Introduction
In the realm of medical device development, the significance of design control cannot be overstated. This systematic process is essential for ensuring that products not only meet safety and efficacy standards but also comply with stringent regulatory requirements set forth by authorities such as INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute.
As organizations navigate the complexities of design inputs, outputs, verification, and validation, they must also integrate risk management and maintain meticulous documentation to enhance product quality and mitigate potential hazards.
This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of design control, offering insights into best practices, regulatory compliance, and the critical role of collaboration among stakeholders in the medical device industry.
By understanding and implementing a robust design control framework, companies can streamline their development processes and ultimately deliver safer, more effective medical devices to the market.
Understanding Design Control: The Foundation of Medical Device Development
The medical device design control process is a comprehensive and systematic approach that governs the design and development of healthcare products, which is crucial for ensuring product safety, efficacy, and adherence to regulatory standards set forth by authorities like INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute. Founded in 1992, INVIMA is tasked with examining and overseeing the promotion and production of health products, including healthcare instruments, and has been designated as a Level 4 regional reference health authority by PAHO/WHO. This classification emphasizes its ability in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of health products in Colombia.
The Directorate for Medical Devices, a key entity within INVIMA, is tasked with monitoring and controlling medical devices, suggesting technical standards, and overseeing pre- and post-market programs. The structured activities within the medical device design control process include:
- The definition of inputs and outputs
- Verification and validation protocols
- Systematic reviews
According to Procedure STAT-18: Statistical Techniques for Normality Testing and Transformations, utilizing statistical methods can significantly improve the control processes by ensuring the validity of the data employed in the development and aligning with INVIMA's compliance requirements.
By applying a strong control framework that complies with INVIMA's regulations, organizations can effectively reduce risks, enhance product quality, and streamline the medical device design control process. As emphasized by the co-founder and CEO at Attract Group, utilizing quality management systems can enhance centralized control and documentation, supporting compliance. This viewpoint emphasizes the importance of engaging all parties—engineers, project managers, and compliance professionals—in the medical device design control process to ensure that healthcare products not only meet established quality standards but also satisfy compliance obligations.
Moreover, the case study named 'Statistical Techniques for Setting Specifications' demonstrates the use of statistical methods in establishing specifications for healthcare products, highlighting that accurate specification setting is crucial for compliance with regulations and product performance. This case study provides practical insights into how statistical methods can be utilized to meet INVIMA's standards. Additionally, the availability of two versions of spreadsheets—one protected for validation and another unprotected for customization—provides practical tools that enhance the medical device design control process, making it more relevant and applicable for clinical research directors.
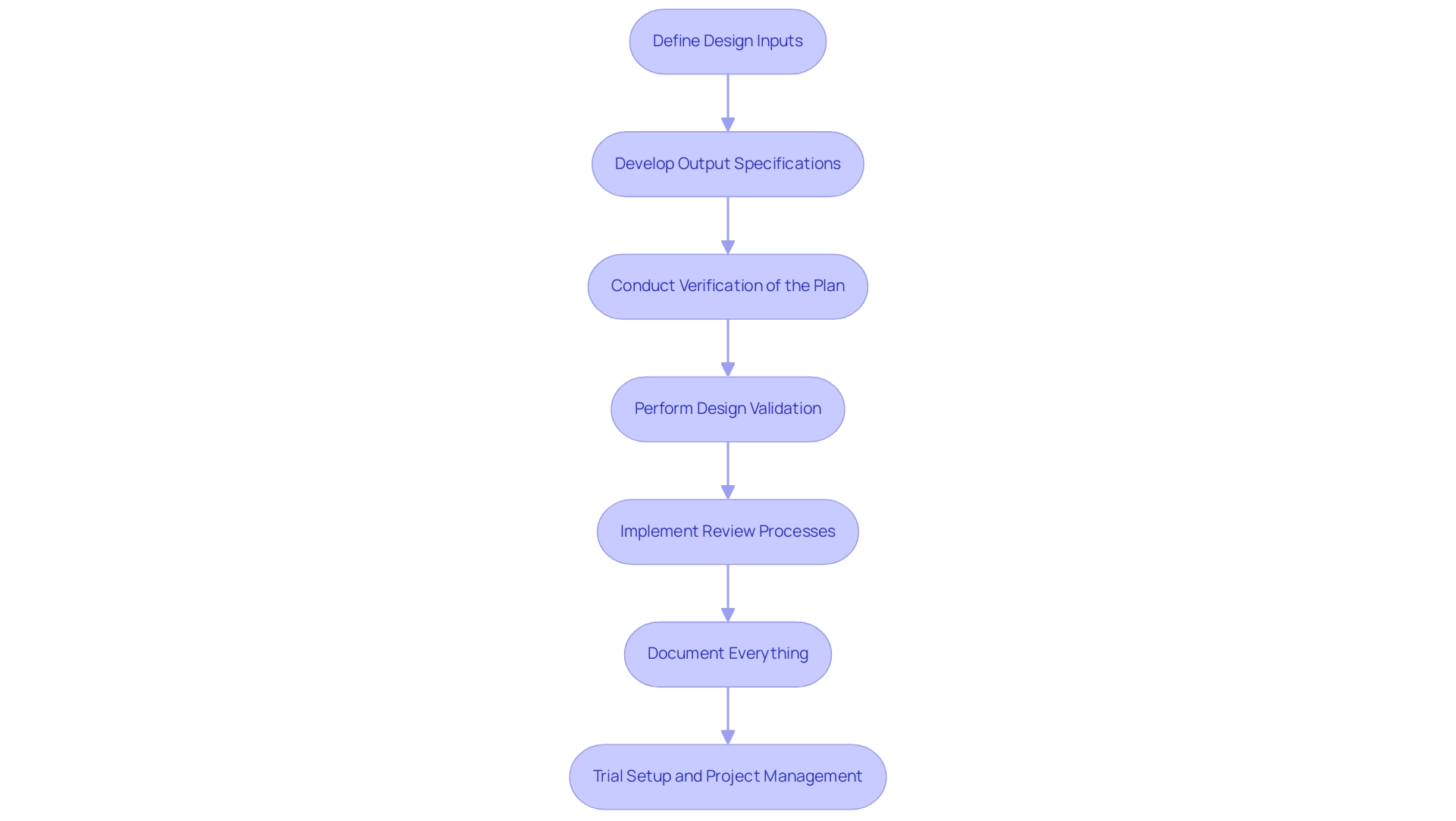
Navigating the Step-by-Step Design Control Process for Medical Devices
-
Define Design Inputs: Begin by identifying the essential requirements your healthcare product must fulfill, including user needs, regulatory mandates, and performance specifications. This foundational step is critical, as noted by Dr. Wayne A. Taylor, who emphasizes that this book is designed for engineers and scientists working within the medical device design control process. This underscores the technical rigor necessary in this phase.
-
Develop Output Specifications: Following the identification of inputs, create detailed specifications, drawings, and documentation that accurately reflect these inputs. Well-structured outputs provide clarity and serve as a blueprint for development.
Conduct Verification of the Plan: Implement a series of tests and analyses to ensure that the outputs meet the established inputs. This process is based on the assumption that if units can be manufactured accurately under worst-case conditions, only a limited number of units are required for testing, thereby covering the specification range effectively. This approach is supported by the statistical context that suggests focusing on worst-case scenarios can optimize testing efficiency.
-
Perform Design Validation: Validate the final product to confirm that it meets user needs and intended uses. This can be achieved through rigorous clinical evaluations or user testing, which are essential to ensuring the product’s practical applicability.
-
Implement Review Processes: Conduct regular evaluations with cross-functional teams. These reviews are instrumental in identifying potential issues early in the development process and ensuring that the project remains aligned with its goals. The necessity of effective control planning in the medical device design control process is highlighted in case studies, such as the one titled 'Medical Device Control Planning,' which demonstrates that such planning requires documented procedures and frequent communication to effectively manage the R&D process.
Document Everything: Maintain comprehensive records of all control activities. This documentation is essential for ensuring traceability and adherence to requirements, reflecting the practices outlined by INVIMA, Colombia's national authority, which oversees medical device compliance. Additionally, thorough documentation contributes to the understanding of how Medtech clinical studies impact local economies, including job creation and healthcare improvement. By following these steps and keeping thorough records, organizations can improve their verification success rates and remain updated on recent advancements in the field.
Trial Setup and Project Management: Ensure that the trial setup is meticulously planned, including site selection and the recruitment of principal investigators (PIs). Effective project management is crucial throughout the clinical trial process, encompassing monitoring study progress, managing inventory, and reporting serious and non-serious adverse events. This comprehensive approach not only ensures adherence to standards but also maximizes the potential for successful outcomes in clinical research.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating FDA and ISO Standards in Design Control
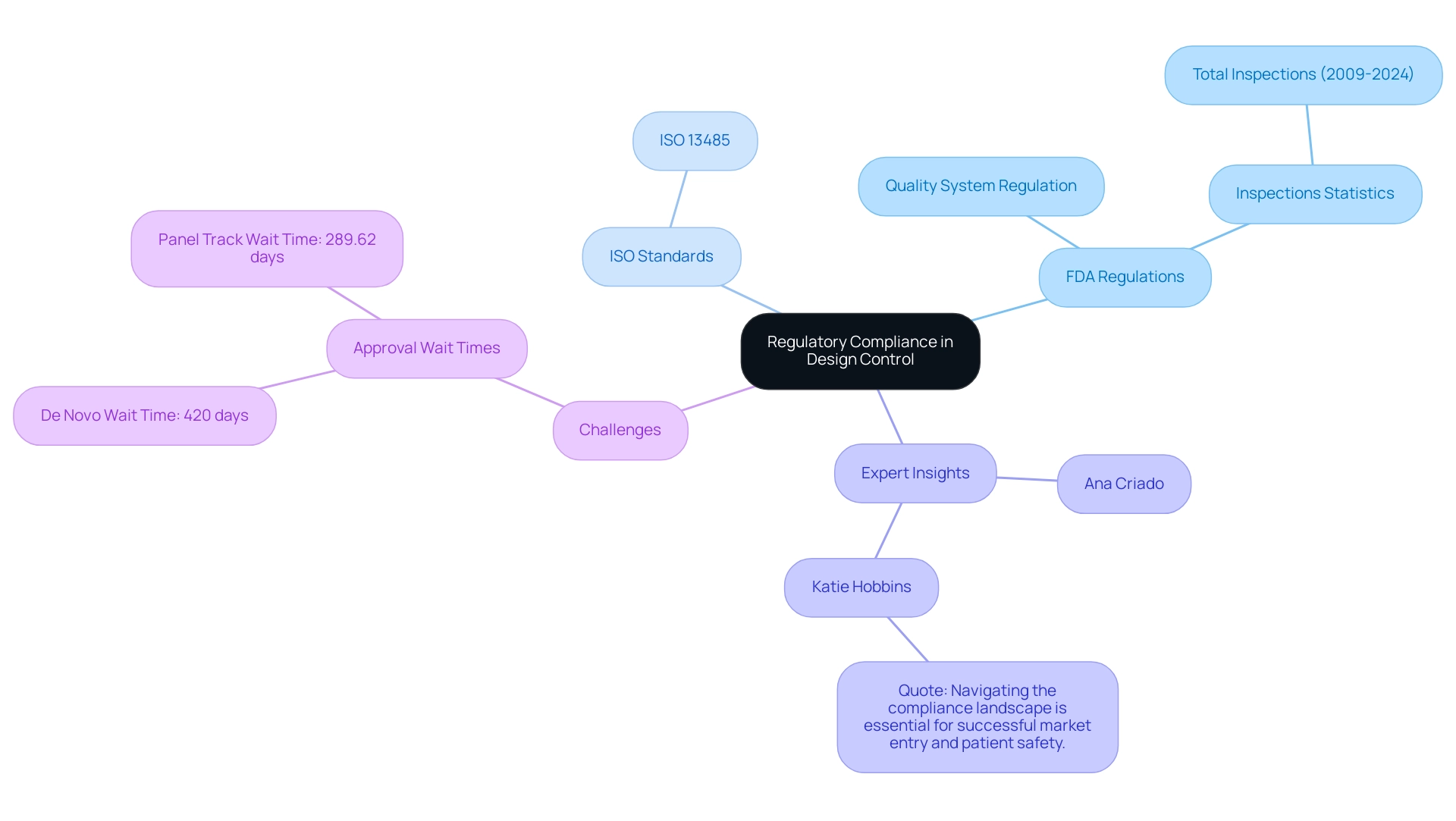
Regulatory compliance is crucial in the design control process for healthcare products, as it ensures that items meet established safety and efficacy standards. Experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, along with Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, emphasize the critical nature of adhering to such regulations. The FDA enforces specific regulations, including the Quality System Regulation (QSR), which requires manufacturers to implement and maintain a robust quality management system.
Furthermore, ISO 13485 outlines crucial requirements for a thorough quality management system, emphasizing the dedication to consistently deliver healthcare products that meet both client and compliance expectations. Recent statistics reveal that there have been a total of 1,500 FDA inspections of medical device establishments from 2009 to 2024, reflecting a rigorous oversight landscape. Despite advancements in some areas, the first half of 2024 saw slight increases in De Novo and Panel Track approval wait times, with De Novo rising to 420 days and Panel Track to 289.62 days.
This data indicates persistent challenges within the governing framework, as highlighted in the case study on De Novo and Panel Track wait times. To add perspective, Katie Hobbins, Managing Editor at MD+DI, emphasizes the importance of compliance by stating, 'Navigating the compliance landscape is essential for successful market entry and patient safety.' To effectively navigate these compliance requirements, professionals should not only familiarize themselves with relevant guidelines but also engage proactively with regulatory bodies early in the development process.
Ensuring thorough and compliant documentation is critical, as it lays the groundwork for successful product approval and market entry, aligning with the latest FDA regulations for health products in 2024.
Integrating Risk Management into the Design Control Framework
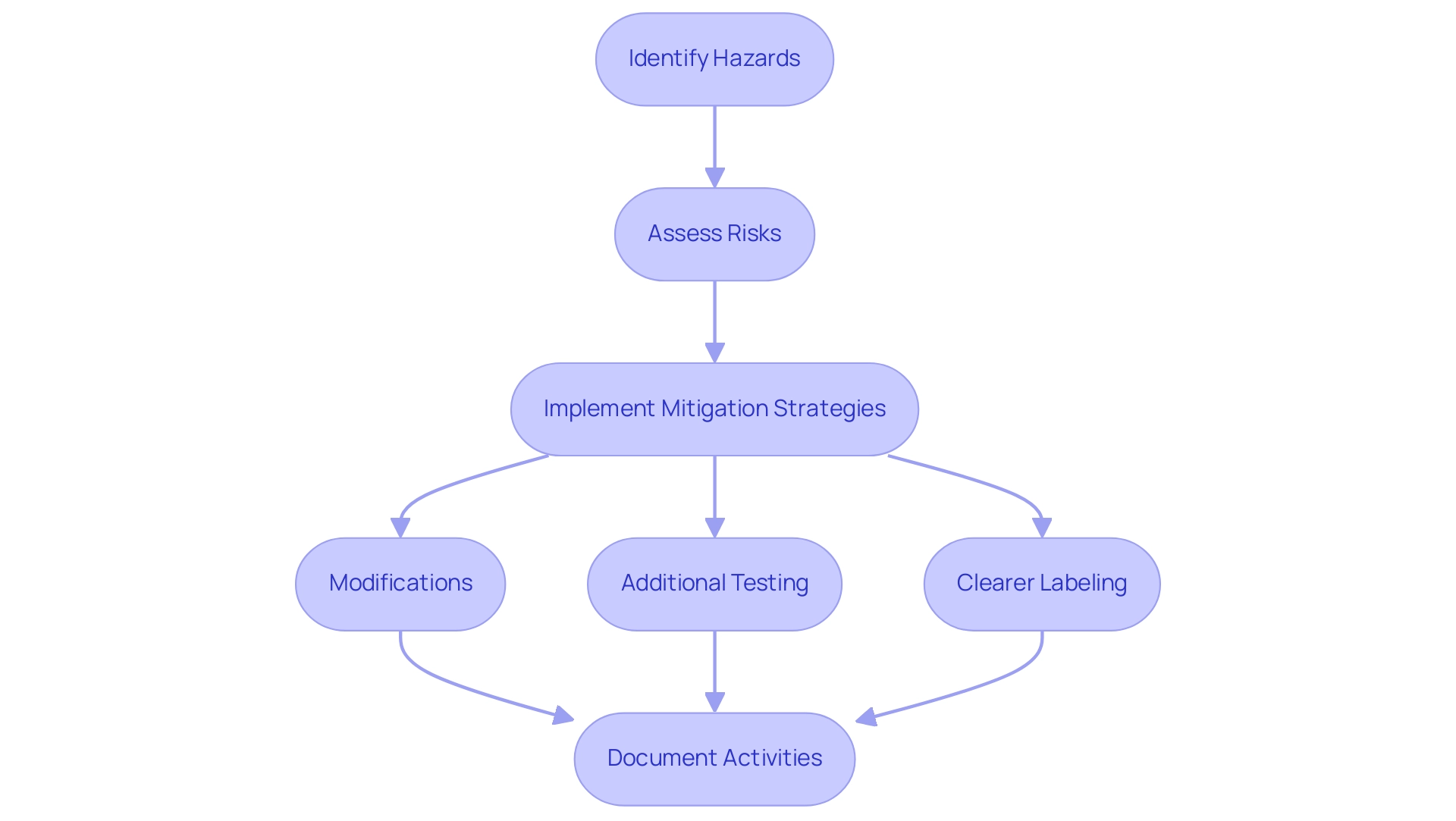
Risk management is a vital and ongoing element of the medical device design control process within the control framework for medical products, especially under the supervision of INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, acknowledged as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO. This framework begins with the identification of potential hazards associated with the device, followed by a thorough assessment of the risks they present. A pivotal tool in this process is Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), which aids in evaluating both the severity and likelihood of each risk.
Upon identifying risks, it is essential to implement effective mitigation strategies, which may include:
- Modifications
- Additional testing
- Clearer labeling to enhance user understanding and safety
Furthermore, meticulous documentation of all risk management activities is vital for compliance with regulatory requirements, including adherence to the medical device design control process and ISO 14971, which is recognized by the FDA as a consensus standard. This documentation also provides a transparent rationale for design decisions, which is an integral part of the medical device design control process and the design history file.
INVIMA plays a significant role in monitoring and controlling healthcare instruments, overseeing pre- and post-market programs, and suggesting technical standards for manufacturing and quality assurance. Experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and a leader in the field, emphasize the significance of a systematic approach to risk management. As mentioned by Dr. Wayne A. Taylor, 'This book is intended for engineers and scientists in the healthcare equipment sector,' highlighting the importance of clear definitions concerning the intended use of a healthcare product.
This clarity influences risk evaluation, especially when taking into account elements like user category and usage context, which are essential for evaluating risks and ensuring that risk management practices are strong and aligned with industry standards, thus improving patient safety and the overall success of healthcare innovations.
The Importance of Design Reviews and Validation in Ensuring Quality
Design reviews are essential organized assessments that occur at important milestones throughout the medical device design control process. These reviews allow cross-functional teams to systematically assess the design's progress against established criteria, facilitating the identification of necessary adjustments. Validation, in contrast, focuses on confirming that the final product aligns with intended uses and user needs.
To gather robust evidence of a product's performance in real-world scenarios, organizations must conduct validation activities, which may include clinical trials or usability studies. For instance, Peter Sebelius has developed a mechanical chest compression apparatus and an ex vivo perfusion machine for lungs, exemplifying innovation in the field. According to industry insights, 'Incorporating lessons from past verification and validation efforts can enhance future product developments,' emphasizing the necessity of learning from previous experiences.
Furthermore, the importance of maintaining detailed documentation during each review cannot be overstated; records should include:
- Minutes
- Signatures of attendees
- Action items
with an independent observer present to ensure transparency. A case study titled 'Best Practices for Validation and Verification in Healthcare Product Development' emphasizes that following optimal procedures, such as setting clear and testable input criteria and keeping thorough documentation, is crucial for ensuring adherence to regulations and attaining high-quality healthcare products. By prioritizing both the medical device design control process and validation processes, organizations enhance product quality, mitigate the risks of post-market issues, and ensure adherence to standards.
In Latin America, collaborating with specialists like bioaccess®—who offer over 20 years of experience and an adaptable approach to clinical trials—can deliver accelerated medical study services, including:
- Early-Feasibility Studies
- First-In-Human studies
- Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up studies
This partnership ensures comprehensive support throughout the clinical trial management process. Understanding the regulatory framework, particularly the functions of INVIMA as a Level 4 health authority, further solidifies the path to successful device approvals and market entry.
Conclusion
The intricate process of design control is foundational to the development of medical devices, ensuring that products not only meet safety and efficacy standards but also comply with rigorous regulatory requirements. By adhering to a structured design control framework, organizations can effectively:
- Define design inputs and outputs
- Conduct thorough verification and validation
- Integrate risk management strategies
Each of these steps plays a critical role in enhancing product quality and mitigating potential hazards, ultimately contributing to the successful market entry of medical devices.
Regulatory compliance, particularly with standards set by authorities such as INVIMA, the FDA, and ISO, is paramount in this process. Engaging proactively with these regulatory bodies and maintaining meticulous documentation are essential practices that lay the groundwork for product approval. Furthermore, incorporating statistical techniques and effective design reviews can optimize the development process, ensuring that medical devices not only fulfill user needs but also align with industry standards.
In conclusion, the successful navigation of the design control process requires a collaborative effort among all stakeholders, including engineers, project managers, and regulatory affairs professionals. By prioritizing a robust design control framework, organizations can streamline their development processes and deliver innovative, safe, and effective medical devices to the market, ultimately enhancing patient safety and improving healthcare outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the medical device design control process?
The medical device design control process is a structured approach that governs the design and development of healthcare products, ensuring their safety, efficacy, and compliance with regulatory standards set by authorities like INVIMA.
What role does INVIMA play in the medical device industry?
INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, oversees the promotion and production of health products, including medical devices. It is designated as a Level 4 regional reference health authority by PAHO/WHO, emphasizing its capability in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of health products in Colombia.
What are the key activities involved in the medical device design control process?
Key activities include defining inputs and outputs, implementing verification and validation protocols, and conducting systematic reviews.
How can statistical methods improve the design control process?
Utilizing statistical methods can enhance control processes by ensuring the validity of data used in development, aligning with INVIMA's compliance requirements, and improving overall product quality.
What is the significance of engaging all parties in the design control process?
Engaging engineers, project managers, and compliance professionals is crucial to ensure that healthcare products meet established quality standards and satisfy compliance obligations.
What does the case study on statistical techniques for setting specifications illustrate?
The case study highlights the importance of accurate specification setting for regulatory compliance and product performance, demonstrating how statistical methods can be effectively applied in this context.
What are the steps involved in the medical device design control process?
The steps include: 1. Define design inputs (requirements). 2. Develop output specifications (detailed documentation). 3. Conduct verification of the plan (tests and analyses). 4. Perform design validation (confirming user needs). 5. Implement review processes (cross-functional evaluations). 6. Document everything (maintaining comprehensive records). 7. Trial setup and project management (planning and monitoring clinical trials).
Why is documentation important in the design control process?
Comprehensive documentation is essential for traceability, adherence to requirements, and understanding the impact of Medtech clinical studies on local economies, including job creation and healthcare improvement.
What is the role of project management in clinical trials?
Effective project management in clinical trials involves meticulous planning of trial setups, site selection, recruitment of principal investigators, monitoring study progress, managing inventory, and reporting adverse events to ensure adherence to standards and maximize successful outcomes.




