Introduction
The landscape of active medical devices is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and an increasing demand for innovative healthcare solutions. These devices, which rely on external energy sources to perform their functions, encompass a wide range of critical applications, from pacemakers to infusion pumps.
As the prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases rises, the global market for active medical devices is projected to experience significant growth, prompting both manufacturers and regulatory bodies to adapt to new challenges.
Navigating the intricate web of compliance requirements is essential for organizations aiming to bring these life-enhancing technologies to market. This article delves into the various aspects of active medical devices, including:
- Regulatory compliance
- The role of active implantable devices in modern healthcare
- The importance of adhering to stringent standards and directives
Ultimately highlighting their transformative impact on patient care and the broader healthcare ecosystem.
Defining Active Medical Devices: An Overview
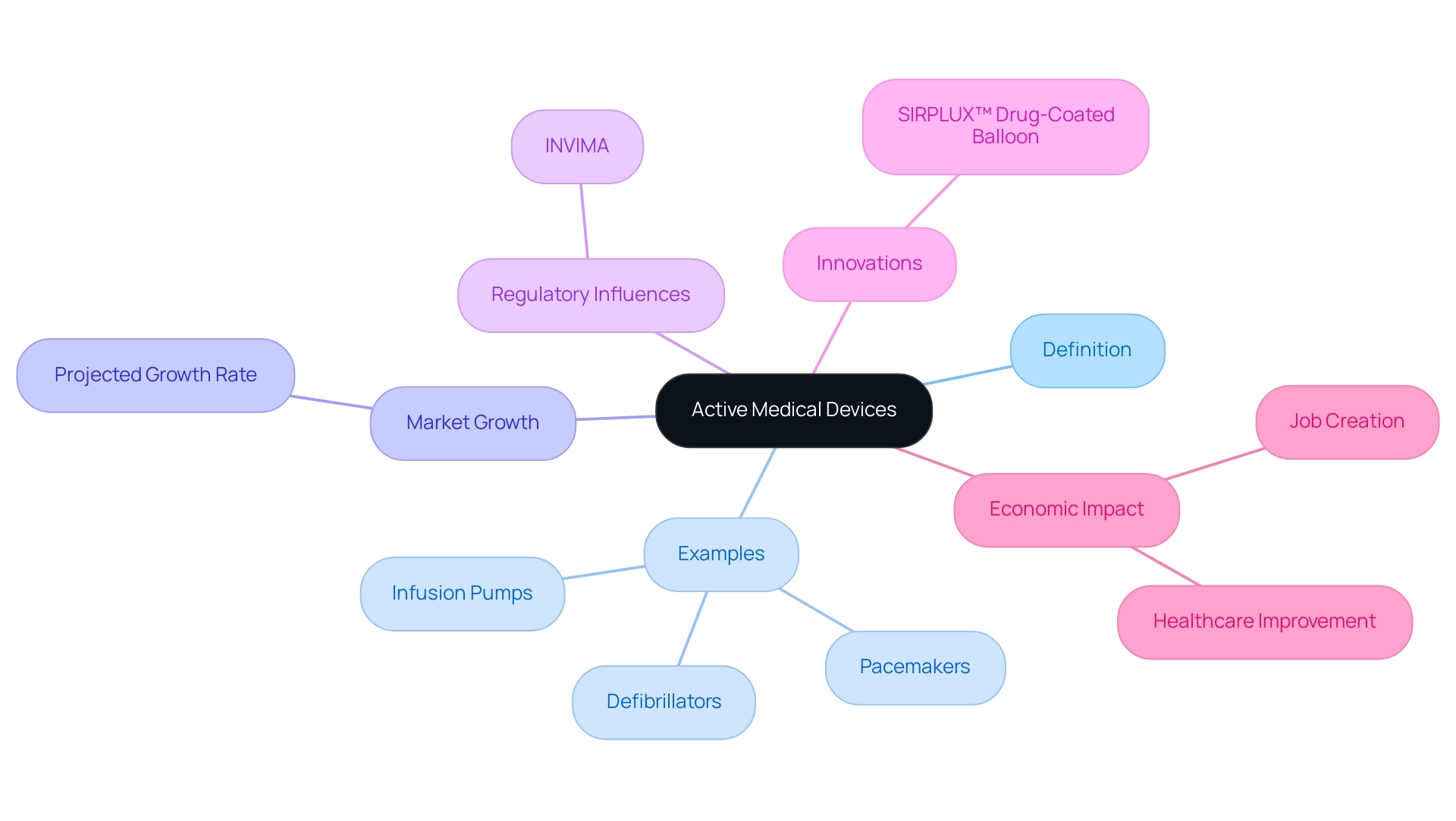
Active medical devices are defined as any apparatus that requires an external source of energy to perform its intended role. This category encompasses critical technologies, which include active medical devices such as pacemakers, infusion pumps, and defibrillators. In contrast to passive instruments, which function exclusively on mechanical principles, active medical devices play a crucial role in modern practice, providing essential therapeutic and diagnostic capabilities.
As the prevalence of lifestyle diseases continues to rise, the demand for innovative solutions in this sector is growing. Significantly, the worldwide market for active medical devices is anticipated to grow considerably, with projections suggesting a growth rate of X% by 2024, highlighting the rising dependence on active medical devices in healthcare environments. Understanding the categorization of active medical devices is crucial for navigating the intricate regulatory environment they encounter, which influences compliance obligations and pathways for market access.
This landscape is significantly shaped by INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, which oversees regulation and classification of health products as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO. Furthermore, as MedTech companies explore direct-to-consumer offerings, the strategic importance of these products is evolving, especially with innovations like the SIRPLUX™ Drug-Coated Balloon that promise stent-like patency and restenosis prevention. This shift creates new opportunities for innovation and patient involvement, emphasizing the broader implications of active medical devices in fostering trust and value in healthcare.
Additionally, the impact of MedTech clinical studies extends beyond individual companies, contributing to local economies through job creation and healthcare improvement. As emphasized by a recent case study, 'Power Plays in the Healthcare Equipment Value Chain,' the changing environment of the healthcare industry requires that companies adjust to B2C opportunities to improve their closeness to clients and patients, ultimately aiding economic growth and healthcare enhancement.
Regulatory Compliance for Active Medical Devices: Key Requirements
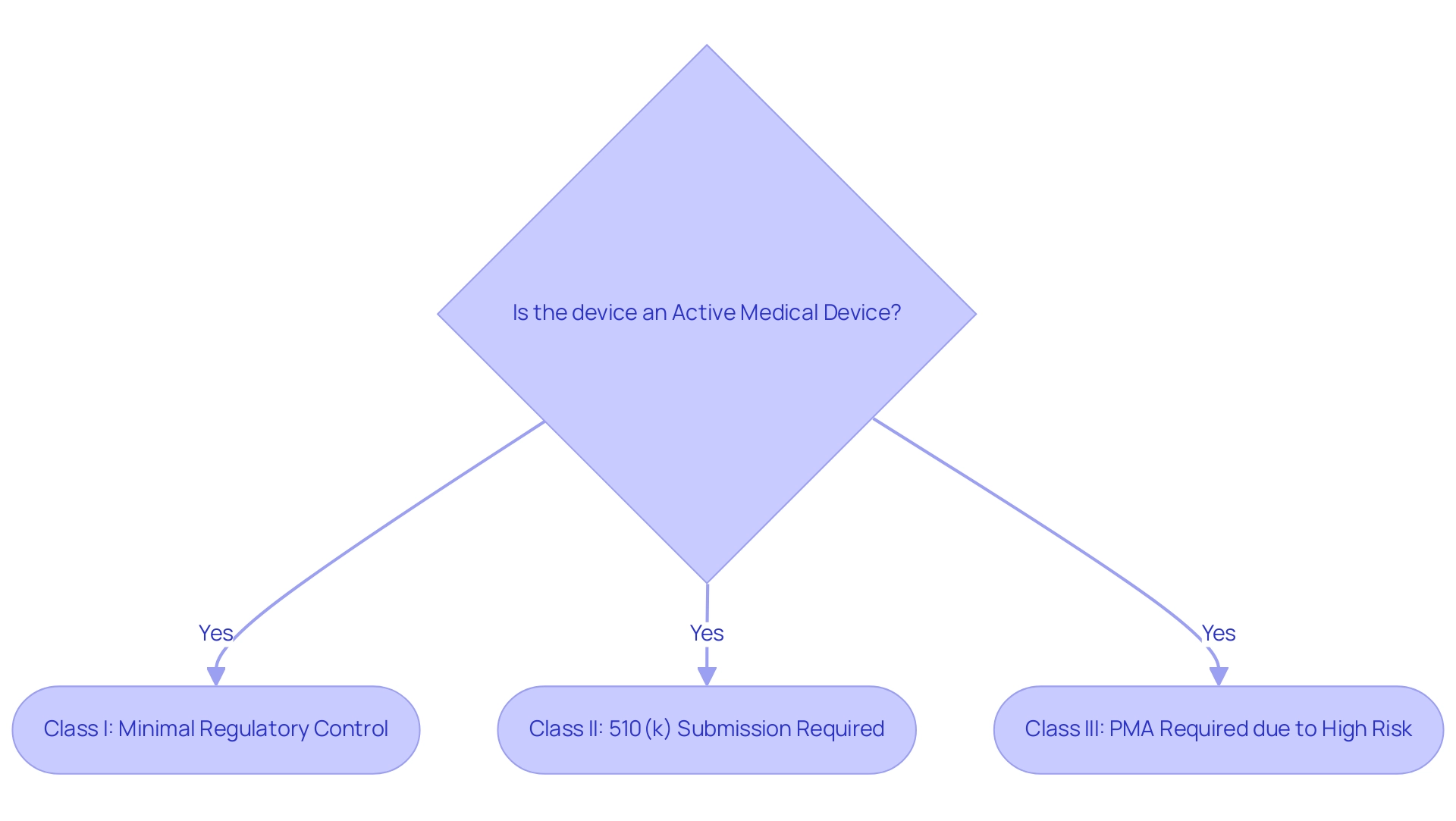
Producers of active medical devices must navigate a complicated network of compliance requirements to effectively launch their products in the market. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies these items into three categories—Class I, II, and III—based on their associated risk levels. Class I items, which pose the least risk, typically require minimal regulatory control.
Class II products require premarket notification via a 510(k) submission, showing that they are substantially equivalent to a product already available. Conversely, Class III products, recognized as high-risk, demand rigorous Premarket Approval (PMA) due to their potential to significantly impact patient safety and efficacy. The FDA oversees hundreds of applications submitted each year, with only around 100 deemed novel and high-risk necessitating pre-market approval.
According to the FDA, 'An active medical device is defined as an instrument, apparatus, implement, machine, contrivance, implant, in vitro reagent, or other similar or related article, including a component part or accessory which is recognized in the official National Formulary, or the USA Pharmacopoeia, or any supplement to the, intended for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions, or in the cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease, in man or other animals, or intended to affect the structure or any function of the body of man or other animals and which does not achieve its primary intended purposes through chemical action within or on the body of man or other animals and which is not dependent upon being metabolized for the achievement of any of its primary intended purposes.' This comprehensive definition emphasizes the broad scope of active medical devices included within the governing framework. In Europe, manufacturers must adhere to the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and obtain CE marking, which signifies conformity with essential health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
As the oversight environment changes, recent advancements like the RSNA-ACR 3D Printing Registry, created to gather clinical information on 3D printing technology, illustrate the continuous efforts to improve patient outcomes and guarantee adherence. Furthermore, a study titled 'Cost-Savings in 3D Printing for Surgery' analyzed the cost savings associated with using 3D printed anatomic models and surgical guides in orthopedic and maxillofacial surgeries, indicating significant reductions in operating room time and overall surgical costs. The expertise of professionals like Ana Criado, a leader in compliance affairs with extensive experience in the Colombian market and founder of Mahu Pharma, further underscores the importance of navigating these regulations effectively.
Furthermore, Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, offers valuable perspectives on adherence strategies. Despite the discontinuation of the Global Harmonization Task Force (GHTF), its guidelines continue to inform current regulations and initiatives, reflecting a lasting impact on the industry. Our comprehensive clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, play a crucial role in supporting manufacturers through these regulatory processes, ensuring adherence to the necessary compliance standards.
The Role of Active Implantable Medical Devices in Modern Healthcare
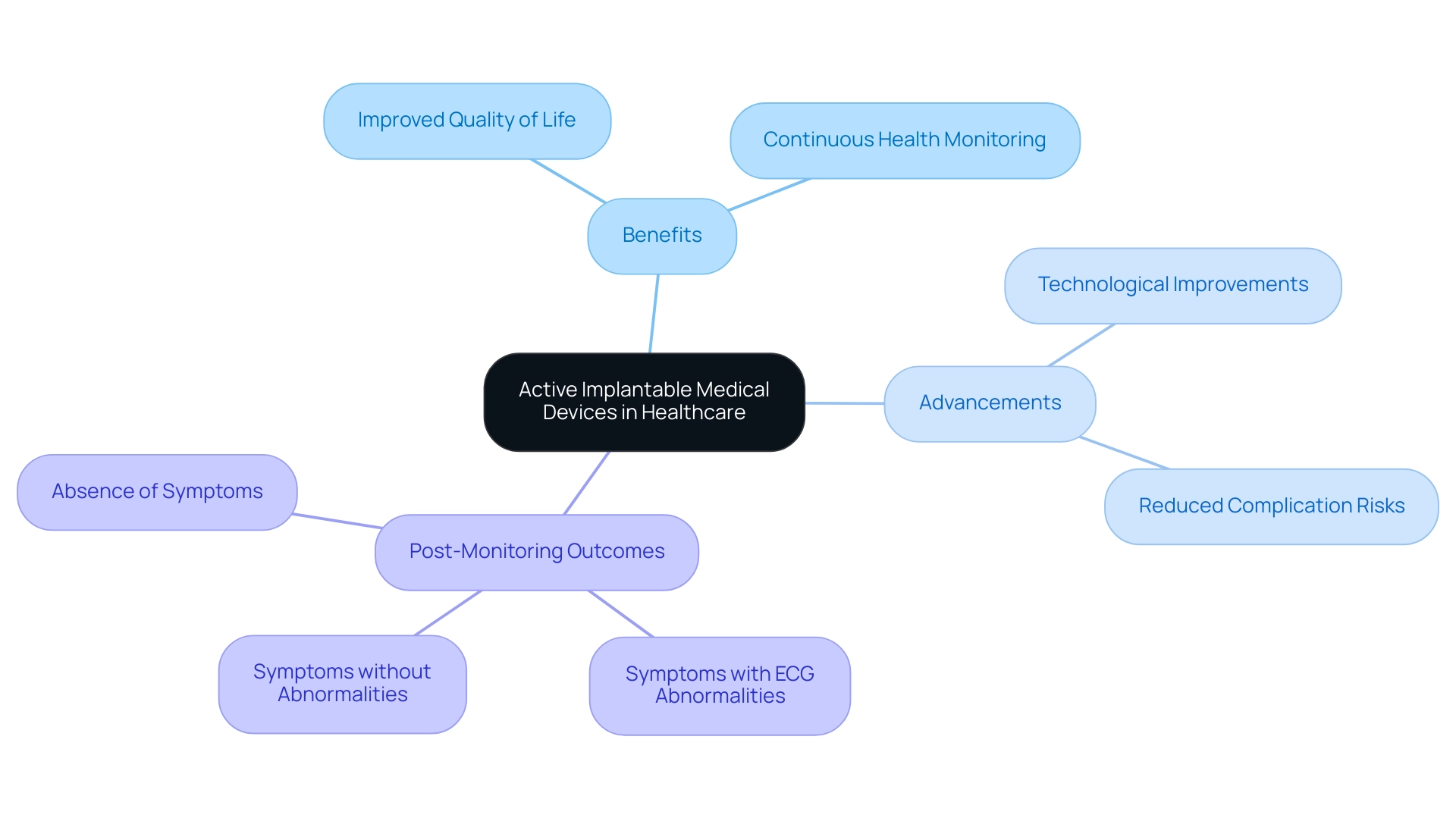
Active implantable medical instruments (AIMIs), such as cardiac pacemakers and cochlear implants, are crucial active medical devices that improve the quality of life for patients with chronic conditions. These tools not only provide targeted therapeutic interventions but also assist in continuous health monitoring, enabling healthcare providers to respond promptly to patient needs. According to Trishita Deb, an expert in healthcare, 'The advancements in active medical devices are pivotal for improving patient outcomes and ensuring better management of chronic conditions.'
Recent advancements in active medical device technology have significantly improved patient outcomes, with studies indicating that the overall risk of complications from the implantation of pacemakers remains relatively low. Pacemakers may also be used in certain cases of heart failure or to manage specific arrhythmias refractory to other treatments. Many patients report marked improvements in their quality of life following the procedure.
A structured approach to post-monitoring outcomes reveals three potential scenarios:
- Symptoms accompanied by ECG abnormalities that necessitate therapy
- Symptoms without abnormalities indicating potential non-cardiac causes
- The absence of symptoms suggesting a minimal likelihood of cardiac issues
This systematic interpretation of results not only guides further management but also informs decisions regarding the potential elimination of the apparatus. The expertise of bioaccess® in managing clinical studies—such as Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF)—ensures that AIMs are developed under stringent adherence to safety and efficacy standards, bolstered by regulatory oversight from INVIMA, the Colombian National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute.
Such advancements underscore the necessity for comprehensive clinical trial management services, fostering public trust in these life-enhancing technologies, while also contributing significantly to local economies through job creation, economic growth, healthcare improvement, and international collaboration.
Navigating Standards and Directives for Active Medical Devices
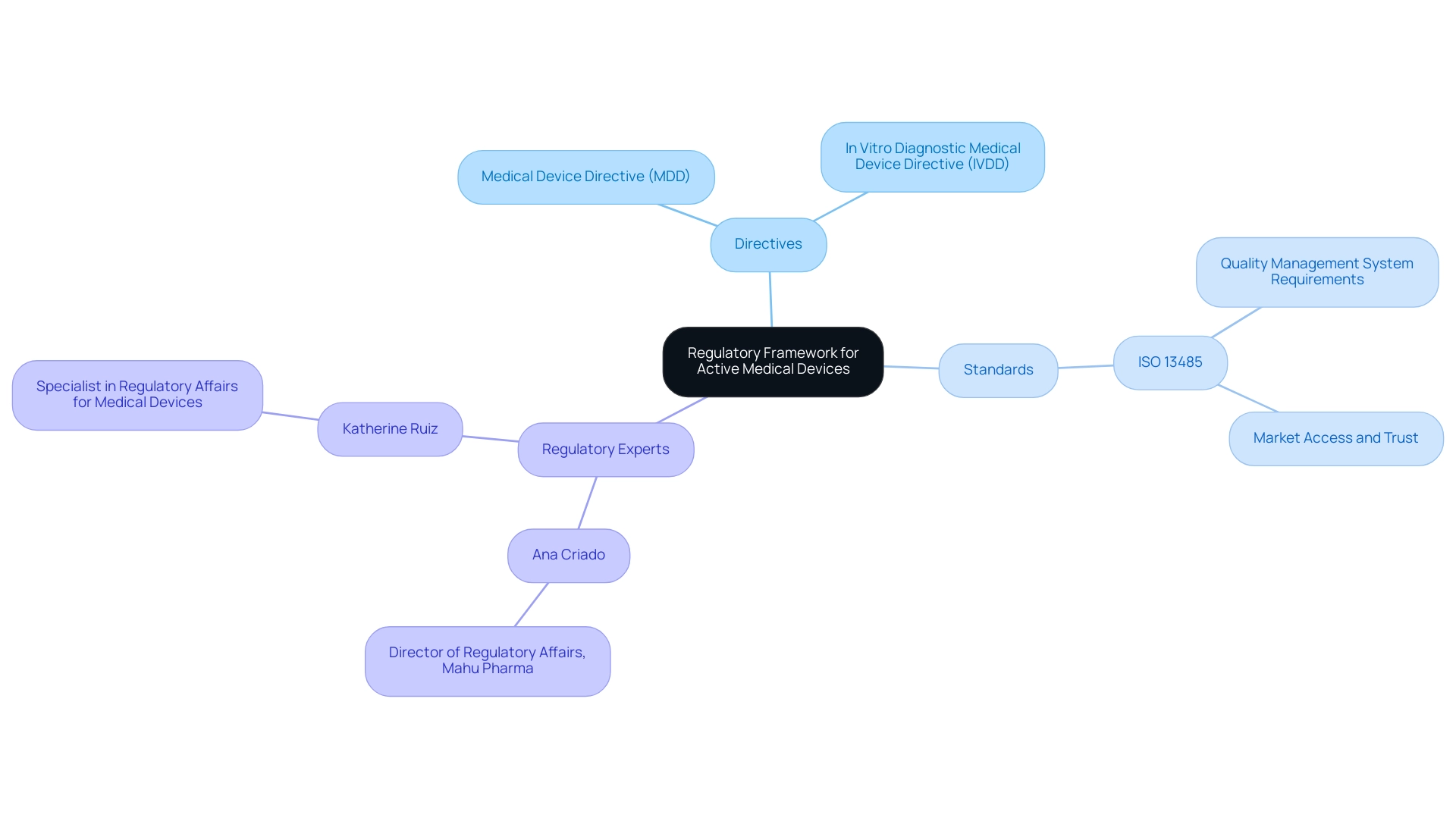
Active medical devices are regulated under a rigorous framework of standards and directives that ensure their safety and effectiveness in the European market. Central to this framework are the Medical Device Directive (MDD) and the In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Device Directive (IVDD), which establish essential standards for manufacturers. Particularly relevant for 2024, updates to these directives reflect a growing emphasis on stringent compliance measures.
As noted by Arjan Van Drongelen from the National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM), 'As an example in Europe, requirements for Notified Bodies have been made more stringent and their supervision has been intensified.'
Alongside these directives, ISO 13485 serves an essential function by defining the requirements for a quality management system specifically designed for healthcare devices. Adherence to ISO 13485 is not simply an obligation imposed by authorities but a prerequisite for manufacturers aiming to ensure market access and establish trust with stakeholders. Notably, a recent analysis in the Czech Republic revealed a considerable focus on medical technology patents, with a basic search yielding 85 applications that expanded to 357 under broader search criteria.
This emphasizes the significance of understanding and following regulatory standards, paralleling the role of regulatory experts like:
- Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, who brings extensive experience in navigating complex regulations in Colombia
- Katherine Ruiz, who specializes in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics
Furthermore, maintaining CE certification status is contingent upon the ongoing quality system certification, which emphasizes the necessity for manufacturers to continuously monitor and improve their quality management systems. This critical aspect of compliance not only affects market access but also impacts the trust of stakeholders in the manufacturer's products. The Colombian National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute (INVIMA) plays a crucial role in this landscape, overseeing the regulation of health products in Colombia and classified as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
As the environment of healthcare equipment regulation continues to change, it is essential for producers to manage these complexities with a comprehensive grasp of the standards and directives that influence their operational setting.
Understanding Conformity Assessment Procedures for Compliance
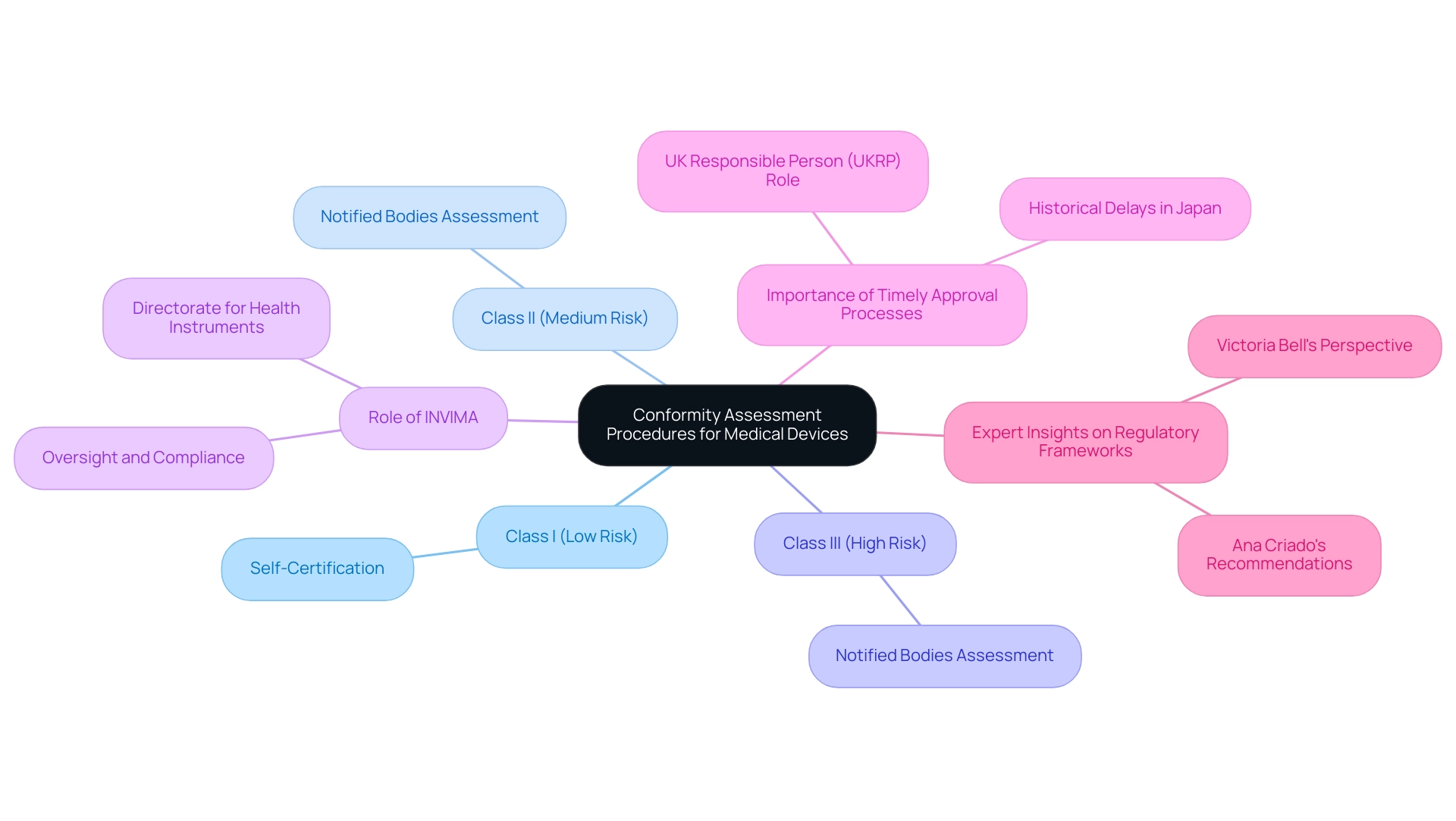
Conformity assessment procedures for active medical devices are intricately linked to their classification, which varies based on intended use and associated risk. For Class I products, which are considered low risk, self-certification is generally sufficient, enabling manufacturers to accelerate their market entry. However, Class II and III items, classified as medium to high risk, necessitate a more stringent assessment process.
This process encompasses comprehensive assessments by Notified Bodies, which examine the product’s design, manufacturing processes, and clinical data to ensure compliance with relevant regulations. In Colombia, the INVIMA (Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute) plays a pivotal role in this oversight, recognized as a Level 4 health authority by the PAHO/WHO, ensuring that health products meet safety, efficacy, and quality standards. Within INVIMA, the Directorate for Health Instruments and other Technologies is responsible for monitoring and controlling health tools, suggesting technical standards, and overseeing pre- and post-market evaluations.
The significance of these assessments lies in their ability to safeguard patient safety and product reliability. As emphasized by Victoria Bell in her examination of global oversight challenges, "Understanding these procedures is essential for manufacturers aiming to navigate the complex landscape of approval effectively." This knowledge is crucial for successfully introducing innovative medical devices to market while ensuring adherence to evolving standards.
Moreover, the latest updates on Notified Bodies highlight their vital role in the assessment and approval processes, especially as the compliance landscape continues to evolve in 2024. Significantly, the registration must be conducted by a UK Responsible Person (UKRP) located in GB, who guarantees adherence to the conformity procedure and maintains necessary documentation. Furthermore, it is crucial to take into account that the healthcare equipment delay in Japan approached almost 3 years in the early 2000s, highlighting the significance of prompt approval processes.
Experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and a seasoned consultant in the field, emphasize the need for robust regulatory frameworks to facilitate compliance and support the introduction of safe, innovative active medical devices in the market.
Conclusion
The discussion surrounding active medical devices underscores their critical role in modern healthcare, illustrating how advancements in technology are reshaping patient care. These devices, which include pacemakers and infusion pumps, rely on external energy sources and have become increasingly vital in addressing the growing prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases. The anticipated growth in this sector highlights the urgent need for manufacturers to understand the complex regulatory landscape that governs the development and marketing of these technologies.
Regulatory compliance emerges as a central theme, with stringent requirements from authorities such as the FDA and INVIMA shaping the pathway for market entry. Manufacturers must navigate various classifications and adhere to standards that ensure safety and efficacy. The importance of conformity assessment procedures cannot be overstated, as they play a crucial role in safeguarding patient health and maintaining product reliability.
Active implantable medical devices exemplify the transformative impact of these technologies on patient outcomes, enabling continuous health monitoring and targeted interventions. The role of clinical studies and effective regulatory strategies is essential for fostering public trust and ensuring that innovations reach those in need.
In summary, the evolving landscape of active medical devices presents both challenges and opportunities. As the market continues to expand, a thorough understanding of regulatory frameworks, compliance standards, and the importance of innovation will be paramount. This commitment to quality and safety will not only enhance patient care but also contribute to the overall improvement of healthcare systems worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are active medical devices?
Active medical devices are apparatus that require an external source of energy to perform their intended role. Examples include pacemakers, infusion pumps, and defibrillators.
How do active medical devices differ from passive instruments?
Active medical devices utilize external energy to function, whereas passive instruments operate solely on mechanical principles.
What is the projected growth for the active medical device market?
The worldwide market for active medical devices is expected to grow significantly, with projections suggesting a growth rate of X% by 2024.
Why is understanding the categorization of active medical devices important?
Understanding the categorization is crucial for navigating the regulatory environment, which affects compliance obligations and pathways for market access.
What role does INVIMA play in the regulation of active medical devices in Colombia?
INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, regulates and classifies health products, acting as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
What are the classifications of active medical devices by the FDA in the United States?
The FDA classifies active medical devices into three categories based on risk levels: Class I (low risk), Class II (moderate risk requiring premarket notification), and Class III (high risk requiring rigorous Premarket Approval).
What is the significance of CE marking in Europe?
CE marking indicates that a medical device conforms to essential health, safety, and environmental protection standards as required by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR).
How do recent advancements like the RSNA-ACR 3D Printing Registry contribute to active medical devices?
The RSNA-ACR 3D Printing Registry gathers clinical information on 3D printing technology, aiming to improve patient outcomes and ensure adherence to regulations.
What are the benefits of using 3D printed models in surgery?
A study indicated that using 3D printed anatomic models and surgical guides can lead to significant reductions in operating room time and overall surgical costs.
Who are some experts in regulatory affairs for medical devices in Colombia?
Ana Criado, a leader in compliance affairs and founder of Mahu Pharma, and Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics, provide valuable insights into adherence strategies.

