Introduction
In the realm of clinical research and regulatory compliance, 21 CFR Part 11 stands as a critical framework governing the use of electronic records and signatures. Established by the FDA, this regulation sets forth stringent criteria that ensure the integrity and reliability of digital documentation, which has become increasingly vital in a world where data management is paramount.
Entities involved in clinical studies, from sponsors to Contract Research Organizations (CROs), must navigate the complexities of this regulation while adhering to additional local and international guidelines. With the rise of electronic systems and the need for robust compliance strategies, understanding the nuances of 21 CFR Part 11 is essential for maintaining data integrity and fostering accountability in research practices.
This article delves into the key components of the regulation, including:
- The role of predicate rules
- Effective compliance strategies
- Electronic signature requirements
- The importance of training for compliance professionals
By providing a comprehensive overview of these aspects, the article aims to equip those aiming to excel in a challenging regulatory landscape.
Understanding 21 CFR Part 11: A Regulatory Overview
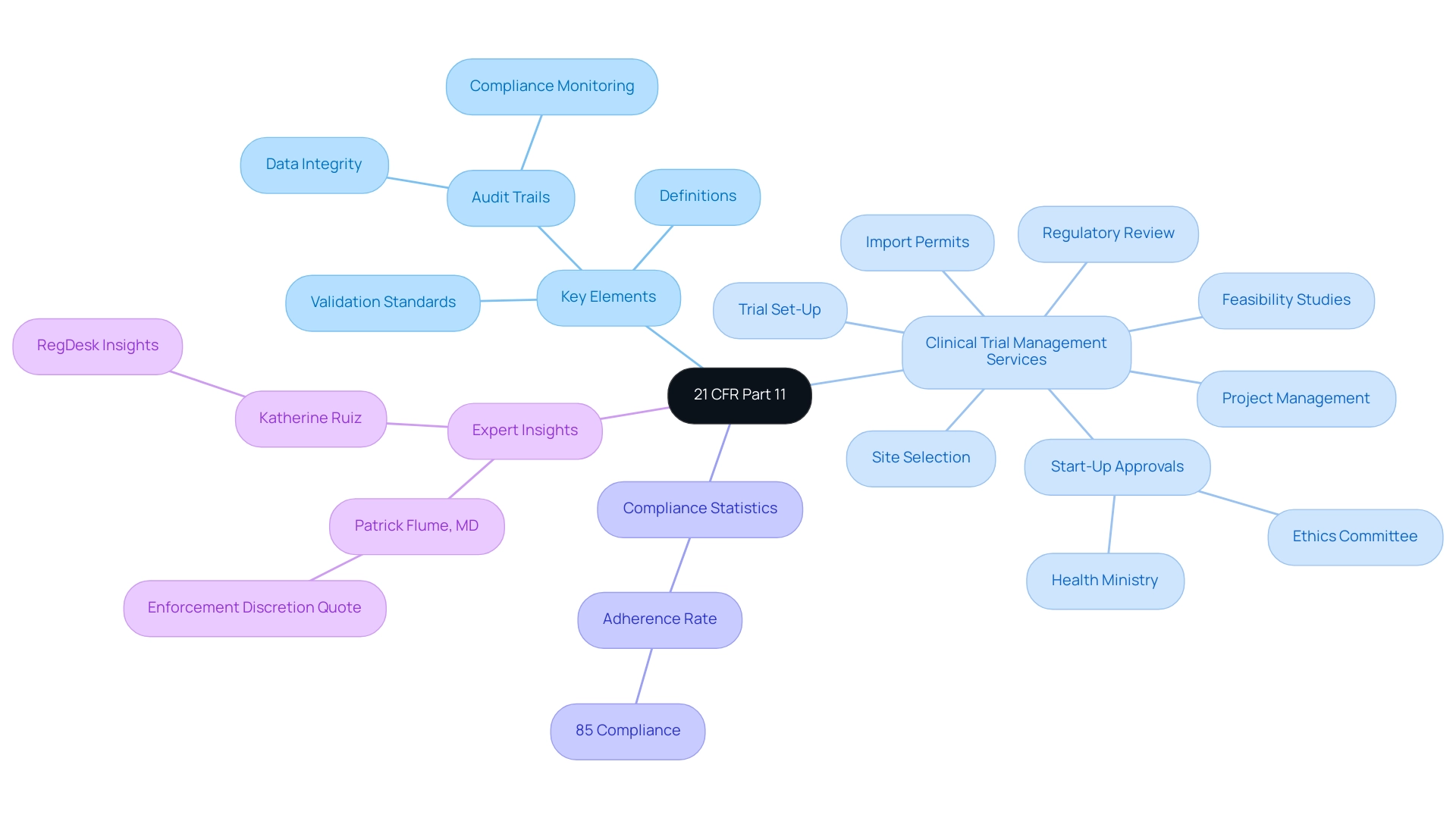
21 CFR Part 11 is a crucial regulation set by the FDA that outlines the standards under which digital files and marks are considered trustworthy, reliable, and comparable to conventional paper documents. This regulation is pertinent to all entities involved in clinical research, including sponsors, Contract Research Organizations (CROs), and research institutions. Key elements of 21 CFR Part 11 include:
- Detailed definitions of digital documents and credentials
- Strict validation standards
- The requirement to preserve an audit trail that monitors pertinent actions over a specified timeframe
These audit trails are essential for ensuring data integrity and adherence to regulatory standards. As Patrick Flume, MD, Associate Vice President for Clinical Research, emphasizes, 'FDA has specified that it will exercise enforcement discretion where electronic records and signatures are committed to physical writings and appropriately countersigned to assure security and non-repudiation.'
Moreover, the clinical trial management services provided encompass:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Review of regulations
- Trial set-up
- Start-up approvals (ethics committee and health ministry)
- Import permits and nationalization of investigational devices
- Project management
These services ensure adherence to local regulations such as those governed by INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, recognized as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, underscores the importance of these services in navigating the complex regulatory landscape. Furthermore, RegDesk simplifies global expansion for companies in the medical device and pharma sectors by assisting with these regulations. A relevant case study titled 'Application of Part 11 Predicate Rules' illustrates how the regulation applies to electronic records and signatures, demonstrating its importance in protecting records from unauthorized access and ensuring accountability through unique electronic signatures linked to individuals.
Additionally, current statistics reveal that adherence to 21 CFR Part 11 has reached 85% among leading organizations, underscoring the regulation's significance in the clinical research landscape. A thorough understanding of these elements, including reporting on study status, inventory, and serious and non-serious adverse events, is vital for professionals seeking to navigate the complex regulatory landscape effectively.
The Role of Predicate Rules in 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance
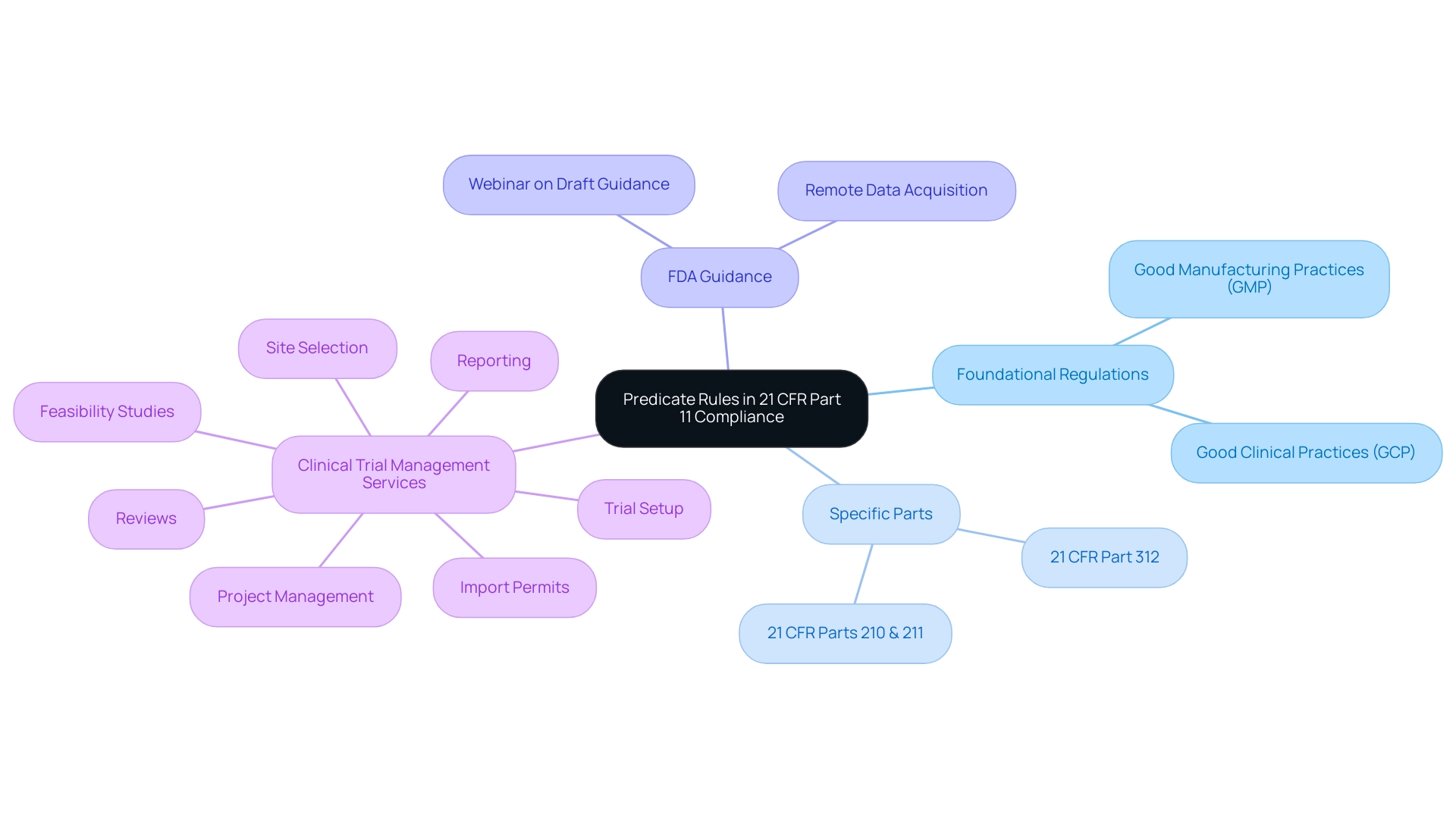
Predicate rules are foundational regulations that govern the utilization of digital records in various sectors, notably within Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Good Clinical Practices (GCP). These rules are vital for ensuring data integrity and robust record-keeping, which are paramount in clinical research. For instance:
- 21 CFR Parts 210 and 211 delineate the requirements pertinent to manufacturing processes.
- 21 CFR Part 312 specifically addresses investigational new drugs.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) emphasizes the significance of 'remote data acquisition' in the 2023 guidance, reflecting a critical shift towards allowing data collection from locations distant from the investigator or trial personnel, which is essential for modern clinical trials. This evolution highlights the need for regulatory professionals to fully understand the part 11 predicate rules, particularly in relation to comprehensive clinical trial management services, including:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
Moreover, with an FDA webinar on the draft guidance scheduled for April 25, 2023, stakeholders are presented with a timely opportunity to deepen their understanding of these changes.
By aligning electronic systems with regulatory frameworks and investing in adherence analysis, organizations can enhance decision-making processes in drug development, particularly amidst rising trial costs. Additionally, the Medication Adherence Perspective case study highlights the public health and economic consequences of medication nonadherence, illustrating the critical role that following predicate rules plays in improving adherence rates and overall healthcare outcomes, thereby contributing to job creation and economic growth in the Medtech sector.
Implementing Effective Compliance Strategies for 21 CFR Part 11
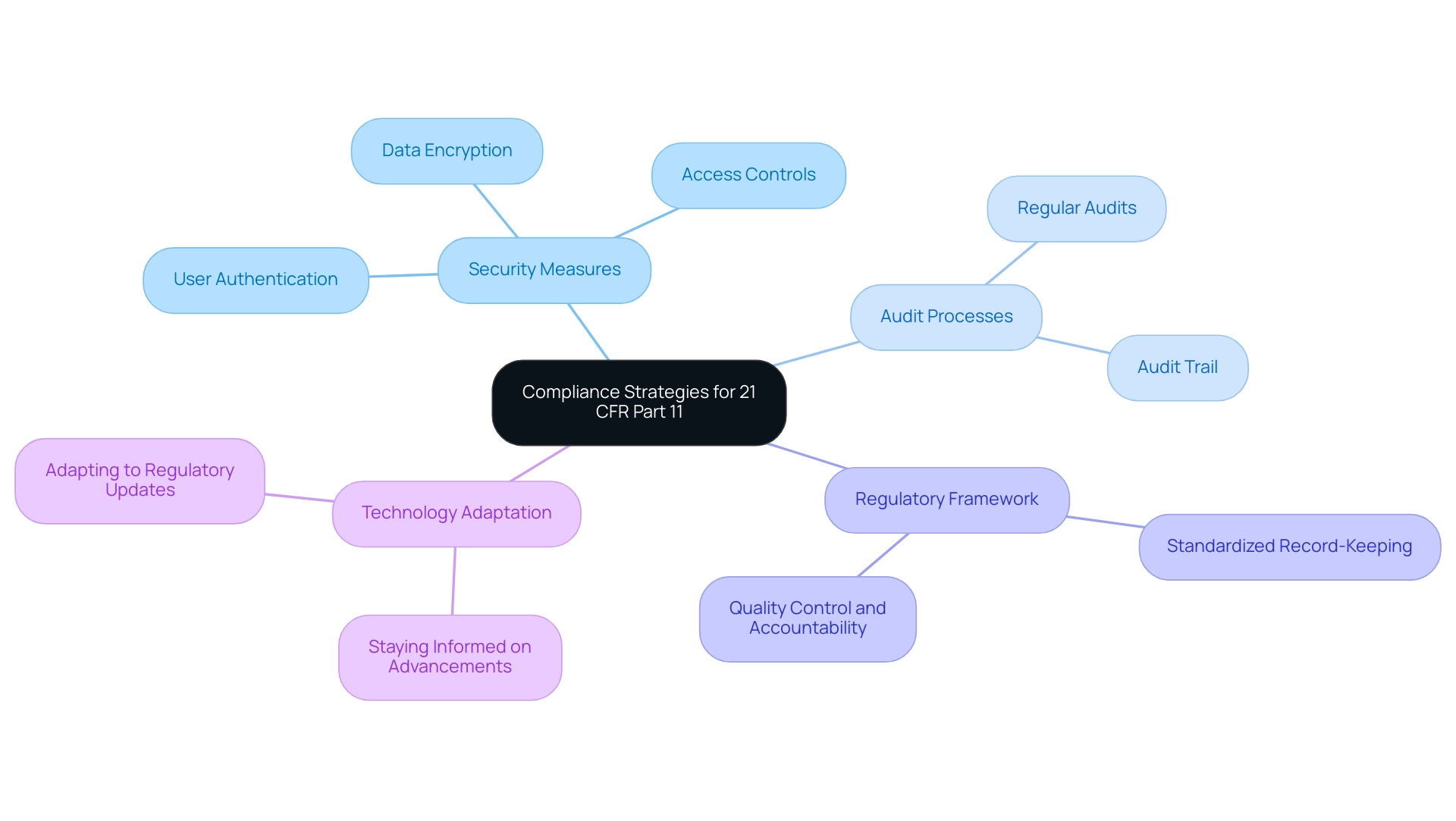
Achieving compliance with the part 11 predicate rules necessitates the implementation of stringent security measures, including robust user authentication, comprehensive access controls, and advanced data encryption techniques. Regular audits and systematic monitoring of digital systems are vital for upholding data integrity and regulatory adherence. A thorough audit trail is indispensable, as it documents all system activities and modifications related to electronic records, thus ensuring accountability and transparency.
Creating a comprehensive regulatory framework that incorporates these essential elements not only aligns with legal requirements but also promotes improved quality control and accountability within organizations. For instance, the case study titled 'Enhanced Quality Control and Accountability' illustrates how adherence to part 11 predicate rules fosters standardized record-keeping practices, leading to improved quality control processes and maintaining accountability for data. As emphasized by Dr. Patrick Flume, Associate Vice President for Clinical Research, the FDA has indicated that it will apply 'enforcement discretion' where digital documentation and signatures are committed to physical writings and properly countersigned to ensure security and non-repudiation.
This method highlights the importance of effective regulatory strategies in protecting data against breaches and boosting consumer confidence. Furthermore, staying informed about advancements in digital record systems is crucial for compliance, ensuring that organizations can adapt to new technologies and regulatory updates that enhance data security.
Navigating Electronic Signature Requirements in 21 CFR Part 11
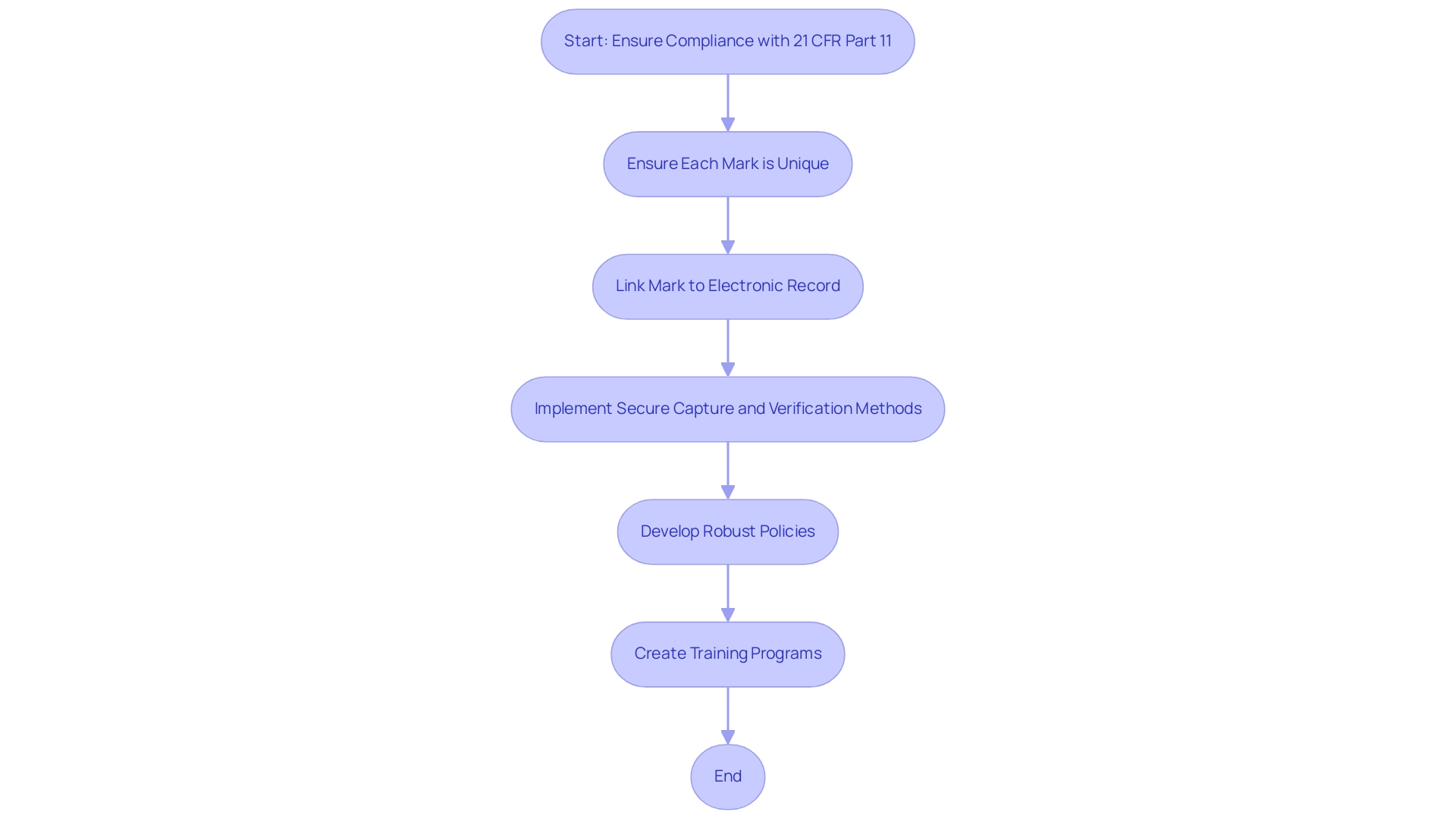
To be considered valid under the part 11 predicate rules of 21 CFR, digital markers must comply with several essential criteria. First and foremost, each mark must be unique to the individual, ensuring that it cannot be replicated or misattributed. Additionally, the mark must be directly linked to the corresponding electronic record, providing an unbroken chain of accountability.
Organizations are also required to implement secure methods for capturing and verifying these marks, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the documentation process. It is crucial for organizations to develop robust policies that guarantee compliance with part 11 predicate rules. This involves creating thorough training programs that instruct users on the correct application and administration of digital identifiers.
As highlighted in the case study titled "Importance of E-signatures in Digital Processes," 60% of IT professionals consider e-signatures to be a 'very important' or 'critical' aspect of digital document processes, underscoring the necessity for effective management strategies. Moreover, remaining updated on the latest news is crucial, as Europe is anticipated to have the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the digital authentication market, highlighting the increasing significance of validation processes in regulated sectors. An expert from one of the largest companies in the defense industry stated, "Thank you for sending the market report and data.
It looks quite comprehensive and the data is exactly what I was looking for. I value the promptness and attentiveness of you and your team, emphasizing the importance of timely and precise information in handling signature requirements.
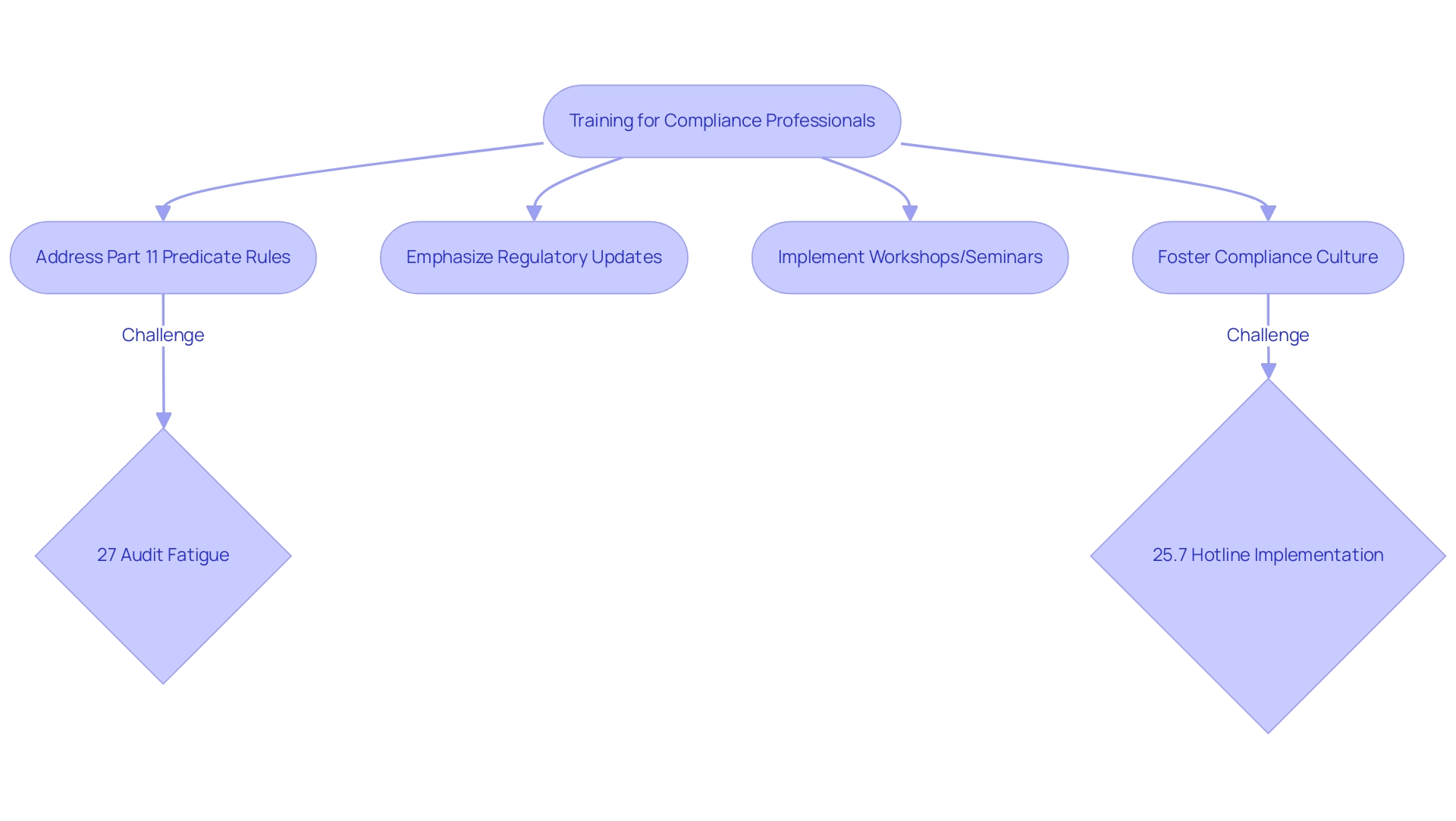
The Importance of Training for Compliance Professionals in 21 CFR Part 11
Training programs tailored for regulatory professionals must thoroughly address the complexities of the part 11 predicate rules, emphasizing the latest regulatory updates and best practices for electronic records management. Recent trends suggest that a significant 27% of security and IT professionals recognize alleviating internal audit fatigue from assessments as the foremost challenge in regulatory programs. This underscores the necessity for continuous learning opportunities, such as regular workshops and seminars, to keep teams abreast of evolving industry standards.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of adherence within the organization is vital; it enables all employees to prioritize regulatory observance. Nicole Stryker emphasizes the significance of this approach, noting that while 84% of Chief Compliance Officers (CCOs) have established risk assessment processes, 32% remain uncertain about the participation of their business units in these evaluations. Furthermore, the low implementation rate of whistleblower hotlines, particularly in small organizations—only 25.7%—raises concerns about accessible reporting mechanisms for employees, emphasizing the need for robust training that includes the development of effective Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and other process documents.
By investing in comprehensive training programs, organizations not only bolster their capacity to maintain compliance with the part 11 predicate rules but also enhance overall research quality. Such training is not merely a regulatory necessity but a strategic investment in the integrity of research practices.
Conclusion
Understanding and adhering to 21 CFR Part 11 is crucial for all entities involved in clinical research, as it establishes the framework necessary for the integrity and reliability of electronic records and signatures. This regulation, along with its predicate rules, serves as the foundation for compliance, ensuring that data integrity is maintained through stringent validation requirements and comprehensive audit trails. The importance of robust compliance strategies, including effective security measures and regular audits, cannot be overstated, as these elements not only align with regulatory expectations but also enhance organizational accountability and quality control.
Moreover, the effective management of electronic signature requirements is essential for maintaining a transparent and secure documentation process. By ensuring that electronic signatures are unique, securely captured, and linked to their respective records, organizations can foster a culture of compliance that safeguards data against breaches and builds consumer confidence. Training programs for compliance professionals play a pivotal role in navigating the complexities of 21 CFR Part 11, equipping teams with the knowledge and skills necessary to adapt to evolving regulations and technological advancements.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of 21 CFR Part 11 and its associated components is imperative for success in the clinical research landscape. By prioritizing compliance through effective strategies, robust training, and a commitment to continuous improvement, organizations can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance the overall quality and integrity of their research practices. As the field continues to evolve, embracing these principles will ensure that entities remain at the forefront of regulatory compliance and data management excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 21 CFR Part 11?
21 CFR Part 11 is a regulation set by the FDA that outlines the standards for digital files and marks to be considered trustworthy, reliable, and comparable to traditional paper documents. It is applicable to entities involved in clinical research, such as sponsors, Contract Research Organizations (CROs), and research institutions.
What are the key elements of 21 CFR Part 11?
Key elements include detailed definitions of digital documents and credentials, strict validation standards, and the requirement to maintain an audit trail that monitors relevant actions over a specified timeframe to ensure data integrity.
Why are audit trails important in 21 CFR Part 11?
Audit trails are essential for ensuring data integrity and compliance with regulatory standards by tracking pertinent actions and maintaining accountability.
What services are encompassed in clinical trial management?
Clinical trial management services include feasibility studies, site selection, regulatory reviews, trial setup, start-up approvals, import permits, and project management.
How does RegDesk assist companies in the medical device and pharma sectors?
RegDesk simplifies global expansion for companies by helping them navigate complex regulatory landscapes, including adherence to local regulations such as those governed by INVIMA in Colombia.
What is the significance of the 'Application of Part 11 Predicate Rules' case study?
This case study illustrates the application of 21 CFR Part 11 to electronic records and signatures, emphasizing the importance of protecting records from unauthorized access and ensuring accountability through unique electronic signatures linked to individuals.
What is the current compliance rate with 21 CFR Part 11 among leading organizations?
Current statistics indicate that adherence to 21 CFR Part 11 has reached 85% among leading organizations, highlighting its significance in the clinical research landscape.
What are predicate rules, and why are they important?
Predicate rules are foundational regulations that govern the use of digital records, particularly in Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Good Clinical Practices (GCP), ensuring data integrity and robust record-keeping in clinical research.
How has the FDA's guidance on remote data acquisition evolved?
The FDA's 2023 guidance emphasizes the importance of remote data acquisition, allowing data collection from locations distant from the investigator or trial personnel, which is crucial for modern clinical trials.
What opportunity is available for stakeholders to learn about changes in regulations?
An FDA webinar on draft guidance is scheduled for April 25, 2023, providing stakeholders with an opportunity to deepen their understanding of the changes related to predicate rules and clinical trial management.




