Introduction
The evaluation of biocompatibility is a critical aspect in the development of medical devices, influencing both patient safety and the efficacy of these products. Defined as the ability of a material to provoke an appropriate biological response upon introduction to the body, biocompatibility shapes the regulatory landscape that developers must navigate.
Central to this process is the ISO 10993 series, a set of international standards that provide a comprehensive framework for assessing the biocompatibility of medical devices. Understanding these standards is essential, as they delineate the necessary testing protocols that ensure devices do not elicit adverse biological reactions.
As the regulatory environment evolves, staying abreast of the latest updates and methodologies in ISO 10993 is paramount for developers aiming for successful market entry, particularly in jurisdictions like Colombia, where compliance with local authorities such as INVIMA is crucial.
This article delves into the intricacies of biocompatibility testing, the role of regulatory bodies, and the recent advancements that shape the future of medical device safety.
Introduction to Biocompatibility and ISO 10993
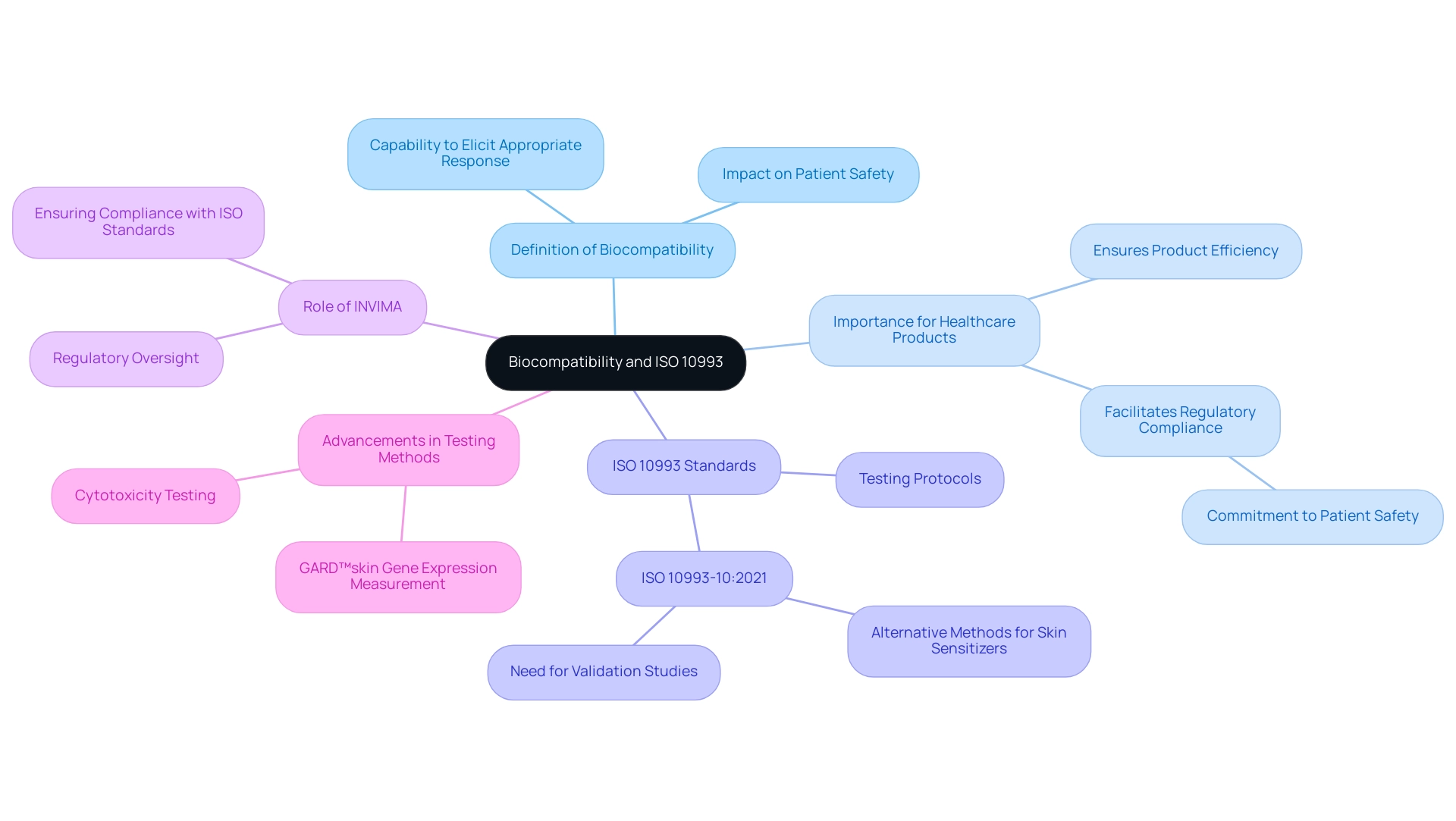
Biocompatibility is defined as the capability of a material to elicit an appropriate response from the host when introduced into the body. It is a basic aspect in the creation of health equipment, as it directly affects patient safety and the overall efficiency of the product. The ISO 10993 series consists of international standards that define the framework for assessing biocompatibility of healthcare products, offering vital guidelines for testing and evaluation.
For healthcare product developers, understanding these standards is essential; they outline the necessary testing protocols to ensure that products do not trigger negative biological responses. This understanding not only facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements but also underscores the commitment to patient safety, a principle highlighted by industry leaders and experts, including Katherine Ruiz, who specializes in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia. INVIMA, as the regulatory body supervising healthcare products in Colombia, plays a vital role in ensuring adherence to these ISO standards.
The agency oversees the testing procedures specified in ISO 10993, ensuring that all healthcare instruments satisfy the essential biocompatibility standards prior to being marketed. Moreover, the ISO 10993-10:2021 recognizes the advancement of alternative methods for identifying skin sensitisers, although their relevance to healthcare products remains uncertain. Ongoing validation studies are essential to demonstrate the reliability of these alternative tests, as emphasized by ISO/TC 194's Working Group 8.
As the terrain of healthcare product regulation changes, staying informed about the latest advancements and updates regarding biocompatibility becomes increasingly essential for developers pursuing successful market entry, particularly within the regulatory framework set by INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, acknowledged as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
Key Testing Methods in ISO 10993 for Medical Devices
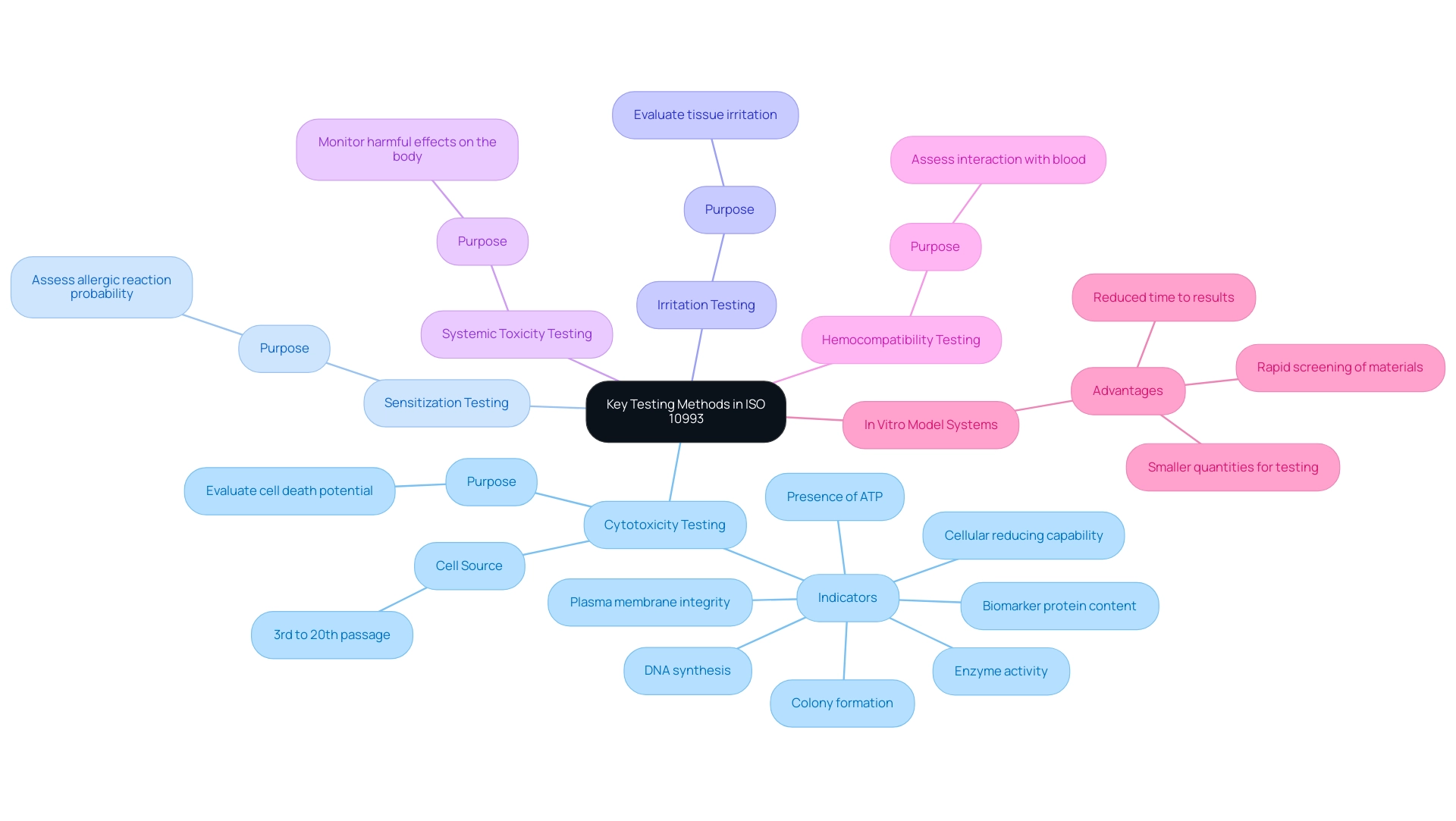
ISO 10993 outlines a comprehensive array of testing methods essential for evaluating the biocompatibility of medical devices. These methods include:
- Cytotoxicity Testing - This test evaluates the potential of a substance to induce cell death, an important measure of its safety. According to Mosmann, "Plasma membrane integrity, colony formation, DNA synthesis, DNA content, biomarker protein content and/or enzyme activity, presence of ATP, and cellular reducing capability are known indicators of cell viability and cell death," all of which are essential in assessing cellular responses to substances. Cells used in these tests were sourced from the 3rd passage after thawing until the 20th passage, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
- Sensitization Testing - This assesses the probability that a substance will trigger an allergic reaction in users. Comprehending sensitization is essential, particularly considering the common occurrence of allergic responses associated with medical equipment.
- Irritation Testing - This approach evaluates whether a substance induces irritation to tissues, offering insights into the comfort and safety of products upon contact with the body.
- Systemic Toxicity Testing - This assesses potential harmful effects on the entire body after exposure, ensuring that systemic responses are carefully monitored.
- Hemocompatibility Testing - This test assesses how substances interact with blood, which is crucial for instruments that will be in contact with the circulatory system.
Each of these tests plays a crucial role in understanding how substances will function in a biological context, particularly in assessing their biocompatibility 10993, thus guiding developers in making informed choices about selection and design. Recent advancements in cytotoxicity testing methods have further enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of these assessments, supporting the case for in vitro model systems that provide quicker results and require smaller quantities of resources. As emphasized in case studies on healthcare instrument toxicity evaluation, these in vitro models offer benefits like decreased time to results and swift examination of substances.
Regulatory Framework: FDA's Role in Biocompatibility Assessment
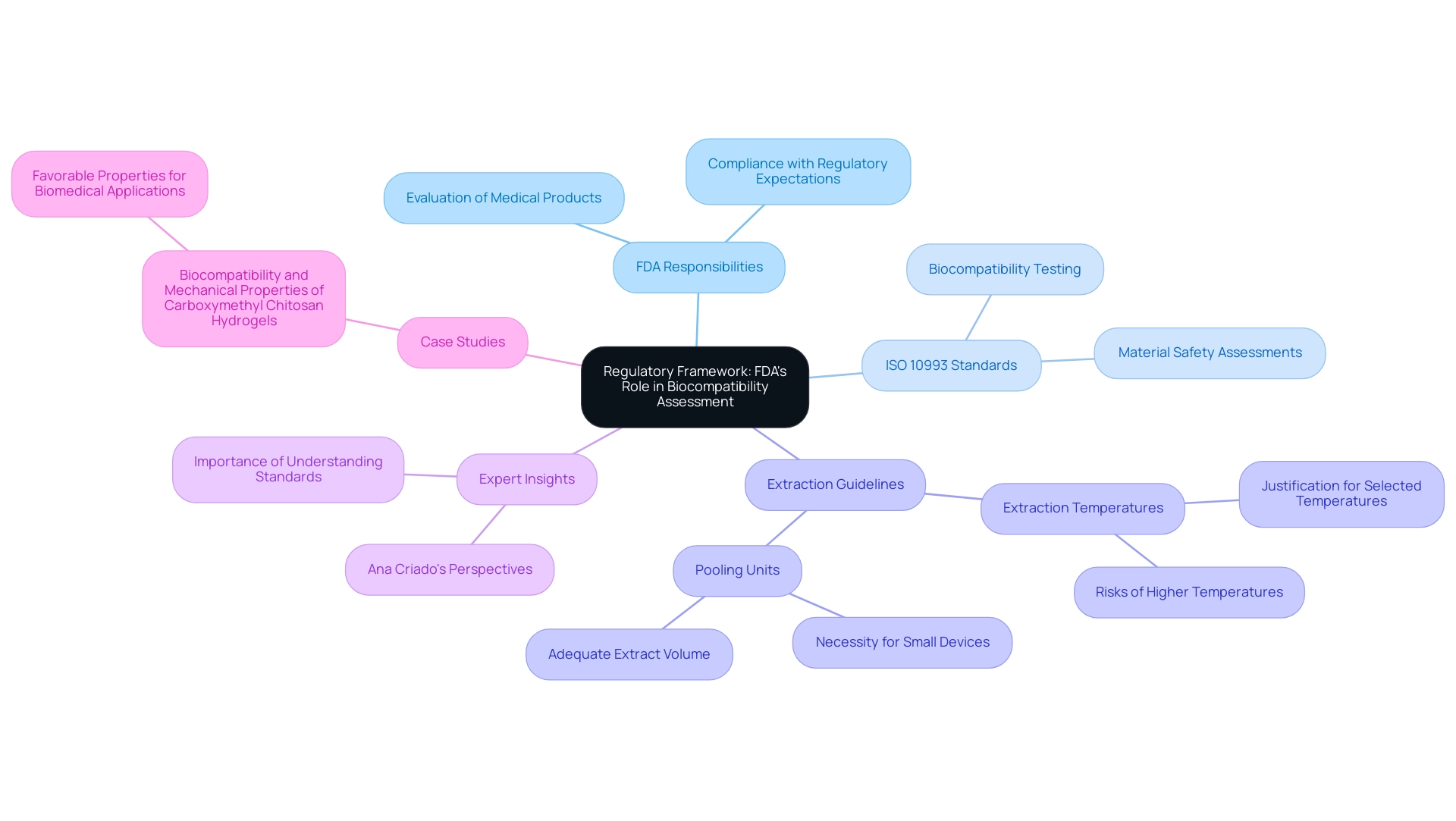
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in the evaluation of medical products, particularly concerning their biocompatibility. Developers are required to present compelling evidence of biocompatibility 10993 when submitting a premarket notification (510(k)) or a premarket approval (PMA), adhering to the protocols outlined in ISO 10993 standards. This includes offering justifications for extraction temperatures, particularly when higher temperatures may risk degrading the materials.
As the FDA states, for items that are very small or have limited surface areas, pooling multiple units for extraction might be necessary to produce adequate extract volume for analysis. Additionally, 'Attachment G: Biocompatibility of Certain Devices in Contact with Intact Skin' provides important guidance that should be considered. Experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and esteemed professor, emphasize the necessity of understanding these standards in the context of her consulting roles for global companies, including those in the biomedical sector.
A relevant case study titled 'Biocompatibility and Mechanical Properties of Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogels' investigates the biocompatibility and mechanical properties of these hydrogels, indicating their favorable properties for potential biomedical applications. Staying informed about the latest FDA guidelines and recommendations is imperative for developers, as it not only streamlines the approval process but also ensures compliance with regulatory expectations. Recent updates in 2024 have highlighted the significance of comprehensive biocompatibility 10993 evaluations, reflecting the FDA's continuous dedication to patient safety in the healthcare landscape.
Moreover, comprehending the specific requirements of biocompatibility 10993 is crucial for ensuring that the materials utilized in healthcare products are safe and effective, which directly influences the success of the regulatory approval process.
Recent Changes and Updates to ISO 10993 Standards
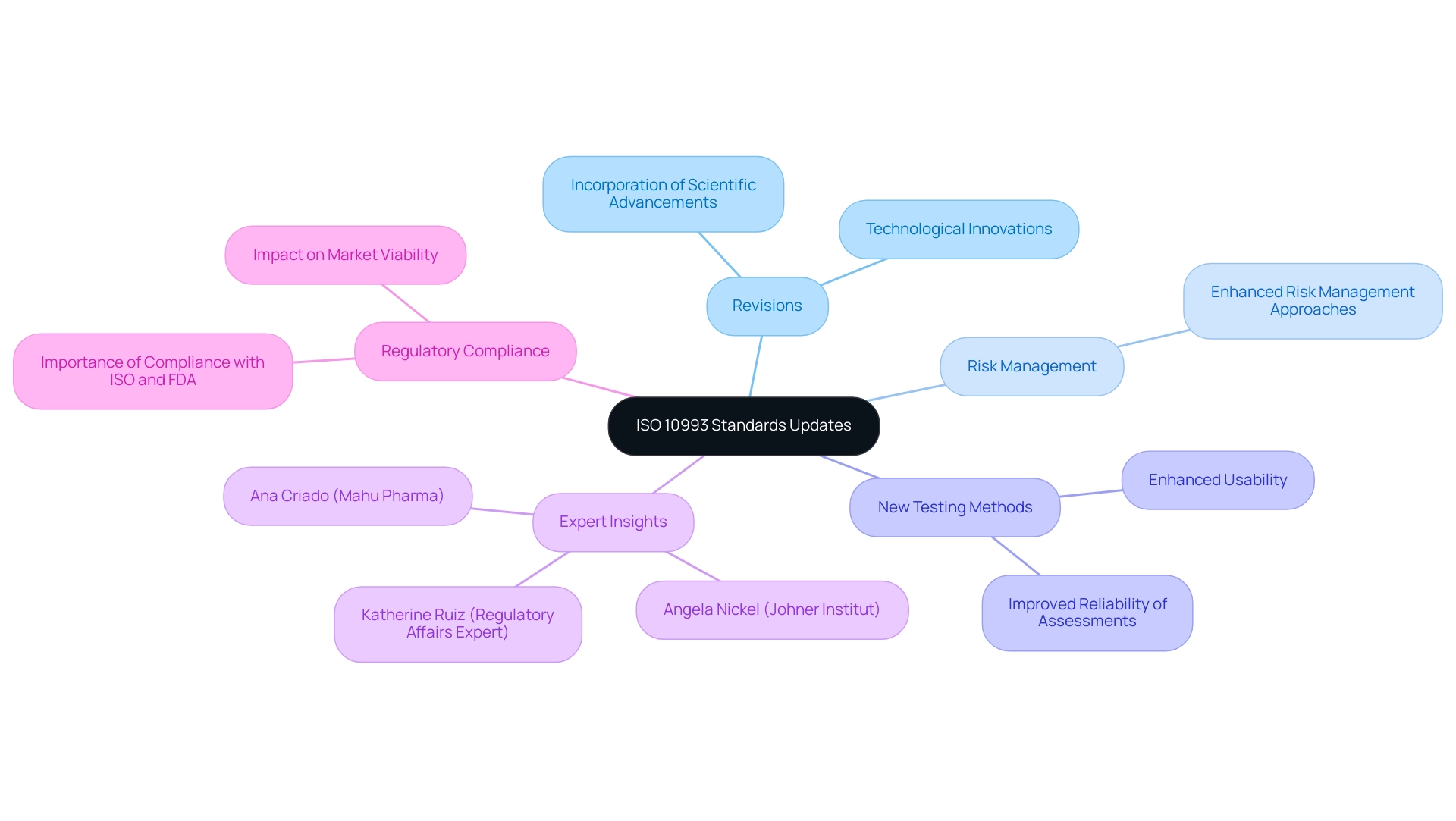
The ISO 10993 standards have undergone significant revisions to incorporate the latest scientific advancements and technological innovations. These updates emphasize enhanced risk management approaches and introduce new testing methods, designed to improve the reliability of biocompatibility assessments. For instance, Trokamed's recent updates to the instructions for use of their nephroscope sheath exemplify how these changes can enhance usability and safety for healthcare professionals.
As Angela Nickel from the Johner Institut GmbH observes, 'The outcomes clearly indicate that the criteria established by the ISO 10993-5 are not specific enough to achieve comparable results for an identical health product.' This underscores the ongoing need for clarity in biocompatibility testing. It is essential for healthcare product developers to remain vigilant about these changes, as they directly influence the testing strategies and documentation required for regulatory submissions.
By routinely reviewing updates from both the ISO and the FDA, developers can ensure compliance with the latest requirements, thus safeguarding their products' market viability and enhancing patient safety. Furthermore, insights from experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, and Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, can provide valuable perspectives on the implications of these advancements in biocompatibility testing. In particular, Ana Criado's knowledge in regulatory matters can assist developers in grasping how the changes to ISO 10993 affect their compliance strategies, while Katherine Ruiz's insights can aid in navigating the regulatory environment for health-related products in Colombia, ensuring that developers are well-equipped to meet the evolving standards.
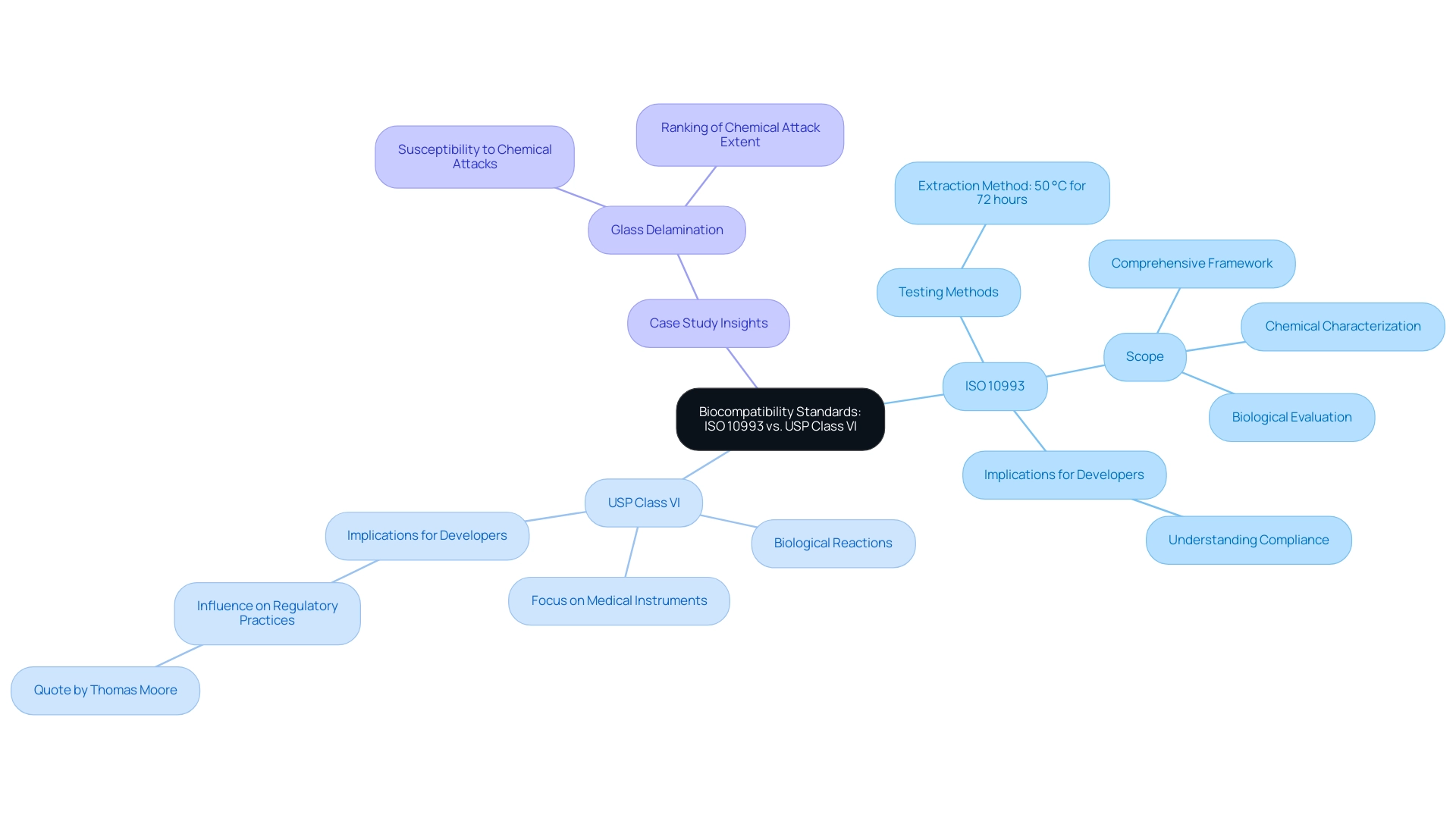
Comparative Analysis: ISO 10993 vs. USP Class VI
ISO 10993 and USP Class VI are pivotal standards in the biocompatibility landscape, each serving distinct purposes. ISO 10993 provides a comprehensive framework for assessing the biocompatibility of healthcare products through various testing methods, including extraction carried out at 50 °C for 72 hours as outlined in ISO 10993-12. This standard encompasses a broader range of assessments, including chemical characterization and biological evaluation, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of how substances interact with biological systems.
On the other hand, USP Class VI is more specifically concentrated, evaluating the biological reactions of substances intended for application in medical instruments, especially those that have direct contact with patients. Comprehending these differences is essential for developers as they navigate regulatory requirements and choose the suitable standard aligned with their product's unique attributes. Thomas Moore emphasizes this importance, stating,
USP testing methods are widely accepted in the United States and have a significant influence on regulatory practices and quality control in the pharmaceutical industry.
Furthermore, the implications of compliance with both standards are often not fully understood, which can lead to significant challenges in the development process. For instance, a recent case study on glass delamination highlights that while glass is considered an ideal storage material for pharmaceutical drugs, it is susceptible to chemical attacks from the drugs it stores, ranking the extent of these attacks based on differences in the interior surface of various types of glass. Ultimately, adherence to the correct standards not only facilitates compliance but also guarantees the safety and efficacy of medical devices for patient use.
Conclusion
The evaluation of biocompatibility is an indispensable component in the development and regulatory approval of medical devices. By understanding the ISO 10993 series, developers can ensure that their products meet the necessary testing protocols to avoid adverse biological reactions, thereby prioritizing patient safety. The comprehensive testing methods outlined in these standards, including:
- Cytotoxicity
- Sensitization
- Hemocompatibility testing
provide critical insights into how materials will perform in biological environments.
Regulatory bodies, particularly the FDA and INVIMA, play a vital role in enforcing these standards, ensuring that medical devices are rigorously assessed before market entry. Recent updates to ISO 10993 reflect ongoing advancements in science and technology, emphasizing the need for developers to stay informed about changes that may impact their testing strategies and compliance efforts.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of both ISO 10993 and USP Class VI standards is essential for medical device developers. By adhering to these guidelines, they not only facilitate regulatory compliance but also contribute to the overall safety and efficacy of medical devices. As the landscape of medical device regulation continues to evolve, commitment to biocompatibility will remain a cornerstone of successful product development, ensuring that innovation aligns with the highest standards of patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is biocompatibility?
Biocompatibility is the capability of a material to elicit an appropriate response from the host when introduced into the body, which is crucial for patient safety and product efficiency in healthcare equipment.
Why are ISO 10993 standards important for healthcare product developers?
The ISO 10993 standards provide essential guidelines for assessing the biocompatibility of healthcare products, outlining necessary testing protocols to ensure that products do not trigger negative biological responses and facilitating compliance with regulatory requirements.
What role does INVIMA play in biocompatibility testing in Colombia?
INVIMA, as the regulatory body in Colombia, oversees the testing procedures specified in ISO 10993, ensuring that healthcare instruments meet essential biocompatibility standards before being marketed.
What are the key testing methods outlined in ISO 10993 for evaluating biocompatibility?
The key testing methods include: 1. Cytotoxicity Testing 2. Sensitization Testing 3. Irritation Testing 4. Systemic Toxicity Testing 5. Hemocompatibility Testing.
What does cytotoxicity testing evaluate?
Cytotoxicity testing evaluates the potential of a substance to induce cell death, assessing various indicators of cell viability and death to determine safety.
How does sensitization testing contribute to patient safety?
Sensitization testing assesses the likelihood that a substance will trigger an allergic reaction in users, which is important due to the common occurrence of allergic responses associated with medical equipment.
What does irritation testing measure?
Irritation testing measures whether a substance induces irritation to tissues, providing insights into the comfort and safety of products upon contact with the body.
Why is systemic toxicity testing important?
Systemic toxicity testing is important as it assesses potential harmful effects on the entire body after exposure to a substance, ensuring comprehensive monitoring of systemic responses.
What is hemocompatibility testing and why is it crucial?
Hemocompatibility testing assesses how substances interact with blood, which is crucial for instruments that will be in contact with the circulatory system.
What advancements have been made in cytotoxicity testing methods?
Recent advancements in cytotoxicity testing methods have improved efficiency and accuracy, particularly through the use of in vitro model systems that provide quicker results and require smaller quantities of resources.




