Overview
The article focuses on the importance of biological evaluation in the development of medical devices, emphasizing the need for thorough assessment of biocompatibility to ensure safety and effectiveness. It supports this by detailing the role of regulatory bodies like INVIMA in overseeing evaluations, the significance of standards such as ISO 10993, and the challenges faced by manufacturers due to the lack of standardized testing methods, which can hinder innovation and market entry.
Introduction
The biological evaluation of medical devices stands as a fundamental pillar in ensuring their safety and efficacy, particularly within the regulatory landscape of Colombia. This meticulous process involves a comprehensive assessment of how device materials interact with biological systems, addressing potential toxicological risks and compliance with established standards.
As the demand for innovative medical solutions continues to surge, understanding the intricacies of biological evaluation becomes imperative for stakeholders across the healthcare spectrum.
With INVIMA at the helm of regulatory oversight, the interplay between rigorous evaluation processes and the need for streamlined innovation emerges as a critical focus.
This article delves into the essential principles, standards, and recent developments surrounding biological evaluation, highlighting the challenges faced by manufacturers and the evolving regulatory landscape that shapes the future of medical device safety.
Fundamentals of Biological Evaluation in Medical Devices
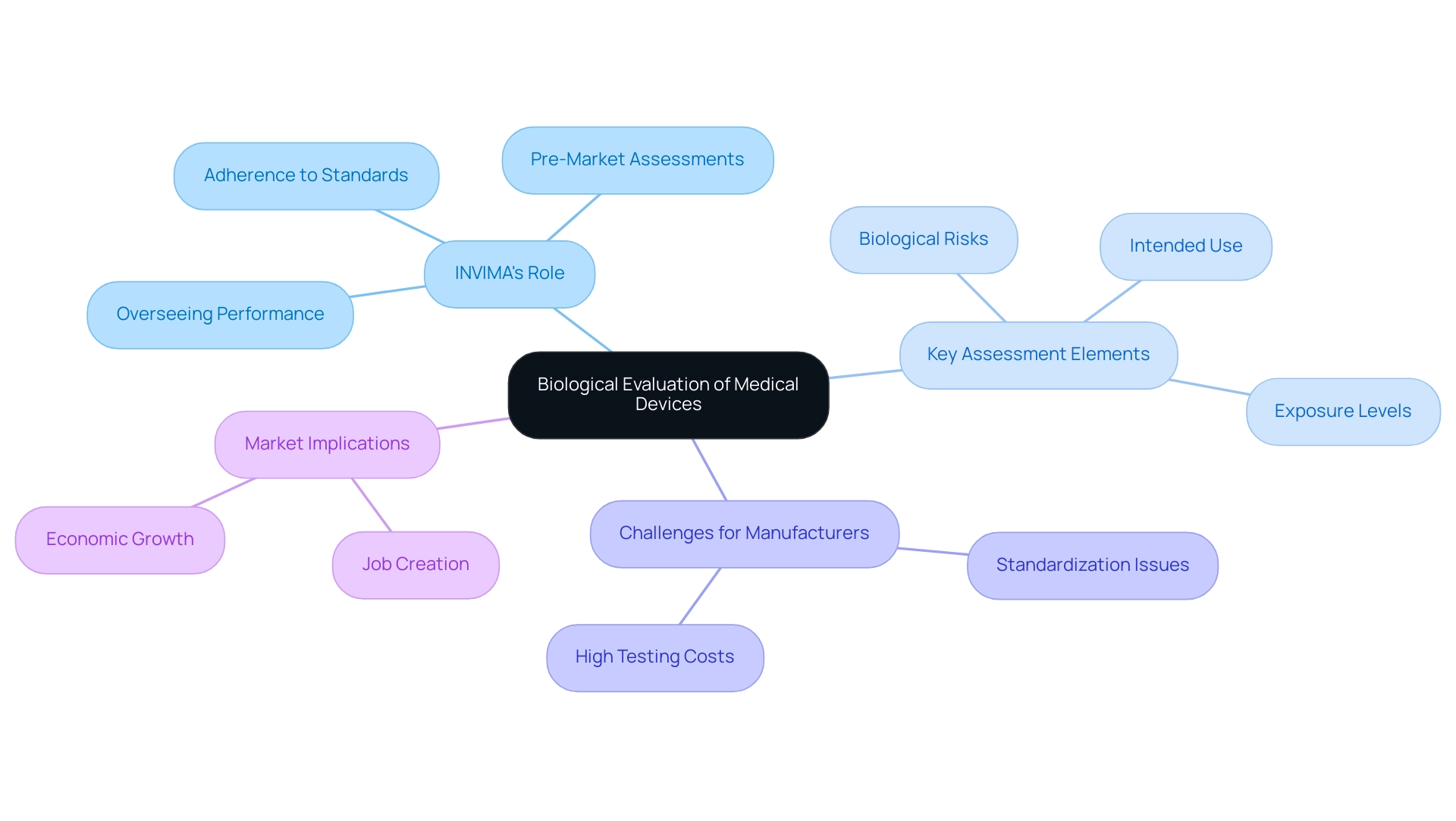
The biological evaluation of medical devices is a cornerstone in the development of medical tools, meticulously examining the biocompatibility of the materials utilized. This assessment process is not simply procedural; it critically analyzes how instruments interact with biological systems as part of the biological evaluation of medical devices, including potential toxicological implications. Grasping the core principles of the biological evaluation of medical devices is crucial for stakeholders, especially regarding INVIMA (Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute), which plays a pivotal role in ensuring adherence to these evaluations under its regulatory framework.
INVIMA's Directorate for Medical Equipment is tasked with supervising the evaluation of products to ensure their security, effectiveness, and quality, thereby reducing risks linked to equipment implantation and use. This directorate's duties encompass:
- Overseeing equipment performance
- Carrying out pre-market assessments
- Ensuring adherence to technical standards, which are essential for upholding high safety levels in health-related products
Key elements of this assessment include:
- Identification of potential biological risks
- Analysis of exposure levels
- Review of the instrument's intended clinical use
As Sarah Gruber, a specialist in the field, observes, 'The following shall be considered for their relevance to overall biological assessment of the healthcare instrument: process contaminants and residues, packaging materials, leachable substances, and degradation products.' This essential knowledge is crucial for all professionals within the healthcare landscape, including researchers and regulatory specialists, particularly considering the recent statistic showing that the hospital sector represented 35% of total revenue in 2023. This highlights the increasing significance of the biological evaluation of medical devices as the need for healthcare products continues to grow, particularly in a market regulated by strong authorities such as INVIMA.
However, it is crucial to recognize that the lack of standardized testing methods for the biological evaluation of medical devices can lead to inconsistencies in biocompatibility assessments, which introduces uncertainty for manufacturers. These inconsistencies can be particularly detrimental for small and medium-sized enterprises, which often face high testing costs and navigate a complex regulatory environment, as highlighted in the case study titled 'Restraints in Biocompatibility Testing.' The case study illustrates how these challenges may hinder innovation and market entry, ultimately affecting overall market growth and the local economy.
For instance, regions with active Medtech clinical studies have reported job creation and economic growth, emphasizing the need for a supportive regulatory environment that fosters innovation while ensuring safety.
Key Standards and Guidelines: ISO 10993 and Beyond
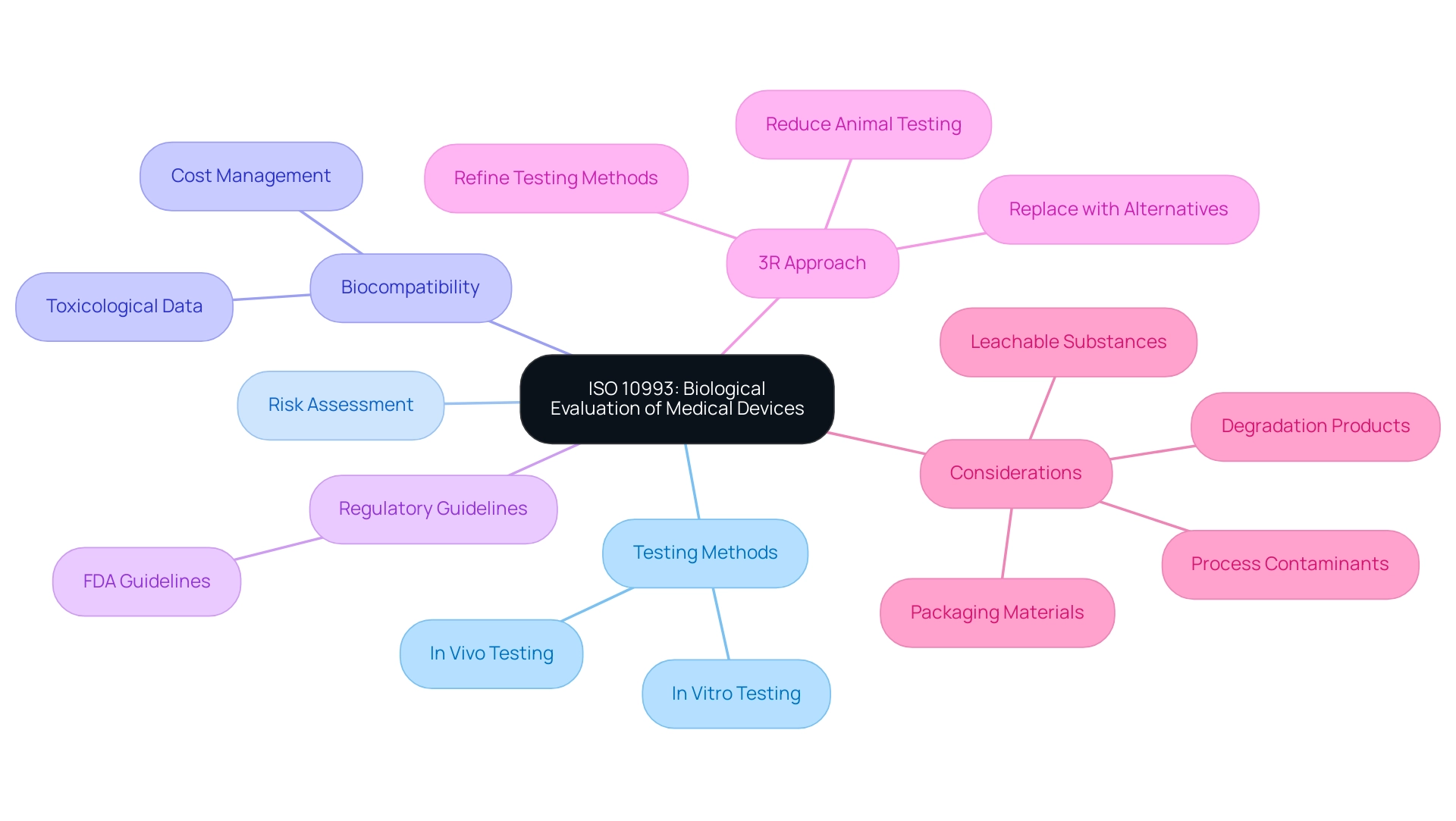
ISO 10993 acts as the foundation for the biological evaluation of medical devices, consisting of several sections that provide comprehensive guidance on testing methods, risk assessment, and the analysis of biological responses. This standard outlines critical components, including the identification of materials, in vitro and in vivo testing protocols, as well as effective risk management strategies. A noteworthy update in 2023 was the addition of Annex G, which reinforces the '3R approach'—reducing, refining, and replacing animal testing—thereby promoting ethical practices in biocompatibility assessments.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies like the FDA provide supplementary guidelines that further enhance the biological assessment process. A vital element of this assessment is the gathering and analysis of toxicological information on released materials, which is necessary for recognizing possible risks linked to healthcare instruments. Comprehending these standards is essential for guaranteeing that instruments not only meet compliance and efficacy criteria but also conform to the latest regulatory expectations.
Additionally, demonstrating biocompatibility can incur significant costs; therefore, strategic planning and a risk-based approach are vital to minimize unnecessary testing and manage these expenses effectively. As emphasized in a case study, the quality of toxicological data is essential, with high-quality data aiding the derivation of dependable limit values, which improves the safety evaluation of the health product. As Sarah Gruber, a specialist in the field, aptly notes,
- The following shall be considered for their relevance to overall biological assessment of the healthcare apparatus:
- process contaminants and residues
- packaging materials
- leachable substances
- degradation products
This insight emphasizes the necessity of a comprehensive review in the biological evaluation of medical devices, ensuring that all potential hazards are meticulously evaluated before a product reaches the market.
Implementing Biological Evaluation: Plans and Testing Procedures
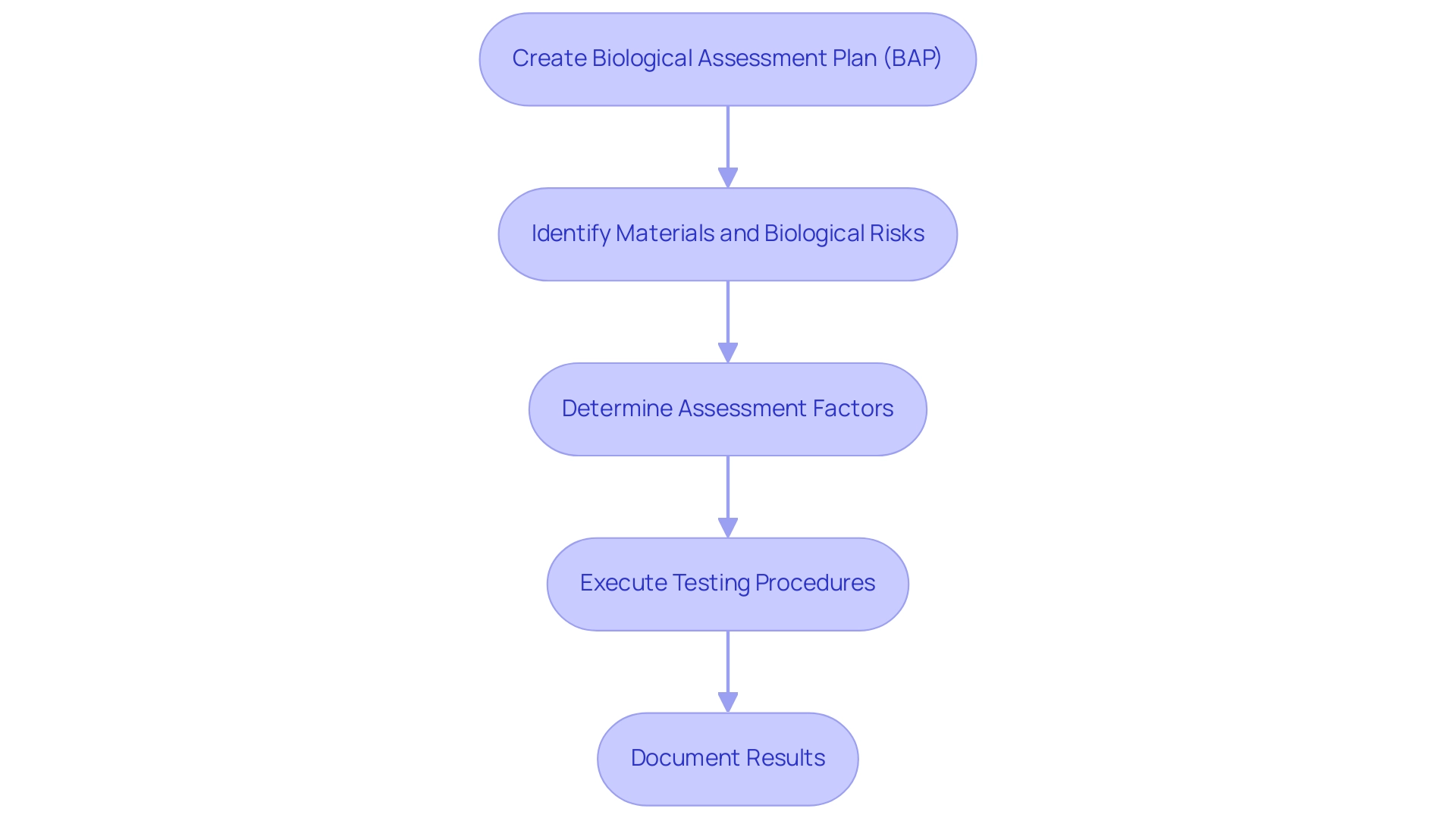
The execution of a biological evaluation of medical devices for healthcare instruments begins with the creation of a comprehensive Biological Assessment Plan (BAP). This essential document outlines the scope, objectives, and methodologies that will be employed during the evaluation process, ensuring alignment with Colombian regulations as outlined by INVIMA, the National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute. INVIMA plays an essential role in monitoring the security and effectiveness of healthcare instruments in Colombia, categorized as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO, which emphasizes its proficiency in health regulation.
It is crucial to identify the materials involved, potential biological risks, and the intended application of the medical instrument, as these factors significantly influence the biocompatibility assessment. According to current standards, biocompatibility assessment is based on various factors, including:
- The nature of contact
- Type of contact
- Frequency and duration of contact
- Materials
All of which are critical in determining the safety of the device. For instance, the nature of contact can vary from surface contact to systemic exposure, each necessitating different assessment strategies.
Once the BEP is established, testing procedures must be meticulously executed, adhering to established standards that encompass:
- In vitro cytotoxicity tests
- Sensitization tests
- Implantation studies where relevant
Thorough documentation of test results, along with any deviations from anticipated outcomes, is essential for regulatory submissions and future assessments. Such a structured approach not only ensures that the assessment is exhaustive but also aligns with compliance requirements, particularly under the guidance of experts like Ana Criado, who leads Regulatory Affairs at Mahu Pharma and consults on best practices in the industry.
A pertinent case study highlights the significance of the biological evaluation of medical devices and the Biological Evaluation Report (BER) in demonstrating adherence to standards during clinical application, illustrating how these documents summarize information supporting the biological security of health products. Additionally, as highlighted by Adrienne R. Lenz, Principal Medical Device Regulation Expert, 'In order to be more helpful to industry, reasonable recommendations to reduce animal testing in practice (rather than theory) are still needed.' This emphasizes the significance of corporate best practices in vitro testing as part of the assessment process.
Furthermore, it is important to note that the comment period for the draft guidance has been extended to December 19, 2024, allowing stakeholders to provide feedback before the final version is developed. Ultimately, a well-crafted BEP and adherence to testing protocols, including methodologies such as ISO 10993 standards, are paramount for demonstrating the reliability and effectiveness of healthcare tools.
Integrating Risk Management into Biological Evaluations
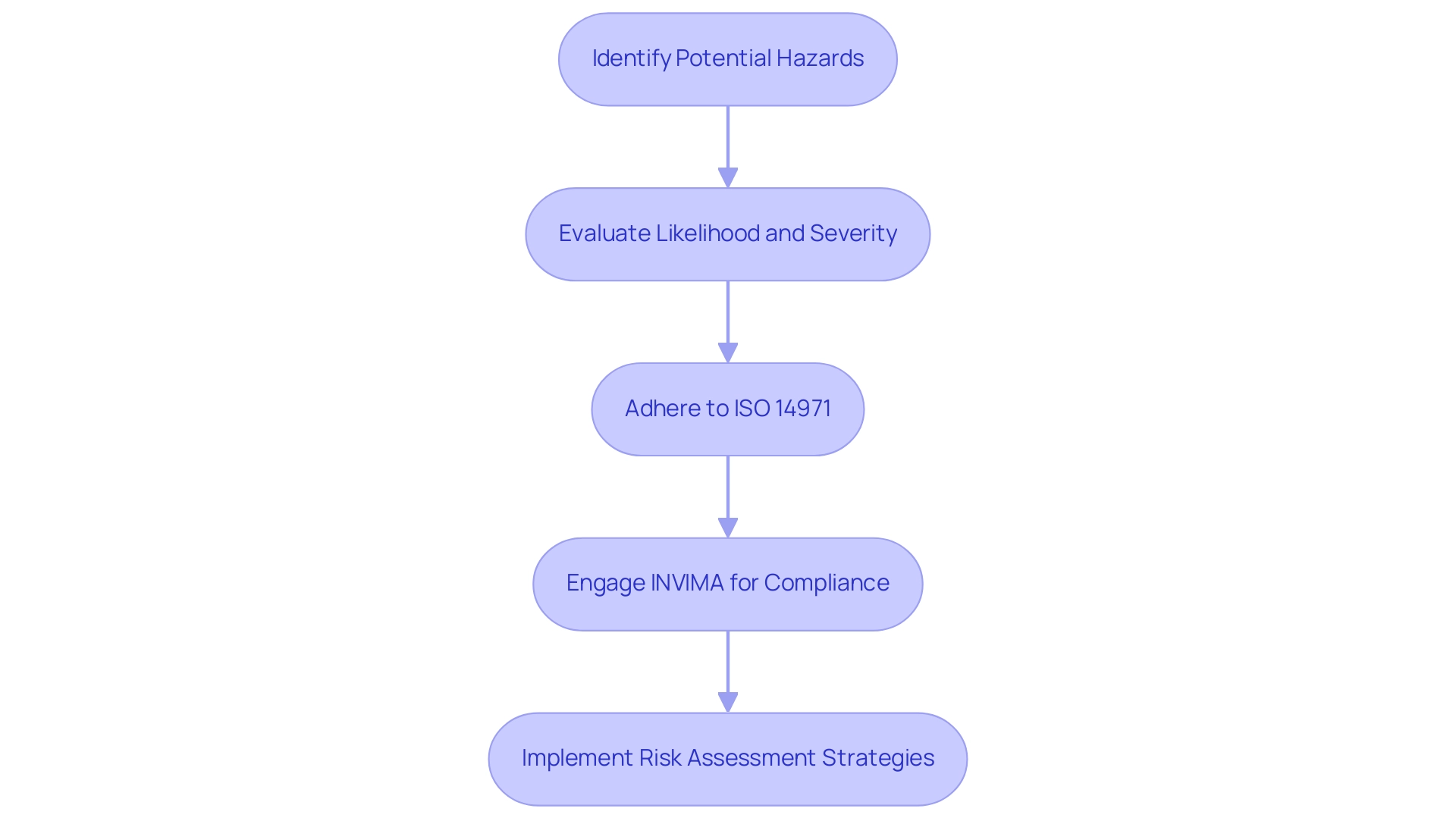
Incorporating risk management into the biological evaluation of medical devices is crucial for guaranteeing the safety and effectiveness of healthcare instruments. This process starts with recognizing potential hazards related to the equipment, followed by a comprehensive evaluation of their likelihood and severity. Adhering to ISO 14971, the established international standard for risk management in healthcare products, is crucial in guiding this evaluation process.
Furthermore, grasping the function of INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, is crucial for adherence, as it supervises the marketing and production of health products, including medical apparatus. INVIMA's classification as a Level 4 health authority highlights its proficiency in regulating health products and ensuring compliance with quality standards. By implementing systematic risk assessment strategies and engaging in comprehensive clinical trial management services—such as feasibility studies, site selection, and project management—stakeholders can optimize device reliability and performance while enhancing regulatory compliance in alignment with INVIMA's standards through the biological evaluation of medical devices.
This proactive approach fosters trust among stakeholders and supports an ongoing commitment to patient safety, especially as the healthcare landscape evolves. The significance of a robust risk management framework is further underscored by recent developments, such as labor strikes and staff shortages that may compromise patient care. The recent charges brought by the U.S. Department of Justice against 78 defendants for their involvement in fraud and opioid abuse schemes, totaling over $2.5 billion, highlight the critical need for compliance and risk management in healthcare.
Furthermore, Richard Williams, Global Healthcare Practice Leader at Protiviti, emphasizes that 'Artificial intelligence and other emerging digital technologies are poised to transform the way healthcare delivery and operations are conducted over the next decade, but organizations must be acutely aware of and prepared for the risk of cyber attack and the need to safeguard patient/member data in an evolving threat landscape.' Additionally, the U.S. Office of Inspector General's updated guidance on compliance programs for healthcare organizations serves as a real-world example of how compliance and risk management are being modernized to enhance adherence in the healthcare sector. Addressing these challenges effectively is vital for maintaining high standards of care in an increasingly complex environment.
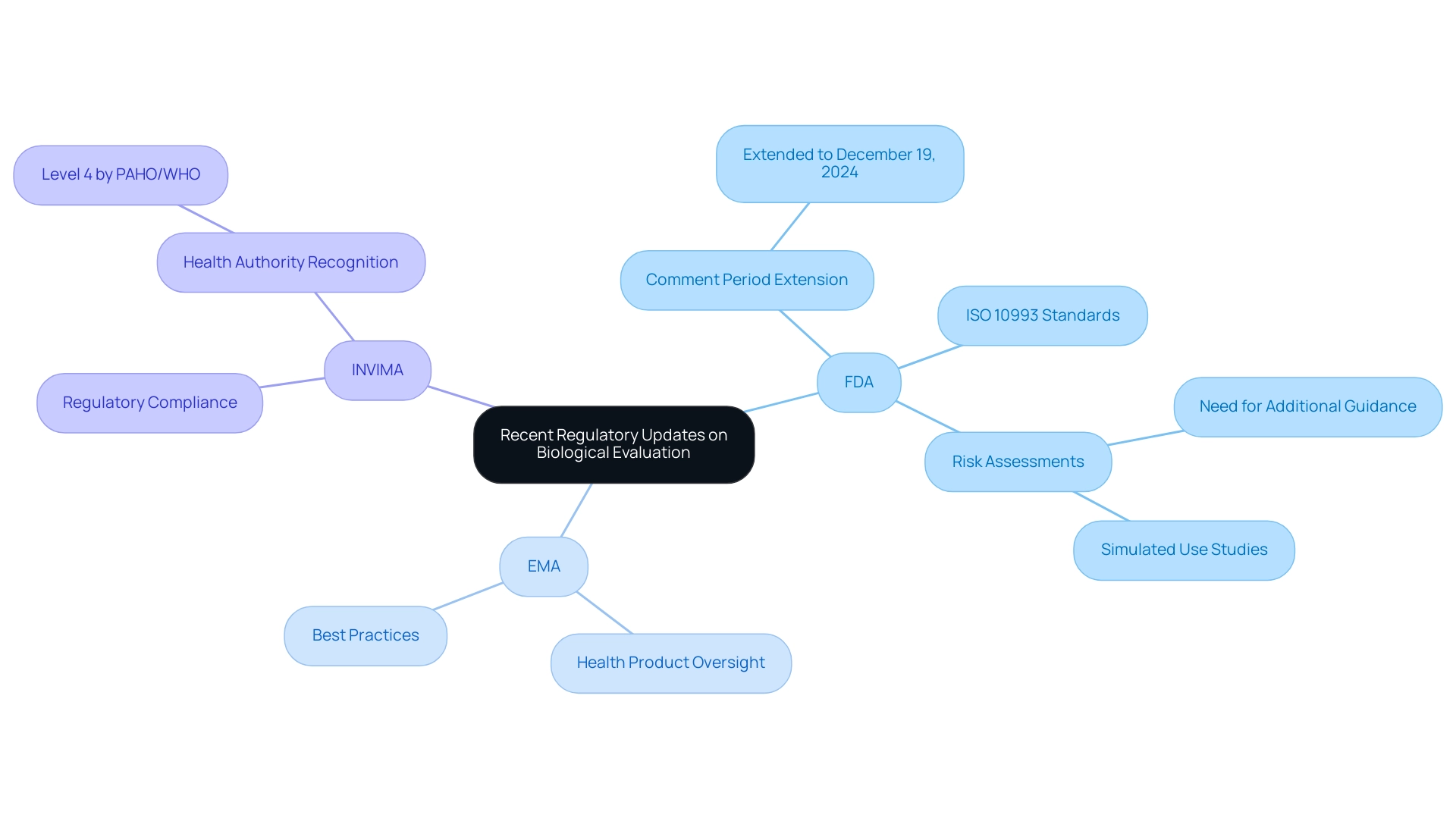
Recent Regulatory Updates and Guidance on Biological Evaluation
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA, the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and Colombia's INVIMA (Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute), play a pivotal role in influencing the biological evaluation of medical devices through their periodic updates and guidance documents. Founded in 1992, INVIMA is responsible for inspecting and overseeing health products, including the monitoring and regulation of healthcare instruments through its Directorate for Medical Instruments and other Technologies. This directorate is responsible for ensuring compliance with health standards and implementing best practices, and INVIMA has been recognized as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO, underscoring its competence in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of medical devices.
Recent communications from the FDA, especially the announcement prolonging the comment period for the draft guidance to December 19, 2024, highlight the significance of stakeholder input in creating strong assessment frameworks. These publications highlight the necessity of aligning with the latest ISO 10993 standards and stress the importance of comprehensive risk assessments in the biological evaluation of medical devices assessment process. For instance, the case study titled 'Need for Additional Guidance on Simulated Use Studies' highlights how simulated use and release kinetics studies could provide valuable insights, especially for products incompatible with harsh solvents.
The authors advocate for the FDA to release additional guidance on these topics to better support industry efforts to reduce animal testing and enhance the biological evaluation of medical devices. Additionally, enhanced guidance on characterizing equipment and identifying biological hazards is included, reinforcing the argument for thorough risk assessments in the biological evaluation of medical devices. Furthermore, the integration of real-world evidence and post-market surveillance is gaining traction in regulatory discussions, as these elements are crucial for understanding performance in practical settings.
As Adrienne R. Lenz, Principal Medical Device Regulation Expert, notes, 'In order to be more helpful to industry, reasonable recommendations to reduce animal testing in practice (rather than theory) are still needed.' Additionally, professionals like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and a key figure in Colombian medical device regulation, emphasize the importance of staying abreast of these updates to ensure compliance with the most current standards and practices, ultimately fostering safer and more effective medical innovations.
Conclusion
The biological evaluation of medical devices is a critical aspect of ensuring their safety and efficacy, particularly within the regulatory framework established by INVIMA in Colombia. This comprehensive assessment not only examines the biocompatibility of materials but also addresses potential toxicological risks associated with device usage. As the demand for medical devices continues to grow, understanding the principles underpinning biological evaluation becomes increasingly vital for manufacturers, regulatory bodies, and healthcare professionals alike.
Key standards such as ISO 10993 provide essential guidelines for conducting thorough evaluations, emphasizing the importance of ethical practices and the reduction of animal testing. Additionally, the implementation of robust Biological Evaluation Plans (BEPs) and adherence to established testing protocols are paramount in demonstrating compliance with safety standards. By integrating risk management strategies, stakeholders can proactively identify and assess potential hazards, ensuring that products meet the necessary safety and quality benchmarks.
Recent updates from regulatory authorities highlight the ongoing evolution of biological evaluation practices, reinforcing the need for continuous dialogue among industry professionals and regulators. The incorporation of real-world evidence and post-market surveillance further enhances the understanding of device performance, ultimately fostering innovation while prioritizing patient safety.
In conclusion, the complexities of biological evaluation cannot be understated, as they play a crucial role in shaping the future of medical device safety. By navigating these challenges with diligence and adhering to established standards, stakeholders can contribute to a more secure healthcare landscape, ensuring that innovative medical solutions are both safe and effective for patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the biological evaluation of medical devices?
The biological evaluation of medical devices is a critical process that examines the biocompatibility of materials used in medical tools, analyzing how these instruments interact with biological systems and potential toxicological implications.
Why is the biological evaluation important for stakeholders?
Understanding the core principles of the biological evaluation is crucial for stakeholders, especially concerning regulatory bodies like INVIMA, which ensures adherence to these evaluations for safety, effectiveness, and quality of medical devices.
What role does INVIMA play in the evaluation of medical devices?
INVIMA's Directorate for Medical Equipment supervises the evaluation of medical products to ensure their safety, effectiveness, and quality, which includes overseeing equipment performance, conducting pre-market assessments, and ensuring compliance with technical standards.
What are the key elements of the biological evaluation assessment?
Key elements include identifying potential biological risks, analyzing exposure levels, and reviewing the intended clinical use of the instrument.
What challenges do manufacturers face regarding biocompatibility testing?
The lack of standardized testing methods can lead to inconsistencies in biocompatibility assessments, which may introduce uncertainty for manufacturers, particularly affecting small and medium-sized enterprises due to high testing costs and complex regulations.
How does ISO 10993 relate to the biological evaluation of medical devices?
ISO 10993 serves as the foundation for the biological evaluation, providing guidance on testing methods, risk assessment, and biological response analysis, including in vitro and in vivo testing protocols.
What is the significance of the 2023 update to ISO 10993?
The 2023 update included Annex G, which emphasizes the '3R approach'—reducing, refining, and replacing animal testing—promoting ethical practices in biocompatibility assessments.
What role do regulatory bodies like the FDA play in biological assessments?
Regulatory bodies like the FDA provide additional guidelines that enhance the biological assessment process, including the gathering and analysis of toxicological information on released materials.
What considerations should be made in the biological assessment of healthcare instruments?
Considerations include process contaminants, residues, packaging materials, leachable substances, and degradation products, all of which are vital for a comprehensive evaluation before market entry.
How can manufacturers manage the costs associated with demonstrating biocompatibility?
Strategic planning and a risk-based approach are essential to minimize unnecessary testing and manage expenses effectively during the biocompatibility assessment process.

