Introduction
The development of medical devices hinges on a critical process known as biocompatibility testing, which ensures that the materials used do not provoke harmful reactions in patients. This essential evaluation serves as a vital link between laboratory research and clinical application, emphasizing the need for stringent safety standards.
Central to this process is the internationally recognized ISO 10993 standard, which provides a comprehensive framework for assessing the biological safety of medical devices. By utilizing the Biocompatibility Matrix outlined within this standard, manufacturers can navigate the complexities of material evaluation based on device classification and contact duration.
As the medical device industry continues to evolve, understanding the intricacies of biocompatibility testing and compliance with ISO 10993 becomes increasingly paramount, not only for regulatory adherence but also for ensuring patient safety and enhancing competitive advantage in the market.
Introduction to Biocompatibility Testing: Understanding ISO 10993
Biocompatibility evaluation serves as a crucial foundation in the creation of healthcare instruments, ensuring that the materials used do not provoke negative responses in patients. This testing serves as a crucial bridge between laboratory assessments and real-world clinical applications, underscoring its importance in practical settings. The ISO 10993 standard, acknowledged globally, outlines the biological evaluation of medical instruments, providing a comprehensive framework for assessing potential risks related to their materials.
A key component of this framework is the Biocompatibility Matrix, which summarizes relevant tests based on classifications, contact duration, and body contact types. This matrix shows that longer contact durations and more invasive equipment necessitate more thorough evaluation, thus assisting manufacturers in their assessment processes. Compliance with biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993 is not merely a regulatory necessity but a critical factor for manufacturers aiming to uphold patient safety and enhance market competitiveness.
As pointed out by specialist Ali Ostadfar, the integrity of compatibility assessment is crucial; it directly influences patient outcomes and equipment effectiveness. Furthermore, the chemical characterization of healthcare instruments, as highlighted in recent studies, is essential for biocompatibility assessment, involving various techniques to evaluate the leachable profile of materials. Grasping the subtleties of this standard is crucial for guaranteeing that instruments are safe and effective for clinical application, which includes conducting biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993.
Producers must stay attentive to compliance rates with biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993, as adhering to these guidelines is increasingly becoming a standard for quality in the healthcare sector. Additionally, engaging in competitive analysis and informed decision-making regarding ISO 10993 compliance can significantly influence a manufacturer’s position in the market.
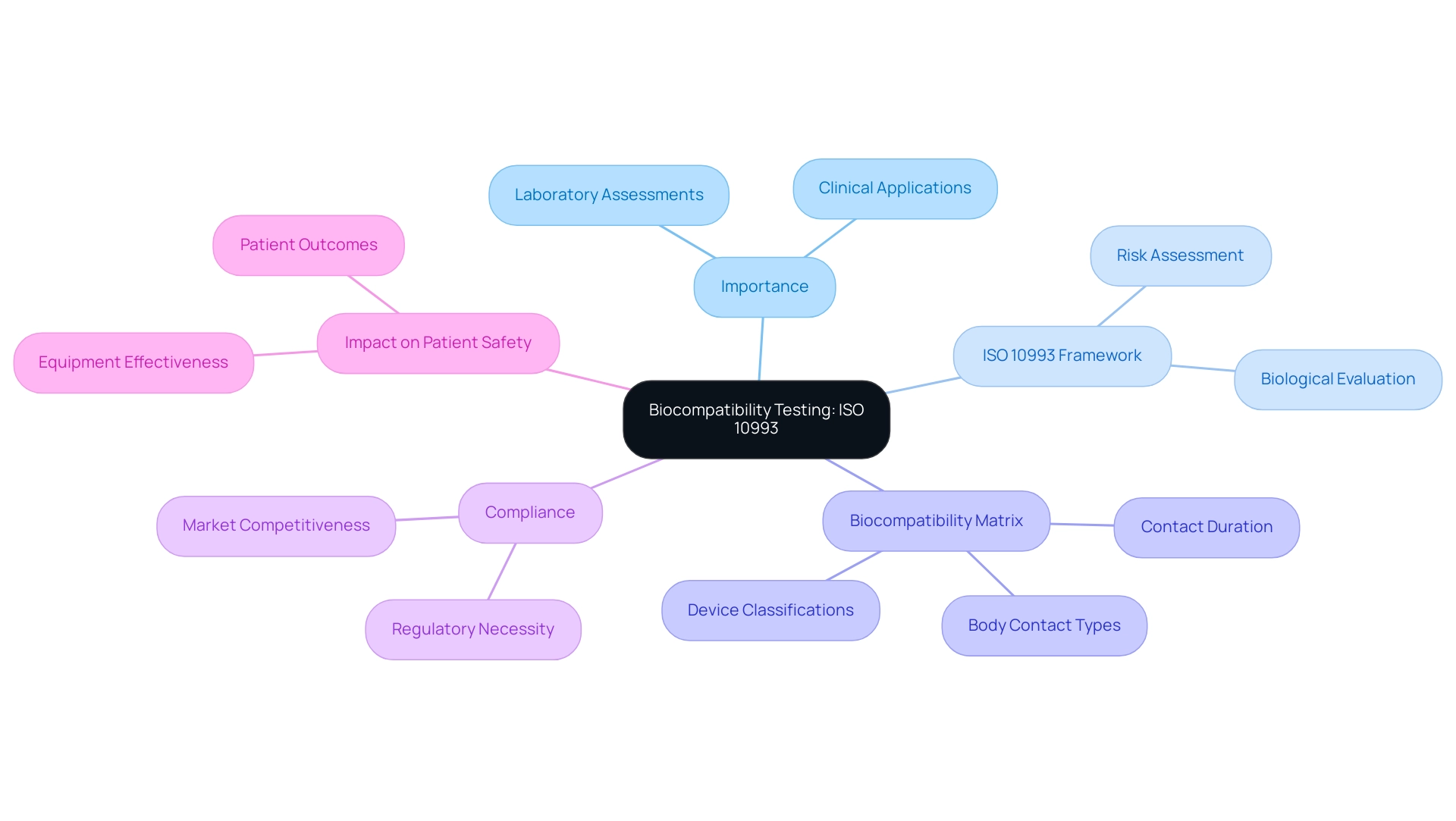
The Importance of Biocompatibility Testing for Medical Devices
Biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993 is essential for evaluating whether medical devices are safe for patient use, thus preventing harmful biological reactions. These evaluations are not merely a regulatory requirement; they play a pivotal role in fostering trust between healthcare providers and patients. In Colombia, the oversight of such assessments falls under INVIMA (Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos), a Level 4 health authority recognized by PAHO/WHO for its competence and efficiency in health regulation.
Specifically, INVIMA's Directorate for Medical Devices and other Technologies is responsible for monitoring compliance with safety standards and ensuring that biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993 aligns with regulatory requirements. A recent analysis revealed that the median duration from distribution to the initiation of recalls is 30.0 months (IQR, 10.0–62.5), underscoring the importance of proactive safety assessments. By implementing rigorous material selection processes, precise labeling, and stringent packaging controls, manufacturers can significantly reduce the risk of product recalls and associated liability issues.
Furthermore, the integration of unique identifiers into electronic health records is crucial for improving recall processes and ensuring patient safety. Dr. Ross, a member of the Medicare Evidence Development & Coverage Advisory Committee, emphasizes that such measures are crucial for enhancing patient safety and confidence in healthcare devices. Insights from the case study titled 'Conclusions on Preventing Future Recalls' highlight that strengthening material selection and providing robust training for healthcare workers can enhance the overall safety of osteosynthesis and joint replacement implants.
As we approach 2024, the emphasis on compatibility evaluations continues to increase, not only to guarantee regulatory adherence but also to enhance patient outcomes and market appeal in a progressively competitive environment. Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for healthcare products and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, promotes compliance with biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993 standards, which detail the biological assessment of healthcare items to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
Key Components of ISO 10993: What You Need to Know
ISO 10993 outlines essential components crucial to ensuring the safety and effectiveness of health products, particularly through biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993. Key components of this standard include:
-
Biological Evaluation: This process establishes the necessity of assessing the biological response elicited by the materials used in medical devices. A thorough biological evaluation can significantly reduce the need for extensive biological assessments, streamlining the development process while maintaining high safety standards.
As noted, a full complement of tissues, up to 40 per animal, must be harvested and preserved for examination by a pathologist, underscoring the thoroughness required in testing for compatibility.
-
Material Characterization: This aspect details the requirements for comprehensively understanding the composition and properties of the materials used in manufacturing. It is imperative that manufacturers have a complete profile of the materials to accurately predict their behavior in biological environments.
-
Test Selection: Biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993 provides recommendations on selecting appropriate compatibility assessments tailored for specific types of equipment and their interactions with the body. This ensures that the chosen tests are relevant and effective in assessing potential risks. These components collectively form the backbone of a strong compatibility evaluation, ensuring that all potential risks are systematically assessed.
Additionally, the ethical responsibility of ensuring patient safety is highlighted by the FDA's labeling recommendations for vulnerable patient populations, which inform caretakers about potential skin reactions. As conversations about ISO 10993 progress, especially with expected revisions in 2024, it is essential for stakeholders in the healthcare equipment sector to stay informed and proactive in their compliance initiatives.
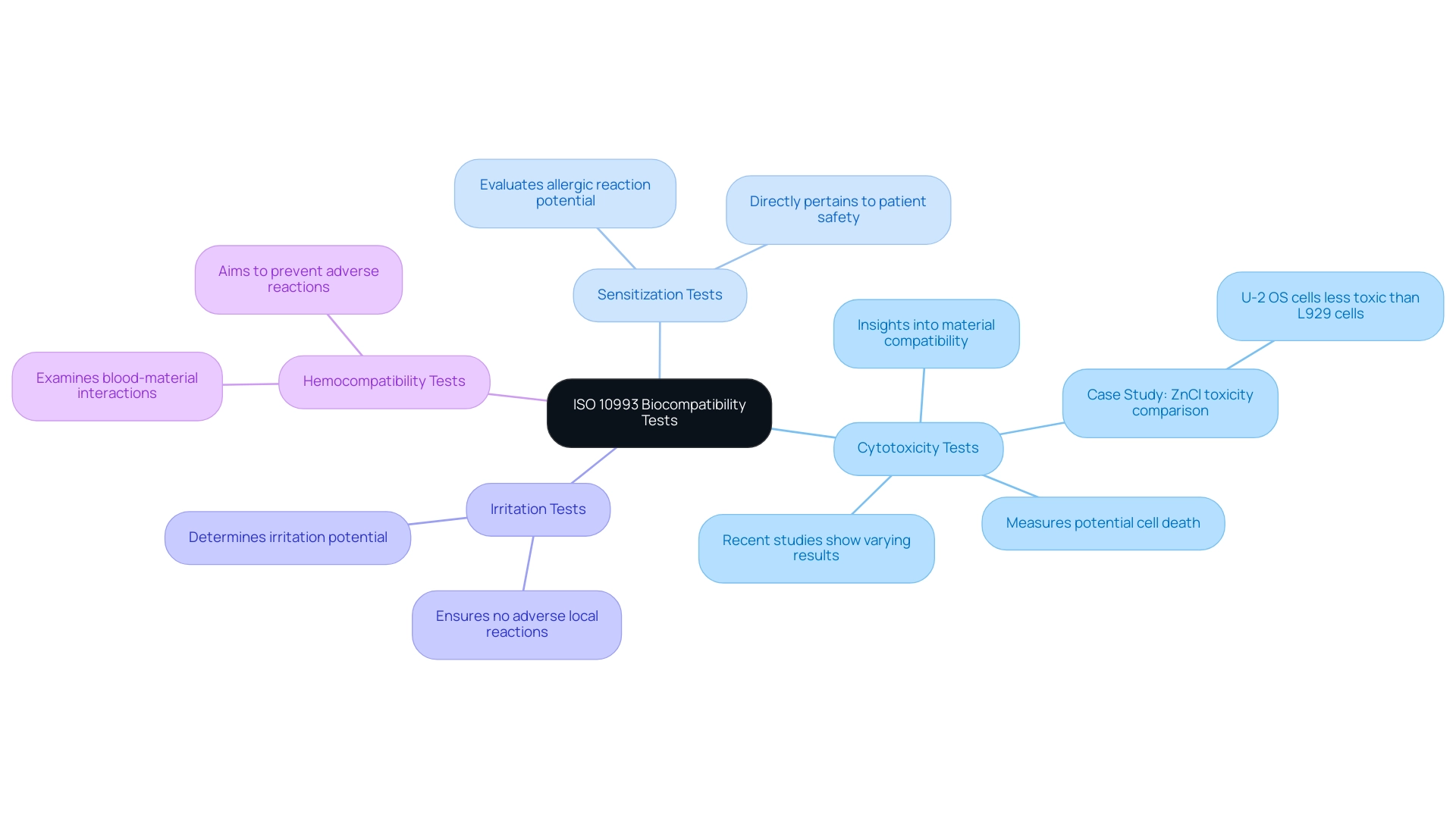
Types of Biocompatibility Tests Required by ISO 10993
The ISO 10993 standard specifies several essential tests for evaluating the biocompatibility of medical devices, each designed to assess different safety aspects:
- Cytotoxicity Tests: These tests measure the potential of a material to induce cell death, providing crucial insights into the material's compatibility with biological tissues. Recent studies, such as real-time xCELLigence impedance analysis, have shown varying cytotoxicity results across different materials, including dental composites, which can significantly impact clinical outcomes. For instance, a case study on the toxicity of ZnCl solutions revealed that U-2 OS cells exhibit significantly less toxicity compared to L929 cells, highlighting the importance of cell type in cytotoxicity assessments.
- Sensitization Tests: These assessments evaluate the likelihood of a material to elicit an allergic reaction in patients. Comprehending sensitization is essential, as it directly pertains to patient safety and acceptance of the equipment.
- Irritation Tests: These tests determine the potential of a material to cause irritation upon contact with biological tissues. The results of these assessments are essential for ensuring that healthcare instruments do not provoke adverse local reactions.
- Hemocompatibility Tests: These analyses examine how blood interacts with the materials utilized in healthcare apparatus, aiming to prevent adverse reactions that could compromise patient safety.
Each of these tests, including biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993, aids in a thorough understanding of a healthcare instrument's safety profile, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. As highlighted in recent discussions, regulatory agencies are increasingly cautious about certain methods, such as the agar diffusion assay, due to concerns over leachables that may affect test outcomes. This reluctance affects the selection of assessment methodologies, emphasizing the need for robust alternatives.
The blend of stringent evaluation techniques and professional examination is crucial for providing healthcare tools that are both efficient and secure for patient application. As mentioned by Anja Segschneider and associates, "We would also like to acknowledge the contributions of our colleagues Anja Segschneider, Bettina Martin, Hanna Lutz, Manuel Baur, and Nadine Jurrmann who reviewed the manuscript," highlighting the joint effort in enhancing compatibility assessment.
Regulatory Implications of Biocompatibility Testing in Medical Device Development
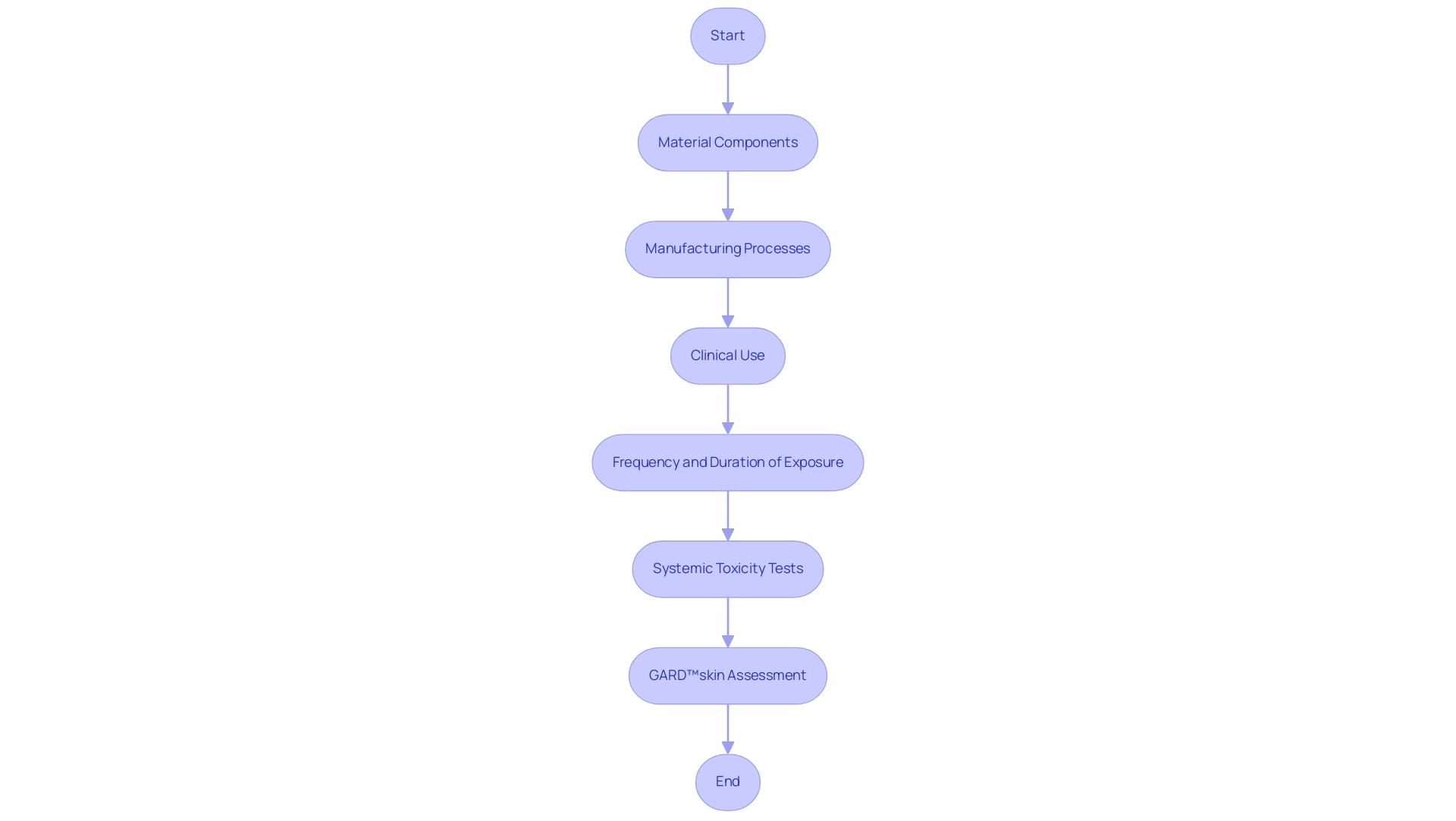
The regulatory consequences of compatibility assessment are significant, acting as a crucial step for gaining market approval for medical equipment. Regulatory authorities, including the FDA and EMA, mandate the submission of extensive biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993 data, which is integral to the evaluation process. According to the FDA, such a process should generally begin with assessment of the equipment, including:
- The material components
- The manufacturing processes
- The clinical use of the equipment, including the intended anatomical location
- The frequency and duration of exposure
Experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, alongside Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, emphasize that biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993 is crucial as it not only streamlines regulatory interactions but also bolsters the credibility of the device among regulators and healthcare professionals. Inadequate demonstration of compatibility with biological entities can result in significant delays in approval, increased scrutiny during the review process, and even the risk of market withdrawal. Therefore, it is essential for manufacturers to prioritize biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993 evaluation protocols to effectively navigate the complexities of regulatory requirements.
Systemic toxicity tests can also assess pyrogenicity, measuring body temperature variations in response to potential pyrogens present in device extracts, which adds another layer of scrutiny to the compatibility assessment. Moreover, the GARD™skin assessment illustrates how compatibility evaluation is utilized; it detects skin sensitizers through genomic interpretation of chemical effects on dendritic cell-like cells, measuring the expression of 200 genes associated with dendritic cell activation and maturation, thereby offering a thorough sensitization profile. The present environment emphasizes a gap in research regarding biocompatible packaging materials, underscoring the need for further investigation to achieve an optimal balance between performance and suitability for living organisms.
As the landscape evolves, staying abreast of the latest regulations and trends in biocompatibility testing for medical devices ISO 10993 will be essential for successful market entry in 2024 and beyond.
Conclusion
Biocompatibility testing is a critical aspect of medical device development, ensuring that materials used do not provoke harmful reactions in patients. The ISO 10993 standard serves as a vital framework for evaluating biological safety, guiding manufacturers in compliance and enhancing their competitive edge.
Beyond regulatory requirements, biocompatibility testing fosters trust between healthcare providers and patients. Regulatory bodies like INVIMA ensure that compliance is monitored, making proactive safety assessments essential. Furthermore, integrating unique device identifiers and providing thorough training for medical professionals significantly improve patient safety and streamline recall processes.
Key components of ISO 10993, such as biological evaluation, material characterization, and appropriate test selection, are foundational for comprehensive biocompatibility assessments. Tests like cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation are crucial for identifying potential risks associated with medical device materials. With increasing regulatory scrutiny, manufacturers must prioritize compliance to navigate the complexities of the approval process effectively.
In conclusion, understanding biocompatibility testing and adhering to ISO 10993 standards are imperative for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical devices. This commitment not only reinforces regulatory compliance but also enhances patient outcomes and marketability. Prioritizing biocompatibility is essential for delivering safe and effective medical devices that meet the needs of patients and healthcare providers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of biocompatibility evaluation in healthcare instruments?
Biocompatibility evaluation ensures that the materials used in healthcare instruments do not provoke negative responses in patients, serving as a crucial bridge between laboratory assessments and real-world clinical applications.
What standard outlines the biological evaluation of medical instruments?
The ISO 10993 standard provides a comprehensive framework for assessing potential risks related to the materials used in medical instruments.
What is the Biocompatibility Matrix?
The Biocompatibility Matrix summarizes relevant tests based on classifications, contact duration, and body contact types, indicating that longer contact durations and more invasive equipment require more thorough evaluation.
Why is compliance with ISO 10993 important for manufacturers?
Compliance with ISO 10993 is critical for patient safety, enhances market competitiveness, and is increasingly becoming a standard for quality in the healthcare sector.
Who oversees biocompatibility testing in Colombia?
In Colombia, the oversight of biocompatibility testing falls under INVIMA (Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos), which monitors compliance with safety standards.
What are the potential consequences of inadequate biocompatibility testing?
Inadequate testing can lead to harmful biological reactions, product recalls, and associated liability issues, as highlighted by the median duration from distribution to recall being 30.0 months.
How can manufacturers reduce the risk of product recalls?
Manufacturers can reduce the risk of recalls by implementing rigorous material selection processes, precise labeling, and stringent packaging controls.
What role do unique identifiers play in patient safety?
Unique identifiers integrated into electronic health records are crucial for improving recall processes and ensuring patient safety.
How is the emphasis on compatibility evaluations expected to change as we approach 2024?
The emphasis on compatibility evaluations is increasing to guarantee regulatory adherence and enhance patient outcomes as well as market appeal in a competitive environment.
What does Katherine Ruiz advocate for regarding biocompatibility testing?
Katherine Ruiz promotes compliance with ISO 10993 standards, which detail the biological assessment of healthcare items to ensure their safety and effectiveness.




