Overview
User-centered device trials are crafted to prioritize the needs and experiences of end-users, ensuring that medical products are not only functional but also intuitive and safe. This approach is pivotal in the realm of clinical research, as it directly influences the effectiveness of medical innovations.
The incorporation of user feedback through rigorous research, prototyping, and iterative testing significantly enhances product development. Such practices lead to improved patient outcomes, a fact supported by successful case studies and compelling statistical insights.
By understanding the dynamics of user-centered design, stakeholders can better navigate the complexities of the Medtech landscape and address key challenges effectively.
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of medical technology, the significance of user-centered design (UCD) in medical device trials is paramount. By placing the end-user at the forefront of the development process, UCD enhances not only the functionality and safety of devices but also significantly improves patient outcomes and satisfaction. As healthcare becomes increasingly complex, understanding the needs and preferences of both patients and healthcare providers is crucial for creating innovative solutions.
This article explores the critical aspects of UCD in medical device trials, examining:
- Fundamental principles
- Best practices
- Emerging trends that are shaping the future of healthcare technology
Through a comprehensive examination of methodologies, regulatory challenges, and the role of early-feasibility studies, it reveals how a user-centric approach can bridge the gap between innovation and real-world application, ultimately driving success in the medical device landscape.
Understanding User-Centered Design in Medical Device Trials
User-centered design (UCD) is an essential iterative process that prioritizes the user throughout the development of medical products. In the context of medical equipment trials, designing for user-centered device trials focuses on comprehensively understanding the needs, preferences, and limitations of end-users, including both patients and healthcare providers. This approach not only ensures that equipment is functional but also enhances its intuitiveness and safety.
The key components of UCD include:
- User Research: Engaging in interviews, surveys, and observational studies to collect valuable insights into user needs and experiences. This foundational step is crucial for customizing equipment to meet real-world demands.
- Prototyping: Developing initial versions of the product enables practical usability testing and the gathering of user feedback, which is vital for detecting potential issues early in the design process.
- Iterative Testing: Continuously refining the product based on user feedback fosters improvements in design and functionality, ensuring that the final outcome aligns closely with user expectations.
Recent findings underscore the importance of designing for user-centered device trials in medical research, indicating that products developed with a user-centered approach can lead to improved patient outcomes and greater user satisfaction. For instance, a study on the iMHere system, designed to assist individuals with disabilities, demonstrated that redesigned modules significantly improved usability, leading to better self-management and independence for users. As Bambang Parmanto noted, "Medication mismanagement and inadequate care of pressure injuries are the causes of high rates of hospitalization in the people with disabilities population and significantly increase morbidity."
This highlights the critical need for effective design in medical tools to mitigate such risks.
Moreover, current statistics reveal that Kaiser’s measure of sampling accuracy for user-centered design initiatives stands at 0.68, indicating an acceptable level of reliability in user feedback processes. This emphasizes the significance of designing for user-centered device trials by integrating user perspectives into the design and testing phases of medical equipment. Additionally, future research should explore the impact of designers' characteristics, project contexts, and stakeholder involvement on design processes, which can further enhance the effectiveness of UCD.
As the landscape of medical technology evolves, designing for user-centered device trials will be essential in addressing the complexities of user needs and ensuring the successful adoption of innovative solutions in healthcare. Furthermore, the advancement of medical tools for epilepsy management highlights the need for comfort, acceptance, and adaptability to individual seizure characteristics, reinforcing the significance of user-centered design in creating effective healthcare solutions.
Fundamental Principles of Designing Device Trials
Designing effective medical device trials necessitates adherence to several fundamental principles that ensure both regulatory compliance and user satisfaction:
- Clear Objectives: Establish specific, measurable objectives for the trial, encompassing both primary and secondary endpoints. This clarity is essential for guiding the study and evaluating its success.
- User Involvement: Actively engage users throughout the design process. Their insights are invaluable in shaping a device that meets real-world needs and expectations, ultimately enhancing user acceptance and satisfaction. Research suggests that experiments incorporating user feedback have significantly higher success rates, underscoring the importance of this involvement.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the study design aligns with relevant regulatory guidelines, such as those established by the FDA or EMA. Adhering to these standards not only facilitates smoother approval processes but also enhances the credibility of the results. bioaccess® focuses on maneuvering through these regulatory environments, offering crucial assistance in compliance evaluations, study setup, and the import permit and nationalization of investigational products.
- Robust Methodology: Choose suitable study designs, such as randomized controlled studies, which are essential for adequately evaluating the device's safety and efficacy. For crucial studies, a sample size typically ranges from 100 to 300 participants, providing a solid foundation for statistical analysis. This statistic underscores the significance of robust methodology in ensuring dependable outcomes.
- Data Integrity: Implement stringent data collection and management practices to guarantee the reliability of results. This includes maintaining accurate records and ensuring that data is handled in compliance with established protocols.
- Preparedness for Challenges: Be prepared for unexpected challenges during the design phase. This readiness is crucial for navigating the complexities that may arise throughout the process, particularly for startups facing regulatory hurdles and competition.
By following these principles, researchers can create studies that not only meet regulatory standards but also provide valuable insights into the product's performance in real-world environments. For instance, non-inferiority studies for Class III medical devices illustrate the importance of statistical rigor in confirming that a new device's effectiveness is not significantly worse than that of a control device. Such frameworks assist in estimating sample sizes and determining non-inferiority margins, ensuring that research studies are both scientifically sound and relevant to user needs.
As emphasized in the ICH E9(R1) addendum, "the statistical analysis, aligned to the estimand, will be associated with assumptions and data limitations, the impact of which can be investigated through sensitivity analysis." This emphasizes the essential nature of statistical principles in research study design. Ultimately, bioaccess® aims to advance medical equipment sooner by designing for user-centered device trials, providing a valuable solution for companies in the medtech industry.
Furthermore, bioaccess® possesses the expertise to oversee different kinds of research, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF), ensuring thorough assistance throughout the study process.
Critical-to-Quality Factors in Device Trials
Critical-to-quality (CtQ) factors are essential components that significantly influence the success of medical equipment studies. Among these, several key factors stand out:
- Patient Safety: The foremost priority in any clinical trial is ensuring that the device does not pose undue risk to participants. A strong emphasis on patient safety not only safeguards participants but also enhances the credibility of the results. As Robert Deans states, "The target product profile is an extensive document that covers both the biological properties of the product and its safety and quality attributes," underscoring the critical nature of these factors.
- Data Quality: Accurate and complete data collection is essential for supporting valid conclusions. High-quality data management systems (CDMS) play a crucial role in maintaining data integrity throughout the clinical study lifecycle, ensuring regulatory compliance and bolstering the reliability of results.
- Protocol Adherence: Strict compliance with the research protocol is vital for ensuring consistency and reliability in the investigation. Deviations can lead to variability in outcomes, undermining the study's validity. A case study on study design emphasizes that the choice of design—whether parallel-group, crossover, or factorial—can directly impact the study's ability to effectively address specific research questions.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving all relevant stakeholders—including patients, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies—ensures comprehensive feedback and support. This engagement is critical for aligning the objectives with the needs and expectations of those affected by the device. bioaccess® excels in this area, leveraging over 20 years of Medtech experience to facilitate effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
- Risk Management: Early identification of potential risks and the implementation of mitigation strategies are essential for navigating the complexities of clinical studies. Effective risk management not only protects participants but also aids in the overall success of the study. Community efforts and collaboration with standards development organizations can help establish best practices and reliable protocols for effective management of trials. bioaccess® offers extensive clinical study management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, study setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, ensuring that all aspects of risk are meticulously addressed.
Focusing on these CtQ factors can significantly enhance the quality of equipment evaluations, leading to more dependable results and enabling smoother regulatory processes. By prioritizing these essential components, researchers can bolster patient safety and ultimately drive the success of medical equipment studies, especially within the evolving landscape of Latin America. Furthermore, the impact of clinical studies on local economies, such as job creation and healthcare enhancement, underscores the significance of these experiments in fostering international collaboration and economic growth.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements for Device Trials
Navigating the regulatory landscape for medical equipment evaluations requires a strategic approach, encompassing several essential steps:
-
Equipment Classification: Accurately determining the classification of the apparatus—whether Class I, II, or III—is crucial. This classification dictates the regulatory requirements that must be met, influencing the overall study design and execution.
-
Pre-market Submissions: Preparing and submitting the necessary documentation, such as Investigational Device Exemptions (IDEs) or Premarket Approval (PMA) applications, is a vital step. Successful pre-market submissions are frequently dependent on extensive data that shows the product's safety and effectiveness, which can greatly influence study success rates.
-
Compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP): Following GCP guidelines is crucial for safeguarding participant rights and ensuring the integrity of the information gathered during studies. This compliance not only cultivates trust among stakeholders but also corresponds with regulatory expectations.
-
Ethics Committee Approval: Obtaining approval from an ethics committee or institutional review board (IRB) is a prerequisite before starting any study. This step ensures that the study meets ethical standards and safeguards participant welfare.
-
Import Permits and Nationalization of Investigational Tools: Understanding the process for obtaining import permits and nationalizing investigational tools is critical for compliance and smooth trial execution.
-
Post-Market Surveillance: Planning for ongoing monitoring of the tool's performance after it reaches the market is critical. This surveillance helps ensure continued safety and efficacy, addressing any potential issues that may arise post-approval.
In light of recent updates in regulatory frameworks, such as the European Commission's introduction of new regulations in May 2017, which classify medical products into four risk classes, it is imperative for researchers to stay informed about current requirements. These regulations necessitate that medium- and high-risk products undergo pre-market authorization by a Notified Body, reflecting the evolving landscape of medical product regulation. With more than 20 years of experience in the Medtech sector, bioaccess® is well-prepared to support clients in navigating these changes effectively, providing comprehensive clinical research management services that include feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting on research status and adverse events.
By thoroughly understanding and adhering to these regulatory requirements, researchers can facilitate smoother research processes, ultimately enhancing the likelihood of successful product approval and advancing medical technologies more efficiently. bioaccess®'s unique value proposition lies in bridging the gap for innovative medtech companies in Latin America, ensuring that they can navigate the regulatory landscape with confidence and speed. Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for medical products and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, plays a pivotal role in guiding clients through these complex processes.
Methodological Considerations in User-Centered Device Trials
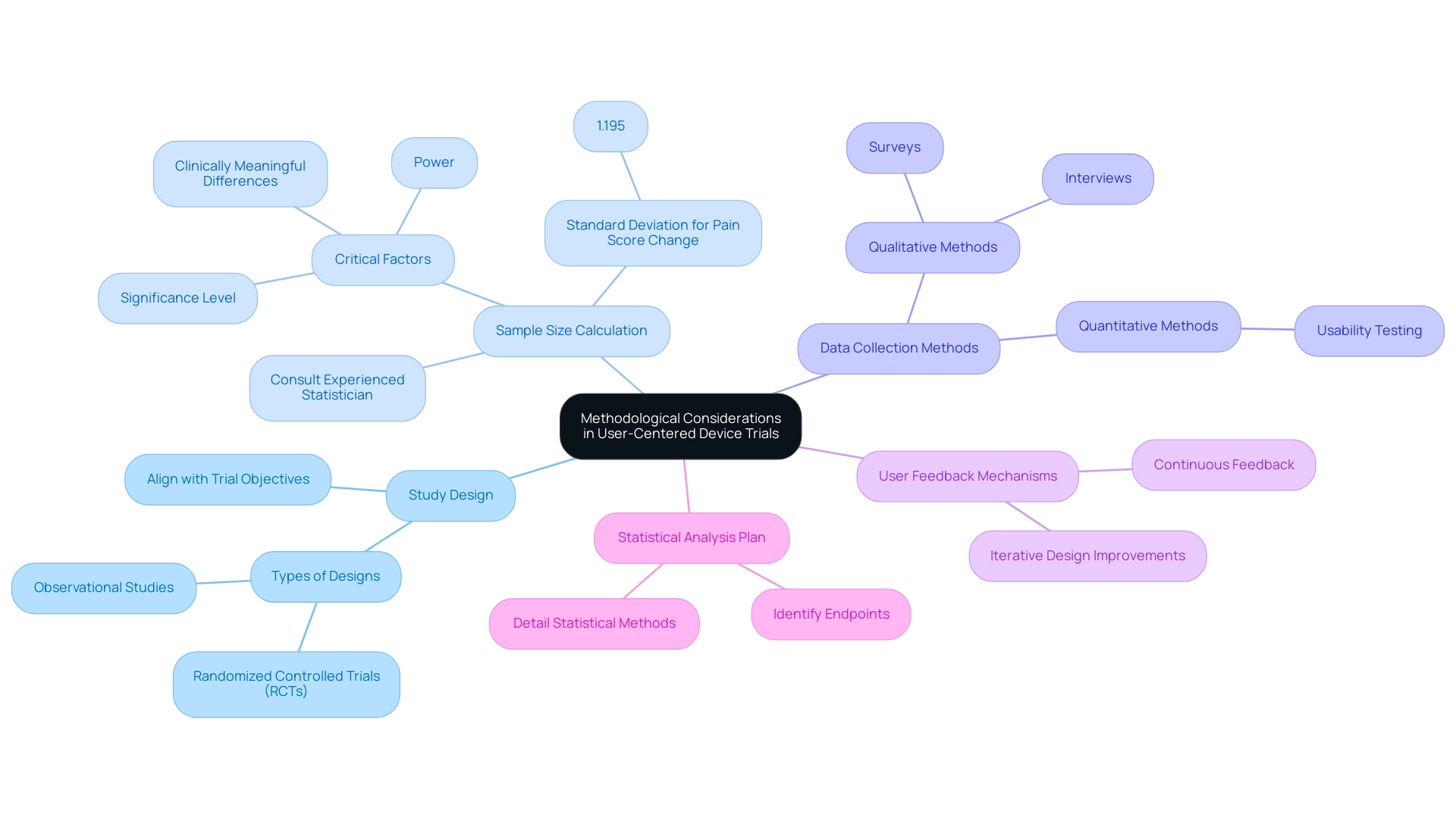
Designing user-centered device trials necessitates meticulous attention to several methodological considerations that can significantly influence the trial's success.
-
Study Design: It is imperative to select a design that aligns with the trial objectives, such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or observational studies. The choice of design is crucial as it directly impacts the reliability and applicability of the trial outcomes.
-
Sample Size Calculation: Accurate sample size estimation is essential to ensure the statistical power and validity of the results. A well-calculated sample size minimizes the risk of Type I and Type II errors, which could result in the rejection of effective devices or the approval of ineffective ones. For example, the standard deviation for the pain score change is 1.195, a critical factor in determining sample size. Consulting an experienced statistician is advisable to navigate the complexities of this process, as highlighted in the case analysis titled "Basic Rules for Estimating Sample Size in Clinical Trials." This analysis emphasizes the importance of significance level, power, and clinically meaningful differences in determining sample size. Francesca Botta, a Senior Biostatistician, notes, "Although techniques for sample size calculation are described in various statistical books, performing these calculations can be complicated, and it is desirable to consult an experienced biostatistician to estimate this vital study parameter."
-
Data Collection Methods: Employing a combination of qualitative and quantitative data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, and usability testing, is essential. This mixed-methods strategy enables a thorough comprehension of user experiences and equipment performance, offering deeper insights into the study's results.
-
User Feedback Mechanisms: It is crucial to establish mechanisms for continuous user feedback throughout the testing phase. This iterative process not only informs design improvements but also enhances user engagement and satisfaction, ultimately leading to better usability.
-
Statistical Analysis Plan: Formulating a clear statistical analysis plan is vital, outlining how the collected data will be analyzed. This involves identifying endpoints and detailing the statistical methods to be utilized, ensuring that the analysis aligns with the objectives and hypotheses of the study.
By meticulously addressing these methodological considerations, researchers can significantly enhance the effectiveness and reliability of designing user-centered device trials, paving the way for successful outcomes in the Medtech sector. Furthermore, bioaccess® plays an essential role in connecting innovative Medtech companies with unexplored opportunities for conducting research projects in Latin America. With over 20 years of experience, bioaccess® provides extensive clinical research management services, including feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting.
Their expertise in Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies ensures that medical companies can effectively navigate the complexities of the Latin American market.
The Role of Early-Feasibility and Pilot Studies
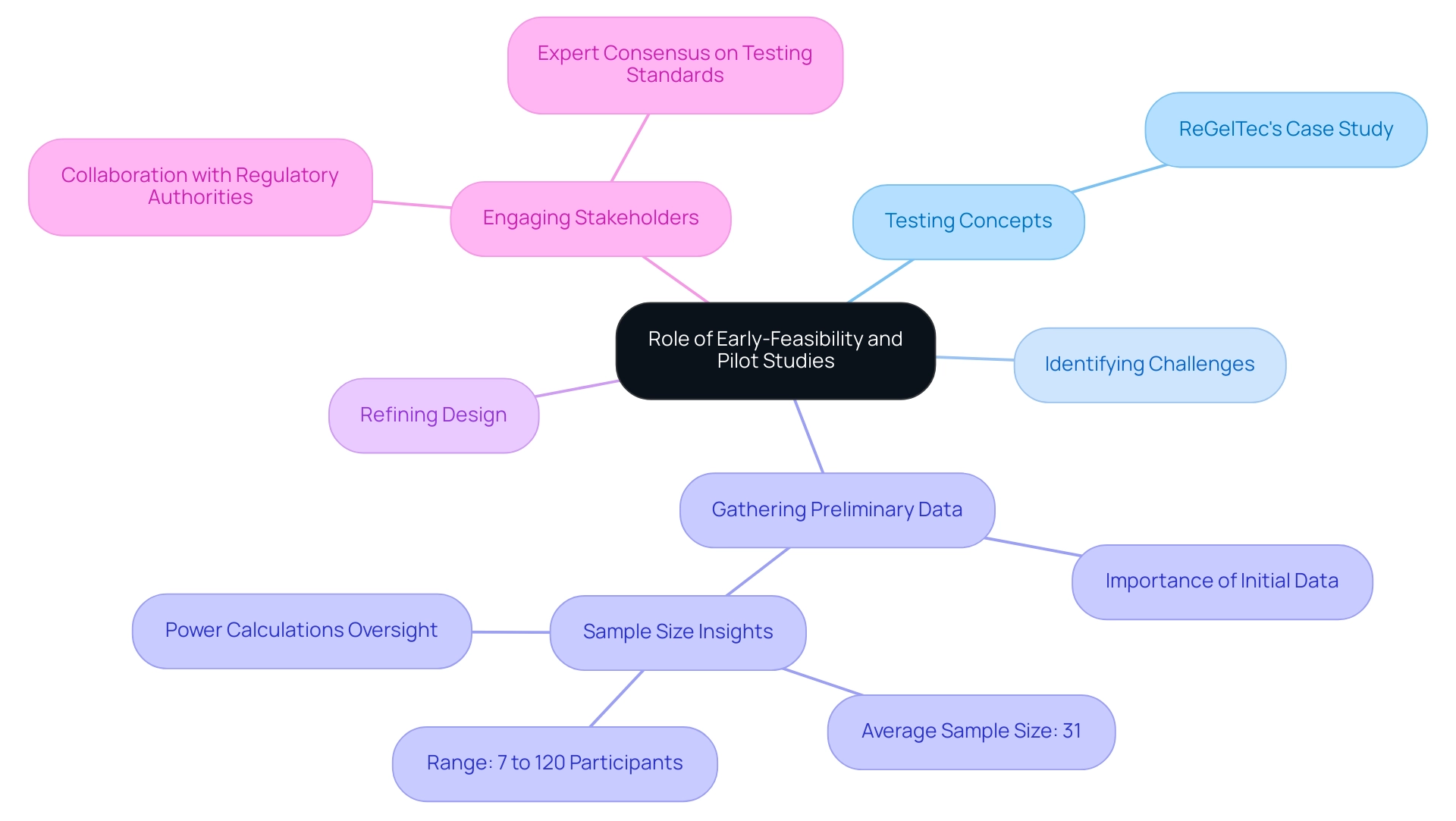
Preliminary assessments and pilot projects play a pivotal role in the effective advancement of medical devices, fulfilling various essential functions.
-
Testing Concepts: These evaluations empower researchers to evaluate the viability of device ideas in practical settings before embarking on comprehensive testing, ensuring that the design is both practical and user-friendly. A notable example is ReGelTec's Early Feasibility Assessment in Colombia, managed by bioaccess, which successfully treated eleven patients with chronic low back pain using their innovative HYDRAFIL™ treatment. This case exemplifies the practical application of early evaluations in real-world scenarios.
-
Identifying Challenges: Early assessments are instrumental in identifying potential challenges and user issues within the development process. This proactive approach allows teams to address these concerns prior to the commencement of larger trials, ultimately conserving both time and resources.
-
Gathering Preliminary Data: Early-feasibility evaluations provide essential initial information on safety and efficacy, which significantly guides further development and regulatory submissions. Such data is crucial for demonstrating the apparatus's potential to stakeholders and regulatory bodies. The success of ReGelTec's research underscores the importance of collecting this data early on.
-
Refining Design: These investigations facilitate iterative design improvements based on direct user feedback and performance observations. This iterative process is vital for user-centered device trials before progressing to more extensive testing phases.
-
Engaging Stakeholders: Early engagement with stakeholders, including regulatory authorities, is a key advantage of these analyses. This collaboration helps align expectations and requirements, fostering a smoother path to market entry. bioaccess® excels in this regard, leveraging over 20 years of expertise in overseeing clinical evaluations across Latin America, including Early-Feasibility and First-In-Human research.
The significance of pilot evaluations in clinical assessments is profound. Statistics reveal that pilot experiments often yield a success rate that greatly influences the outcomes of subsequent tests. For instance, a review of pilot research indicated an average sample size of 31 participants, ranging from 7 to 120.
However, many of these investigations did not perform power calculations, which are essential for ensuring the reliability of effect size estimates in future experiments. This oversight can result in inaccuracies in sample size projections for definitive trials, highlighting the necessity for meticulous planning in pilot projects. Furthermore, the lack of a structured framework for early-feasibility assessments in regions like Europe may impede early-stage R&D investments, diminishing the appeal of European investigation centers.
As observed, Italy has conducted five investigations, reflecting ongoing efforts in this domain. Expert consensus indicates that while these examinations are valuable, they should not replace thorough nonclinical testing or diminish the acceptability of trials. This agreement reinforces the importance of maintaining rigorous testing standards.
Moreover, optimal early-feasibility research locations should demonstrate a commitment to clinical research quality, established infrastructure, and a history of successful trial execution. By strategically integrating early-feasibility and pilot examinations into the development process, researchers can enhance the outcomes of designing user-centered device trials, significantly increasing the likelihood of successful equipment evaluations and enabling timely market entry.
Challenges in Clinical Research Management for Device Trials
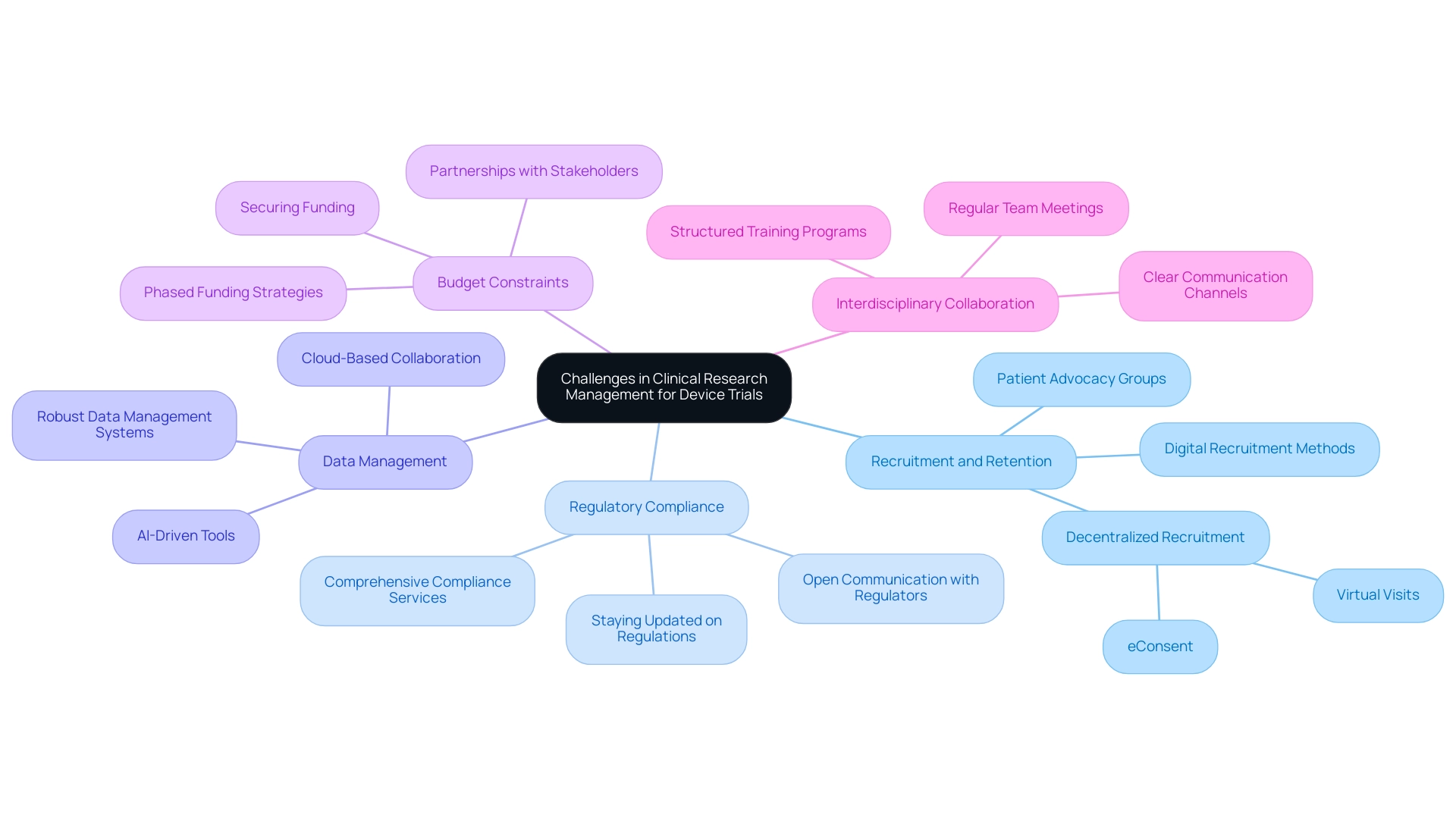
Clinical research management for device evaluations presents a range of challenges that can significantly influence the success of investigations. Key areas of concern include:
- Recruitment and Retention: The struggle to recruit and retain participants is a common hurdle that can stall trial progress. To combat this, leveraging digital recruitment methods and engaging with patient advocacy groups has proven effective. Recent analyses indicate a notable shift towards decentralized recruitment strategies, including the use of eConsent and virtual visits, which have gained traction in the post-pandemic landscape. Given that 80% of internet users search for health information online, utilizing online resources for recruitment is increasingly vital.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the intricate web of regulatory requirements can be daunting for researchers. Maintaining open lines of communication with regulatory bodies and staying abreast of evolving regulations are essential strategies to mitigate compliance challenges. This proactive approach not only ensures adherence but also fosters a collaborative relationship with regulators. bioaccess® provides extensive services that encompass feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, and import permits, ensuring that all regulatory aspects are meticulously managed.
- Data Management: Precise and prompt data gathering is essential for the integrity of medical studies. Implementing robust data management systems, coupled with comprehensive training for staff, enhances data accuracy and reliability. The integration of AI-driven tools and cloud-based collaboration platforms can further streamline data processes, making them more efficient and less prone to error. bioaccess® is committed to ensuring information security and client trust, with established grievance and data protection procedures to address any concerns regarding data handling. For any queries or concerns about the processing of your information, you may contact our Grievance Officer at IMH ASSETS CORP (doing business as "bioaccess®"), 1200 Brickell Avenue, Suite 1950 #1034, email: info@bioaccessla.com.
- Budget Constraints: Financial limitations often restrict the scope of clinical studies. As noted by M.H., Principal Investigator, "This study was funded by USANA Health Sciences, Inc.," highlighting the importance of securing funding. Prioritizing essential activities and actively seeking funding opportunities can help manage costs effectively. Innovative budgeting strategies, such as phased funding or partnerships with stakeholders, can also provide additional financial support. bioaccess® helps clients in exploring funding options to support their studies.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Coordinating efforts among diverse teams can pose significant challenges. Establishing clear communication channels and scheduling regular meetings can foster collaboration and ensure that all team members are aligned with the project's objectives. The preparation and advancement of a research group, as demonstrated in a recent case example, highlights the significance of organized training efforts that improve team skills in overseeing equipment tests.
By actively tackling these challenges, researchers can greatly improve the efficiency and efficacy of research management in equipment studies, particularly through designing for user-centered device trials, ultimately resulting in more favorable outcomes. With bioaccess®'s expertise in accelerated medical product clinical study services in Latin America, including Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies, clients can navigate the complexities of clinical research with confidence.
Best Practices for Successful User-Centered Device Trials
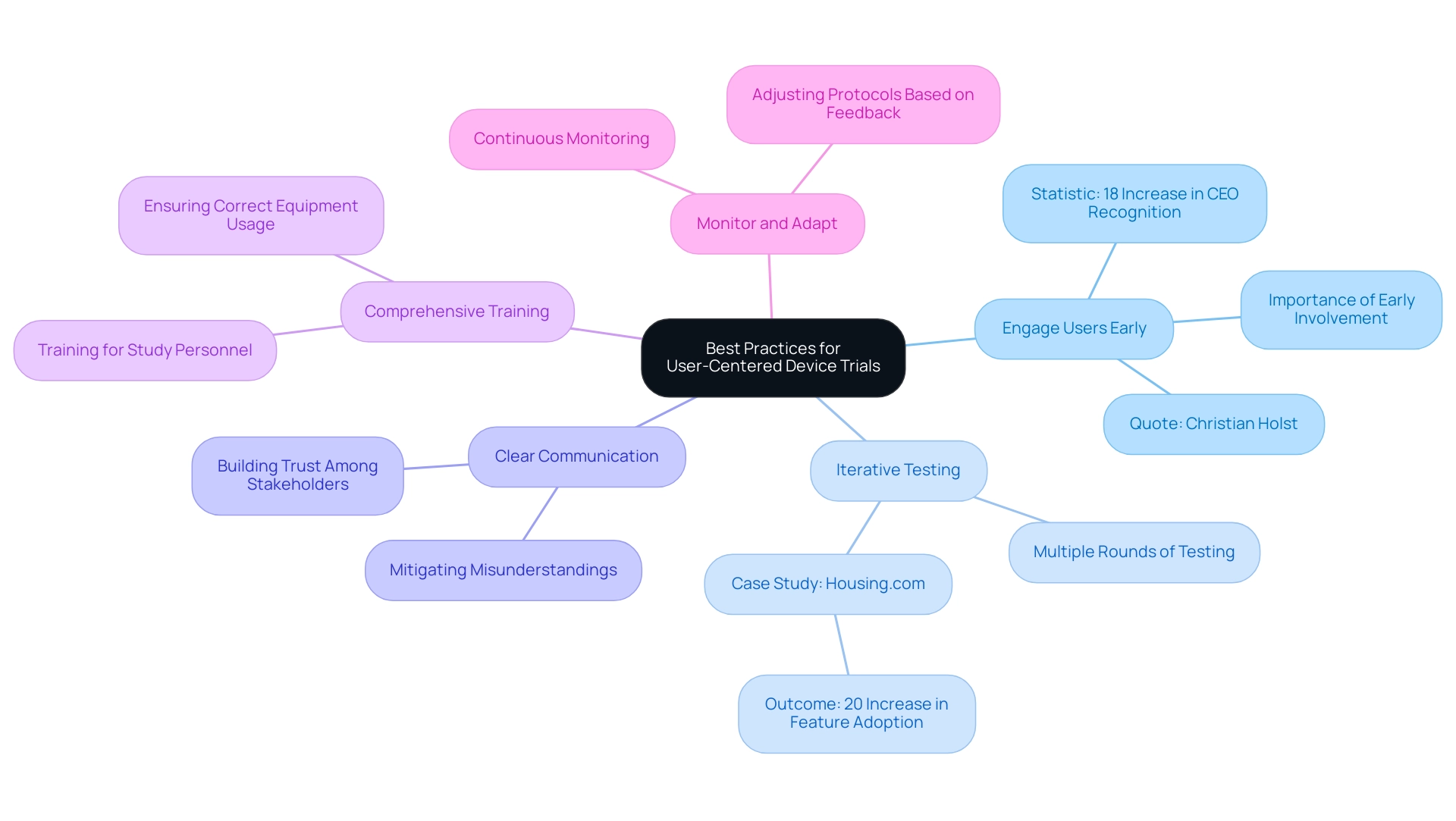
To ensure the success of user-centered device trials, implementing the following best practices is essential:
-
Engage Users Early: Involving users from the initial design and testing phases is crucial. Early involvement enables researchers to collect valuable insights and feedback, significantly impacting the study's direction and outcomes. A notable statistic highlights that the percentage of enterprise CEOs recognizing user experience as a competitive differentiator rose by 18% in 2019, underscoring the growing importance of user-centric approaches. As Christian Holst, Research Director and Co-Founder at Baymard, emphasizes, 'User experience is not just a nice-to-have; it is a critical component that can determine the success of a clinical study.'
-
Iterative Testing: Conducting multiple rounds of testing and refinement is vital to address usability issues before the main trial. This iterative process not only enhances the device's functionality but also fosters user confidence. For instance, a case study involving Housing.com demonstrated that redesigning its search functionality to improve user experience led to a 20% increase in feature adoption, illustrating the tangible benefits of iterative testing.
-
Clear Communication: Maintaining transparent communication with all stakeholders—including participants, regulatory bodies, and team members—is essential for building trust and ensuring everyone is aligned with the objectives of the study. Effective communication can mitigate misunderstandings and enhance collaboration throughout the process. The incorporation of foundational elements in clinical research promotes excellence and nurtures trust among stakeholders, which is essential for designing user-centered device trials.
-
Comprehensive Training: Offering extensive training for study personnel and participants is essential to guarantee the correct usage of the equipment and compliance with protocols. Well-prepared participants are more likely to interact effectively with the system, resulting in more dependable data gathering and enhanced study results.
-
Monitor and Adapt: Continuously monitoring progress and being prepared to adjust protocols based on real-time feedback and observations is key to addressing unforeseen challenges. This flexibility can lead to better outcomes and a more user-friendly experience.
By following these best practices, researchers can significantly improve the chances of successful outcomes when designing user-centered device trials. bioaccess® plays a crucial role in connecting innovative medtech companies and carrying out research projects in Latin America, ultimately promoting the advancement of medical technologies that enhance lives. With more than 20 years of expertise, bioaccess® provides extensive research management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance evaluations, setup, import permits, project oversight, and reporting, ensuring that studies are conducted efficiently and effectively in the diverse Latin American market.
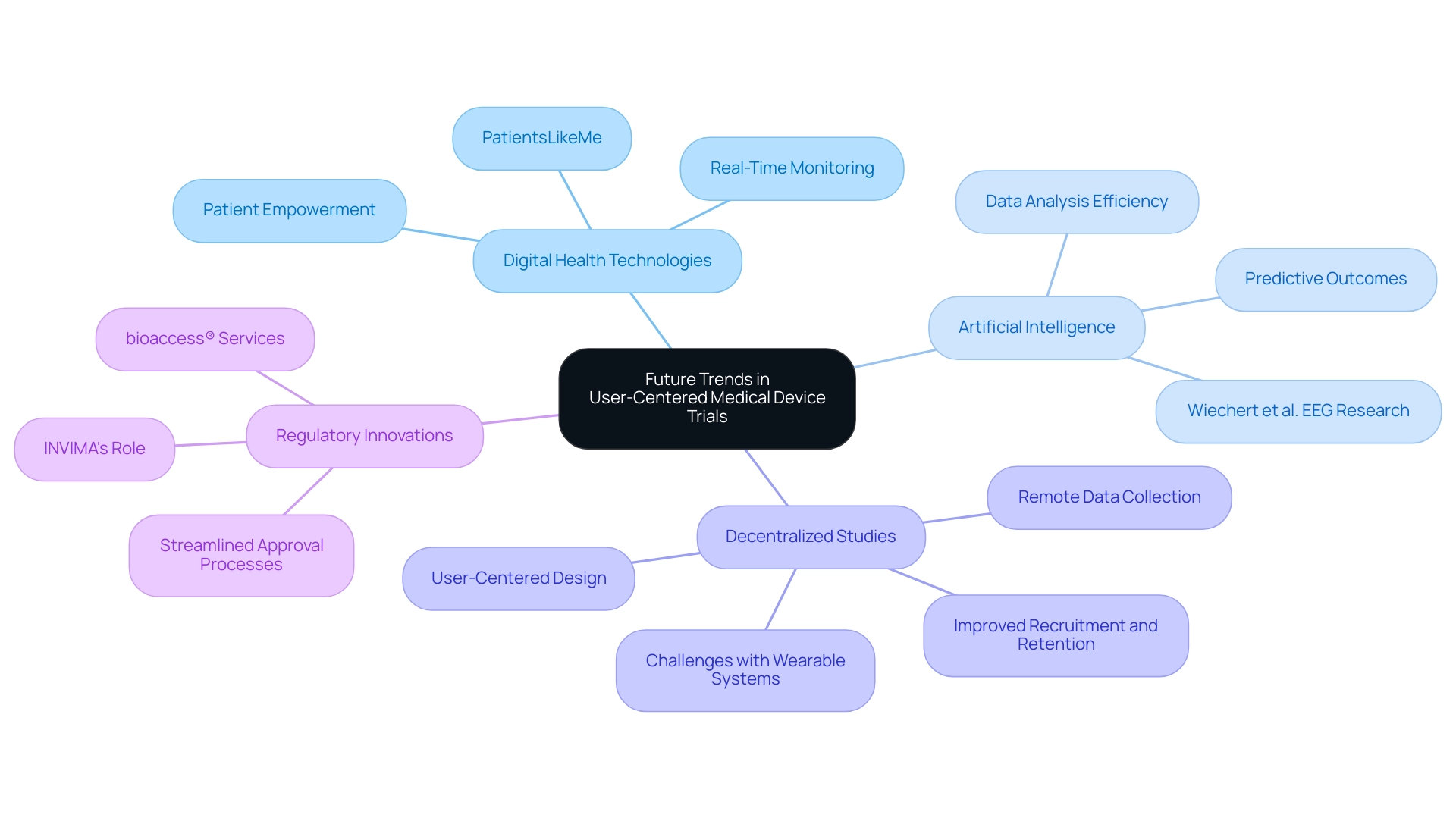
Future Trends in User-Centered Medical Device Trials
The landscape of user-centered medical device evaluations is experiencing a significant transformation, driven by several key trends reshaping research methodologies and outcomes.
-
Digital Health Technologies: The integration of digital health technologies, such as telemedicine and mobile health applications, is revolutionizing patient engagement and data collection. For instance, PatientsLikeMe tracks over 200,000 patients and monitors 1,500 illnesses, underscoring the scale of patient engagement in digital health. These tools not only facilitate real-time monitoring but also empower patients to take an active role in their health management, ultimately enhancing the quality of data gathered during studies.
-
Artificial Intelligence: The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in clinical studies is becoming increasingly prevalent. AI algorithms are utilized to analyze extensive amounts of data efficiently, uncovering patterns and predicting outcomes. This capability leads to more informed decision-making and can significantly reduce the time required to bring medical devices to market. Innovative applications, such as Wiechert et al.'s research on EEG brain waves, demonstrate how technology can identify individuals and their activities, further illustrating the potential of AI in medical environments.
-
Decentralized Studies: A notable shift towards decentralized studies is enhancing flexibility and accessibility for participants. This approach allows for remote data collection and monitoring, which can improve recruitment and retention rates. Decentralized trials cater to a broader demographic, including those in underserved regions, by minimizing the need for participants to travel to clinical sites. Moreover, they emphasize designing for user-centered device trials. This focus on usability and satisfaction not only enhances participant experience but also increases the likelihood of successful outcomes, as tools are customized to fulfill actual user needs. The challenges of integrating new wearable systems, particularly in balancing additional functions with energy consumption, highlight the complexities involved in achieving this goal.
-
Regulatory Innovations: Regulatory bodies, such as INVIMA in Colombia, are evolving alongside technological advancements, adapting their frameworks to accommodate new methodologies. As a Level 4 health authority recognized by PAHO/WHO, INVIMA plays a crucial role in overseeing medical equipment regulations, ensuring compliance and safety. This responsiveness is streamlining approval processes for innovative devices, allowing for quicker access to the market while maintaining safety and efficacy standards. The comprehensive clinical trial management services provided by bioaccess®, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, are essential in navigating this complex landscape.
Conclusion
User-centered design (UCD) stands as a cornerstone in medical device trials, significantly enhancing functionality, safety, and patient satisfaction. By prioritizing the needs of patients and healthcare providers, UCD ensures that devices are both intuitive and effective. Essential components such as user research, prototyping, and iterative testing play a crucial role in achieving positive patient outcomes.
Successful trial design hinges on adherence to fundamental principles, including:
- Clear objectives
- User involvement
- Regulatory compliance
Emphasizing critical-to-quality factors like patient safety and data integrity is vital for meticulous planning and execution. As regulations evolve, a thorough understanding of compliance becomes necessary to streamline trial processes and expedite market access.
Emerging trends, including digital health technologies, artificial intelligence, and decentralized trials, are reshaping UCD in medical device development. These innovations not only enhance patient engagement but also optimize data collection, contributing to more efficient clinical research.
In conclusion, the integration of UCD principles and best practices in medical device trials is pivotal for advancing healthcare solutions. By focusing on user needs and leveraging technological advancements, the medical device industry can improve patient care and outcomes, leading to the development of more effective and user-friendly devices. Embracing these methodologies will undoubtedly foster a brighter future for healthcare technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is user-centered design (UCD) in the context of medical products?
User-centered design (UCD) is an iterative process that prioritizes the user throughout the development of medical products, focusing on understanding the needs, preferences, and limitations of end-users, including patients and healthcare providers.
What are the key components of user-centered design?
The key components of UCD include: User Research, which involves engaging in interviews, surveys, and observational studies to gather insights into user needs and experiences; Prototyping, which develops initial product versions for usability testing and user feedback; and Iterative Testing, which continuously refines the product based on user feedback to align with user expectations.
How does user-centered design impact medical research and patient outcomes?
Designing for user-centered device trials can lead to improved patient outcomes and greater user satisfaction, as products developed with this approach are more functional, intuitive, and safe.
What findings support the effectiveness of user-centered design in medical devices?
A study on the iMHere system, which assists individuals with disabilities, showed that redesigned modules significantly improved usability, leading to better self-management and independence for users.
What is the significance of user involvement in medical device trials?
Actively engaging users throughout the design process is crucial as their insights help shape devices that meet real-world needs, enhancing user acceptance and satisfaction, and increasing the likelihood of trial success.
What principles should be followed when designing medical device trials?
Key principles include establishing clear objectives, ensuring regulatory compliance, engaging users, employing robust methodologies, maintaining data integrity, and being prepared for challenges.
What are critical-to-quality (CtQ) factors in medical equipment studies?
CtQ factors include patient safety, data quality, protocol adherence, stakeholder engagement, and risk management, all of which significantly influence the success of clinical trials.
Why is patient safety prioritized in clinical trials?
Patient safety is the foremost priority to ensure participants are not at undue risk, which enhances the credibility of the study results.
How does bioaccess® contribute to the design and execution of medical device trials?
Bioaccess® offers expertise in navigating regulatory environments, facilitating stakeholder engagement, and managing clinical studies, ensuring adherence to best practices and effective risk management.

