Introduction
Navigating the intricate landscape of medical device regulation is paramount for manufacturers aiming to ensure patient safety and market readiness. At the forefront of this regulatory framework is the Premarket Approval (PMA) process, a rigorous pathway mandated by the FDA for high-risk devices. This comprehensive review not only assesses the safety and efficacy of medical technologies but also highlights the critical importance of compliance with established guidelines.
As the medical device industry continues to evolve, understanding the nuances of PMA—especially within the context of Colombian regulations governed by INVIMA—becomes essential. Insights from industry experts shed light on the best practices, timelines, and key components necessary for a successful application, ultimately paving the way for innovative solutions that enhance healthcare outcomes.
Understanding Premarket Approval (PMA): An Overview
The premarket application pathway is a crucial regulatory route that the FDA uses to evaluate the safety and efficacy of medical instruments before their market launch. This rigorous process is mandated for items classified as high-risk, encompassing a comprehensive and detailed review mechanism. For medical device manufacturers, particularly those navigating the Colombian landscape with INVIMA—classified as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO—understanding the intricacies of the PMA is paramount.
This includes compliance with FDA regulations, which facilitates smoother submissions and underpins the development of safe and effective medical technologies. As highlighted by Dr. Murad Alam, an expert in dermatology and a prominent figure in multiple medical associations, adhering to these guidelines is essential for ensuring patient safety and advancing technological innovation in healthcare. Furthermore, Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, emphasizes the importance of comprehensive clinical trial management services—ranging from:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Trial setup
- Project management
- Compliance reviews
- Reporting
Notably, a recent statistic revealed that 26.3% of respondents expressed concern that executive sessions could prolong the premarket application process, indicating a significant challenge within the regulatory framework. Additionally, Class III products that do not meet the premarket application requirements are regarded as adulterated and cannot be marketed, underscoring the high stakes involved in compliance. Given recent challenges, such as the disruptions faced by Artivion due to a ransomware attack, it is evident that maintaining robust security and compliance protocols is essential for safeguarding the PMA process.
This incident underscores the potential operational impacts on manufacturers and the importance of addressing security threats to ensure that the premarket application process is not only completed but also successful. Becoming acquainted with the requirements for a premarket application, along with the services provided in clinical trial management, will greatly improve the chances of a successful application, ultimately aiding in the integrity and safety of medical products in the marketplace.
Key Components of a Successful PMA Application
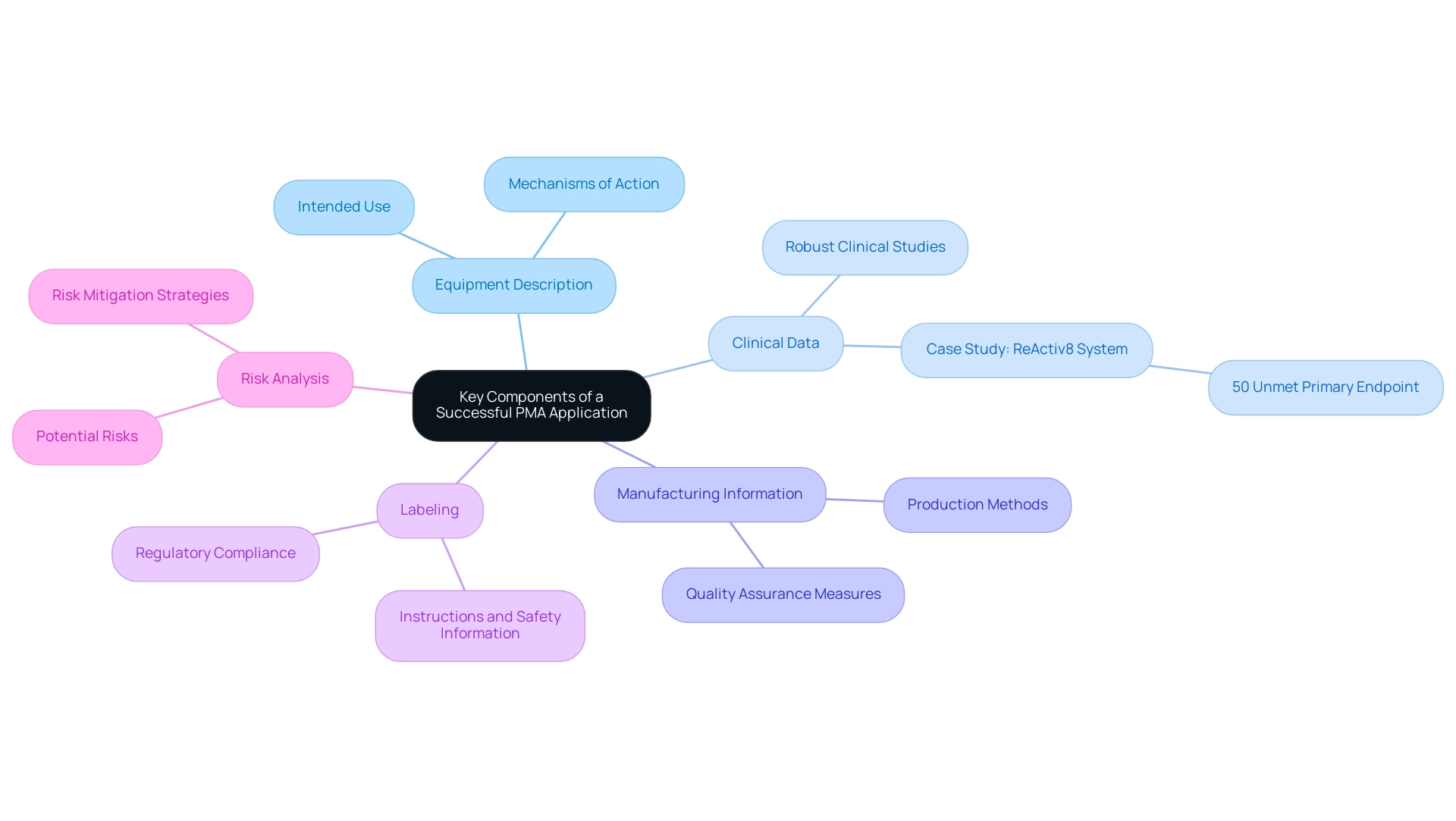
A successful premarket application is essential for demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of a medical product. It typically includes several key components:
-
Equipment Description: This section should provide a comprehensive overview of the equipment, detailing its intended use and mechanisms of action.
A clear and precise description sets the foundation for understanding the functionality of the equipment.
-
Clinical Data: Robust clinical studies are essential, showcasing the apparatus's safety and effectiveness through well-designed trials. For instance, the ReActiv8 implantable neurostimulation system reported a 50% unmet primary endpoint related to pain improvement, highlighting the necessity for thorough clinical evidence to meet regulatory expectations.
-
Manufacturing Information: Comprehensive details regarding the production methods, quality assurance measures, and facilities must be included to assure regulators of the consistency and reliability of the product manufacturing.
-
Labeling: Proposed labeling should comply with all regulatory requirements, providing clear instructions and safety information to users and healthcare professionals.
-
Risk Analysis: An in-depth assessment of potential risks associated with the equipment, along with effective strategies for risk mitigation, is crucial.
This analysis not only helps in compliance but also instills confidence among potential users and stakeholders.
To support the premarket application (PMA) process, comprehensive clinical trial management services—including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, project management, and reporting—are vital. These services ensure that all necessary protocols are adhered to, enhancing the quality of the clinical data submitted. Significantly, the case study concerning instruments used in blood establishments illustrates the necessity of adhering to medical equipment laws and regulations.
The Center for Biologics, Evaluation, and Research (CBER) plays a vital role in reviewing marketing and investigational product applications, ensuring that all relevant laws apply.
Moreover, the expertise of professionals like Katherine Ruiz in Regulatory Affairs for medical products and the oversight provided by INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, are essential in navigating the complexities of premarket application processes. As Dr. Sanket S Dhruva notes, understanding the regulatory landscape is vital for successful premarket application processes. By meticulously addressing each of these components, applicants can significantly enhance their chances of obtaining PMA approval.
Moreover, remaining informed about clinical data requirements for premarket application in 2024 and grasping the implications of recent news concerning Class III items emphasizes the significance of a thorough and well-prepared application.
Timeline for PMA Submission and Review
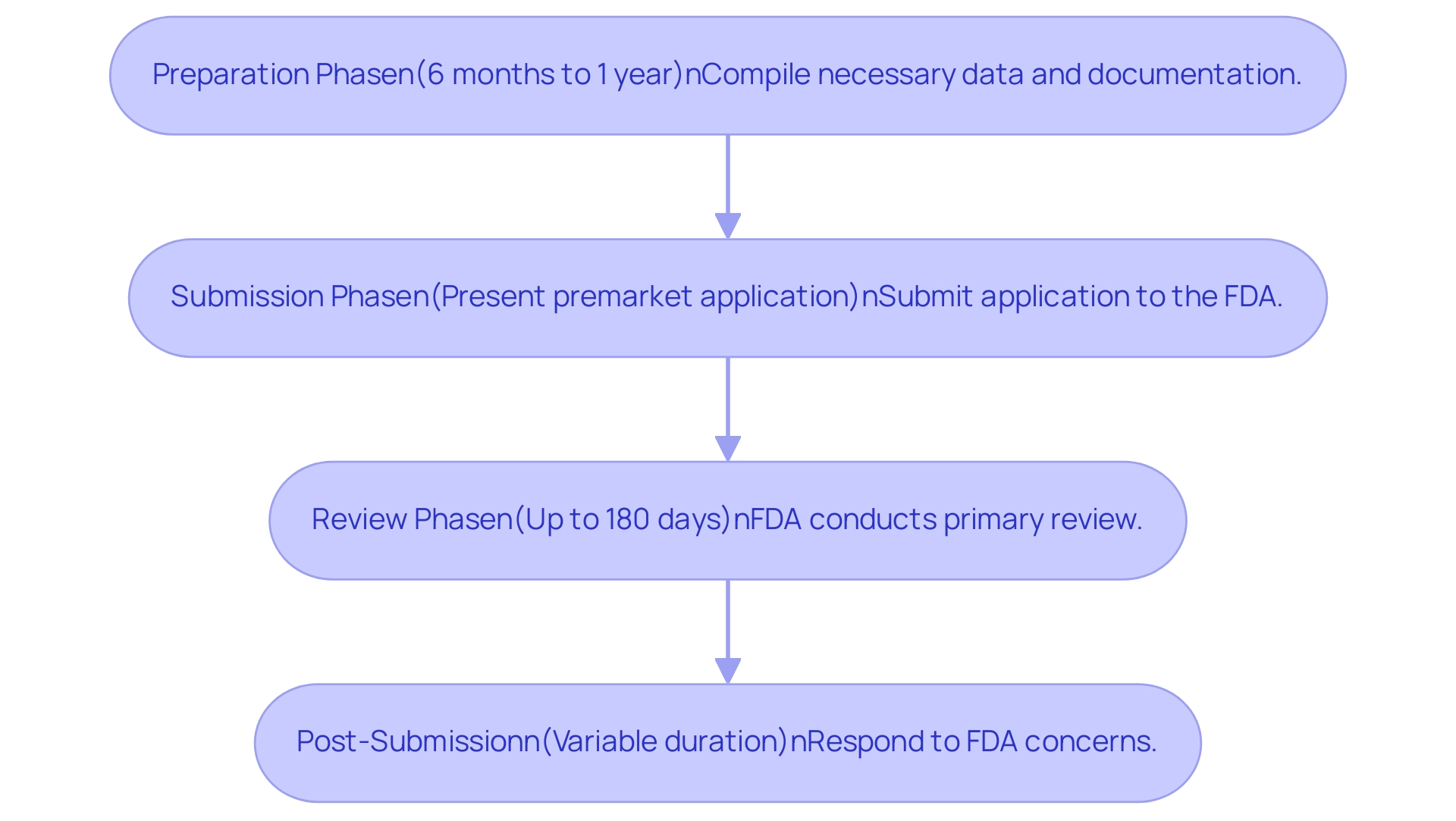
The procedure for the premarket application and review is particularly complex, mirroring the intricacies of the medical equipment sector, shaped by continuous advancements in research, development, and data gathering. Generally, the FDA's evaluation of a premarket application spans from 180 to 300 days and is delineated into several critical stages:
- Preparation Phase: This stage can last between 6 months to 1 year, during which applicants compile necessary data and documentation.
- Submission Phase: This involves the actual presentation of the premarket application to the FDA.
- Review Phase: The FDA typically conducts a primary review within 180 days; however, this may extend if the agency requests additional information.
- Post-Submission: Following the review, there may be further delays as applicants respond to any concerns raised by the FDA.
A heightened awareness of these timelines is vital for applicants, enabling them to allocate resources judiciously and prepare for potential delays. Notably, recent statistics indicate significant improvements, with the average approval time for panel-track supplements declining by 27% in the first half of 2023 compared to the previous year. As Sebastian Rodriguez-Elizalde, M.D., a member of the Scientific Advisory Board at Intellijoint Surgical, emphasizes, understanding these timelines is crucial for effective planning in the medical device sector.
Additionally, bioaccess® specializes in managing various studies, including Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies. Their expertise in these areas, along with insights from Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, further emphasizes the significance of staying informed about the changing landscape of PMA deadlines. Insights from the case study titled 'Impact of New Medical Devices on Patient Outcomes' highlight how timely premarket application submissions can influence patient outcomes, making it essential for clinical research directors to effectively manage these procedures.
Best Practices for Quality and Compliance in PMA Applications
To enhance the quality and compliance of your premarket application, consider implementing the following best practices:
- Feasibility Studies and Site Selection: Conduct thorough feasibility studies to identify suitable research sites and principal investigators (PIs). This foundational step ensures that the selected sites are well-equipped to meet the study's requirements and can effectively contribute to the research objectives.
- Thorough Documentation: It is essential to ensure that all data is meticulously documented and readily accessible. This not only streamlines the review procedure but also aids in addressing any queries from the FDA efficiently.
- Trial Setup and Approval: Ensure that the trial arrangement and start-up procedures comply with all necessary regulations, including obtaining approvals from ethics committees and health ministries. This step is critical for maintaining compliance and facilitating a smooth trial initiation.
- Regular Communication: Establish and maintain open lines of communication with the FDA. This proactive approach allows for clarification of requirements and timely resolution of concerns, which is crucial for a successful premarket application. Notably, the applicant should submit a meeting request for the Day-100 Meeting no later than 70 days from the FDA's receipt of the PMA accepted for filing, emphasizing the importance of timely communication.
- Pre-Submission Meetings: Engaging in pre-submission meetings with the FDA is a vital step. These meetings help align expectations, provide an opportunity to gather feedback, and can significantly impact premarket application approval rates by ensuring that your application meets regulatory standards from the outset.
- Quality Control: Implementing rigorous quality control measures throughout the application process is imperative. Identifying and rectifying potential issues early can prevent delays in approval and enhance overall application quality. When using a non-reference standard for comparison, it is important to note that terms like sensitivity and specificity are not appropriate, ensuring technical accuracy in your application.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Regularly report on study status, inventory, and any serious and non-serious adverse events. This ongoing reporting is essential for maintaining transparency and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Expert Consultation: Consulting with regulatory experts, such as Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, who has extensive experience in managing clinical studies for Class III products, can provide invaluable insights. Expert evaluations before sending can identify areas for improvement and enhance compliance rates. Understanding PMA supplements and amendments is crucial, as producers must provide annual post-approval reports, ensuring ongoing compliance and communication with the FDA about modifications and new information.
By following these best practices, manufacturers can greatly enhance the quality and compliance of their premarket application, ultimately facilitating smoother interactions with the FDA and boosting the chances of successful filing.
PMA vs. 510(k): Understanding the Differences
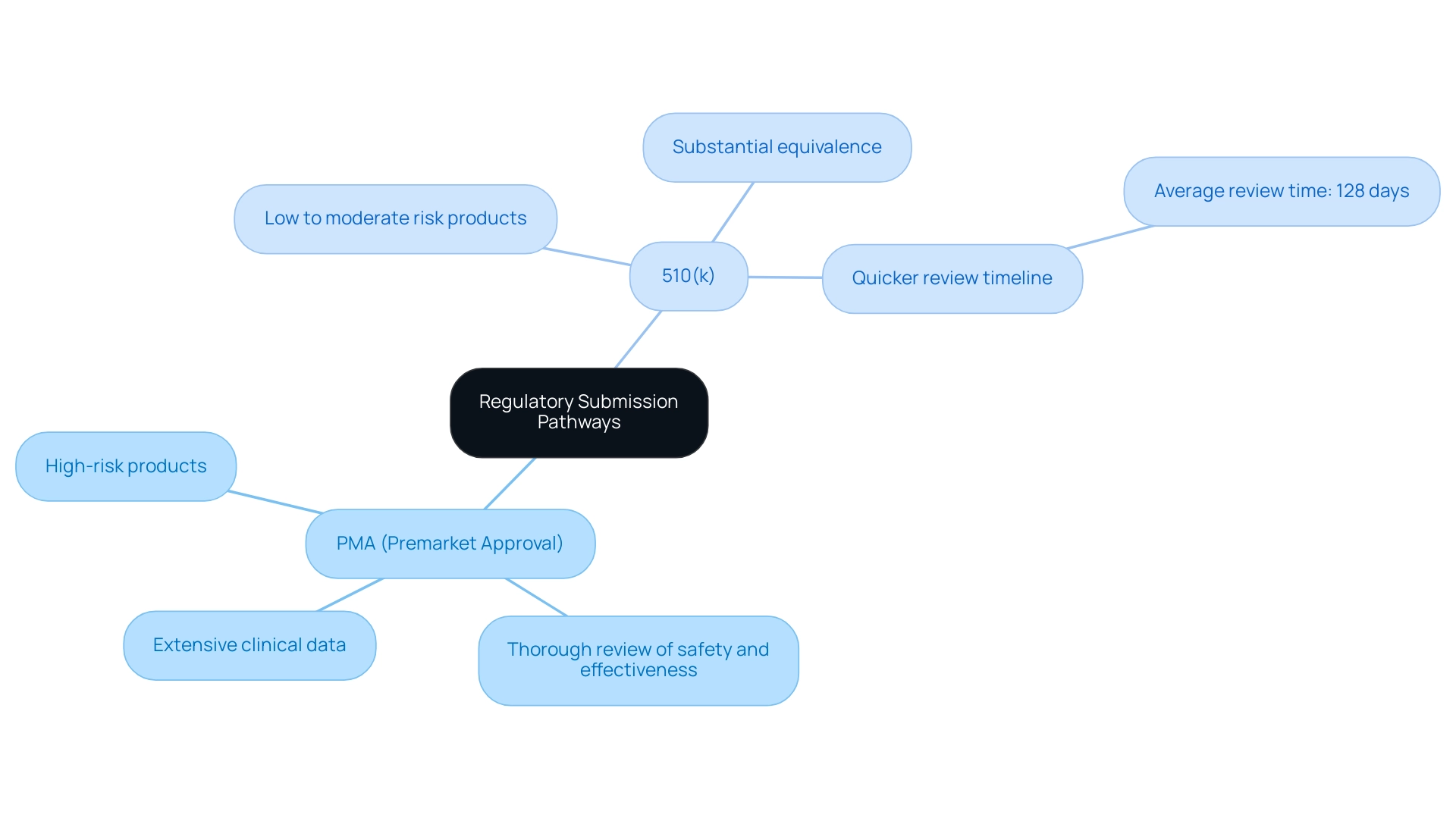
Understanding the regulatory submission pathways for a premarket application of medical products is crucial for ensuring compliance and increasing the likelihood of success. The differences between Premarket Approval (PMA) and the 510(k) process are significant:
-
PMA (Premarket Approval): This pathway is mandatory for high-risk products.
It entails a thorough review of safety and effectiveness, requiring extensive clinical data to support the application. The rigorous nature of PMA ensures that only products meeting strict safety standards are brought to market, reflecting the high stakes involved in their use.
-
510(k): This application method is relevant to items categorized as low to moderate risk.
It requires the manufacturer to demonstrate substantial equivalence to an already marketed product. This procedure requires careful preparation, including thorough documentation of the equipment, which can be less challenging than a PMA application. Consequently, the 510(k) procedure typically has a quicker review timeline; the FDA intends to reach conclusions on 510(k) applications filed in its 2023 financial year within an average of 128 calendar days, according to industry insights by Nick Paul Taylor.
A real-world example of a successful application is the INSIGHTEC EXABLATE, which received marketing authorization (application number P150038) on 07/11/2016. This case demonstrates the practical consequences of the submission methods and emphasizes the significance of comprehending the regulatory environment.
Selecting the suitable premarket application route is crucial because it not only affects regulatory adherence but also impacts the total time to market for new products. With the landscape of medical device regulation evolving, understanding these differences and their implications is essential for clinical researchers navigating the approval pathway. Notably, experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and a professor at top Colombian universities, bring invaluable insights into these processes.
Her extensive background in biomedical engineering and health economics, combined with her consultancy for multinational companies and leadership experience at INVIMA, positions her as a key authority in Regulatory Affairs. Additionally, her role as the CEO of Mahu Pharma, a company licensed to cultivate cannabis for medicinal use, further underscores her expertise in navigating complex regulatory environments.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of the Premarket Approval (PMA) process is essential for manufacturers aiming to ensure that their medical devices meet the high standards of safety and efficacy required by regulatory authorities. This article highlights the multifaceted nature of the PMA process, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive clinical data, meticulous documentation, and adherence to regulatory guidelines. The insights shared by industry experts underscore that a thorough understanding of both FDA and Colombian regulations, particularly those governed by INVIMA, is crucial for successful submissions.
Key components of the PMA process include:
- Device description
- Clinical data
- Manufacturing information
- Risk analysis
These components serve as the foundation for a robust PMA application. Additionally, implementing best practices—ranging from effective communication with regulatory bodies to engaging in pre-submission meetings—can significantly enhance the quality and compliance of applications. As the medical device landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about timelines and regulatory expectations is vital for manufacturers seeking to bring innovative solutions to market.
Ultimately, prioritizing compliance and quality not only facilitates smoother interactions with regulatory authorities but also contributes to the overarching goal of improving healthcare outcomes. By embracing these principles, manufacturers can navigate the PMA process effectively, ensuring that their devices are not only market-ready but also safe for patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the premarket application (PMA) pathway?
The PMA pathway is a regulatory route used by the FDA to evaluate the safety and efficacy of medical instruments before they are launched in the market, particularly for high-risk items.
Why is understanding the PMA process important for medical device manufacturers in Colombia?
Understanding the PMA process is crucial for manufacturers navigating the Colombian regulatory landscape with INVIMA, as it ensures compliance with FDA regulations and facilitates smoother submissions, thereby supporting the development of safe and effective medical technologies.
What are some key components included in a successful premarket application?
A successful PMA typically includes the following key components: 1. Equipment Description 2. Clinical Data 3. Manufacturing Information 4. Labeling 5. Risk Analysis.
What role do clinical trial management services play in the PMA process?
Clinical trial management services, such as feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, project management, and reporting, are vital for ensuring adherence to necessary protocols and enhancing the quality of clinical data submitted.
What challenges are associated with the PMA process?
A significant challenge noted is that 26.3% of respondents expressed concern that executive sessions could prolong the premarket application process, which highlights potential delays within the regulatory framework.
What happens if Class III products do not meet PMA requirements?
Class III products that do not meet the PMA requirements are considered adulterated and cannot be marketed, emphasizing the importance of compliance.
How does security impact the PMA process?
Maintaining robust security and compliance protocols is essential for safeguarding the PMA process, as disruptions, such as those caused by ransomware attacks, can significantly affect manufacturers and the application process.
Who are some experts mentioned in relation to the PMA process?
Experts mentioned include Dr. Murad Alam, who emphasizes the importance of adhering to guidelines for patient safety, and Katherine Ruiz, who focuses on regulatory affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia.




