Overview
To ensure reliability in research, it is crucial to implement standardized procedures, utilize established measurement tools, and conduct thorough training for research staff. The article outlines practical steps such as pilot testing and regular audits, emphasizing that these strategies enhance consistency and credibility in study results, ultimately contributing to the integrity of scientific inquiry.
Introduction
As the landscape of clinical research continues to evolve, the importance of reliability and validity cannot be overstated. These foundational concepts serve as the bedrock for credible scientific inquiry, ensuring that research findings are both consistent and accurately reflective of the intended measures. Researchers must navigate a complex array of methodologies and practices to enhance the integrity of their studies.
This article delves into essential strategies for improving research reliability:
- Conducting thorough data analyses
- Implementing robust quality control measures
- Fostering a culture of continuous learning
By embracing these principles, researchers can significantly elevate the quality of their work, ultimately contributing to advancements in medical science and clinical practices.
Understanding Reliability and Validity in Research
Reliability in investigation signifies the consistency of a measurement, indicating that if an experiment were replicated under identical conditions, the outcomes would remain stable. In contrast, validity assesses whether a study accurately measures the intended concept. Both dependability and validity are essential elements for establishing the credibility of study results.
For example, a reliable measurement tool is expected to produce consistent results over time, while a valid instrument ensures that it accurately measures what it purports to measure. According to Robert Wall Emerson, Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Visual Impairment & Blindness, 'The integrity of study results depends on the trustworthiness and validity of the methods used.' Grasping these foundational concepts allows researchers to create investigations that ensure the reliability and research needed to produce credible and applicable results, which are essential for the progression of medical science.
Long-term investigations, for example, allow scientists to monitor changes and trends by consistently assessing the same participants over time, thus strengthening the dependability of the findings. Recent methodological explorations, such as the Design and Implementation of Content Validity Study, have illustrated this complexity by employing a structured two-step process involving expert evaluations. The study's outcomes affirmed that the patient-centered communication instrument achieved an appropriate level of content validity, underscoring the intricate nature of the validation process.
Considering the most recent developments, an emphasis on these principles is essential for boosting the reliability and research of studies, which ultimately enhances the credibility of scientific investigation.
Practical Steps to Enhance Research Reliability
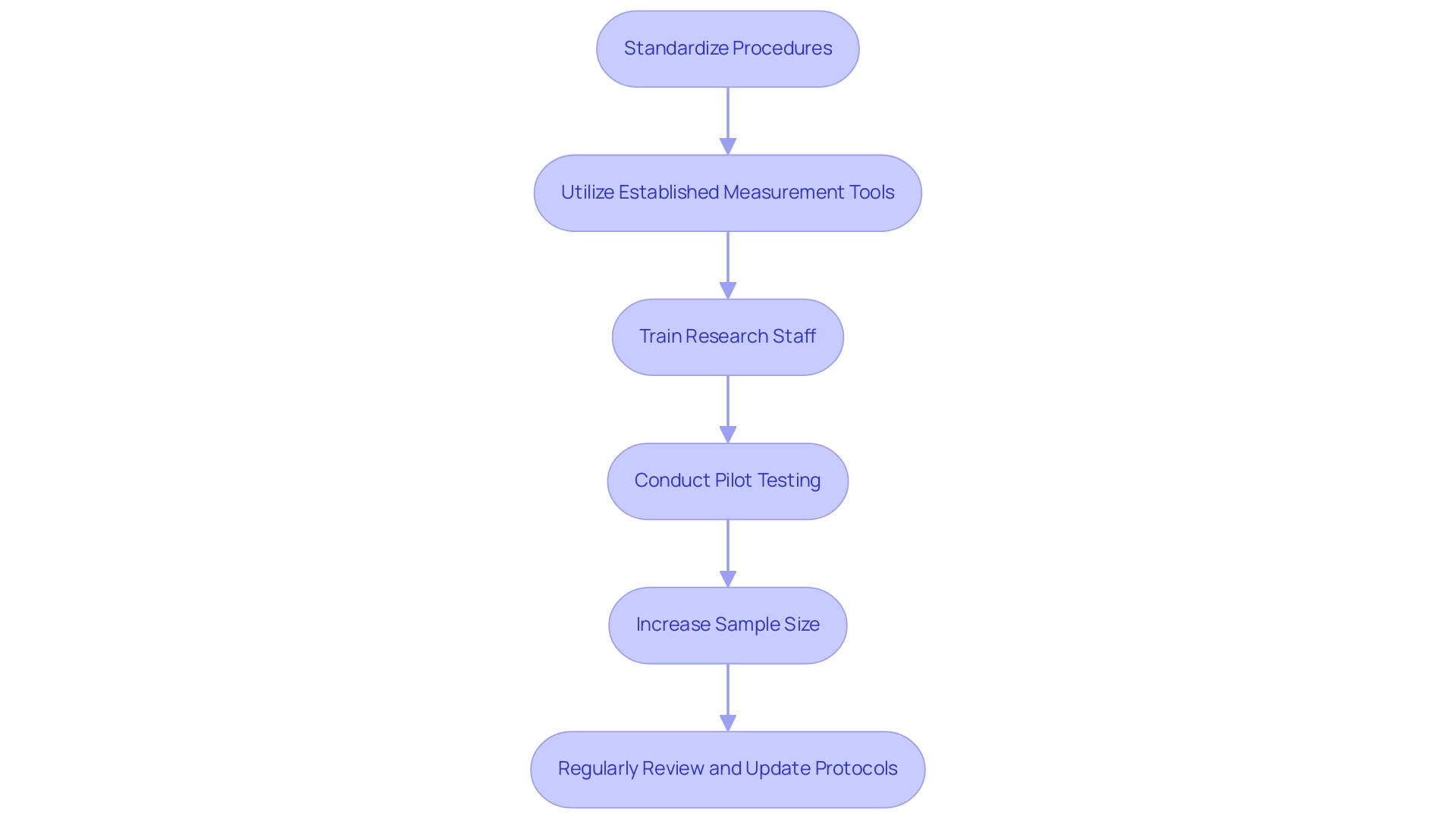
To enhance research reliability, consider implementing the following practical steps:
- Standardize Procedures: Establish and adhere to standardized protocols for data collection and analysis. This practice reduces variability, ensuring consistency across diverse participants and enhancing overall quality. With 219 partners concentrated on assessing advertising performance, the significance of standardization in evaluation processes becomes even more evident.
- Utilize Established Measurement Tools: Opt for measurement instruments that have shown validity and consistency in previous studies. Selecting tools with proven performance ratings greatly enhances the chances of achieving consistent results, thus strengthening the integrity of your research.
- Train Research Staff: Comprehensive training for all personnel involved in information collection is crucial. Consistent and thorough training reduces errors and discrepancies in data management, contributing to the trustworthiness of the findings.
- Conduct Pilot Testing: Implement pilot studies to evaluate the feasibility and consistency of your methods before the full-scale study. This preliminary step enables the identification and rectification of potential issues early in the investigation process.
- Increase Sample Size: A larger sample size enhances the reliability of results by diminishing the influence of outliers and random variation. This approach leads to more robust conclusions and strengthens the study's credibility.
- Regularly Review and Update Protocols: As the field of study evolves, it is vital to regularly review and update your protocols. Integrating the latest best practices guarantees continuous dependability and responsiveness to new findings.
By adopting these strategies, researchers can significantly enhance the reliability and research quality of their studies, leading to more credible outcomes and meaningful contributions to the field of clinical studies. As Igor Sokolov mentions, "Integrating standardized studies and handling procedures into field development strategies offers several advantages, including reduced costs and improved outcomes." Thus, fostering an environment of innovation and operational flexibility is essential for advancing effectiveness in studies.
Additionally, consider the case study on generative design, which illustrates how a structured approach can optimize resources and enhance creativity, ultimately driving sustainability and efficiency in production.
Conducting Thorough Data Analysis
To perform comprehensive information examination in clinical studies, consider the following guidelines:
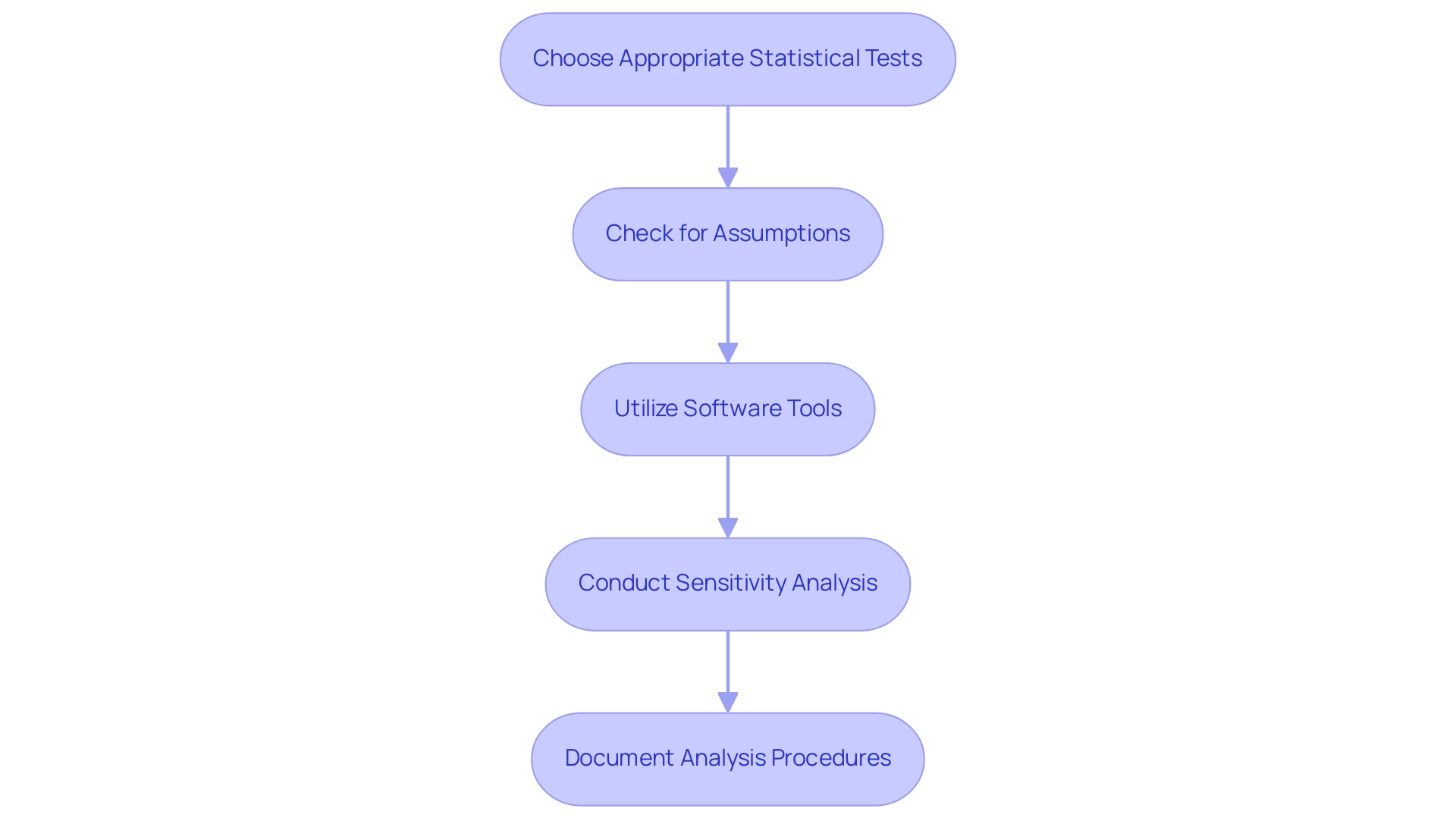
- Choose Appropriate Statistical Tests: It is essential to select statistical tests that correspond with your research design and information type. For instance, utilize t-tests for comparing means between two groups, while One-Way ANOVA is appropriate for examining differences across three or more groups. A case study demonstrated this through a One-Way ANOVA on three groups, yielding an F-statistic of 15.86 and a P-value of approximately 0.00000134, indicating a significant difference between group means. Additionally, understanding the t-statistic, calculated at 2.22 in relevant analyses, can provide deeper insights into the interpretation of results and the comparison of group means.
- Check for Assumptions: Evaluate whether your information satisfies the assumptions necessary for the statistical tests being employed, such as normality and homogeneity of variance. Adhering to these assumptions is critical for ensuring the validity of your results. As highlighted by Yudi Pawitan, the dialogue around statistical significance emphasizes the necessity to abandon rigid thresholds in favor of more nuanced approaches in interpreting data.
- Utilize Software Tools: Leverage statistical software packages like SPSS, R, or SAS to conduct complex analyses. These tools provide advanced features that aid in comprehensive information handling and bolster the reliability and research of your results. Current trends in statistical software, such as the increasing use of machine learning algorithms within R and the integration of user-friendly interfaces in SPSS, continue to evolve, offering researchers more sophisticated options for analysis.
- Conduct Sensitivity Analysis: Engage in sensitivity analysis to evaluate how variations in assumptions or parameters may influence your results. This practice is instrumental in assessing the reliability and research behind your findings, providing deeper insights into the trustworthiness of your conclusions.
- Document Analysis Procedures: Maintain meticulous records of your analysis processes, encompassing the methodologies employed and any adjustments made along the way. This degree of openness is crucial for reproducibility and strengthens the trustworthiness of your study.
By following these methods, scholars can greatly enhance the reliability and research behind their results, ultimately aiding in the progression of clinical inquiry methodologies. Furthermore, a strong foundation in fundamental statistical tests is crucial for scientists, as it equips them with the necessary skills to derive insights and validate their models effectively.
Implementing Quality Control Measures
To effectively implement quality control measures in clinical studies, it is essential to follow a structured approach that enhances reliability and research accuracy. Here are several key steps:
-
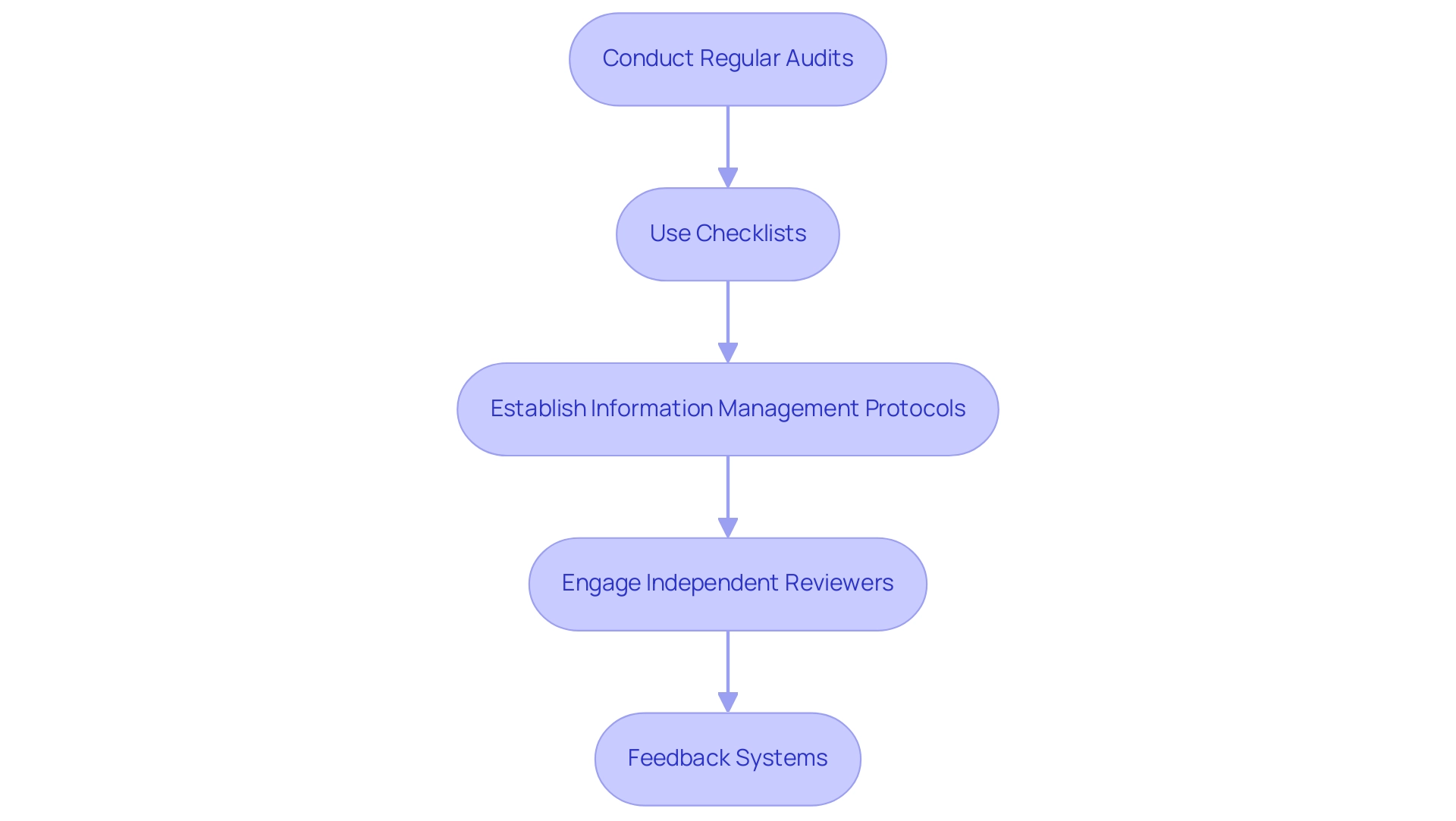
Conduct Regular Audits: Schedule periodic evaluations of research processes and information collection to identify discrepancies and areas needing improvement.
Regular audits serve as a critical checkpoint in maintaining quality standards and ensuring adherence to protocols, ultimately contributing to the delivery of health care and facilitating comprehensive clinical trial management services, including trial setup and project management.
-
Use Checklists: Create comprehensive checklists for information gathering and analysis procedures. These checklists assist in guaranteeing that all essential steps are carried out consistently, minimizing the chances of oversight and improving quality, which is vital for precise interpretation and effective reporting.
-
Establish Information Management Protocols: Create comprehensive protocols for entry, storage, and handling. These protocols are vital for minimizing errors and maintaining the integrity of the data throughout its lifecycle, thereby supporting quality improvement initiatives and enhancing the overall management of clinical trials, including compliance with import permits and nationalization of investigational devices.
-
Engage Independent Reviewers: Involve independent reviewers to assess your methods and findings.
This external viewpoint can greatly improve the trustworthiness of findings, as independent evaluators are less prone to being swayed by internal biases or assumptions, emphasizing the significance of quality management in studies and the credibility of clinical trials.
-
Feedback Systems: Establish strong feedback systems for personnel to report problems or propose enhancements in the information gathering process.
Promoting transparent dialogue cultivates an environment of ongoing enhancement and responsibility.
Integrating these quality assurance practices will enhance the reliability and research of clinical investigations while ensuring that the information gathered is both precise and reliable. As Enrique F. Schisterman aptly stated,
Implementing rigorous and well-defined quality control procedures may help to ensure sound results.
Furthermore, the case study on addressing aging population bias underscores the necessity of recognizing and correcting potential biases during data collection, reinforcing the importance of these quality control steps.
Notably, the labor productivity statistic of 0.125 pieces/person/day highlights the efficiency gains that can be achieved through effective quality control measures. Furthermore, Manuel Sánchez Gómez-Merelo's insights on total quality highlight the importance of quality and safety in clinical studies, advocating for a commitment to zero defects and strong quality control methods that benefit both the healthcare sector and local economic growth.
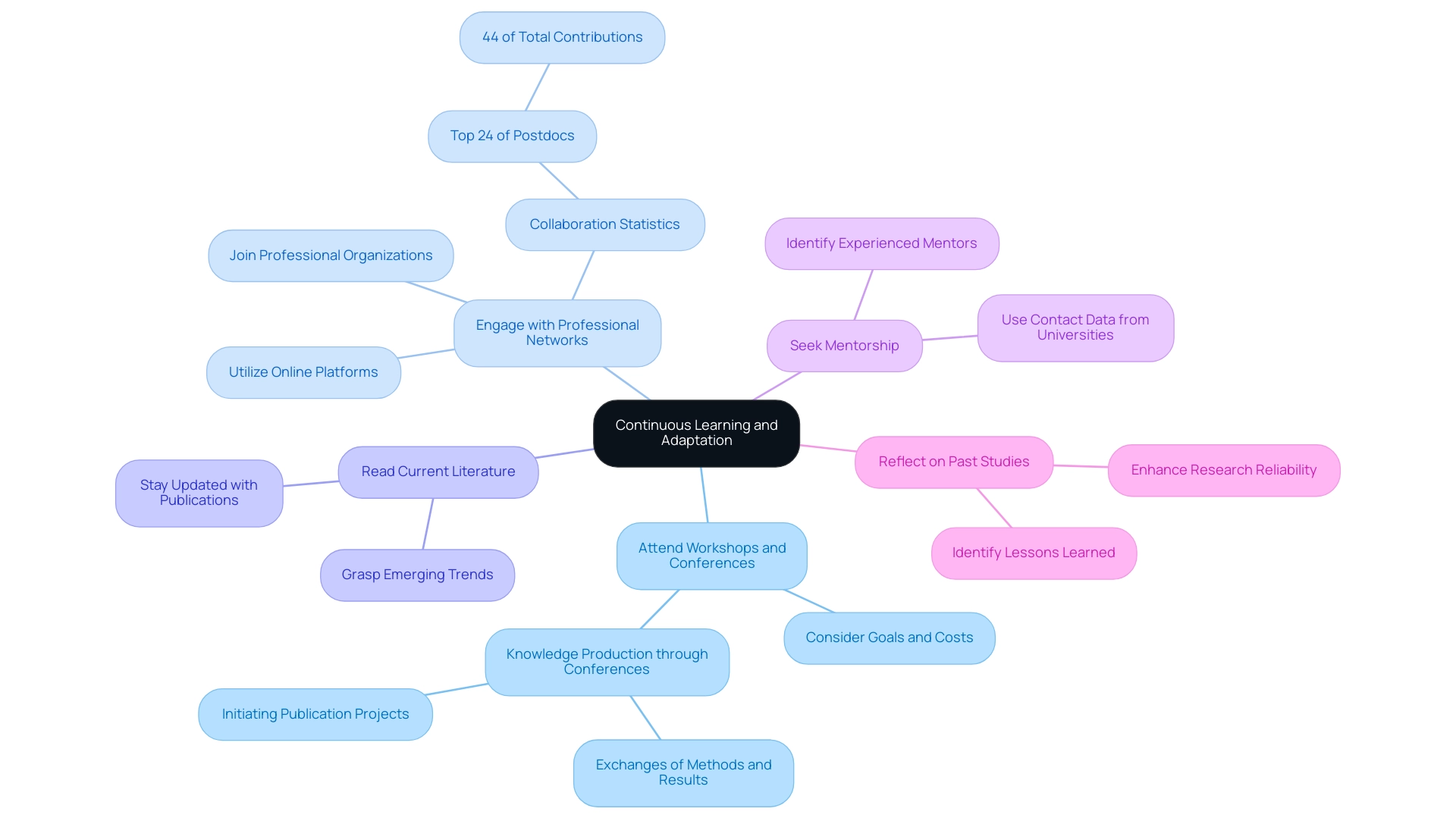
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
To promote ongoing learning and adaptation in clinical studies, it is essential for investigators to embrace several key strategies:
- Attend Workshops and Conferences: Participating in pertinent workshops and conferences is vital for keeping up with the latest methods and discoveries. When choosing a conference, researchers should consider their goals, the type of event, and associated costs. The case study titled Knowledge Production through Conferences illustrates this, revealing that conferences are vital for knowledge dissemination, with many attendees reporting fruitful exchanges of methods and results. These venues not only promote learning but also act as incubators for launching publication projects, especially at international gatherings, thus improving the overall quality of outputs.
- Engage with Professional Networks: Joining professional organizations and online forums allows researchers to connect with peers and share insights on best practices. Networking in academia is not just beneficial; it is essential. Current trends show that researchers are increasingly utilizing online platforms to foster connections and collaborate on projects. Statistics indicate that the top 24% of the most productive postdocs accounted for about 44% of total reported contributions, underscoring the importance of collaboration and shared knowledge.
- Read Current Literature: Staying updated with recent publications and journals is essential for grasping emerging trends and methodologies. This continuous engagement with literature ensures that researchers remain at the forefront of their fields.
- Seek Mentorship: Identifying mentors who can offer guidance based on their experience in the field is invaluable. As noted by Ambrasat and Tesch, researchers often rely on available contact data from universities and funding organizations to draw samples and seek mentorship. This highlights the interconnected nature of academic communities and the importance of mentorship in navigating the complexities of inquiry.
- Reflect on Past Studies: Regularly reviewing and reflecting on previous projects can lead to identifying lessons learned and areas for improvement. This introspective practice is key to refining approaches and enhancing the reliability and research process.
By committing to these continuous learning strategies, researchers can significantly enhance their skills and knowledge, ensuring that their work remains reliable, impactful, and aligned with the evolving landscape of clinical research.
Conclusion
Emphasizing the significance of reliability and validity in research underscores their role as essential pillars of credible scientific inquiry. By understanding these foundational concepts, researchers can design studies that not only yield trustworthy results but also contribute meaningfully to the advancement of medical science.
Implementing practical strategies such as:
- Standardizing procedures
- Utilizing established measurement tools
- Conducting thorough data analyses
plays a crucial role in enhancing research reliability. Additionally, quality control measures and fostering a culture of continuous learning further solidify the integrity of research outcomes. These steps are instrumental in ensuring that findings are consistent, accurate, and reflective of the intended measures.
Ultimately, the commitment to improving reliability and validity is not merely an academic exercise; it is a vital undertaking that impacts the broader field of clinical research. As researchers embrace these principles, they not only elevate the quality of their work but also drive innovation and excellence in medical practices, paving the way for future advancements in healthcare. The collective efforts in adhering to these standards will undoubtedly yield significant benefits for the scientific community and society at large.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between reliability and validity in research?
Reliability refers to the consistency of a measurement, indicating that if an experiment were replicated under identical conditions, the outcomes would remain stable. Validity, on the other hand, assesses whether a study accurately measures the intended concept.
Why are reliability and validity important in research?
Both reliability and validity are essential for establishing the credibility of study results. They ensure that findings are trustworthy and accurately reflect what they are intended to measure.
How can researchers enhance the reliability of their studies?
Researchers can enhance reliability by standardizing procedures, utilizing established measurement tools, training research staff, conducting pilot testing, increasing sample size, and regularly reviewing and updating protocols.
What role does standardization play in research reliability?
Standardization reduces variability by establishing and adhering to consistent protocols for data collection and analysis, which enhances the overall quality and reliability of the research.
How does training research staff contribute to research reliability?
Comprehensive training for all personnel involved in data collection reduces errors and discrepancies in data management, contributing to the trustworthiness of the findings.
What is the purpose of conducting pilot testing in research?
Pilot testing evaluates the feasibility and consistency of methods before the full-scale study, allowing researchers to identify and rectify potential issues early in the investigation process.
How does increasing sample size affect research reliability?
A larger sample size enhances the reliability of results by diminishing the influence of outliers and random variation, leading to more robust conclusions.
Why is it important to regularly review and update research protocols?
Regularly reviewing and updating protocols ensures that research remains dependable and responsive to new findings and best practices in the field.
What is the significance of utilizing established measurement tools in research?
Using measurement instruments that have shown validity and consistency in previous studies enhances the chances of achieving reliable results, thus strengthening the integrity of the research.
How can the principles of reliability and validity impact the progression of medical science?
By ensuring the reliability and validity of studies, researchers can produce credible and applicable results, which are essential for advancing knowledge and practices in medical science.




