy, a randomized controlled trial design becomes more appropriate, as it allows for rigorous comparisons between treatment groups.
In Brazil, pilot studies for medical devices have led to advancements in experimental methodologies, with a significant emphasis on adhering to best practice guidelines from applicable reporting standards. This approach not only enhances the quality of the research but also ensures that findings are robust and applicable to real-world scenarios. Moreover, a recent analysis emphasized that achieving total follow-up in at least 95% of enrolled participants is essential for the success of initial trials, particularly in pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil, as demonstrated in the POET Pilot Trial.
Expert advice indicates that researchers should examine preliminary investigations with the same thoroughness as full-scale trials, ensuring that findings are published in peer-reviewed journals to enhance the broader evidence base. Furthermore, establishing a suitable sample size is essential for preliminary research, as it influences the dependability of the findings and the capacity to draw significant conclusions.
The synthesis of current literature on methodologies for preliminary trials underscores the necessity for standardized guidelines, as highlighted in the case analysis titled 'Quality of Implementation Trials.' This analysis addresses issues regarding the quality of implementation trials and their role in the evidence base, strengthening the case for standardized practices. By thoughtfully selecting the suitable methodology and adhering to best practices, researchers can enhance the efficiency of preliminary investigations, ultimately advancing the development of innovative medical devices—a goal that bioaccess® is committed to in the field of research.
Strategies for Recruiting Participants in Pilot Studies
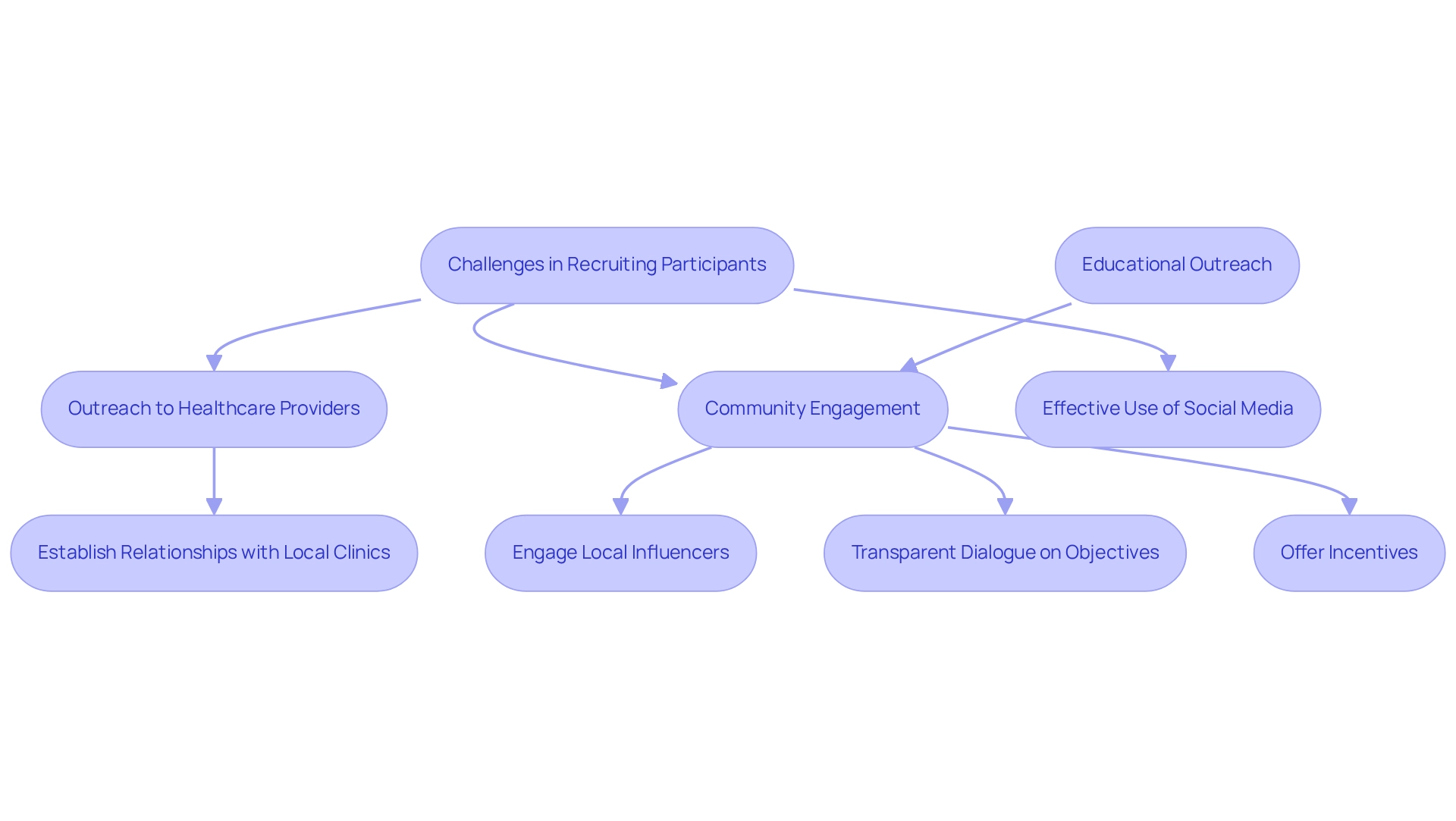
Enlisting individuals for preliminary research in Brazil presents unique challenges due to the nation's diverse population and varying levels of understanding regarding clinical trials. To enhance recruitment efforts, researchers must adopt a multifaceted strategy that includes:
- Outreach to healthcare providers
- Community engagement
- Effective use of social media platforms
Establishing strong relationships with local clinics and hospitals can significantly improve access to potential participants for pilot studies involving medical devices in Brazil, thereby creating a supportive network for recruitment initiatives.
Transparent dialogue regarding the project's objectives, potential benefits, and participant rights is essential to foster trust and promote enrollment. Researchers should clearly articulate how participation can positively influence both community and individual health outcomes. Furthermore, offering incentives, such as reimbursement for travel expenses or access to innovative treatments, can serve as a compelling motivator for individuals considering participation.
As Aline Scianni noted, "Providing transport should, therefore, increase the rate of recruitment as well as the attendance at the training sessions."
Statistics reveal that 62.4% of potential participants report limited knowledge of trial procedures, underscoring the necessity for educational outreach as part of recruitment strategies. By addressing these knowledge gaps and providing comprehensive information, researchers can cultivate a more informed participant base.
Moreover, effective recruitment strategies for pilot studies involving medical devices in Brazil often necessitate customized messaging that resonates with the target audience. Engaging local influencers or community leaders can amplify outreach efforts and enhance credibility. Given bioaccess's expertise in managing preliminary experiments and other research trials, leveraging their knowledge can significantly improve recruitment processes.
As the patient recruitment services sector is projected to grow from USD 5.7 million in 2023 to USD 10.1 million by 2030, particularly in Brazil, pilot studies for medical devices will be crucial in overcoming recruitment challenges and ensuring the success of preliminary trials. The impact of Medtech clinical research on local economies, including job creation and healthcare improvement, emphasizes the importance of these initiatives in fostering international cooperation and economic development.
Data Collection and Analysis: Key Components of Pilot Studies
Efficient data gathering in pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil is essential for guaranteeing the reliability and validity of results. A systematic and well-structured approach is crucial, utilizing a variety of tools such as surveys, electronic health records, and direct observations to gather comprehensive data. Establishing clear protocols for data entry and management is vital to minimize errors and enhance data integrity.
In 2025, the landscape of data gathering techniques for pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil continues to advance, focusing on organized methodologies that enable precise analysis. For instance, in a recent preliminary research managed by bioaccess®, Group HL received an injection of 0.5 mg/kg of 1% lidocaine at 41℃, showcasing a specific data collection method that can be employed in clinical settings. Common statistical techniques used in preliminary analysis, including those applied in pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil, involve Bayesian methods that enable researchers to combine prior beliefs with observed data, guiding essential Go/No-Go decisions concerning health technologies.
This method underscores the importance of carefully selecting prior distributions, as they significantly influence outcomes. A case analysis titled 'Bayesian Methods in Pilot Trials' illustrates how these approaches can provide a nuanced understanding of treatment effects and probabilities of success in pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil.
Expert opinions emphasize that recognizing shared challenges linked to inadequately sized test studies—such as mis-specification of effect size or nuisance parameters—is crucial for effective data management. Ronan Fitzpatrick, Head of Statistics at nQuery, highlights the necessity to tackle these challenges to improve the quality of trial research. By utilizing strong statistical methods, researchers can identify trends, evaluate the viability of medical instruments, and conduct pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil to derive actionable insights for potential enhancements.
Furthermore, it is essential to clearly outline elements before moving forward with a trial to ensure its effectiveness. Utilizing advanced software tools for data analysis not only streamlines the analytical process but also enhances the accuracy of findings, ultimately supporting the advancement of medical devices. As the field advances, the incorporation of innovative data collection techniques will play a crucial role in the success of pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil, ensuring that these studies meet the rigorous demands of clinical research, particularly under the expert guidance of bioaccess®, which specializes in Early-Feasibility Evaluations, First-In-Human Trials, Preliminary Assessments, Pivotal Evaluations, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Assessments, backed by over 20 years of experience in the Medtech sector in Latin America.
Building Partnerships: Collaborating with Local Stakeholders
Creating collaborations with local stakeholders—such as healthcare providers, academic institutions, and patient advocacy groups—is crucial for the success of pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil. These collaborations not only broaden the participant pool but also facilitate efficient data collection and provide valuable insights into local healthcare practices. Involving stakeholders early in the research design process enables the identification of potential challenges and simplifies regulatory approvals, which is essential in a context where Brazil's diverse healthcare system can present unique obstacles.
Consistent communication and teamwork throughout the research are essential. This ongoing dialogue fosters a supportive environment that encourages participant engagement, ultimately enhancing the quality of the research. A recent survey emphasized the necessity for heightened public awareness about the advantages of medical research, which is essential for enhancing recruitment levels in trials.
This issue is exacerbated by the restricted access to information regarding ongoing trials, as highlighted in the case analysis titled "Need for Public Awareness in Clinical Research." By collaborating with local stakeholders, researchers can introduce initiatives focused on informing both patients and healthcare providers about the importance of research trials, thus addressing this gap.
Furthermore, successful collaborations have been recorded in various pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil, which highlight the tangible advantages of these partnerships. Statistics suggest that research involving local stakeholders experiences higher recruitment rates and enhanced participant retention, which are key factors in the overall success of medical research. As Carlos H Barrios, who has stock and other ownership interests in MedSIR and Tummi, observes, the integration of local insights and expertise is invaluable in navigating the complexities of medical research in Brazil.
Additionally, GOC investigators have secured funding from pharmaceutical companies for various research projects, highlighting the financial support available that may encourage local stakeholder engagement. By emphasizing these collaborations, organizations can greatly improve their preliminary research results and aid in the progress of medical equipment in the area. Significantly, bioaccess's effective management of clinical trials, including Early-Feasibility and First-In-Human research, has favorably influenced local economies through job creation and healthcare enhancement, as demonstrated by the collaboration with GlobalCare Clinical Trials, which accomplished over a 50% reduction in recruitment time and a retention rate surpassing 95%.
Overcoming Challenges in Conducting Pilot Studies
Conducting pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil often presents various challenges, including difficulties in participant recruitment, regulatory barriers, and data management issues. To effectively navigate these obstacles, researchers should develop a comprehensive project plan that clearly outlines potential risks and corresponding mitigation strategies. Engaging stakeholders early in the process is crucial; this collaboration can help identify potential barriers and streamline the navigation of regulatory requirements.
Recruitment challenges are especially prevalent in pilot projects, where the target population may be restricted. Strategies such as leveraging local networks, utilizing social media outreach, and offering incentives can enhance participant engagement. Additionally, understanding the demographics and preferences of the target population can inform tailored recruitment strategies.
Regulatory hurdles can also pose significant challenges, particularly for pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil, where navigating the complex landscape of medical device regulations requires careful planning. Successful strategies include maintaining open communication with regulatory bodies and utilizing local expertise, such as that offered by bioaccess®, to ensure compliance with national standards. With over 20 years of experience in the Medtech field, bioaccess® is well-equipped to assist researchers in overcoming these challenges.
Flexibility in research design is crucial, enabling investigators to adjust to unexpected situations that may occur during the investigation. Consistent monitoring and assessment of the project's progress are essential for recognizing problems early, allowing for prompt interventions. For example, if safety issues are identified during a preliminary trial, it is crucial to report group-specific rates with 95 percent confidence intervals for adverse events, as this clarity can inform future decision-making.
As Natasha A Karp pointed out, "We need to remember the constraints of operators in our decision-making and data presentation." This viewpoint highlights the significance of acknowledging the limitations of pilot research. Furthermore, the potential for formal guidelines to standardize their use could significantly enhance their utility in clinical research.
Pilot experiments are not just initial assessments; they act as vital learning opportunities. An unsuccessful preliminary investigation can offer valuable insights, assisting researchers in avoiding the waste of resources on impractical projects. As emphasized in a case analysis on the role of preliminary trials in intervention development, when carried out effectively, these assessments can significantly enhance the design and execution of subsequent clinical experiments, ultimately improving the overall research process.
By implementing these approaches, researchers can more effectively navigate the challenges of preliminary investigations, including pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil, and aid in the successful progress of medical instruments, utilizing the knowledge of organizations like bioaccess®, which focuses on Early-Feasibility Evaluations, First-In-Human Trials, Preliminary Investigations, Pivotal Trials, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Evaluations.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Pilot Studies in Brazil
The medical device environment in Brazil is undergoing substantial transformation, as pilot studies for medical devices are poised to embrace innovative technologies and methodologies. The incorporation of digital health solutions, including telemedicine and remote monitoring, is anticipated to significantly enhance participant engagement and streamline data collection processes. A recent pilot investigation revealed that the effect size identified in a small walking intervention for cancer fatigue was 'over optimistic,' underscoring the challenges faced in pilot projects.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on patient-centered research is likely to influence the design and implementation of these investigations, ensuring they are tailored to meet the needs and preferences of patients.
In this evolving landscape, bioaccess® stands out with its comprehensive trial management services, specializing in Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, as well as Pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, their compliance-driven approach and meticulous attention to regulatory requirements establish them as a trusted partner in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices. Their customized strategy and adaptability in managing trials are essential for navigating the complexities of the regulatory environment.
As this environment continues to evolve, researchers must remain informed about modifications and advancements in research methodologies to adeptly navigate the future of trial projects. This proactive approach will not only support compliance but also facilitate the successful integration of digital health solutions, ultimately enhancing the efficacy and efficiency of medical research in Brazil. Moreover, emerging trends in medical device data analytics, such as federated learning and explainable AI, are set to influence pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil, highlighting the importance of data interoperability in improving patient care and operational efficiencies.
The impact of these clinical studies extends beyond research, contributing to job creation, economic growth, and healthcare improvement in local communities.
Conclusion
Pilot studies are essential to the medical device development process, especially in Brazil, where regulatory complexities amplify their importance. These preliminary investigations not only evaluate the viability of new technologies but also refine protocols and gather critical data for larger clinical trials. By concentrating on safety, usability, and efficacy, pilot studies help identify potential pitfalls early, thus enhancing the overall quality of research.
As Brazil's landscape evolves, adopting innovative methodologies and digital health solutions will be crucial for future pilot studies. Effective recruitment strategies and robust partnerships with local stakeholders can significantly improve participant engagement and data collection. The focus on patient-centered research will ensure that studies are tailored to meet the needs of those involved, ultimately driving successful outcomes.
In conclusion, the role of pilot studies transcends mere feasibility assessments; they are vital for fostering innovation and ensuring compliance within the medical device sector. By committing to rigorous methodologies and adhering to regulatory standards, researchers can navigate the challenges of clinical trials more effectively. As the industry continues to advance, integrating new technologies and collaborative efforts will be key to enhancing patient care and driving economic growth in Brazil's healthcare landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are pilot investigations in the context of medical devices?
Pilot investigations, also known as feasibility assessments, are preliminary evaluations that assess the viability of medical devices before extensive clinical trials. They focus on safety, usability, and initial effectiveness using a limited sample size.
Why are pilot studies particularly important in Brazil?
In Brazil, pilot studies are crucial due to complex regulatory frameworks. They help ensure compliance with local regulations and improve the overall development process of medical devices.
What recent statistics highlight the need for more pilot studies in cancer fatigue interventions?
Recent statistics indicate that only one trial has specifically addressed the issue of over-optimistic effect sizes in interventions for cancer fatigue, emphasizing the need for more comprehensive preliminary investigations in this area.
What guidelines should researchers follow for initial and feasibility research?
Researchers, reviewers, and journals must adhere to the recently released reporting guidelines for initial and feasibility research, as emphasized by Nancy Mayo from McGill University, to maintain the integrity and reliability of results.
How can feasibility progression criteria enhance preliminary trials?
Employing feasibility progression criteria in preliminary trials can significantly enhance the likelihood of effective screening in full-scale trials.
What are some evidence-based goals for conducting initial research in rehabilitation?
Seven evidence-based goals for conducting initial research include assessing protocol integrity and estimating recruitment rates, although the extent to which these objectives are met remains uncertain.
What has been the trend regarding pilot studies for medical devices in Brazil as of 2025?
In 2025, Brazil has seen a surge in pilot studies for medical devices, indicating a growing recognition of their importance in the development process.
What specific example illustrates the success of a preliminary investigation in medical device development?
ReGelTec's Early Feasibility Assessment on HYDRAFIL™, aimed at addressing chronic low back pain in Colombia, is an example of a successful preliminary investigation that contributes to the advancement of innovative medical technologies.
What role does ANVISA play in the pilot study process for medical devices in Brazil?
ANVISA (Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária) is the regulatory authority overseeing medical devices in Brazil, and researchers must ensure compliance with its regulations before launching pilot studies.
What are the key steps to ensure compliance with ANVISA for pilot studies?
Key steps include understanding risk classification, ensuring documentation compliance with Brazilian Good Manufacturing Practices, adhering to Resolution RDC 837/2023, and securing import permits and nationalizing investigational equipment.
How can researchers navigate regulatory challenges in Brazil?
Researchers can leverage the expertise of trial management services, like bioaccess®, which provide support in feasibility assessments, compliance reviews, trial setup, and other regulatory processes to enhance their likelihood of success.




