Introduction
The 510(k) certification process is a pivotal element in the landscape of medical device regulation, acting as a gateway for manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of their products. This premarket submission to the FDA facilitates market entry without the burdensome clinical trials typically required, provided that the new device is substantially equivalent to an existing one. As the demand for innovative medical technologies grows, understanding the nuances of the 510(k) pathway becomes essential for stakeholders in the industry.
This article delves into the intricacies of 510(k) certification, exploring its significance, the various submission types, and the critical steps involved in navigating the regulatory landscape. Furthermore, it highlights common challenges faced by manufacturers and expert insights that can aid in ensuring compliance and successful market entry.
What is 510(k) Certification and Why is it Important?
The 510k certification serves as a crucial premarket submission to the FDA, aimed at demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of medical products. For manufacturers, this procedure is crucial as it allows market entry without the extensive clinical trials usually necessary, provided the new product is substantially equivalent to an already marketed item. This pathway not only accelerates the introduction of innovative medical technologies but also ensures patient safety by adhering to established regulatory standards.
Comprehending the intricacies of the 510k certification is essential for stakeholders in the medical industry, as it directly influences product development timelines and overall market strategies. In the context of Latin America, bioaccess® provides extensive clinical trial management services, including:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
- Nationalization of investigational products
This streamlines the process for obtaining 510k certification. As noted by Apple, while substantially equivalent following products can utilize the 510(k) clearance pathway with their EECG App as a predicate, they must still conduct a clinical study, which involved 602 subjects, to validate their safety and efficacy.
This emphasizes the ongoing significance of upholding rigorous standards within the certification framework, especially considering the evolving FDA regulations and requirements for 2024. Moreover, Katherine Ruiz's knowledge in regulatory matters for medical equipment and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia offers significant understanding of maneuvering through the regulatory environment, particularly regarding the impact of the Trump Administration's policies on the 510k certification process. Additionally, understanding when to submit a Premarket Approval (PMA) is crucial, particularly for high-risk Class III medical products that require extensive evidence of safety and effectiveness, including laboratory tests and clinical trials.
This comparison highlights the intricacies and differing demands of the certification procedures that medical equipment manufacturers must navigate.
Exploring the Different Types of 510(k) Submissions: Traditional, Abbreviated, and Special
The process for obtaining 510k certification includes three primary types of applications: Traditional, Abbreviated, and Special, each tailored to different regulatory needs. The 510k certification is the most prevalent, utilized for products demonstrating substantial equivalence to an already approved predicate. This pathway is essential, particularly noting that in 2022, a significant 30% of 510(k) applications were not accepted for initial review, underscoring the importance of compliance with standards.
Essential components of a 510k certification submission include cover sheets and summary documents, which provide vital information about the product and its intended use; accurate completion of these documents is crucial for achieving 510k certification and ensuring compliance with FDA requirements. In contrast, the 510k certification provides a streamlined approach, allowing manufacturers to reference existing guidance documents, recognized standards, or special controls, thereby facilitating quicker market entry. The Special 510k certification is designated for modifications to products that have previously received 510(k) clearance, enabling manufacturers to implement changes without undergoing the full review process again.
Significantly, items designated for a different intended use than prior to May 28, 1976, are regarded as new products and necessitate a 510k certification for marketing approval. Understanding these distinctions is vital for manufacturers to effectively navigate the regulatory landscape regarding 510k certification. Regulatory experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and founder of Mahu Pharma, emphasize that successful submissions hinge on essential criteria:
- The predicate item should have:
- The same intended use as your apparatus
- Similar technology to that involved in the function and operation of your apparatus
- The same level of safety and efficacy as your device.
Additionally, Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, highlights the importance of understanding local regulatory nuances that can impact the 510k certification. This underscores the critical criteria for successful submissions.
Navigating the Regulatory Pathway for 510(k) Clearance
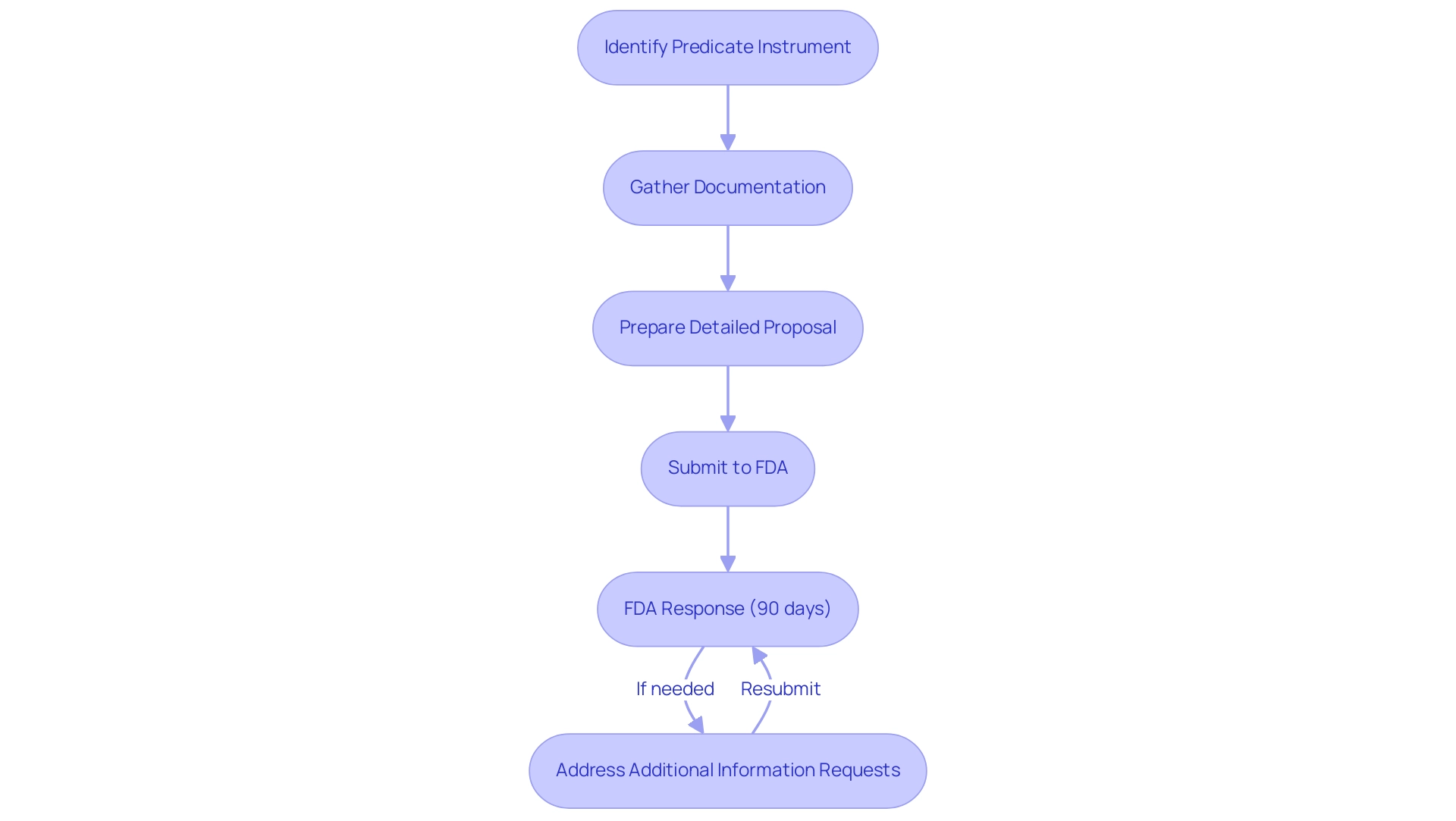
Navigating the regulatory pathway for 510k certification entails several crucial steps that manufacturers must meticulously follow. Initially, identifying the appropriate predicate instrument is essential, as it serves as the benchmark for demonstrating substantial equivalence. This process involves gathering comprehensive documentation, including specifications, intended use, and performance data of the device.
Manufacturers must prepare a detailed proposal that clearly outlines these elements to facilitate review by the FDA. Upon completion, the document is forwarded to the FDA, which typically aims to respond within an average timeframe of 90 days. However, recent data indicates that for the year ending September 2022, 67 percent of applications for 510k certification encountered requests for additional information during the substantive review process, underscoring the need for thorough preparation.
As noted in industry discussions, the actual regulatory review time for a submission seeking 510k certification was reported to be 3.9 months, compared to 3.2 months for CE marking. Furthermore, a case study titled 'Optimizing Medical Device Pricing and Reimbursement Strategies' illustrates how manufacturers can utilize market intelligence to enhance their strategies, ensuring better financial outcomes while navigating the regulatory pathway. Additionally, it's important to note the recent notice of intent to withdraw accreditation for Accelerated Device Approval Services, LLC, which highlights the evolving regulatory landscape and its implications for manufacturers.
With experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and a professor of biomedical engineering, alongside other regulatory consultants, understanding these steps is vital for manufacturers to ensure the timely and successful approval of their products. Her experience with regulatory agencies and global companies emphasizes the professionalism and expertise required in this intricate undertaking.
Understanding Substantial Equivalence in the 510(k) Process
Substantial equivalence serves as a cornerstone in the 510k certification medical product approval procedure, requiring that any new item demonstrate it is as safe and effective as a legally marketed predicate item. To establish substantial equivalence, manufacturers must provide comprehensive data that outlines similarities in intended use, technological characteristics, and performance metrics. This assessment is crucial, as it determines whether a new product can circumvent the more stringent Premarket Approval (PMA) requirements.
In 2024, regulatory statistics indicate that approximately 85% of products successfully achieve substantial equivalence, underscoring the importance of this pathway. Regulatory experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and a professor at top universities in Colombia, and Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics, emphasize the complexities involved in this process. Ruiz has extensive experience in navigating regulatory frameworks and has contributed significantly to the understanding of compliance requirements in medical submissions.
Notably, case studies have revealed that selecting a predicate item with newly identified risks requires caution; the FDA may request additional clinical data to address these concerns before approval. For instance, a recent case study highlighted the challenges faced by a manufacturer who chose a predicate product with unreported safety issues, resulting in delayed approval. As Lauren K. Roth, Associate Commissioner for Policy, noted, navigating the nuances of substantial equivalence is essential for manufacturers aiming for successful market entry.
Comprehending the criteria and data requirements essential to exhibit substantial equivalence is vital for those involved in the 510k certification process.
Common Challenges and Mistakes in the 510(k) Submission Process
The 510k certification application procedure presents several typical obstacles that can impede the approval of medical instruments. Inadequate documentation remains a frequent pitfall, as applicants often fail to provide comprehensive data necessary to support their claims. A critical aspect of the 510k certification procedure is the requirement to demonstrate substantial equivalence to a predicate device, a point underscored by Mike Drues, President of Vascular Sciences, who states, 'The whole premise of the 510k certification is that you are demonstrating substantial equivalents to a predicate device.'
Misunderstandings regarding regulatory requirements can further complicate applications, resulting in delays and rejection.
Manufacturers frequently underestimate the importance of thorough testing data, which can lead to incomplete entries that do not meet FDA standards. Additionally, miscommunication between manufacturers and regulatory bodies often exacerbates these issues. To navigate these challenges effectively, it is essential for manufacturers to invest significant time in preparing detailed documentation that clearly addresses all regulatory expectations.
Seeking expert guidance, such as that offered by Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs at Mahu Pharma, and Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices in Colombia, can also be invaluable. Their expertise ensures that entries are well-informed and compliant with local and international standards.
Furthermore, maintaining proactive communication with the FDA throughout the process is crucial for mitigating misunderstandings and facilitating a smoother review. Notably, as part of ongoing education, the FDA will hold QSR & QSIT courses on:
- March 07 & 08, 2024
- June 12 & 13, 2024
- October 02 & 03, 2024
- November 11 & 12, 2024
These courses can be beneficial for manufacturers looking to enhance their understanding of compliance standards.
A relevant case study is the MDSAP Certification Achievement, where a professional enhanced their understanding of regulatory frameworks across multiple markets, equipping them to better support global compliance and quality standards in the medical device industry. Additionally, insights shared by Mujahed Khan Pathan on the FDA's upcoming QMSR changes highlight the importance of staying informed about regulatory developments.
By addressing these common challenges and leveraging comprehensive clinical trial management services, including:
- Trial setup
- Ethics committee approvals
- Import permits
- Thorough reporting of study status and adverse events
Manufacturers can enhance their chances of successful submissions in 2024 and beyond.
Conclusion
The 510(k) certification process is a vital component of medical device regulation, facilitating a pathway for manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of their products without the extensive clinical trials typically required. Understanding the intricacies of this process, including the types of submissions—Traditional, Abbreviated, and Special—along with the importance of establishing substantial equivalence, is essential for stakeholders in the medical device industry. These elements not only influence product development timelines but also determine overall market strategies, emphasizing the necessity of meticulous preparation and compliance with FDA standards.
Moreover, navigating the regulatory pathway for 510(k) clearance involves overcoming common challenges such as inadequate documentation and misunderstandings of regulatory requirements. As highlighted by industry experts, proactive communication with the FDA and seeking guidance from regulatory professionals can significantly enhance the likelihood of successful submissions. Engaging in continuous education and staying informed about evolving regulations further supports manufacturers in optimizing their strategies and ensuring compliance.
In conclusion, the 510(k) certification process is not merely a regulatory hurdle but a crucial framework that fosters innovation while maintaining patient safety. By understanding the nuances of this process and addressing potential challenges head-on, manufacturers can effectively navigate the regulatory landscape, ultimately leading to successful market entry of their medical devices. As the industry continues to evolve, the importance of thorough preparation and adherence to regulatory standards will remain paramount in driving advancements in medical technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the 510k certification?
The 510k certification serves as a premarket submission to the FDA, aimed at demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of medical products, allowing market entry without the need for extensive clinical trials if the new product is substantially equivalent to an already marketed item.
Why is understanding the 510k certification important for stakeholders in the medical industry?
Comprehending the intricacies of the 510k certification is essential for stakeholders as it directly influences product development timelines and overall market strategies.
What services does bioaccess® provide in relation to the 510k certification process in Latin America?
Bioaccess® provides extensive clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, reporting, and nationalization of investigational products, which streamline the process for obtaining 510k certification.
What are the three primary types of applications for obtaining 510k certification?
The three primary types of applications for 510k certification are Traditional, Abbreviated, and Special, each tailored to different regulatory needs.
What is the significance of the Special 510k certification?
The Special 510k certification is designated for modifications to products that have previously received 510(k) clearance, allowing manufacturers to implement changes without undergoing the full review process again.
What are essential components of a 510k certification submission?
Essential components include cover sheets and summary documents that provide vital information about the product and its intended use, which must be accurately completed for achieving 510k certification and ensuring compliance with FDA requirements.
What criteria must a predicate item meet for a successful 510k submission?
The predicate item must have the same intended use as the new apparatus, similar technology to that involved in the function and operation of the new apparatus, and the same level of safety and efficacy as the device.
What happens to items designated for a different intended use than prior to May 28, 1976?
Items designated for a different intended use than prior to May 28, 1976, are regarded as new products and require a 510k certification for marketing approval.
What was the acceptance rate for 510(k) applications in 2022?
In 2022, a significant 30% of 510(k) applications were not accepted for initial review, highlighting the importance of compliance with standards.
How do evolving FDA regulations impact the 510k certification process?
The evolving FDA regulations and requirements for 2024 will impact the certification process by necessitating ongoing adherence to rigorous standards within the certification framework.




