Overview
Creating a sample clinical evaluation report (CER) involves a structured approach that includes defining objectives, detailing methodologies, presenting results, and ensuring compliance with regulatory guidelines. The article outlines essential steps for structuring a CER and emphasizes the importance of rigorous evaluation processes and qualified evaluators to enhance the report's credibility and effectiveness in demonstrating medical device safety and efficacy.
Introduction
In the realm of medical device development, the significance of Clinical Evaluation Reports (CERs) cannot be overstated. These comprehensive documents serve as critical assessments that validate the safety and effectiveness of medical devices, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
As organizations strive to navigate the complexities of clinical evaluations, understanding the structured approach to creating a robust CER becomes paramount. This article delves into the essential components of a CER, the types of clinical data required, and the regulatory guidelines that govern the evaluation process.
By illuminating best practices and methodologies, this discussion aims to equip researchers and stakeholders with the knowledge necessary to produce credible and impactful clinical evaluation reports, ultimately contributing to the advancement of medical technology and patient care.
Understanding Clinical Evaluation Reports: Definitions and Objectives
A sample clinical evaluation report (CER) functions as a thorough analysis of the medical information related to a healthcare product or intervention. Its primary objectives encompass demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of the equipment, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards, and substantiating clinical claims. To achieve these objectives, our service capabilities play a crucial role.
This includes conducting feasibility studies to assess the suitability of research sites and principal investigators (PIs), as well as providing thorough reviews and feedback on study documents to ensure compliance with country requirements. The structured approach to trial management, which includes trial set-up, start-up, and approval processes involving ethics committees and health ministries, is critical for the successful development of a sample clinical evaluation report. Furthermore, obtaining import permits and nationalizing investigational equipment is essential for regulatory compliance.
Researchers must recognize that a meticulously organized sample clinical evaluation report is not just a regulatory necessity; it is also an invaluable asset for stakeholders, including healthcare professionals and patients. The report should explicitly detail the rationale for the evaluation, the methodologies utilized, and the outcomes observed. This structured approach not only enhances the credibility of the report but also enriches the collective understanding of medical device safety and effectiveness.
As emphasized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), states that participate in verification or utilize advanced tools to detect healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) are likely to identify and report a greater number of infections than those that do not prioritize verification. This highlights the importance of rigorous evaluation processes. Additionally, state health departments must have access to 2023 information from NHSN to perform quality checks, as this is crucial for accurate HAI reporting.
States that conduct audits may potentially report higher Standardized Infection Ratios (SIRs), emphasizing the significant impact of data quality checks and validation efforts on reporting accuracy. Furthermore, the success of medical evaluations is heavily influenced by the qualifications and experience of evaluators, particularly their understanding of systematic literature review (SLR) methodologies and regulatory stipulations. Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, underscores the necessity of having qualified professionals involved in creating a robust sample clinical evaluation report.
The case study on the importance of experienced evaluators illustrates that failure to meet the requisite qualifications can lead to the rejection of a CER by Notified Bodies, regardless of the report's inherent quality. Therefore, for researchers in healthcare environments, creating a robust sample clinical evaluation report is critical—not only for regulatory compliance but also for making a meaningful contribution to the body of medical knowledge.
Step-by-Step Guide to Structuring Your Clinical Evaluation Report
To effectively structure your Clinical Evaluation Report (CER), follow these essential steps:
- Title Page: Clearly state the report’s title, date, and authorship information to establish authority.
- Table of Contents: Offer a detailed outline of the report’s sections, facilitating easy navigation for readers.
- Executive Summary: Present a concise summary of key findings and recommendations, providing a snapshot of the report’s significance.
- Introduction: Articulate the purpose of the report, emphasizing its relevance within the medical context and how it aligns with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR).
- Methods: Detail the methodologies utilized for information collection and analysis, ensuring transparency in your approach. This is crucial for compliance reviews and enhances the credibility of your findings.
- Results: Clearly present findings from the research data, incorporating statistical analyses and relevant visuals to enhance understanding. Effective reporting is essential, especially when involving regulatory bodies like INVIMA.
- Discussion: Interpret the results by discussing their implications for medical practice and future research directions, as noted by experts in the field. As Dr. Valentin Fuster, Editor-in-Chief, emphasizes, "Listen to this manuscript's audio summary by JACC Editor-in-Chief Dr. Valentin Fuster."
- Conclusion: Summarize the overall findings and their broader significance, reinforcing the report's impact.
- References: Compile a comprehensive list of all sources cited throughout the report to uphold credibility and transparency.
- Appendices: Include supplementary materials that support the report’s content, enhancing its value.
By following this structure and utilizing comprehensive trial management services—such as feasibility studies, site selection, project management, and compliance reviews—you will create a compliant and thorough report that effectively analyzes evidence. These services guarantee that the CER complies with regulatory requirements and improves the quality of evaluations. This approach is crucial, particularly for Class I devices that require notified body involvement due to their sterile supply, reusability, or measuring functions.
As emphasized in the case study titled 'Clinical Evidence in Clinical Evaluation Reports,' the identification and analysis of evidence are central to writing a CER under the MDR, requiring evidence from both manufacturer-generated information and independent literature. Moreover, tackling statistical challenges and controversies in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) is essential for ensuring appropriate reporting standards in medical assessments.
The Role of Clinical Data in Evaluations: Types and Analysis
Clinical information used in assessments can be categorized into several unique groups, each playing an essential role in analyzing medical instruments:
- Clinical Trials Information: This includes details obtained from controlled studies aimed at assessing the safety and efficacy of a medical instrument, offering foundational insights into its performance. At bioaccess®, our 20+ years of expertise in Medtech ensures that these trials are conducted with the highest standards in Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Follow-Up studies. Our adaptable and personalized approach enables us to customize each study to address the specific requirements of our clients.
- Post-Market Surveillance Information: Collected once a product is commercially available, this information offers valuable insights regarding long-term safety and effectiveness, ensuring continued patient safety and product reliability, which is a primary focus of our comprehensive trial management services that include feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting.
- Literature Review Information: This type of information is gathered from existing studies and publications, supporting the analysis by providing context and corroborating evidence.
To analyze health information effectively, the following methods are recommended:
- Statistical Analysis: Employ suitable statistical methods, including Bayesian techniques, which integrate prior beliefs into statistical inference, improving the strength of assessments. Current findings indicate that only 6.1% of studies reporting non-significant findings included a statistical power analysis, underlining the need for thorough statistical scrutiny.
- Comparative Analysis: Assess performance by comparing information against established benchmarks or previous studies, facilitating a clearer understanding of a device's efficacy, an approach we apply in our trial setups.
- Qualitative Analysis: This involves assessing non-numerical data, such as patient feedback, to gather insights into user experiences, which can significantly inform medical decisions.
Grasping these data types along with their respective analysis methods is essential for substantiating the claims made in a sample clinical evaluation report. As Howard Barkan, an affiliated researcher and consulting statistician at the School of Public Health, University of California Berkeley, aptly states,
One central goal in conducting methodologically robust studies is to build a sound evidence base for healthcare.
This reinforces the importance of rigorous methodologies in establishing credible assessments.
Navigating Regulatory Guidelines for Clinical Evaluation Reports
When preparing a sample clinical evaluation report, it is crucial to adhere to established regulatory guidelines to ensure compliance and credibility. A thorough procedure that includes the following standards and practices is crucial:
- ISO 14155: This global standard outlines the criteria for carrying out trials involving medical products, aiming to maintain ethical principles and scientific quality in research. As highlighted in ISO 14155, documentation and reporting of adverse events and device deficiencies related to medical devices is extremely significant.
- MEDDEV 2.7/1: Issued by the European Commission, this guidance document provides comprehensive instructions regarding the content and structure of research assessment reports, thereby enhancing their quality and consistency.
- FDA Guidance: In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration offers detailed guidelines for medical device assessment, outlining the necessary data required to substantiate claims related to safety and efficacy.
To navigate the complexities of research trials, it is also crucial to engage in feasibility studies and select appropriate research sites alongside qualified principal investigators (PIs). This ensures that the trial aligns with country-specific requirements, including the necessary approvals from ethics committees and health ministries, and facilitates the importation of investigational devices.
The trial setup process involves careful planning and coordination to ensure compliance with all regulatory requirements. Project management is essential in supervising the trial's progress, ensuring that all milestones are achieved, and that any significant or insignificant adverse events are reported swiftly and precisely.
In statistical assessments, it's noteworthy that a two-sided test at the 5% level corresponds to a one-sided test at the 2.5% level, highlighting the importance of statistical rigor in medical assessments. Moreover, as value-based healthcare strategies are being developed for commercializing oncology treatments, understanding and complying with these regulatory guidelines becomes even more critical. This compliance not only ensures the integrity of the medical assessment but also aligns with emerging healthcare strategies that focus on patient outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
Additionally, choosing a partner like Katherine Ruiz, who possesses regulatory expertise, can significantly aid manufacturers in conducting trials in compliance with ISO 14155 and EU MDR standards, thereby enhancing the overall credibility and acceptance of the medical assessment report.
Familiarizing yourself with these regulations is not merely a procedural requirement; it significantly enhances the acceptance and credibility of your medical assessment report among regulatory bodies, ultimately facilitating a smoother approval process. To discuss your trial needs and explore how we can assist you, please schedule a meeting.
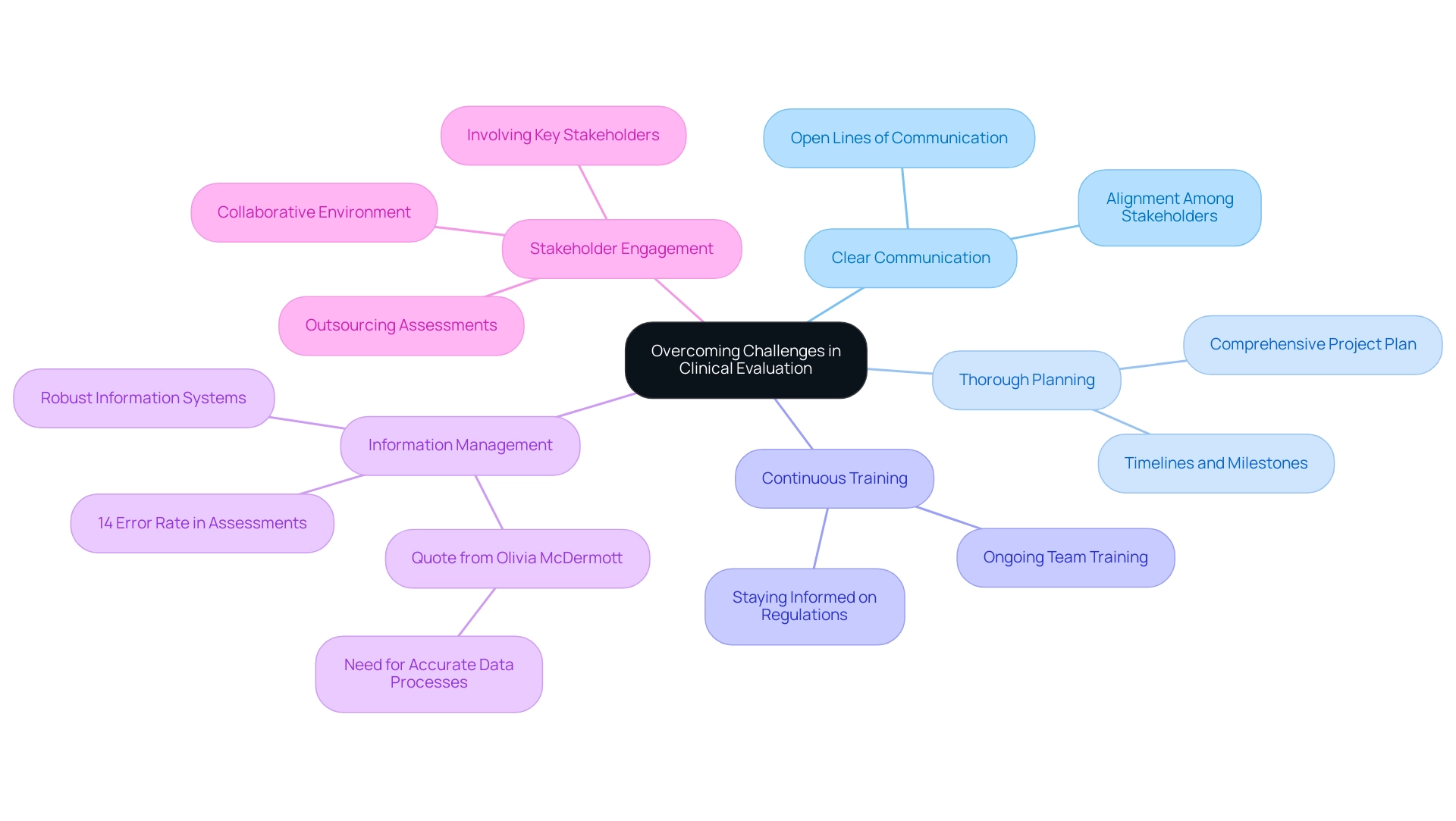
Overcoming Challenges in Clinical Evaluation: Best Practices and Tips
To effectively navigate the challenges inherent in medical assessment, implementing the following best practices is crucial:
- Clear Communication: Establish and maintain open lines of communication among team members, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies. This promotes alignment and facilitates the prompt resolution of issues as they arise.
- Thorough Planning: Create a comprehensive project plan that delineates timelines, roles, and milestones. Such clarity is vital for keeping assessments on track and meeting regulatory expectations, particularly in the context of bioaccess®'s expertise in managing Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS) and First-In-Human (FIH) studies.
- Continuous Training: Commit to ongoing training for your team to ensure they remain abreast of the latest regulations, methodologies, and technologies within the clinical evaluation landscape. Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for medical devices, emphasizes the importance of staying informed in a rapidly evolving field.
- Information Management: Invest in robust information management systems to enhance the efficiency of collection, analysis, and reporting processes. As highlighted by Olivia McDermott from the University of Galway,
A process for collating, synthesizing, and analyzing data to generate accurate and reliable conclusions is needed—companies do not know how to establish this process.
Moreover, it's crucial to recognize that 14% of errors associated with the use of medical assessments developed under the MDD for submissions under the MDR emphasize the necessity of adopting these best practices.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Actively involve key stakeholders from the outset of the assessment process to gather valuable insights and cultivate a collaborative environment. This is especially pertinent considering the rise in outsourcing assessments due to insufficient internal knowledge among manufacturers, making stakeholder participation even more essential, and aligns with bioaccess®’s tailored strategy in addressing challenges.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can greatly improve the quality of their assessment reports, including the sample clinical evaluation report, and better handle the difficulties they encounter in a swiftly changing regulatory landscape. The case study regarding manufacturers considering removing devices from the EU market due to difficulties in meeting new sample clinical evaluation report requirements further underscores the importance of adhering to these recommendations. With bioaccess®'s specialized services in EFS, FIH, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF), companies can effectively navigate these complexities and achieve successful outcomes.
Conclusion
The importance of Clinical Evaluation Reports (CERs) in the medical device development process is clear. These reports serve not only as essential documents for demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of devices but also as vital tools for ensuring compliance with rigorous regulatory standards. By following a structured approach to crafting a CER, researchers and stakeholders can enhance the credibility of their evaluations and contribute significantly to the medical field.
Throughout the article, the key components of a robust CER have been outlined, from the meticulous structuring of the report to the critical analysis of clinical data. Understanding the diverse types of clinical data, including:
- Clinical trials
- Post-market surveillance
- Literature reviews
is fundamental for substantiating claims made within the report. Furthermore, adherence to established regulatory guidelines such as ISO 14155 and MEDDEV 2.7/1 is crucial for ensuring the integrity and acceptance of the CER by regulatory bodies.
Challenges in clinical evaluation can be effectively navigated through best practices such as:
- Clear communication
- Thorough planning
- Continuous training
Engaging stakeholders early in the process fosters a collaborative environment that can lead to more comprehensive evaluations and successful outcomes.
In conclusion, the creation of a well-structured and meticulously researched Clinical Evaluation Report is indispensable for advancing medical technology and improving patient care. By equipping themselves with the knowledge of best practices and regulatory requirements, researchers can ensure that their evaluations not only meet compliance standards but also contribute meaningfully to the body of medical knowledge, ultimately enhancing patient safety and the reliability of medical devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Clinical Evaluation Report (CER)?
A Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) is a comprehensive analysis of medical information related to a healthcare product or intervention, aimed at demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of the equipment, ensuring regulatory compliance, and substantiating clinical claims.
What are the main objectives of a CER?
The primary objectives of a CER include demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of a healthcare product, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards, and substantiating clinical claims.
What services are involved in creating a CER?
Services involved in creating a CER include conducting feasibility studies, providing reviews and feedback on study documents, managing trial processes, obtaining import permits, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Why is a well-organized CER important?
A meticulously organized CER is not only a regulatory necessity but also an invaluable asset for stakeholders, including healthcare professionals and patients, as it enhances credibility and contributes to the understanding of medical device safety and effectiveness.
How do state health departments ensure accurate reporting of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs)?
State health departments must have access to up-to-date information from the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) to perform quality checks, which are crucial for accurate HAI reporting.
What impact do audits have on reporting Standardized Infection Ratios (SIRs)?
States that conduct audits may report higher Standardized Infection Ratios (SIRs), indicating that data quality checks and validation efforts significantly impact reporting accuracy.
What qualifications are necessary for evaluators involved in creating a CER?
Evaluators should possess qualifications and experience in systematic literature review methodologies and regulatory stipulations to ensure a robust CER, as failure to meet these qualifications can lead to rejection by Notified Bodies.
What are the essential steps for structuring a CER?
The essential steps for structuring a CER include creating a title page, table of contents, executive summary, introduction, methods, results, discussion, conclusion, references, and appendices.
Why is it important to detail methodologies in a CER?
Detailing methodologies in a CER ensures transparency in the approach, which is crucial for compliance reviews and enhances the credibility of the findings.
What is the significance of including statistical analyses in the results section of a CER?
Including statistical analyses in the results section is essential for effective reporting, especially when involving regulatory bodies, as it helps present findings clearly and supports the overall conclusions of the report.

