Introduction
The regulatory landscape for medical devices is complex, shaped by various pathways that dictate how products can enter the market. Among these, the Premarket Approval (PMA) and 510(k) processes stand out, each tailored to address different risk levels associated with medical devices.
While PMA ensures rigorous scrutiny for high-risk devices, the 510(k) pathway offers a more efficient route for those deemed substantially equivalent to existing products. As manufacturers navigate these pathways, understanding the implications of device classification and regulatory requirements becomes crucial.
Recent trends indicate a shift towards integrating real-world evidence and adaptive trial designs, which promise to reshape the future of medical device regulation. This article delves into the intricacies of these pathways, their respective advantages and challenges, and the evolving dynamics that manufacturers must consider in their regulatory strategies.
Overview of Regulatory Pathways: Premarket Approval vs 510(k)
The Premarket Approval (PMA) and 510(k) pathways illustrate the differences in premarket approval vs 510k, as both are vital systems created by the FDA for overseeing medical equipment, fulfilling unique roles according to the risk profiles of the items involved. PMA is a rigorous procedure mainly designated for Class III items, which are defined by their considerable potential hazards. This pathway necessitates extensive clinical data to support claims of safety and efficacy, ensuring that only the most rigorously tested products reach the market.
Conversely, the 510(k) process offers a more streamlined approach for Class I and II devices, allowing manufacturers to establish substantial equivalence to existing, marketed devices. This differentiation highlights the essential contrasts in complexity and compliance requirements between premarket approval vs 510k submissions.
In Latin America, leveraging the expertise of bioaccess® can significantly enhance the management of clinical trials associated with these pathways. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® specializes in a comprehensive suite of clinical trial management services, including:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
Their focus on Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF) ensures that clients navigate the complexities of compliance approval effectively.
Bioaccess®'s flexibility and specialized knowledge are critical assets in addressing the challenges faced in the comparison of premarket approval vs 510k, enabling timely assessments and efficient management of the review process.
Recent statistics reveal that 41% of De Novo decisions have successfully met the current Medical Device User Fee Amendments (MDUFA) review goals, indicating progress within the FDA’s oversight framework. However, the 510(k) program faces notable challenges, including a surge in review volume and the pressing need for timely assessments. These challenges have prompted calls for thoughtful reforms aimed at enhancing efficiency and ensuring that products can be reviewed and approved in a timely manner.
Experts promote a balanced oversight strategy; Dr. Jonathan R. Dubin from the Department of Orthopedic Surgery at Truman Medical Center highlights,
Enhancing postmarketing monitoring strategies and crucial trials may enhance safety of the product.
This viewpoint is especially pertinent considering industry changes, as almost 90% of medical equipment leaders now prioritize U.S. authorization over the European Union's new Medical Equipment Regulation (MDR) because of the latter's complexities. This shift reflects a significant change in oversight priorities, with 23% of participants indicating they would also focus on the Japanese and Chinese markets.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider the findings that challenge previous literature suggesting a higher recall risk for products associated with premarket approval vs 510(k) products. This insight emphasizes the evolving understanding of equipment safety and regulatory effectiveness.
This foundational understanding of PMA and 510(k) pathways not only sets the stage for a deeper analysis of their respective advantages and drawbacks but also emphasizes the evolving landscape of medical product regulation as we look ahead to 2024, particularly when supported by the tailored services of bioaccess®.
Key Requirements and Submission Processes for PMA and 510(k)
The submission procedure for a Premarket Approval (PMA) application is notably rigorous, especially in the context of premarket approval vs 510k, as it requires a detailed compilation of clinical trial data, comprehensive manufacturing information, and an in-depth risk-benefit analysis. Manufacturers must present a PMA application that encapsulates all pertinent studies and data substantiating the product's safety and efficacy. Our clinical trial management services include:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
These services ensure compliance with local regulations, such as those set forth by INVIMA, Colombia's Level 4 health authority.
Furthermore, our services include:
- Comprehensive compliance evaluations
- Trial preparation
- Import authorization for investigational tools
These are essential for successful study commencement. Manufacturers must also submit post-approval study reports at specified intervals, including updates on study progress and safety data, which are essential components of the PMA procedure. In contrast, the process of premarket approval vs 510k submission is comparatively streamlined, emphasizing the demonstration of substantial equivalence to a predicate instrument.
Given that over 200,000 medical professionals are already excelling in this field, familiarity with these submission requirements is essential. As Chris Rush aptly remarks,
I cannot stress the importance of your clinical data (and non-clinical testing data) enough,
underscoring the critical role of robust data in the PMA pathway. Moreover, with the changing oversight landscapes, including insights from experts like Katherine Ruiz in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, it is essential for manufacturers to stay updated on PMA amendments and supplements.
A pertinent example is the July 2024 warning letter issued to Globus Medical regarding their Excelsius GPS surgical robot, which revealed significant quality system violations and offers crucial lessons on maintaining robust quality systems for complex surgical devices. Grasping these differences, especially regarding premarket approval vs 510k, and the associated requirements is essential for effective navigation of the compliance landscape and ensuring adherence.
Pros and Cons of Premarket Approval and 510(k) Pathways
The comparison of premarket approval vs 510k highlights that the Premarket Approval (PMA) pathway is known for its rigorous data requirements and comprehensive review process, making it a time-consuming and costly option for manufacturers. Successful submissions through this pathway not only enhance market confidence by ensuring that high-risk devices—such as those that support or sustain human life—meet stringent safety standards, but also provide significant product differentiation. Our comprehensive clinical trial management services encompass:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews—ensuring adherence to standards crucial for the PMA pathway
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
This reporting includes serious and non-serious adverse events, which are essential for navigating the complexities of regulatory frameworks such as INVIMA in Colombia. This oversight by the National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, classified as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO, ensures that medical products meet necessary standards for market approval. In contrast, the 510(k) pathway provides a quicker, more economical option for medium-risk medical instruments, highlighting the differences in efficiency between premarket approval vs 510k, primarily benefiting those showing substantial equivalence to current products.
While this expedited pathway allows quicker market entry, it may lead to less rigorous scrutiny, potentially affecting the perceived credibility of the product among stakeholders. A notable case is the streamlined 510(k) submission process, which is often the fastest way to get a medical device cleared for the U.S. market, with the FDA advising submission at least 90 days before marketing. Producers must thoroughly assess these advantages and disadvantages, taking into account the effects of each policy approach on market confidence and their overall strategy for product development and launch, particularly in the context of premarket approval vs 510k.
Consistent interaction with FDA guidance and active involvement in industry associations can improve comprehension and navigation of these compliance landscapes, as highlighted by industry leaders. Furthermore, the 2017 FDA recall of a pacemaker due to cybersecurity vulnerabilities underscores the critical importance of rigorous scrutiny in the PMA process and its implications for market confidence, further reinforcing the need for comprehensive project management in clinical trials.
Impact of Device Classification on Regulatory Strategy
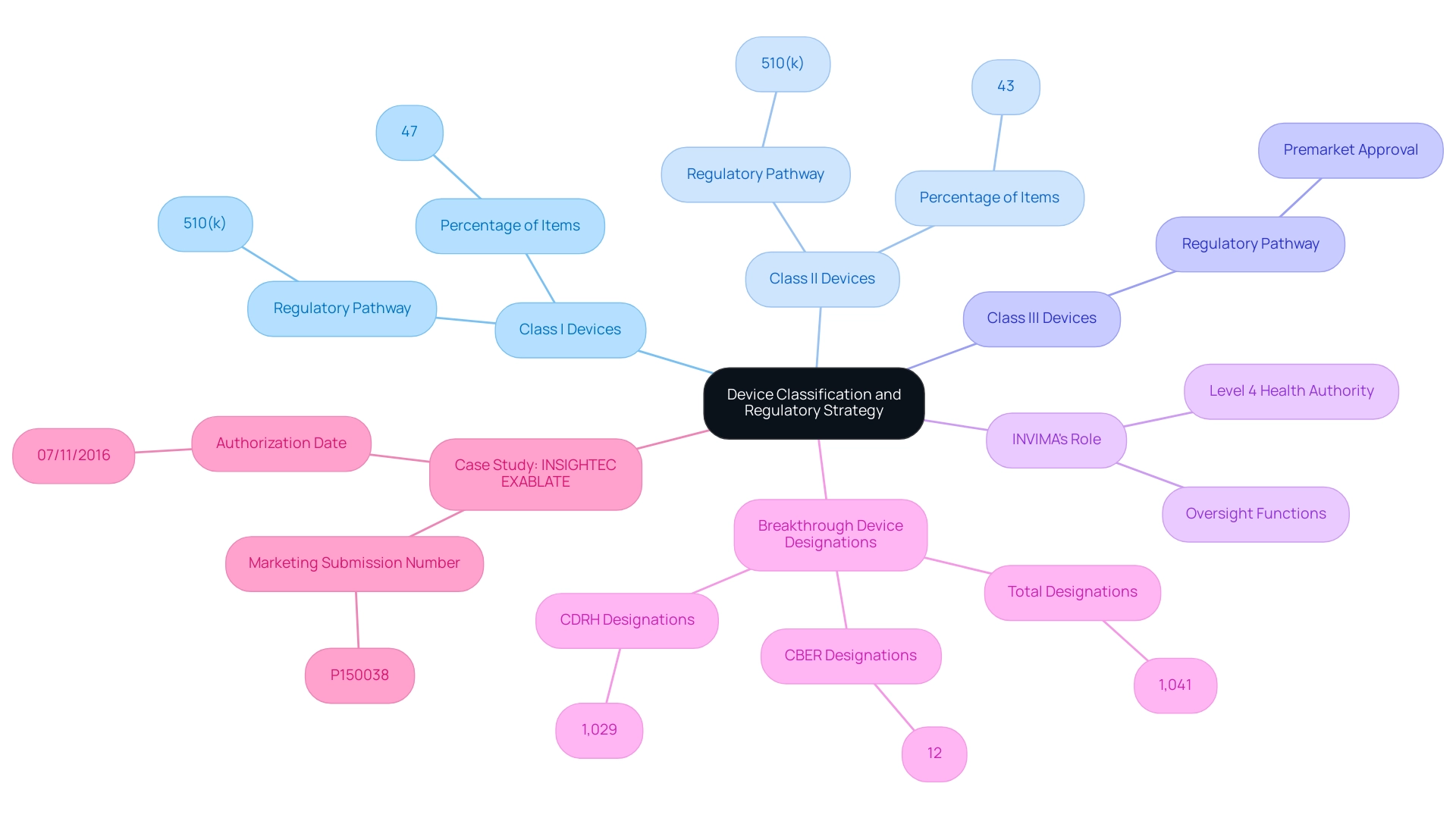
Device classification plays a critical role in determining whether a medical product will proceed through premarket approval vs 510k pathways. In Colombia, the governing authority responsible for overseeing these classifications is INVIMA, or the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute. Founded in 1992 under the Ministry of Health and Social Protection, INVIMA is responsible for inspecting and supervising health products, including medical equipment, to ensure adherence to safety and efficacy standards.
Notably, INVIMA is acknowledged as a Level 4 health authority by the Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization, underscoring its credibility in oversight functions. Class I products, which are generally regarded as low-risk, typically require minimal regulatory oversight and can often be marketed utilizing the 510(k) process. In fact, approximately 47% of items fall into this category, highlighting the streamlined approach for such products.
Class II products, associated with moderate risk, usually also follow the 510(k) route but may involve additional requirements, making up about 43% of medical equipment. On the other hand, Class III products, categorized as high-risk because of their substantial effects on patient safety, require a premarket approval vs 510k submission, which entails a more stringent evaluation procedure reflecting the vital nature of these items. As emphasized by Dr. Gail A. Van Norman, there are distinct compliance challenges associated with the device approval procedures that manufacturers must navigate.
Comprehending these classifications is crucial for manufacturers to devise effective compliance strategies and enhance their submission processes, particularly when considering premarket approval vs 510k. Significantly, as of September 30, 2024, the FDA has awarded a total of 1,041 Breakthrough Device designations, with 1,029 from the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) and 12 from the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), highlighting the dynamic nature of oversight pathways.
The implications of Unique Device Identifiers for Class I Medical Device Recalls are significant within INVIMA's oversight framework, as they enhance tracking and accountability for these devices. The FDA also encourages early contact and collaboration with sponsors through pre-submission meetings, which can significantly aid manufacturers in navigating the PMA process effectively. The case study of INSIGHTEC’s EXABLATE, which received marketing authorization (P150038) on July 11, 2016, exemplifies the successful navigation of these classification systems and strategies.
By thoroughly understanding these differences among Class I, II, and III products, along with the insights from experts like Ana Criado, Director of Compliance and an experienced consultant in the medical equipment field, manufacturers can significantly improve their strategic approach to submissions in both the US and Colombia.
Future Trends in Medical Device Regulation: What to Expect
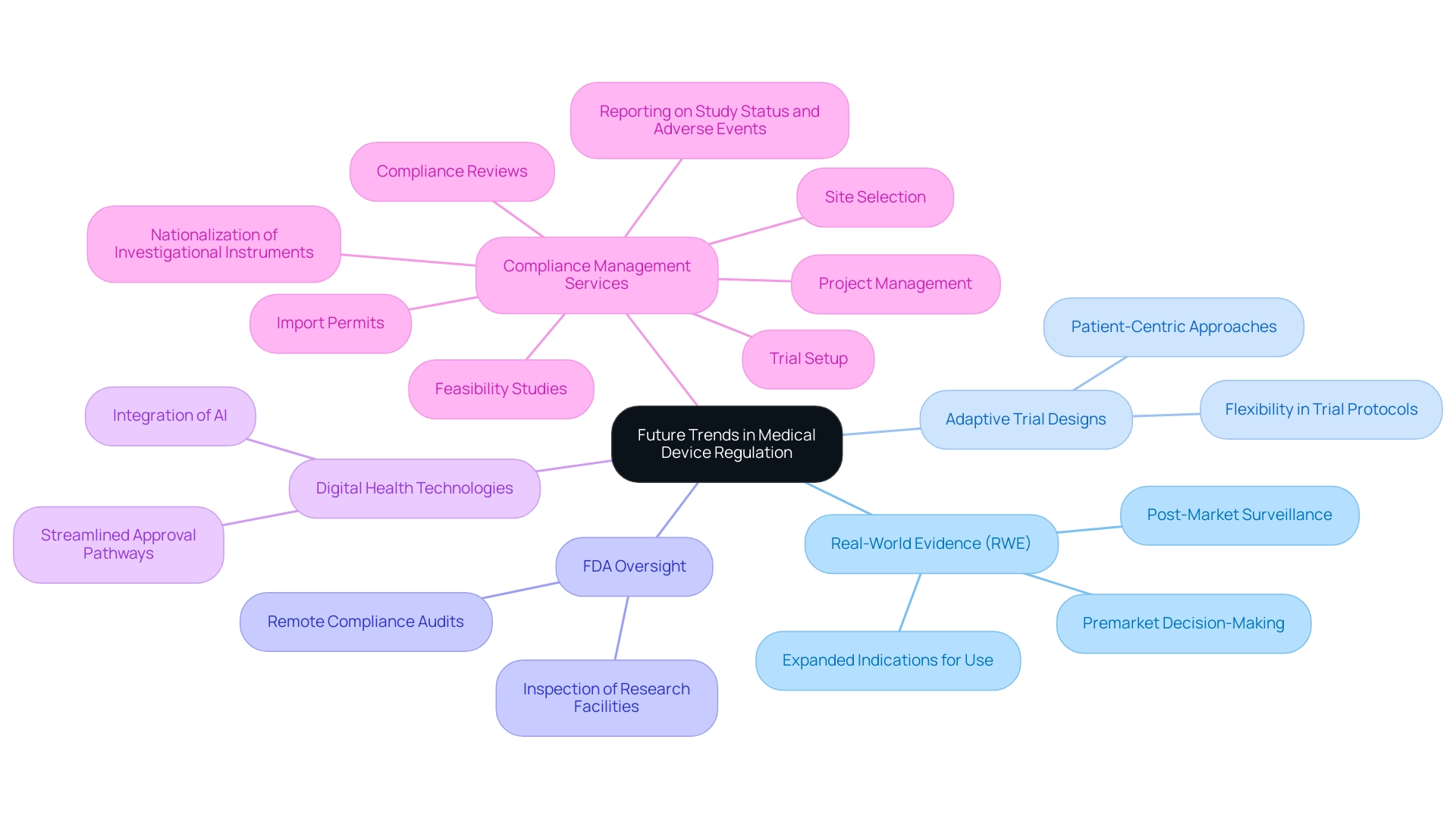
The landscape of medical equipment regulation is undergoing significant transformation, driven by emerging trends such as an increased focus on real-world evidence (RWE) and adaptive trial designs. The FDA emphasizes the significance of RWE, pointing out that the RWE/RWD produced through NEST may be utilized not only for post-market surveillance, but it may also support premarket decision-making and expanded indications for use after clearance or approval. This transition towards incorporating RWE into the governance framework is anticipated to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of product approvals.
In 2022, the FDA acquired increased oversight power to perform remote compliance audits and examine facilities conducting research on equipment, further bolstering its oversight abilities. Moreover, as digital health technologies and artificial intelligence applications continue to advance, the FDA is likely to adopt more flexible approaches to accommodate these innovations, streamlining pathways for their approval. Comprehensive clinical trial management services, including:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Nationalization of investigational instruments
- Project management
- Reporting on study status and adverse events
are vital in this context.
Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in compliance matters for medical instruments and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, plays a crucial role in guiding these processes. A case study titled 'Evaluating the Need for AI in Medical Devices' illustrates that manufacturers must assess whether AI is necessary for their product, focusing on patient safety and efficacy. This evaluation can assist manufacturers in selecting the suitable compliance pathway for their devices.
As global standards alignment advances, manufacturers may encounter modifications in submission requirements that enable easier access to international markets. However, they must also navigate the challenges and opportunities affecting the Medical Device Regulatory Affairs Market, including evolving compliance standards and competitive pressures. Staying informed about these trends will be essential for manufacturers aiming to navigate the evolving regulatory environment successfully, particularly as they assess the necessity of AI in their products, ensuring patient safety and efficacy remain at the forefront of their development strategies.
Conclusion
Navigating the regulatory pathways for medical devices—specifically the Premarket Approval (PMA) and 510(k) processes—requires a comprehensive understanding of their distinct characteristics and implications. The PMA pathway, while rigorous and resource-intensive, ensures that high-risk devices undergo thorough scrutiny, reinforcing market confidence in their safety and efficacy. In contrast, the 510(k) process provides a more expedient route for medium-risk devices, enabling quicker market access but potentially at the cost of less rigorous evaluation.
The importance of device classification cannot be overstated, as it dictates the regulatory strategy that manufacturers must adopt. Class I devices benefit from streamlined processes, while Class III devices necessitate the extensive requirements of PMA submissions. This classification system, along with the evolving dynamics of regulatory expectations, highlights the critical need for manufacturers to stay informed and agile in their approach.
Looking ahead, the integration of real-world evidence and adaptive trial designs is poised to reshape medical device regulation. As regulatory bodies like the FDA adapt to technological advancements, manufacturers must remain vigilant, ensuring compliance while leveraging new opportunities for innovation. Understanding these trends is essential for developing effective regulatory strategies that prioritize patient safety and product efficacy.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for medical devices is complex yet navigable for those equipped with the right knowledge and resources. By embracing the nuances of PMA and 510(k) pathways, alongside the evolving regulatory environment, manufacturers can position themselves for success in a competitive marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between the Premarket Approval (PMA) and 510(k) pathways?
PMA is a rigorous process primarily for Class III medical devices, requiring extensive clinical data to prove safety and efficacy. In contrast, the 510(k) pathway is more streamlined for Class I and II devices, allowing manufacturers to demonstrate substantial equivalence to existing products.
What types of services does bioaccess® provide to assist with PMA and 510(k) pathways?
Bioaccess® offers a range of clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, to help navigate the complexities of compliance approval.
What is the significance of Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS) and First-In-Human Studies (FIH)?
EFS and FIH studies are crucial for assessing the safety and effectiveness of new medical devices early in the development process, helping clients manage the approval process effectively.
What challenges does the 510(k) program currently face?
The 510(k) program is experiencing a surge in review volume and a pressing need for timely assessments, leading to calls for reforms to enhance efficiency in the review and approval process.
How do recent statistics reflect the performance of the FDA's De Novo decisions?
Recent statistics indicate that 41% of De Novo decisions have successfully met the Medical Device User Fee Amendments (MDUFA) review goals, suggesting progress in the FDA’s oversight framework.
Why do medical equipment leaders prioritize U.S. authorization over the EU's Medical Equipment Regulation (MDR)?
Nearly 90% of medical equipment leaders now favor U.S. authorization due to the complexities associated with the EU's MDR, reflecting a shift in oversight priorities.
What does the evolving understanding of equipment safety suggest about PMA and 510(k) products?
Recent findings challenge the notion that PMA products have a higher recall risk compared to 510(k) products, indicating a changing perspective on the safety and regulatory effectiveness of medical equipment.
What is required in the PMA submission procedure?
The PMA submission requires a detailed compilation of clinical trial data, manufacturing information, and a risk-benefit analysis, along with post-approval study reports at specified intervals.
How can manufacturers ensure compliance with local regulations during clinical trials?
Manufacturers can utilize bioaccess®'s services, which include comprehensive compliance evaluations and trial preparation to meet local regulatory requirements, such as those from INVIMA in Colombia.
What lessons were highlighted by the July 2024 warning letter issued to Globus Medical?
The warning letter revealed significant quality system violations, emphasizing the importance of maintaining robust quality systems for complex surgical devices to navigate compliance effectively.




