Overview
The top 10 quality standards every medical device must meet include ISO 13485, ISO 14971, and IEC 60601, which collectively ensure rigorous quality control, effective risk management, and safety of electrical equipment in healthcare. The article emphasizes that adherence to these standards is crucial for regulatory compliance, enhancing product reliability, and fostering innovation within the medical device industry, thereby maintaining patient safety and improving marketability.
Introduction
In the intricate world of medical devices, the implementation of Quality Management Systems (QMS) is not just a regulatory requirement but a fundamental pillar that underpins patient safety and product efficacy. As organizations navigate the complexities of compliance, understanding the critical components of QMS becomes essential for ensuring that medical devices not only meet stringent safety standards but also foster innovation within the industry.
This article delves into the multifaceted landscape of quality management in medical devices, exploring key standards such as:
- ISO 13485
- The regulatory frameworks governing device approval
- The vital role of post-market surveillance
By examining these elements, it highlights the importance of maintaining high-quality standards throughout the product lifecycle and the financial implications associated with effective quality management practices.
Understanding Quality Management Systems in Medical Devices
Quality Management Systems (QMS) serve as structured frameworks that organizations utilize to meticulously manage and enhance the standard of their products and services. In the healthcare equipment sector, a strong QMS is not simply advantageous but crucial for ensuring that every quality medical device complies with regulatory requirements and protects patient safety. A comprehensive QMS involves essential processes such as:
- Design control
- Risk management
- Supplier performance management
All of these processes collaborate to promote the creation of safe and effective healthcare products.
Key components of a QMS include:
- Meticulous documentation
- Employee training
- A commitment to continuous improvement
These elements are vital for professionals in the medical device industry to maintain a quality medical device throughout the entire product lifecycle. Recent reports emphasize that training employees on QMS standards, including ISO 9001, significantly assists in ensuring compliance while simultaneously improving overall management. Furthermore, QMS software prices usually start at $13,000 for small companies and can reach up to $100,000 for larger ones, underscoring the financial implications of implementing these systems.
As the market for industry-specific QMS solutions becomes increasingly competitive, with intense rivalry within each solution type, the significance of implementing effective management practices cannot be overstated. Additionally, the emergence of IoMT technologies illustrates how QMS can address cybersecurity challenges, further connecting management to patient safety.
Key Quality Standards for Medical Devices
Several essential criteria influence the field of healthcare equipment production and administration, with ISO 13485 emerging as the most acknowledged. This guideline establishes a framework for a quality management system tailored specifically for a quality medical device, ensuring that manufacturers adhere to rigorous quality control measures. Complementing this, ISO 14971 concentrates on risk management, offering guidelines for identifying and reducing potential risks related to healthcare instruments.
Meanwhile, IEC 60601 acts as an essential guideline that addresses the safety and effectiveness of electrical equipment used in healthcare, ensuring that instruments are safe for patient use. In Colombia, the INVIMA (Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute) plays a vital role in this landscape, overseeing the marketing and manufacturing of health products and ensuring adherence to these international guidelines. INVIMA's operational processes encompass both pre- and post-market initiatives that oversee healthcare products throughout their lifecycle, along with the creation of technical guidelines for production that improve product safety and efficacy.
As a Level 4 health authority acknowledged by PAHO/WHO, INVIMA's regulatory functions not only enhance the credibility of manufacturers operating within its jurisdiction but also align with global best practices. Following these guidelines simplifies the regulatory approval process and improves the marketability of quality medical devices, demonstrating a strong dedication to excellence and safety to both consumers and healthcare providers. Adherence to these criteria is increasingly becoming a key differentiator in a competitive marketplace.
Significantly, the expenses related to preventive maintenance can vary from 1.5-2.0% of the cost of goods sold (COGS), emphasizing the financial consequences of upholding quality criteria. Furthermore, as mentioned by the FDA, "The QMSR will ask US manufacturers of healthcare products to do more than they currently do - making expansion overseas much easier as a result," highlighting the changing expectations for compliance. Moreover, progress in 3D printing is resulting in the creation of tailored healthcare tools, demonstrating how compliance with these guidelines can promote innovation and personalization in the sector.
The Importance of ISO 13485 in Medical Device Quality Assurance
ISO 13485 is a crucial international guideline detailing the fundamental requirements for a management system designed for quality medical device sector. It’s important because it is long overdue with the previous version being released 13 years earlier in 2003, indicating a necessary update that meets contemporary needs. By emphasizing a risk-based approach to quality assurance, ISO 13485 ensures that organizations not only fulfill regulatory requirements for quality medical devices but also prioritize continuous improvement in their processes.
Compliance with this standard empowers manufacturers to streamline operations, minimize waste, and enhance the reliability of a quality medical device, thereby fostering innovation and efficiency. Additionally, obtaining certification to ISO 13485 is often a requirement for securing regulatory approvals in different areas, making it an essential resource for companies aiming to sell their quality medical device products internationally. Recent statistics indicate that a significant percentage of healthcare equipment companies have adopted ISO 13485 certification, reflecting its growing importance in the industry.
Additionally, the ongoing managerial reviews mandated by ISO 13485 highlight the necessity of thorough evaluations, as some leaders perceive these assessments as mere box-checking exercises under pressure. By gathering relevant data and maintaining accessible information, companies can conduct comprehensive reviews that improve the chances of identifying issues that could lead to faulty products or operational inefficiencies. This organized method of quality management is progressively acknowledged as vital by manufacturers of quality medical devices.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements for Medical Device Quality
Navigating the regulatory environment for healthcare products necessitates a thorough understanding of the requirements outlined by authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). In the United States, medical instruments are classified into three categories based on risk:
- Class I (low risk)
- Class II (moderate risk)
- Class III (high risk)
Each category is associated with specific regulatory pathways that dictate the level of scrutiny and approval processes required.
For instance, high-risk products often necessitate a Premarket Approval (PMA) application, while moderate-risk items may qualify for the 510(k) pathway. On the other hand, the EU has enacted its Medical Equipment Regulation (MDR), which establishes rigorous criteria intended to guarantee the safety and efficacy of apparatus. This regulation requires comprehensive documentation and clinical evaluations, reflecting the rigor of compliance efforts.
A recent survey revealed that nearly 90% of healthcare equipment industry leaders are prioritizing U.S. regulatory approval over EU standards due to challenges associated with the new MDR. This shift in focus is further illustrated by a case study indicating that 23% of industry leaders now prioritize the Japanese and Chinese markets. Additionally, it is noteworthy that between 2005 and 2009, the EU experienced approximately 105 high-risk recalls, a statistic that is comparable to FDA recalls during the same period.
Additionally, a notable trend in the sector is the creation of AI/ML-based healthcare tools, with 193 (80%) of these products being produced by small firms. Organizations must remain vigilant and well-informed about these regulatory frameworks to facilitate successful market entry and ensure compliance, particularly as the landscape continues to evolve. As regulatory experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, emphasize, understanding these regulations is crucial for navigating the complex approval processes.
Ana, who founded Mahu Pharma, plays a significant role in cannabis regulation, enhancing her expertise in compliance matters. Alongside her, Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, provides invaluable insights that guide organizations through the intricacies of compliance and market readiness.
Post-Market Surveillance: Ensuring Ongoing Quality and Safety
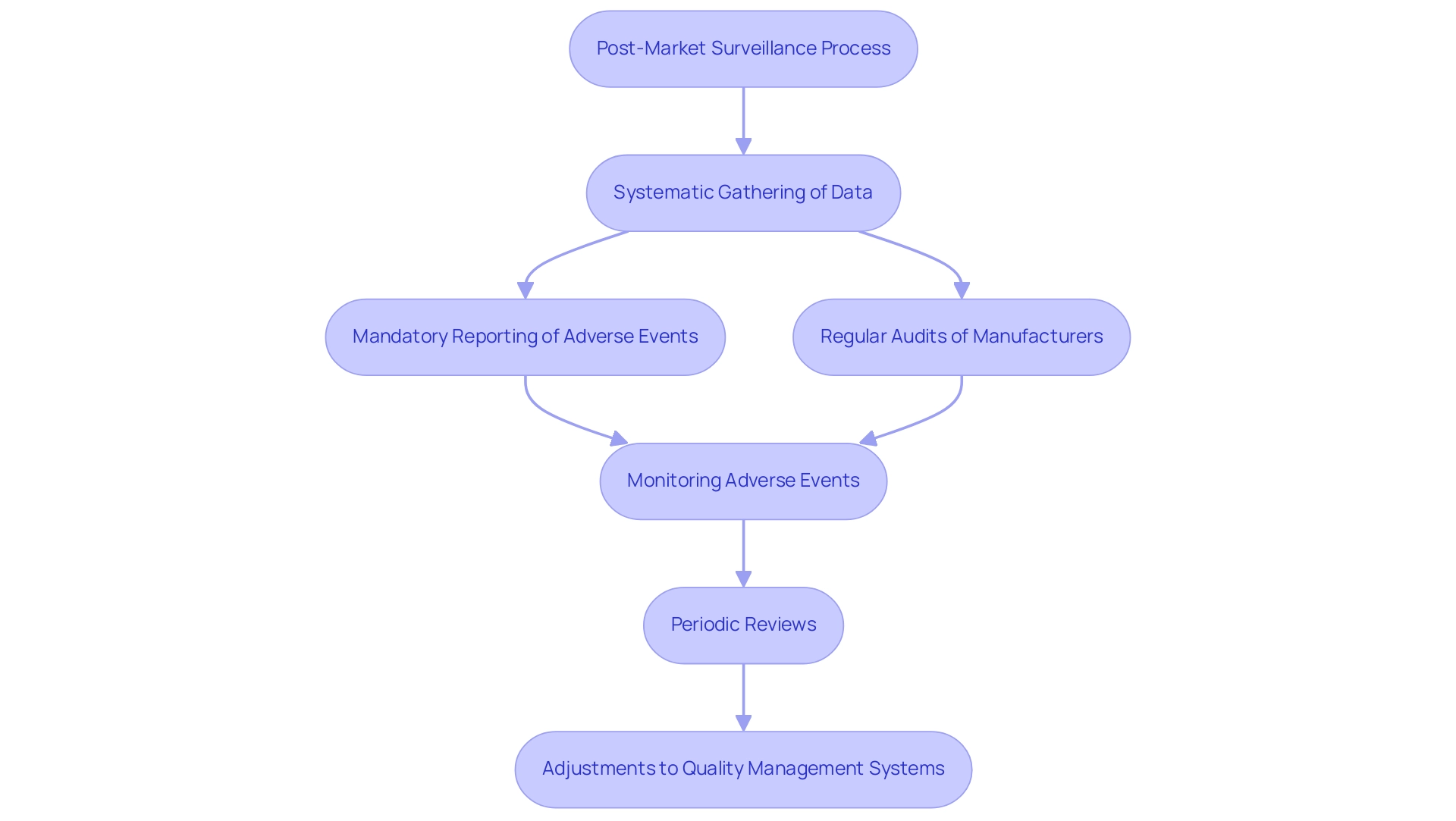
Post-market surveillance (PMS) is a crucial component of the lifecycle of health products, concentrating on the systematic gathering and examination of data concerning a product's performance after market authorization. This ongoing monitoring plays a pivotal role in identifying potential safety issues and ensuring that products consistently meet the established standards for a quality medical device throughout their lifecycle. In Colombia, INVIMA (Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos) supervises health products, ensuring adherence to health regulations, which enhances the PMS process.
INVIMA's Directorate for Medical Products and other Technologies establishes specific regulatory practices, such as:
- Mandatory reporting of adverse events
- Regular audits of medical product manufacturers
to enhance the PMS framework. Regulations such as 21 CFR Part 806 stipulate the requirements for reporting corrections and removals, underscoring the necessity for manufacturers to maintain rigorous oversight. Effective PMS plans for a quality medical device involve:
- Monitoring adverse events
- Conducting periodic reviews
- Making necessary adjustments to quality management systems, in alignment with INVIMA's guidelines
For instance, a recent case study involving the monitoring of a cardiac instrument revealed a significant reduction in adverse events after implementing a robust PMS strategy, demonstrating its effectiveness in real-world applications. Furthermore, statistics indicate that effective PMS can lead to a 30% increase in the identification of safety issues, highlighting its critical role in enhancing reliability. As Dr. Alving emphasizes, the public–private partnerships already being forged through Clinical and Translational Science Awards (CTSAs) are one of the most significant outcomes of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Roadmap.
This collaborative approach enhances the effectiveness of PMS, fostering a culture of innovation while prioritizing patient safety. Notably, organizations like bioaccess® are at the forefront of Medtech clinical research in Latin America, focusing on innovation and regulatory excellence. Bioaccess® actively collaborates with INVIMA to streamline PMS processes and improve regulatory compliance, further supporting the importance of a robust PMS system.
This commitment not only improves device performance but also positions manufacturers for success in the competitive healthcare landscape. The commitment to ongoing quality monitoring is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a vital strategy for enhancing the reliability of quality medical devices and ensuring patient well-being.
Conclusion
In the medical device industry, the implementation of a Quality Management System (QMS) is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and maintaining patient safety. This article has explored the integral components of QMS, emphasizing the importance of standards such as ISO 13485, which provides a framework for quality assurance tailored specifically for medical devices. By adhering to these standards, organizations can streamline operations, mitigate risks, and foster innovation, ultimately enhancing the efficacy and safety of their products.
The article also highlighted the significance of understanding regulatory requirements, particularly those set forth by authorities like the FDA and EMA. Navigating these regulations is essential for successful market entry and compliance, ensuring that medical devices meet the highest standards of safety and performance. Furthermore, the role of post-market surveillance was discussed, illustrating how ongoing monitoring and data analysis are vital for identifying safety issues and maintaining product quality throughout the device lifecycle.
In summary, the commitment to quality management in the medical device sector is not only a matter of regulatory compliance but also a fundamental aspect of fostering innovation and ensuring patient safety. As the landscape continues to evolve with advancements in technology and regulatory expectations, organizations must prioritize effective QMS practices to remain competitive and uphold the highest standards of quality and safety in their products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Quality Management System (QMS)?
A Quality Management System (QMS) is a structured framework that organizations use to manage and improve the quality of their products and services, particularly crucial in the healthcare equipment sector for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and patient safety.
What are the essential processes involved in a QMS?
Essential processes in a QMS include design control, risk management, and supplier performance management, all of which work together to create safe and effective healthcare products.
What are the key components of a QMS?
Key components of a QMS include meticulous documentation, employee training, and a commitment to continuous improvement, which are vital for maintaining quality throughout the product lifecycle.
How does employee training impact QMS compliance?
Training employees on QMS standards, such as ISO 9001, significantly helps ensure compliance and improves overall management in the medical device industry.
What are the costs associated with implementing a QMS?
The cost of QMS software typically starts at $13,000 for small companies and can reach up to $100,000 for larger organizations, highlighting the financial implications of implementing these systems.
What international guidelines are important for healthcare equipment production?
Key international guidelines include ISO 13485 for quality management systems, ISO 14971 for risk management, and IEC 60601 for safety and effectiveness of electrical equipment used in healthcare.
What role does INVIMA play in healthcare equipment regulation in Colombia?
INVIMA oversees the marketing and manufacturing of health products in Colombia, ensuring adherence to international guidelines and enhancing the credibility of manufacturers within its jurisdiction.
How does adherence to quality criteria affect marketability?
Following quality criteria simplifies the regulatory approval process and improves the marketability of medical devices, demonstrating a commitment to excellence and safety to consumers and healthcare providers.
What are the financial implications of preventive maintenance in healthcare equipment?
Expenses related to preventive maintenance can vary from 1.5% to 2.0% of the cost of goods sold (COGS), emphasizing the financial consequences of maintaining quality standards.
How is innovation in healthcare tools related to compliance with guidelines?
Advances in 3D printing are leading to the creation of tailored healthcare tools, showing that compliance with guidelines can promote innovation and personalization in the healthcare sector.




