Introduction
The regulatory landscape surrounding medical device testing is multifaceted and constantly evolving, presenting both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers striving to ensure safety and efficacy. Central to this framework are the stringent standards set forth by regulatory bodies such as the FDA, alongside international guidelines like ISO, which collectively shape the protocols for:
- Device classification
- Premarket approval
- Ongoing surveillance
As innovations in technology, such as artificial intelligence and digital health solutions, continue to emerge, the necessity for comprehensive testing methodologies becomes increasingly critical. This article delves into the essential types of testing required, the importance of compliance with regulatory standards, and the role of preclinical and clinical trials in validating medical devices. Furthermore, it highlights the latest trends and challenges that manufacturers must navigate to remain competitive and compliant in a rapidly changing environment.
Understanding Regulatory Frameworks for Medical Device Testing
A strong framework of guidelines established to ensure safety and effectiveness supports medical device testing requirements. Central to these standards is the FDA's Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, which outlines the requirements for classification, premarket approval, and post-market surveillance. Notably, the recent addition of ISO 17665:2024 to the FDA consensus list for sterilization processes emphasizes the evolving nature of these regulations.
Moreover, ISO 13485 establishes the fundamental standards for a quality management system, requiring organizations to prove their capability to provide healthcare products and associated services that consistently meet customer and compliance expectations. As these frameworks evolve, staying informed is crucial for compliance and effective management of medical device testing requirements. The FDA's recent draft guidance on the use of AI in decision-making exemplifies the ongoing adaptation of the oversight landscape, emphasizing the need for vigilance in understanding these changes.
As mentioned by Hogan Lovells, 'If you have inquiries regarding the use of AI/ML in clinical trials, please reach out to any of the Hogan Lovells authors of this publication for assistance.' Familiarity with these frameworks is not only vital for compliance but also for ensuring the integrity of the medical device testing requirements across the sector. Furthermore, challenges such as compliance obstacles, competition, recruitment issues, and financial constraints are critical for startups navigating clinical trials.
This is where specialists like Ana Criado, Director of Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, can offer invaluable support, given her extensive background in compliance, health economics, and biomedical engineering. Furthermore, Katherine Ruiz's expertise in Regulatory Affairs for healthcare products and in vitro diagnostics further emphasizes the necessity of having informed consultants to assist companies in navigating the intricacies of regulatory requirements. For a comprehensive approach to advancing your healthcare equipment trials, including feasibility studies, site selection, trial set-up, project management, and reporting, we invite you to BOOK A MEETING with our experts.
Key Types of Testing Required for Medical Devices
To ensure the safety and efficacy of medical devices, several critical types of testing are mandated:
- Software Evaluation: This assessment verifies that the software integrated within medical instruments functions properly and complies with specified requirements. The FDA emphasizes the need for a robust software development process to mitigate potential hazardous failures, stating that "effective performance has been defined, and means of verifying both safe and effective performance have been planned, carried out, and properly reviewed." This highlights the regulatory focus on comprehensive software validation.
- Biocompatibility Assessment: This assessment evaluates the compatibility of material components with biological systems, which is essential for patient safety. Recent studies highlight advancements in biocompatibility testing methods, providing updated results relevant to the industry in 2024.
- Usability Testing: This evaluates how easily users can engage with the system, identifying potential user errors that may compromise safety. A matrix-based method applied to five real datasets from usability studies has demonstrated effectiveness in predicting usability problems. The outcome of this application showed that the matrix-based method provided more accurate predictions compared to traditional estimation methods, offering valuable insights into practical applications.
- Performance Testing: This assesses whether the equipment operates as intended under expected conditions, ensuring reliability in real-world scenarios. The integration of automated software evaluation is enhancing this process, making it faster and more accurate. For example, automated assessment tools can swiftly detect software issues and guarantee adherence to changing regulatory standards, tackling the challenges linked to contemporary medical equipment.
- Sterility Testing: This confirms that equipment is free from viable microorganisms, which is especially vital for use in surgical environments. The rigorous nature of this evaluation underlines its importance in maintaining patient safety.
Each of these evaluation categories is essential in the thorough verification of healthcare instruments, which is crucial for meeting medical device testing requirements and ultimately guaranteeing their safety and efficacy for patient use.
Compliance with FDA and ISO Standards in Medical Device Testing
Adherence to FDA and ISO standards is essential for meeting medical device testing requirements in the evaluation of medical equipment. The FDA mandates that manufacturers comply with medical device testing requirements to validate the safety and efficacy of their products prior to market entry. This process typically involves the submission of either a premarket notification (510(k)) or a premarket approval (PMA) application, both of which necessitate robust data derived from various medical device testing requirements.
Among the essential ISO standards, ISO 14971 stands out as the guideline for effective risk management, which assists manufacturers in systematically identifying and mitigating potential risks associated with their products in compliance with medical device testing requirements. Adhering to the medical device testing requirements not only simplifies the approval process but also greatly enhances the product's credibility within the marketplace. Recent updates on the ISO 14971 risk management standards further emphasize the medical device testing requirements, ensuring that manufacturers remain vigilant in managing risks throughout the product lifecycle.
Additionally, extensive clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, and evaluation and input on study documents, are vital in navigating the intricate compliance landscape to meet medical device testing requirements. This encompasses trial set-up, start-up, and approval processes, along with the import permit and nationalization of investigational instruments, all of which must adhere to medical device testing requirements. Reporting on study status, inventory, and serious and non-serious adverse events is essential for fulfilling medical device testing requirements.
The oversight provided by INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, which serves as a Level 4 health authority as classified by PAHO/WHO, is a key aspect of this process. Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, adds valuable insights into this process. As Doug Dziak, CPSC Commissioner, noted, 'The limitations on the CPSC’s civil penalty authority … is a serious impediment to the agency’s efforts to deter large corporate actors from violating consumer protection laws,' which underscores the broader regulatory challenges manufacturers face.
Furthermore, with FDA compliance statistics for healthcare product manufacturers in 2024 indicating a projected rise in enforcement actions, producers must stay informed about medical device testing requirements and adaptable to maintain compliance and uphold the highest standards of safety and effectiveness.
The Role of Preclinical and Clinical Testing in Device Validation
Preclinical evaluation is a vital initial phase that must adhere to medical device testing requirements, involving laboratory and animal studies focused on assessing the safety and effectiveness of a medical instrument before human trials. This stage is instrumental in identifying potential risks and shaping the design of subsequent clinical trials. Following preclinical testing, clinical trials are conducted involving human subjects, systematically progressing through distinct phases to rigorously assess the product's safety and efficacy in real-world conditions.
Specifically, Phase I trials primarily focus on safety, establishing a foundational understanding of the apparatus’s tolerability in humans. In contrast, Phase II and III trials explore further, assessing the efficacy and collecting extensive data on its performance across a broader population. The organized method of the evaluation phases is essential for confirming a device's preparedness for market launch, ensuring that all possible risks are sufficiently managed and that the device complies with the medical device testing requirements for patient safety and effectiveness.
For instance, the Early Feasibility Study conducted by ReGelTec on HYDRAFIL™ for treating chronic low back pain in Colombia exemplifies the importance of rigorous clinical trial management services, including site selection, compliance reviews, and project management, as provided by bioaccess®. Notably, this study successfully treated eleven patients, demonstrating the effectiveness of HYDRAFIL™ and the comprehensive support provided by bioaccess®. As emphasized by Inmaculada B. Aban, a professor of biostatistics,
- 'Consequently, the National Institute of Neurological Diseases calls for more rigorous reporting of these studies to raise awareness on the proper design and conduct of future preclinical studies as well as the proper interpretation of the results of completed studies.'
This underscores the necessity for meticulous design and conduct of these trials. Furthermore, the importance of preclinical evaluations in drug development becomes even more apparent. This extensive evaluation framework, incorporating insights from Colombia's INVIMA oversight, not only reduces risks but also improves the reliability of clinical outcomes, ultimately encouraging greater innovation and enhanced healthcare delivery.
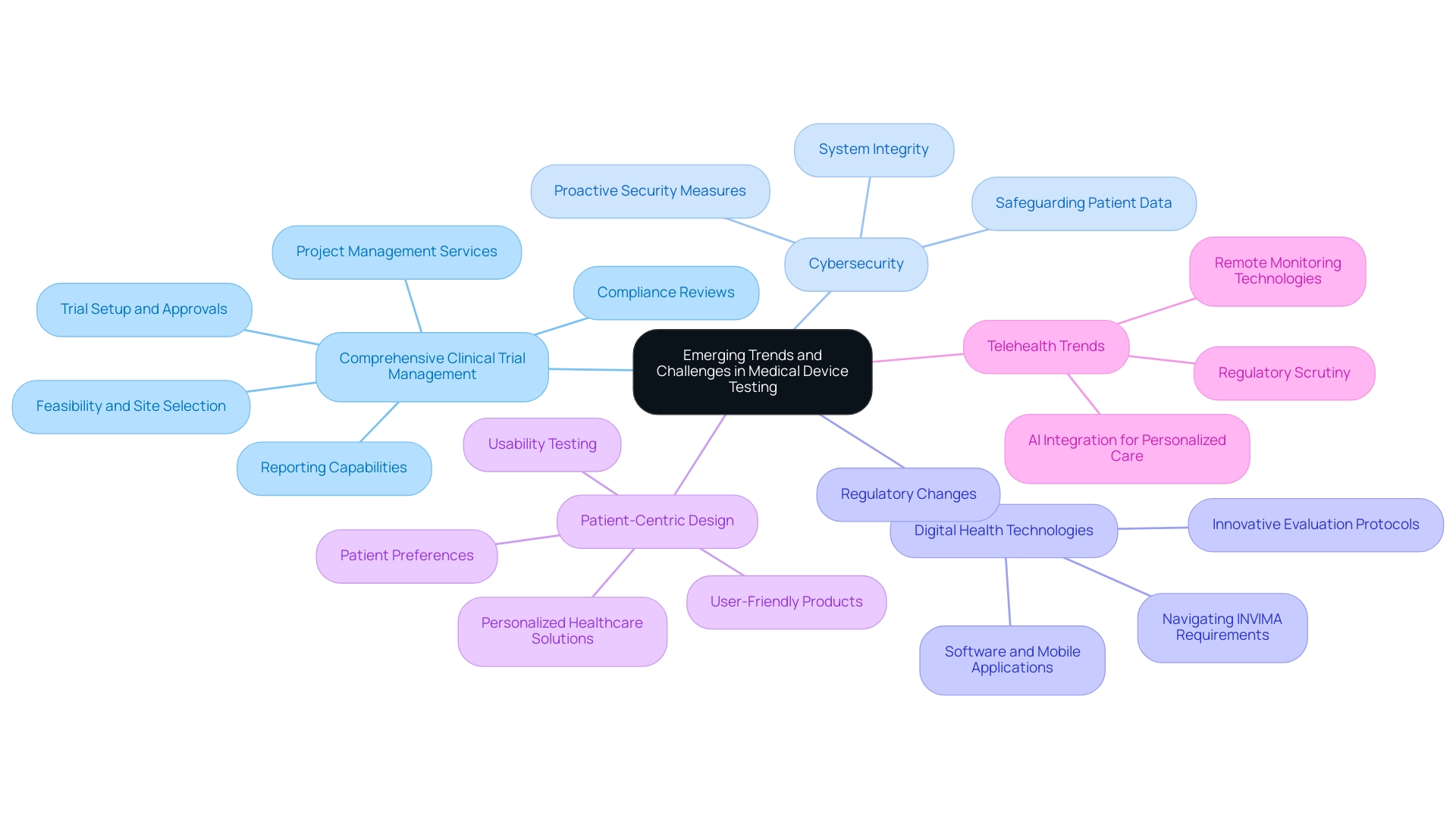
Emerging Trends and Challenges in Medical Device Testing
The landscape of medical equipment evaluation is continuously evolving, shaped by several emerging trends that are redefining industry standards and practices:
- Comprehensive Clinical Trial Management: Our service capabilities encompass feasibility and selection of research sites and principal investigators (PIs), compliance reviews of study documents to meet country requirements, and trial setup, which includes obtaining necessary approvals from ethics committees and health ministries. This integrated method ensures that evaluation aligns with regulatory expectations and enhances market readiness. Additionally, our project management services ensure that all phases of the trial are executed efficiently, while our reporting capabilities provide essential updates on study status, inventory, and any adverse events.
- Cybersecurity: With the proliferation of interconnected systems, safeguarding patient data and ensuring system integrity are critical. Cybersecurity incidents pose significant risks, prompting manufacturers to implement robust security measures. As noted by industry experts, addressing these challenges proactively is essential for maintaining trust and compliance.
- Digital Health Technologies: The rise in digital health technologies has generated a need for innovative evaluation protocols. As devices increasingly rely on software and mobile applications, comprehensive evaluations are necessary to ensure their effectiveness and safety. This shift emphasizes the need for manufacturers to adjust their evaluation methodologies in line with medical device testing requirements to accommodate software-based devices. Regulatory changes are causing the landscape to be in constant flux, with ongoing updates that require manufacturers to refine their medical device testing requirements. Staying ahead of these changes is vital for compliance with medical device testing requirements and ensuring market readiness. Our expertise in navigating the requirements set by INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, is pivotal. As a Level 4 health authority recognized by PAHO/WHO, INVIMA's oversight ensures that medical instruments meet stringent safety and efficacy standards. Furthermore, our services encompass acquiring import permits and nationalization of investigational equipment, which are crucial for compliance with local regulations.
- Patient-Centric Design: There is a growing emphasis on usability and patient experience, driving the need for more thorough usability testing. Manufacturers are increasingly acknowledging that products must not only function effectively but also be user-friendly and accessible. This trend aligns with the broader industry push towards personalized healthcare solutions. According to a recent survey, 78% of patients prefer tools that are easy to use and understand, underscoring the importance of patient-centric design.
- Telehealth Trends: As highlighted, three key trends to watch in telehealth by 2025 include the integration of AI for personalized care, the expansion of remote monitoring technologies, and increased regulatory scrutiny on telehealth services. These trends are anticipated to influence the future of healthcare delivery, highlighting the need for devices to be adaptable and compliant with evolving standards.
These trends offer both opportunities and challenges for device manufacturers, requiring a proactive and strategic approach to testing and compliance. As Arda Ural, PhD, highlights in his discussions on biopharmaceutical strategy, adapting to these emerging trends will be crucial for success in the evolving medical landscape.
Conclusion
The regulatory landscape for medical device testing is characterized by a complex interplay of standards and requirements that manufacturers must navigate to ensure safety and efficacy. Key components of this framework include stringent compliance with FDA regulations and ISO standards, which guide the classification, approval, and ongoing surveillance of medical devices. Understanding the essential types of testing—such as software validation, biocompatibility assessments, usability evaluations, and sterility testing—is crucial for manufacturers aiming to uphold the highest safety standards.
Moreover, the roles of preclinical and clinical testing cannot be overstated. These phases are vital for validating a device’s readiness for market entry, ensuring that all potential risks are comprehensively addressed. The integration of innovative technologies and methodologies in testing processes reflects the industry's commitment to enhancing patient safety and efficacy. As trends such as cybersecurity, digital health technologies, and patient-centric design gain prominence, manufacturers must remain agile, adapting their approaches to meet evolving regulatory demands.
Ultimately, the future of medical device testing hinges on a proactive strategy that embraces these emerging trends while maintaining strict adherence to regulatory standards. By fostering a culture of compliance and innovation, manufacturers can navigate the challenges of this dynamic environment, ensuring their devices not only meet regulatory requirements but also contribute to improved healthcare outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of the FDA's Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21 in medical device testing?
The FDA's Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21 outlines the requirements for classification, premarket approval, and post-market surveillance of medical devices, establishing a strong framework of guidelines to ensure safety and effectiveness.
What is the significance of ISO 17665:2024 in medical device regulations?
ISO 17665:2024 has been recently added to the FDA consensus list for sterilization processes, highlighting the evolving nature of regulations surrounding medical device testing.
What does ISO 13485 establish for organizations in the healthcare sector?
ISO 13485 sets the fundamental standards for a quality management system, requiring organizations to demonstrate their capability to provide healthcare products and services that consistently meet customer and compliance expectations.
Why is it important to stay informed about evolving medical device testing frameworks?
Staying informed is crucial for compliance and effective management of medical device testing requirements, as regulations and guidance, such as the FDA's draft guidance on the use of AI in decision-making, continue to evolve.
What challenges do startups face when navigating clinical trials for medical devices?
Startups often encounter compliance obstacles, competition, recruitment issues, and financial constraints while navigating clinical trials.
Who can provide support for navigating regulatory requirements in medical device testing?
Specialists, such as Ana Criado and Katherine Ruiz, can offer invaluable support due to their extensive backgrounds in compliance, health economics, and regulatory affairs for healthcare products.
What types of testing are mandated to ensure the safety and efficacy of medical devices?
The critical types of testing include Software Evaluation, Biocompatibility Assessment, Usability Testing, Performance Testing, and Sterility Testing.
What is involved in Software Evaluation for medical devices?
Software Evaluation verifies that the software within medical instruments functions properly and complies with specified requirements, emphasizing a robust software development process to mitigate potential hazardous failures.
What does Biocompatibility Assessment evaluate?
Biocompatibility Assessment evaluates the compatibility of material components with biological systems, which is essential for ensuring patient safety.
How does Usability Testing contribute to medical device safety?
Usability Testing evaluates how easily users can engage with the system and identifies potential user errors that may compromise safety, using matrix-based methods to predict usability problems effectively.
What is the purpose of Performance Testing in medical devices?
Performance Testing assesses whether the equipment operates as intended under expected conditions, ensuring reliability in real-world scenarios.
Why is Sterility Testing critical for medical devices?
Sterility Testing confirms that equipment is free from viable microorganisms, which is especially vital for devices used in surgical environments to maintain patient safety.




