Overview
This article delineates the step-by-step process of designing Medtech trials for FDA approval, meticulously detailing the various phases involved, from preclinical studies to post-market surveillance. It underscores the critical importance of each phase in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices. Well-structured trial designs and strict adherence to regulatory guidelines are paramount for successful market entry and ongoing patient safety. Understanding this process is essential for stakeholders in the clinical research landscape, particularly as they navigate the complexities of regulatory requirements.
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of healthcare, medical device clinical trials are pivotal in ensuring that innovative technologies are both safe and effective for patient use. These trials are meticulously structured into distinct phases, each designed to tackle specific challenges and gather essential data. From the initial preclinical studies that establish the groundwork for human testing to post-market surveillance that monitors long-term safety, grasping the intricacies of this process is vital for professionals in the Medtech sector.
As the demand for advanced medical solutions escalates, so does the complexity of navigating regulatory pathways and integrating cutting-edge technologies into trial designs. This article explores the various stages of medical device clinical trials, emphasizing the significance of:
- Pilot studies
- Regulatory compliance
- The incorporation of human factors engineering
Ultimately, these elements contribute to the successful development and approval of medical devices.
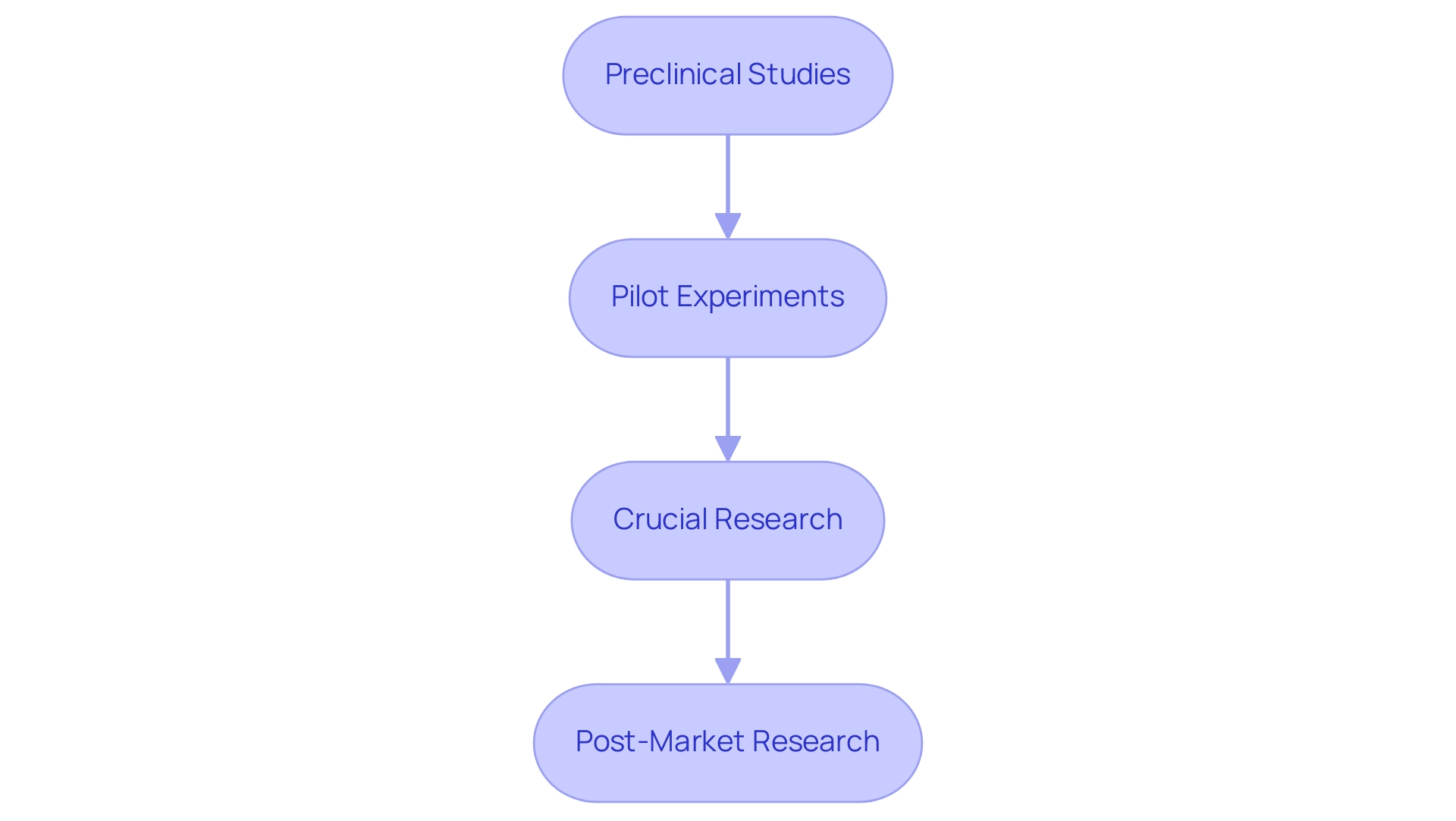
Understanding Medical Device Clinical Trials
Medical equipment clinical studies represent meticulously organized investigations designed to assess the safety and efficacy of medical instruments. These trials are typically divided into several distinct phases, each serving a specific purpose in the overall research process:
- Preclinical Studies: Before human testing, instruments undergo thorough laboratory evaluations to ascertain their safety, functionality, and potential risks. These investigations are essential for identifying any issues before advancing to human testing, ensuring that only the most promising devices proceed.
- Pilot Experiments: These small-scale investigations aim to assess the viability of the design and collect initial data. They help refine methodologies and identify any logistical challenges that may arise during larger trials.
- Crucial Research: Representing a critical phase, crucial research involves larger participant groups and aims to provide definitive evidence regarding the equipment's safety and efficacy. The data collected during this phase is vital for regulatory submissions and can significantly influence approval timelines.
- Post-Market Research: Once an apparatus is available to consumers, continuous evaluations are conducted to assess long-term safety and effectiveness. These studies are crucial for ensuring that any potential issues are identified and addressed promptly, thereby safeguarding patient health.
Understanding these stages is essential for experts engaged in Medtech trial design for FDA approval and the implementation of medical studies for health instruments. Each stage of the Medtech trial design informs the planning and regulatory submission processes, ultimately impacting the speed and success of bringing innovative medical technologies to market.
With over 15 years of experience in the Medtech sector, bioaccess® recognizes the growing demand for innovative solutions in healthcare. Recent statistics suggest that by 2025, the number of medical device studies conducted will experience a significant rise. Moreover, professional insights underscore the importance of preclinical research, which serves as the foundation for effective clinical evaluations.
As the industry evolves, integrating advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning into study design is becoming increasingly common, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. A case analysis on AI-driven medication development illustrates this trend, indicating how these technologies are anticipated to improve testing outcomes and expedite the approval process.
Furthermore, the transition towards risk-based methods in clinical trials is expected to enhance data quality, increase resource efficiency, and shorten timelines, resulting in quicker approvals and reduced trial expenses. As noted by the Head of Clinical Data Engineering, "Traditionally, data management was outsourced to our CRO vendor partners. Part of the initiative is to bring all our research in-house so that our internal teams can start working on it. They can be more hands-on, and we operationalize studies in-house and we are able to take control of our data, and we deliver for our patients with high quality." This highlights the significance of in-house data management for preserving quality and control, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Moreover, bioaccess® is committed to ensuring information security and client trust throughout the research process. The company has established grievance and data protection procedures to address client concerns with compliance and transparency. Partnerships, such as the one between bioaccess® and Caribbean Health Group, aim to establish Barranquilla as a premier location for medical studies in Latin America, supported by Colombia's Minister of Health.
In addition, collaborations with entities like GlobalCare Clinical Trials have improved research ambulatory services in Colombia, resulting in over a 50% decrease in recruitment time and 95% retention rates. These initiatives reflect bioaccess®'s commitment to advancing research and enhancing patient outcomes in the region.
Stages of Medical Device Clinical Trials: From Pilot to Post-Market
The clinical study process for medical devices is structured into several critical stages, each serving a distinct purpose in the development and evaluation of new technologies:
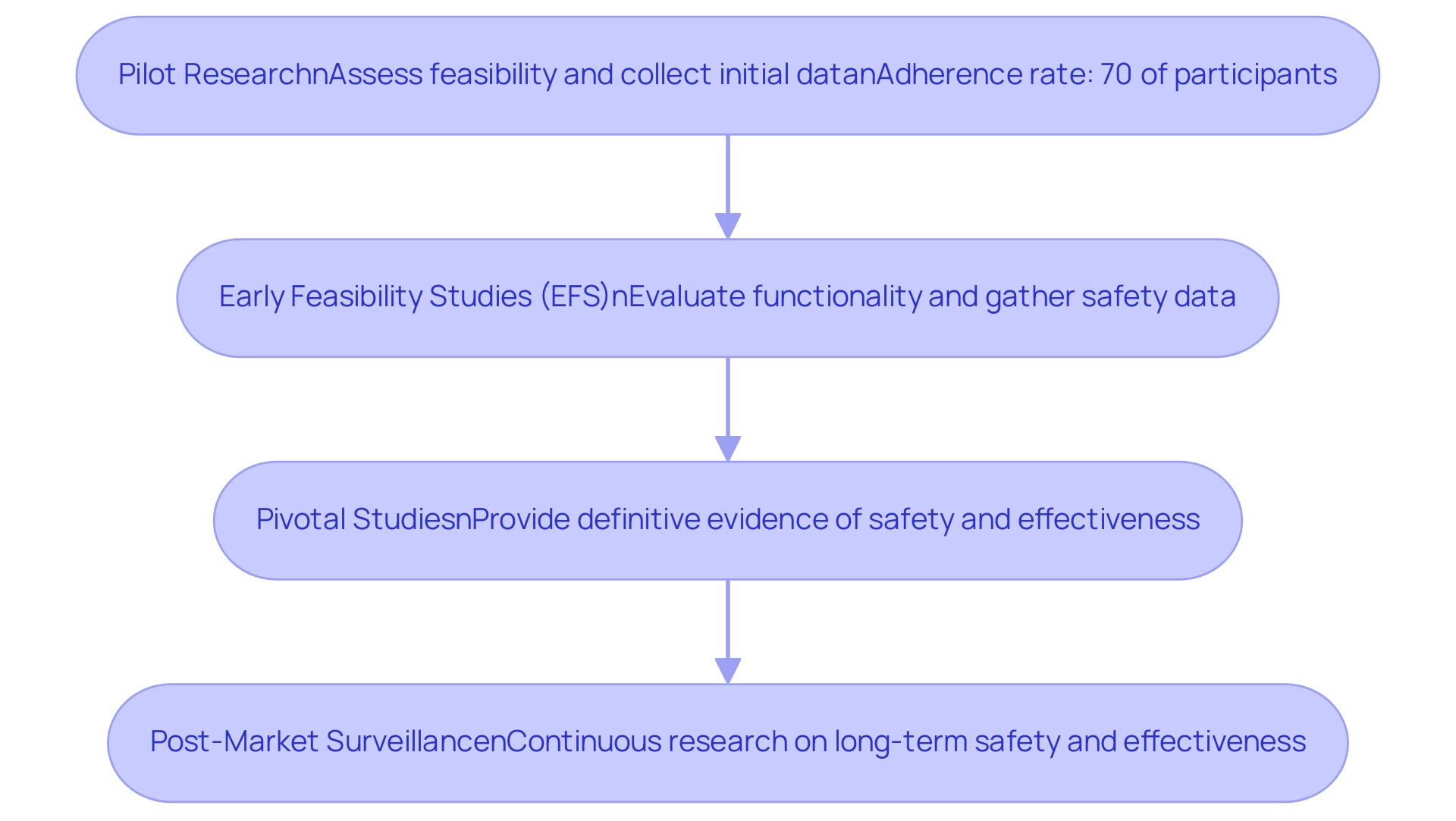
- Pilot Research: These preliminary investigations are essential for assessing the feasibility of the trial design and collecting initial data on safety and efficacy. Typically involving a small group of participants, pilot experiments help identify potential challenges and inform subsequent research designs. Recent benchmarks suggest that adherence rates in pilot trials should aim for at least 70 percent of participants attending a minimum of eight out of twelve scheduled sessions to ensure robust data collection. Companies like bioaccess® utilize their extensive experience in managing pilot projects to navigate the unique challenges of the Latin American market, ensuring that local nuances are considered in the trial design.
- Early Feasibility Studies (EFS): Conducted early in the development process, EFS are crucial for evaluating the functionality of the medical instrument and gathering initial safety data from a limited patient population. These studies allow researchers to make informed adjustments to the device and study design based on real-world feedback. For instance, ReGelTec's recent EFS for HYDRAFIL™ in Colombia demonstrated the effectiveness of remote proctoring, showcasing how innovative approaches can enhance execution in Latin America. Current trends indicate a growing emphasis on utilizing pilot study data to refine EFS, which is crucial for Medtech trial design for FDA approval, ensuring that the insights gained are effectively integrated into the design of full-scale studies.
- Pivotal Studies: These larger, controlled experiments are designed to provide definitive evidence regarding the safety and effectiveness of the device for its intended use. Successful completion of essential research is often a prerequisite for Medtech trial design for FDA approval, making it a crucial element of the clinical testing process. Sample size calculations for these investigations should be based on clinically meaningful differences rather than solely on pilot estimates, ensuring that the results are statistically significant and applicable to broader patient populations. bioaccess® provides extensive assistance in crucial research design, aiding clients in navigating regulatory demands and enhancing project outcomes through their specialized methodologies and expertise.
- Post-Market Surveillance: After a product obtains approval and enters the market, continuous research is carried out to observe its long-term safety and effectiveness. This stage is vital for ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and addressing any emerging safety concerns. By continuously gathering data post-approval, manufacturers can enhance patient care and maintain trust in their products. bioaccess® highlights the significance of strong post-market monitoring strategies to guarantee that medical devices consistently adhere to safety and effectiveness standards in various markets.
Recent advancements in research studies, such as those executed by companies like Alcon, aim to enhance site experiences by simplifying data entry procedures and alleviating the load on research locations. For instance, a Senior Director within a global biopharma’s clinical sciences and research management group noted that eliminating one 20-minute task per visit across 130,000 visits avoids 43,000 hours of work, allowing Cras to focus on what matters. These advancements not only improve data precision but also promote better patient care and study outcomes.
As the landscape of medical equipment trials evolves, the integration of pilot study insights into EFS and pivotal studies will be crucial for advancing the development of safe and effective medical technologies.
Navigating Regulatory Pathways for FDA Approval
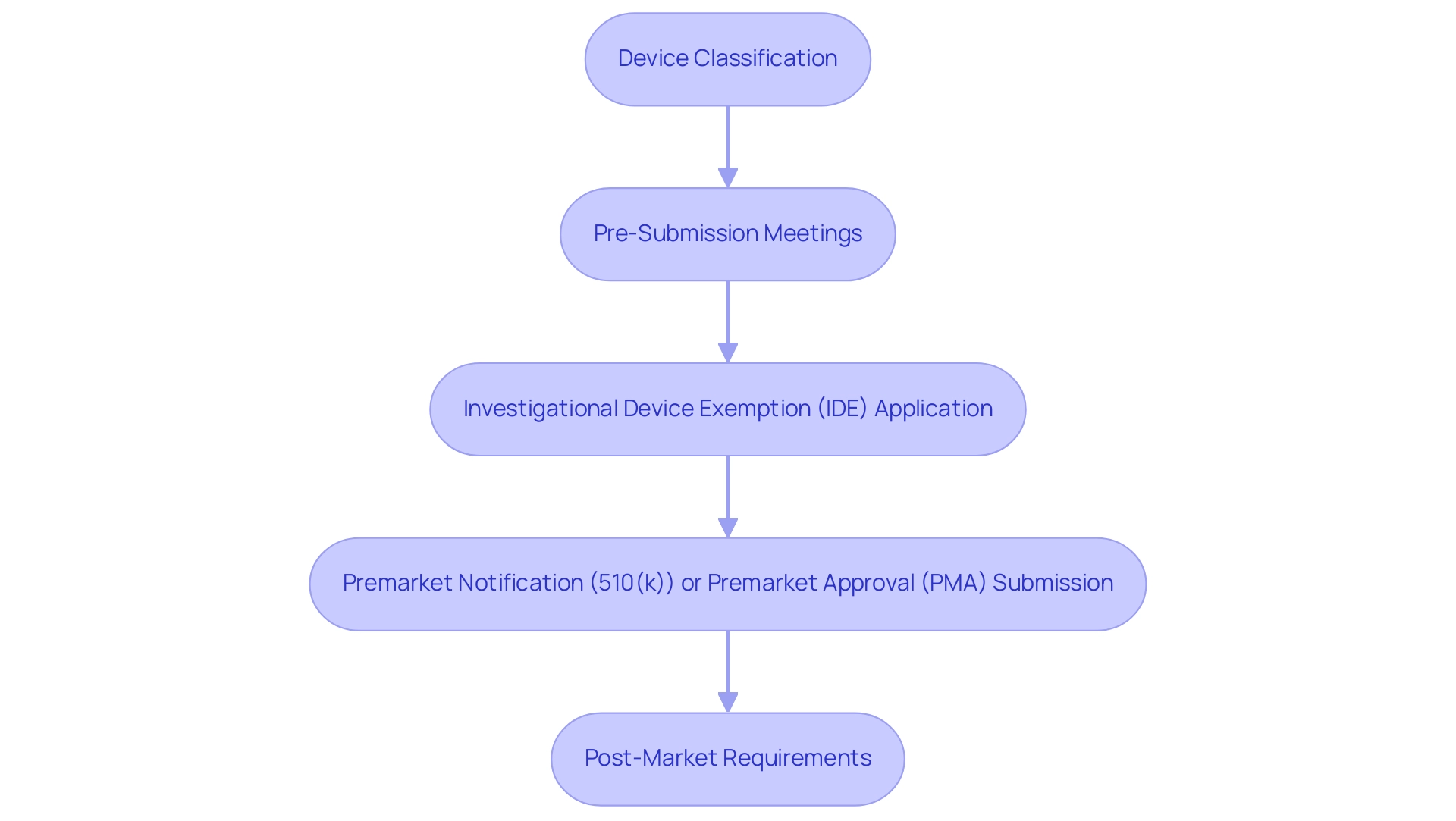
Navigating the regulatory pathways for FDA approval involves several critical steps that ensure compliance and facilitate the successful introduction of medical products to the market.
The first step is Device Classification, determining the classification of the equipment as Class I, II, or III based on its risk level. This classification is pivotal as it dictates the regulatory requirements and the pathway for approval. For instance, Class I devices typically require the least regulatory control, while Class III devices, which pose the highest risk, necessitate more stringent oversight.
Pre-Submission Meetings are essential for engaging with the FDA early in the process. These discussions enable developers to present their proposed Medtech trial design for FDA approval and receive valuable feedback, which can significantly streamline the approval process and address potential concerns before formal submission. If research studies are necessary, submitting an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) application is crucial. This application permits the use of an unapproved instrument in clinical trials, allowing for the collection of safety and effectiveness data. In 2025, the number of IDE applications submitted reflects the growing interest in innovative medical technologies, underscoring the importance of this step.
Depending on the classification, the next step involves submitting either a Premarket Notification (510(k)) application for products that are substantially equivalent to existing ones or a Premarket Approval (PMA) application for high-risk items that require more comprehensive evidence of safety and efficacy. Understanding the nuances of these submissions is vital for successful navigation through the regulatory landscape.
After receiving FDA approval, manufacturers must comply with Post-Market Requirements. This ongoing monitoring is essential to ensure the performance and safety of the equipment in the general population, contributing to public health and safety. Complying with these requirements not only meets regulatory obligations but also fosters trust with users and stakeholders.
In 2009, there were a total of 1,978 FDA inspections of medical establishments, highlighting the regulatory oversight in this sector. Continuous training and education are essential for teams to stay informed about regulatory changes, which is crucial for navigating the FDA approval process. Additionally, examining the European Regulations for Medical Devices can provide valuable insights. In Europe, medical devices are governed by strict regulations that ensure safety and effectiveness, serving as a benchmark for understanding the FDA's requirements, particularly in the context of Medtech trial design for FDA approval. As noted by Donald Trump regarding the Executive Order on AI, the regulatory environment is evolving, and it is important for Medtech companies to stay ahead of these changes to maintain compliance and foster innovation. By diligently following these steps in their Medtech trial design for FDA approval, companies can effectively navigate the complexities of FDA approval, ensuring that their innovative devices reach the market efficiently and safely.
bioaccess® plays an essential role in this environment by connecting innovative Medtech companies in Latin America, enabling research projects that promote the progress of medical technologies. Our comprehensive services encompass feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup of experiments, import permits, project management, reporting (study status, inventory, serious and non-serious adverse events), and grievance procedures to ensure client trust and compliance. Moreover, with Colombia's competitive strengths like cost efficiency, regulatory speed, and high-quality healthcare, bioaccess® is well-situated to assist first-in-human studies, boosting the overall success of medical device development.
Reach out to discover how bioaccess® can assist with your research requirements.
The Role of Pilot and Early Feasibility Studies in Trial Design
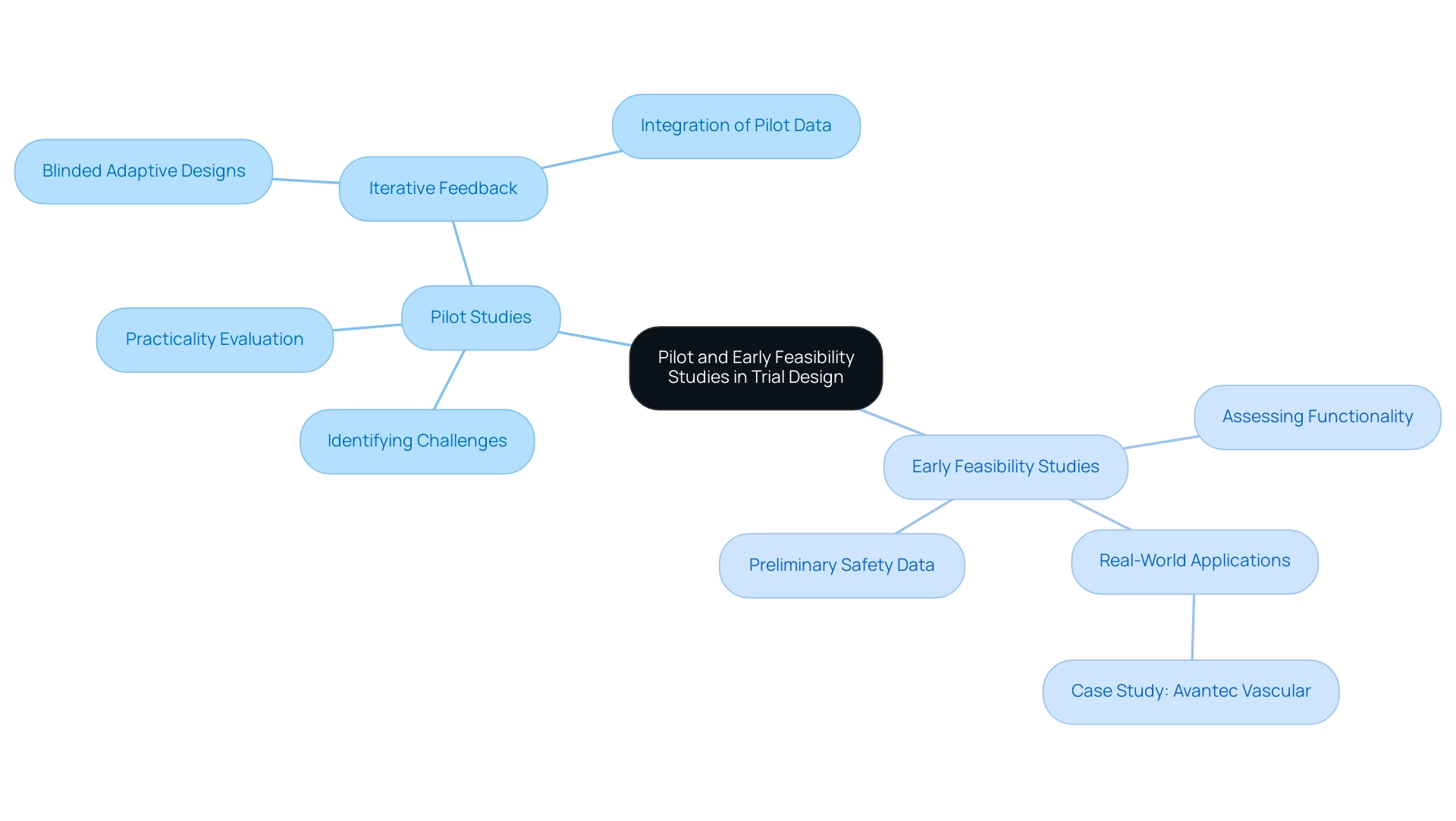
Pilot and early feasibility studies are integral components of the clinical trial process, serving distinct yet complementary roles.
Pilot Studies: These small-scale investigations are essential for identifying potential challenges in study design, including recruitment strategies and data collection methodologies. Pilot experiments are frequently utilized to evaluate the practicality of starting broader investigations, offering essential insights that guide the structure of more extensive research. Notably, pilot experiments do not typically require formal statistical power calculations, allowing for flexibility in their execution. Bioaccess® leverages its extensive experience in managing pilot trials to ensure that potential obstacles are addressed early in the trial process, thereby enhancing the likelihood of success.
Early Feasibility Studies (EFS): EFS are crucial in assessing a medical instrument's functionality and collecting preliminary safety data. Conducted in real-world environments, these investigations enable researchers to evaluate the apparatus's performance and implement necessary modifications before progressing to larger critical trials. The success percentages of EFS in medical assessments have demonstrated encouraging patterns, with numerous investigations reporting improved results due to the knowledge acquired during this phase. For instance, bioaccess® has supported Avantec Vascular in their first-in-human trial of an innovative vascular device in Latin America, showcasing the effectiveness of EFS in real-world applications.
Iterative Feedback: Both pilot and EFS facilitate iterative feedback loops, allowing researchers to refine their methodologies and enhance the likelihood of success in subsequent clinical study phases. This iterative process is crucial, as it helps to mitigate risks and improve the overall design of the trial. For instance, case analyses have highlighted the inadequacies of traditional sample size rules in pilot experiments, advocating for more sophisticated approaches that integrate pilot data into final evaluations. The case analysis titled 'Sample Size for Pilot Investigations: A Quick Guide for Biostatisticians' emphasizes that blinded adaptive designs can enhance power and facilitate the integration of pilot data into final analyses, leading to more effective outcomes. Additionally, the case analysis 'Misuses of Pilot Studies' warns against concentrating on inappropriate outcomes, stressing the importance of evaluating feasibility and acceptability rather than safety evaluations.
The significance of these investigations cannot be exaggerated, as they establish the foundation for successful Medtech trial design for FDA approval in the Medtech field. With over 20 years of experience in the Medtech sector, bioaccess® bridges the gap between innovative device development and thorough assessment, emphasizing that Medtech trial design for FDA approval, along with pilot and early feasibility evaluations, are crucial for advancing medical technologies and ensuring their safety and effectiveness in real-world applications. As Keefe RS pointed out, defining a clinically meaningful effect is essential for the design and interpretation of randomized controlled experiments, further underscoring the importance of pilot investigations and EFS in clinical research.
Furthermore, for those interested in managing cookie preferences related to our digital presence, you can change your cookie settings at any time, ensuring a tailored experience while navigating our services.
Conducting Pivotal Studies: Key Considerations
Conducting crucial research in the Medtech sector necessitates meticulous planning and execution, particularly in the Medtech trial design for FDA approval, to ensure successful outcomes. Here are key considerations to keep in mind:
-
Research Design: Choosing a suitable research design, such as a randomized controlled trial, is essential. This choice should align with the project's objectives and comply with regulatory requirements, ensuring that the design effectively addresses the research questions. At bioaccess®, we leverage over 20 years of Medtech expertise to guide the Medtech trial design for FDA approval, including Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up trials, ensuring they meet both scientific and regulatory standards.
-
Sample Size Calculation: Accurate sample size determination is vital for the statistical power and validity of the results. Research indicates that a recommended sample size to accommodate a 20% nonresponse rate is 245 participants. This calculation must be approached with caution, as it often relies on assumptions that may not hold true. As Alaa Althubaiti notes, "sample size calculation is challenging and often relies on certain assumptions, which are rarely accurate." Consulting experienced biostatisticians can significantly enhance the accuracy of these estimations, preventing underpowered or overpowered research that could lead to ethical dilemmas and inconclusive results. A case analysis titled 'Importance of Sample Size Calculation in Clinical Research' emphasizes the critical role of sample size determination, highlighting its implications for methodological, ethical, and financial perspectives in clinical trials.
-
Endpoints: Clearly defining primary and secondary endpoints is essential for assessing the safety and effectiveness of the medical device. These endpoints should be measurable and relevant to the goals of the research, providing a clear framework for evaluating outcomes. At bioaccess®, we ensure that endpoints are aligned with regulatory expectations, particularly in the context of INVIMA's oversight in Colombia.
-
Data Management: Implementing robust data management practices is critical to maintaining data integrity and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. This includes establishing protocols for data collection, storage, and analysis, which are fundamental to the credibility of the research. Our extensive healthcare study management services include these practices, ensuring that all data is handled with the utmost care.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to FDA regulations and Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines is paramount. Ensuring that all aspects of the research meet these standards is crucial for effective Medtech trial design for FDA approval, facilitating a smoother approval process and enhancing the likelihood of successful commercialization. With bioaccess® as your partner, you can navigate the complexities of regulatory compliance in Latin America, particularly with INVIMA's classification as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
In summary, crucial research in medical device evaluations necessitates a thorough approach that includes careful design, accurate sample size calculations, clearly defined endpoints, meticulous data management, and stringent regulatory adherence. By concentrating on these key areas, researchers can significantly enhance the likelihood of their investigations producing valid and impactful results. Moreover, it is crucial to recognize the ethical consequences of improper sample size calculations, as negligence in this area can lead to the rejection of effective treatments or the approval of ineffective ones.
Additionally, the impact of Medtech clinical studies extends beyond the trials themselves, contributing to local economies through job creation, economic growth, and healthcare improvement.
Post-Market Surveillance: Ensuring Long-Term Safety and Efficacy
Post-market surveillance is a crucial component of the medical product lifecycle, ensuring that items continue to meet safety and efficacy standards after they reach the market. This process involves several key components:
-
Monitoring Equipment Performance: Once a product is available to consumers, manufacturers are responsible for ongoing monitoring of its performance and safety in real-world environments. This vigilance helps identify potential issues that may arise post-launch, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments. At bioaccess®, our expertise in overseeing post-market clinical follow-up evaluations (PMCF) ensures that we effectively monitor product performance, leveraging over 20 years of experience in Medtech.
-
Reporting Adverse Events: Establishing a robust system for reporting and analyzing adverse events is crucial. This system should facilitate the prompt identification of safety concerns, enabling manufacturers to respond swiftly and effectively. In 2025, regulatory frameworks such as the Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation are increasingly recognized for their role in accelerating approval for promising therapies, highlighting the importance of diligent monitoring and reporting practices. bioaccess® is committed to maintaining compliance with these evolving regulations, ensuring that our clients can trust our processes.
-
Extended Research: Carrying out extended research is crucial for evaluating the continuous efficacy and safety of medical instruments. These investigations collect essential information that may not have been recorded during pre-market trials, offering insights into the apparatus's performance over time. Recent case studies have shown that long-term follow-up can reveal significant safety issues that emerge only after widespread use. Our focus on Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, and Pivotal Studies positions us to gather valuable data that informs long-term safety assessments.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to FDA requirements for post-market surveillance is non-negotiable. This includes submitting periodic reports and addressing any identified safety issues promptly. In 2025, regulatory bodies are increasingly emphasizing the need for transparency and robust validation processes, particularly in light of the rapid adoption of AI and machine learning technologies in healthcare. As noted by Michael E. Matheny, MD, MS, MPH, the influence of large language models (LLMs) on electronic health records (EHR) and adverse outcome reporting documentation may significantly impact how safety data is generated and utilized. Compliance not only ensures safety but also fosters trust among healthcare providers and patients. At bioaccess®, we prioritize data protection and have established grievance procedures to address client concerns with compliance and transparency.
Expert insights highlight that effective post-market surveillance is not just a regulatory obligation but a commitment to patient safety and product efficacy. As the landscape of medical technology evolves, particularly with updates in regulations across APAC, LATAM, and MENA aimed at attracting innovation while ensuring safety and quality standards, the importance of comprehensive monitoring and reporting systems will only grow. This ensures that innovations continue to benefit patients while minimizing risks. Furthermore, the credibility assessment framework for AI models is becoming increasingly pertinent in the ongoing monitoring and evaluation of medical instruments, ensuring that emerging technologies are integrated safely and effectively into healthcare practices.
Incorporating Human Factors Engineering in Trial Design
Incorporating human factors engineering (HFE) into Medtech trial design for FDA approval is essential for ensuring usability and enhancing overall clinical outcomes. Actively involving end-users in the design process is crucial. By gathering insights on their needs and preferences, developers can create devices that are intuitive and user-friendly. This approach not only improves usability but also increases user satisfaction and compliance. As Seda Japp notes, it is worthwhile for manufacturers and usability researchers to consider the unique nature of each product and study, particularly in the context of Medtech trial design for FDA approval, when determining sample size and maximizing the detection of use-related issues.
Implementing usability testing during clinical trials is vital for identifying potential issues early on. This process allows researchers to collect feedback on the product's performance in real-world scenarios, which is crucial for Medtech trial design for FDA approval to ensure it meets user expectations and regulatory standards. Recent statistics indicate that effective usability testing can significantly reduce the likelihood of post-market issues, thereby enhancing safety and effectiveness. Additionally, bioaccess® plays a crucial role in connecting innovative Medtech companies and the potential for conducting clinical research in Latin America, emphasizing the significance of Medtech trial design for FDA approval in this context.
Adopting an iterative design approach is essential for refining medical instruments. This method involves making modifications based on user feedback and testing results, which can lead to substantial improvements in usability. For instance, ND Global's case study on human factors engineering illustrates how continuous user input throughout the development lifecycle can enhance safety and usability, ultimately ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. This iterative process is crucial for addressing myths about human factors and design validation, including the misconception that three evaluators are needed for feedback.
It is imperative to integrate HFE principles into the regulatory submission process. Demonstrating that the apparatus has been designed with user safety and effectiveness in mind is crucial for the Medtech trial design for FDA approval, as it facilitates smoother approval processes and builds trust with stakeholders. As emphasized by specialists in the field, a well-documented HFE strategy can significantly enhance the credibility of Medtech trial design for FDA approval. With over 20 years of experience in the Medtech industry, bioaccess® is well-positioned to guide companies in implementing best practices, especially in Medtech trial design for FDA approval, while navigating the regulatory landscape governed by INVIMA in Colombia, which oversees medical product classification and compliance as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
bioaccess® specializes in managing various types of studies, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies (PMCF). By prioritizing these best practices, Medtech companies can enhance the usability of their devices, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and successful market entry. This proactive approach is essential for closing the life science innovation gap between the US, Europe, and patients in Latin America.
Overcoming Challenges in Clinical Research Management
Overcoming challenges in clinical research management necessitates a comprehensive approach that integrates strategic planning and execution across several key areas:
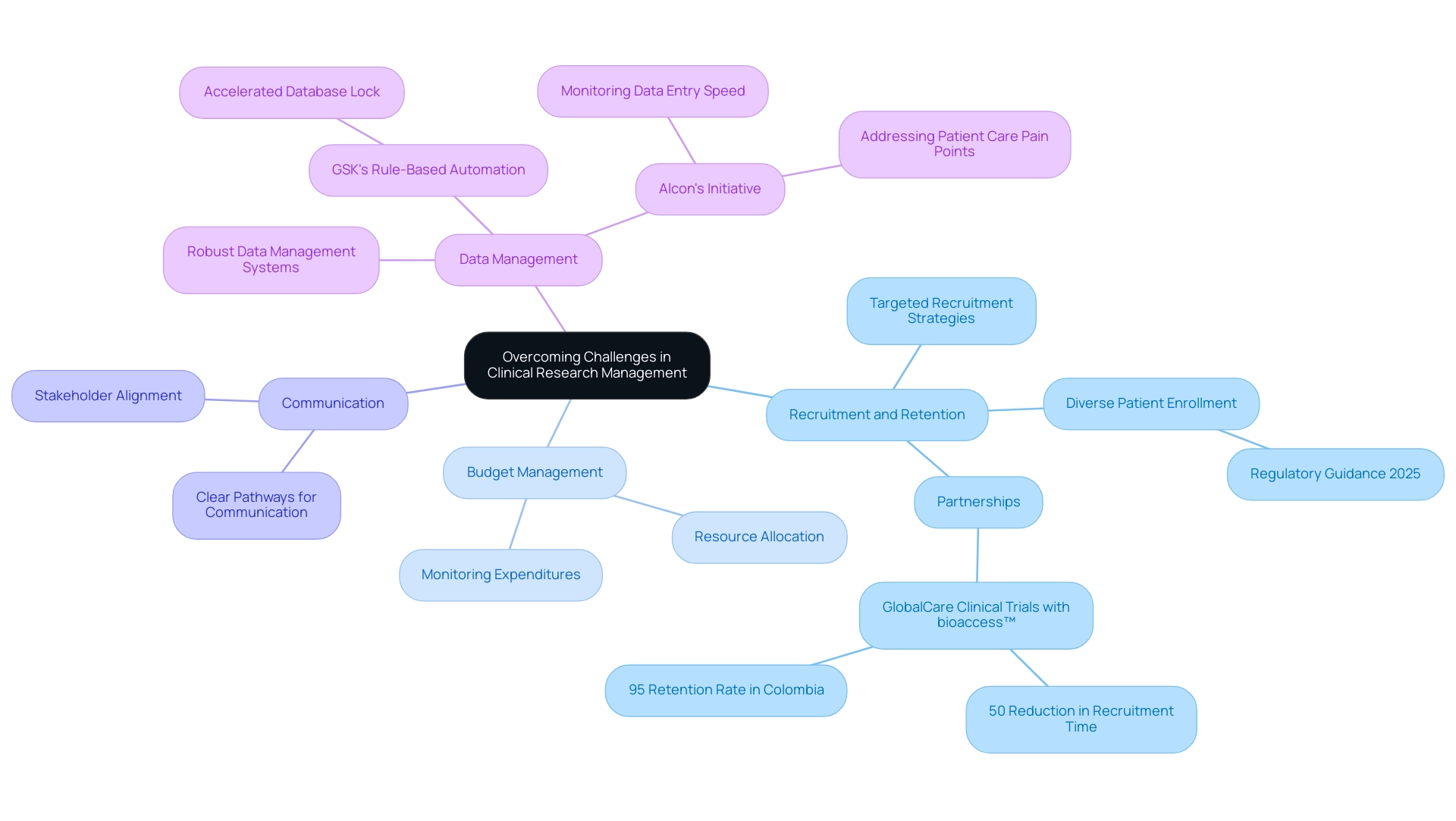
- Recruitment and Retention: Implementing targeted recruitment strategies is essential for engaging participants effectively and ensuring their ongoing involvement throughout the study. Recent statistics suggest that diverse patient enrollment is becoming increasingly significant, with new regulatory guidance in 2025 urging sponsors to include a wider demographic in clinical studies. This shift not only enhances the representativeness of research data but also improves retention rates by fostering a sense of inclusivity among participants. As Vivienne van der Walle, Founder and Medical Director, states, "Anything that takes away time from patients is a pain point for a site, and anyone who resolves that is helping patient care." This viewpoint highlights the necessity for additional choices for patient onboarding and visitations, which can greatly enhance experiences and broaden participation among underserved communities. Notably, partnerships like that of GlobalCare Clinical Trials with bioaccess™ have demonstrated success in this area, achieving over a 50% reduction in recruitment time and a retention rate exceeding 95% in Colombia.
- Budget Management: Effective budget management practices are essential for the successful implementation of research studies. By allocating resources efficiently and monitoring expenditures closely, organizations can maintain financial control and ensure that projects remain within budget. This is especially important in the context of increasing expenses related to clinical research, where strategic financial planning can reduce risks and improve overall study viability.
- Communication: Open and transparent communication among all stakeholders—including investigators, sponsors, and regulatory bodies—is vital for ensuring alignment and addressing issues as they arise. Creating clear pathways for communication can greatly decrease misunderstandings and enable faster resolutions, ultimately resulting in more efficient operations.
- Data Management: The implementation of robust data management systems is essential for streamlining data collection and analysis. These systems not only enhance compliance with regulatory requirements but also improve data integrity, which is essential for the credibility of results. For instance, GSK's application of rule-based automation for data cleaning illustrates how innovative methods can speed up the time to database lock, thereby improving overall study efficiency.
In addition to these strategies, case studies such as Alcon's initiative to improve site experience highlight the importance of monitoring data entry speed and addressing pain points that affect patient care. By streamlining data entry procedures, Alcon has effectively increased the efficiency of research studies while simultaneously enhancing patient experiences. This holistic method to research management, backed by bioaccess's 20+ years of expertise and comprehensive study management services—including Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies—is essential for navigating the complexities of modern studies and ensuring effective Medtech trial design for FDA approval.
Furthermore, the impact of Medtech clinical studies on local economies, such as job creation and healthcare improvement, underscores the importance of these trials in fostering international collaboration and economic growth.
Conclusion
In the intricate journey of medical device clinical trials, understanding each phase—from preclinical studies to post-market surveillance—is crucial for ensuring that innovative technologies are both safe and effective for patient use. The significance of pilot studies, regulatory compliance, and human factors engineering cannot be overstated, as they collectively enhance the likelihood of successful trial outcomes and facilitate smoother market entry.
Pilot studies and early feasibility assessments play a vital role in refining methodologies and addressing potential challenges before larger trials commence. As the Medtech sector evolves, the integration of advanced technologies and risk-based approaches is transforming trial designs, leading to improved data quality and resource efficiency. This evolution is particularly evident in the commitment to post-market surveillance, which underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring to maintain device safety and efficacy.
Navigating the regulatory pathways for FDA approval further emphasizes the necessity for meticulous planning and compliance. By adhering to established guidelines and engaging in early discussions with regulatory bodies, Medtech companies can streamline the approval process and bring innovative solutions to market more effectively.
Ultimately, the dedication to incorporating human factors engineering into trial design not only enhances device usability but also fosters greater patient satisfaction and adherence. As the landscape of medical device trials continues to advance, embracing these principles will be essential for driving innovation and improving patient outcomes in healthcare. The collaborative efforts within the industry, exemplified by partnerships and a commitment to transparency, will pave the way for a future where safer and more effective medical technologies can thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are medical equipment clinical studies?
Medical equipment clinical studies are organized investigations designed to assess the safety and efficacy of medical instruments, typically divided into distinct phases.
What are the phases of medical equipment clinical studies?
The phases include: 1. Preclinical Studies: Laboratory evaluations to assess safety and functionality before human testing. 2. Pilot Experiments: Small-scale studies to assess design viability and collect initial data. 3. Crucial Research: Larger studies providing definitive evidence of safety and efficacy for regulatory submissions. 4. Post-Market Research: Continuous evaluations after market release to monitor long-term safety and effectiveness.
Why are preclinical studies important?
Preclinical studies are essential for identifying potential issues with medical instruments before they proceed to human testing, ensuring that only the most promising devices are advanced.
What is the purpose of pilot experiments?
Pilot experiments assess the feasibility of the trial design and collect initial data, helping to identify logistical challenges and refine methodologies for larger trials.
What is the significance of crucial research in clinical studies?
Crucial research involves larger participant groups and provides definitive evidence regarding the equipment's safety and efficacy, which is vital for regulatory submissions and can influence approval timelines.
What is post-market research and why is it conducted?
Post-market research involves continuous evaluations of medical devices after they are available to consumers, ensuring any potential issues are identified and addressed promptly to safeguard patient health.
How is technology impacting medical equipment clinical studies?
Advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning are increasingly integrated into study designs, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving testing outcomes.
What is the role of in-house data management in clinical trials?
In-house data management allows companies to maintain quality and control over their data, which can lead to better outcomes for patients and healthcare providers.
How do collaborations enhance medical research?
Collaborations, such as those between bioaccess® and Caribbean Health Group, improve research capabilities and efficiency, leading to significant reductions in recruitment time and higher retention rates.
What trends are emerging in medical device studies?
There is a growing emphasis on utilizing data from pilot studies to refine early feasibility studies (EFS) and pivotal studies, which are crucial for effective Medtech trial design and FDA approval.

