Introduction
In the realm of medical devices, the concepts of extractables and leachables (E&L) are paramount to ensuring patient safety and product integrity. These terms refer to the substances that may migrate from device materials into the surrounding environment or the product itself, potentially posing risks during usage.
With regulatory bodies enforcing stringent guidelines, understanding the nuances of E&L testing has become essential for manufacturers striving to comply with safety standards. Recent advancements in analytical technologies and methodologies are not only enhancing the detection of these compounds but also shaping the future landscape of medical device safety.
As the industry evolves, the importance of comprehensive testing and adherence to regulatory frameworks cannot be overstated, making it crucial for stakeholders to stay informed and proactive in their approaches to E&L management.
Defining Extractables and Leachables in Medical Devices
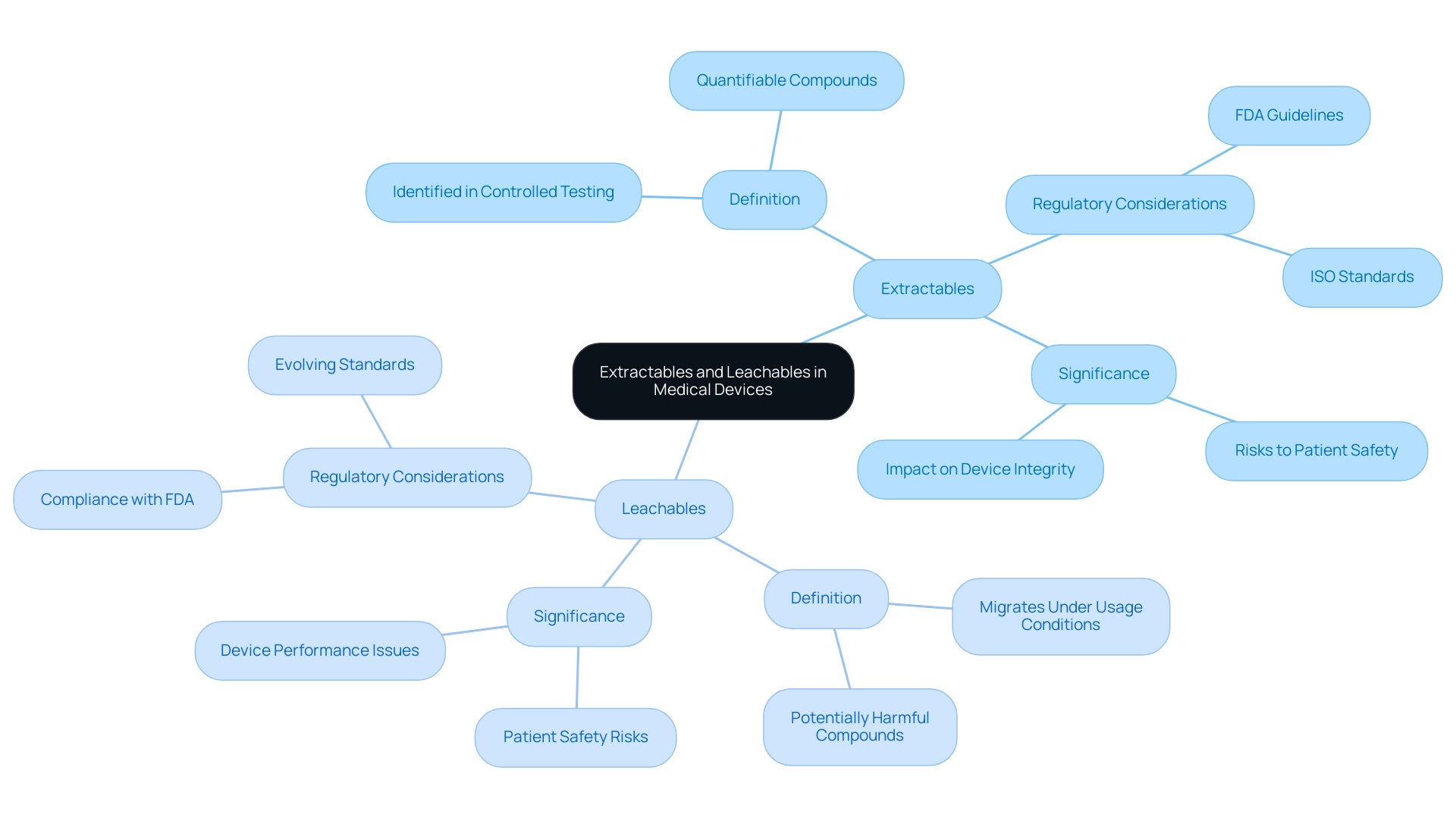
Extractables and leachables medical devices are essential ideas in the assessment of health instruments, referring to substances that can transfer from material components into the item or its surrounding environment. Extractables are compounds that can be identified and quantified during controlled laboratory testing, while leachables are those compounds that can migrate into a product under typical usage conditions. Understanding these definitions is crucial, as both extractables and leachables medical devices can present substantial risks to patient safety and the overall integrity of healthcare instruments.
For instance, the nozzle temperature for a polycarbonate item during manufacturing was recorded at 270 °C, which can influence the release of these compounds. Regulatory organizations, including the FDA and ISO, have established stringent guidelines to assess extractables and leachables medical devices, emphasizing that thorough evaluations are necessary to ensure that these devices are safe for patient use. Recent mass spectra patterns for PLA and PPG oligomers have shown distinct fragmentation, supporting the identification of oligomeric species that may act as extractables.
In light of recent developments, including mergers and acquisitions among key companies in the U.S. and Europe, the market for extractables and leachables medical devices testing services is poised for substantial growth, underscoring the importance of compliance with evolving regulatory standards. A pertinent case study emphasized that the printing process influenced the concentration of phenyl phosphates in printed materials, demonstrating a 55% reduction in concentration compared to the filament extracts. This demonstrates the real-world effects of extractables and leachables medical devices in healthcare products.
As noted by industry expert Morley, when designing and performing studies on drug-device combination items, it is crucially important to have a deep understanding of the similarities and differences between the various extractables and leachables medical devices standards and guidelines. This underscores the continuous necessity for thorough research and compliance with the latest FDA guidelines concerning the management of extractables and leachables medical devices in healthcare products.
The Importance of Testing Extractables and Leachables
Testing for extractables and leachables medical devices is essential in the medical sector for several compelling reasons: it ensures adherence to regulatory standards, protects patient health, and maintains integrity. Regulatory agencies require comprehensive evaluations to identify and quantify these potentially harmful substances, which can lead to adverse effects such as toxicity, allergic reactions, or device failure. The significance of this evaluation is highlighted by recent data showing that investment in technologies for extractables and leachables medical devices can accelerate the market launch of safer items, enabling manufacturers to deliver innovative solutions to healthcare more quickly.
For instance, Intertek's partnership with CrystecPharma demonstrates a forward-thinking approach aimed at enhancing formulation science for dry powder inhalers. The evaluation process employs various methodologies, including solvent extraction and sophisticated analytical techniques such as gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. By rigorously conducting tests on extractables and leachables in medical devices, manufacturers can uncover potential risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them, thereby ensuring compliance with critical regulatory guidelines.
As articulated by Armin Hauk, Principal Scientist in Extractables and Leachables,
Experimental results must prove that they will before you can use them in a process validation, for example.
This validation is integral in assuring that products meet the stringent safety standards required for clinical use. Case studies, like SCHOTT Pharma's independent laboratory practices, emphasize the use of ISO 17025 accreditation and FDA registration in the E&L analysis of extractables and leachables medical devices.
Their laboratory employs multiple analytical techniques to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, including USP <1663>, USP <1664>, and ICH Q3D, focusing on detailed methodologies that analyze extractables and leachables medical devices alongside various packaging materials. Such thorough evaluation not only strengthens patient safety but also enhances the trustworthiness of health equipment in the marketplace. Furthermore, with the recent focus on allogeneic therapies and CRISPR Therapeutics, the changing environment of healthcare tools requires ongoing improvements in safety considerations, further highlighting the essential nature of extractables and leachables medical devices evaluation.
Regulatory Guidelines for Extractables and Leachables Testing
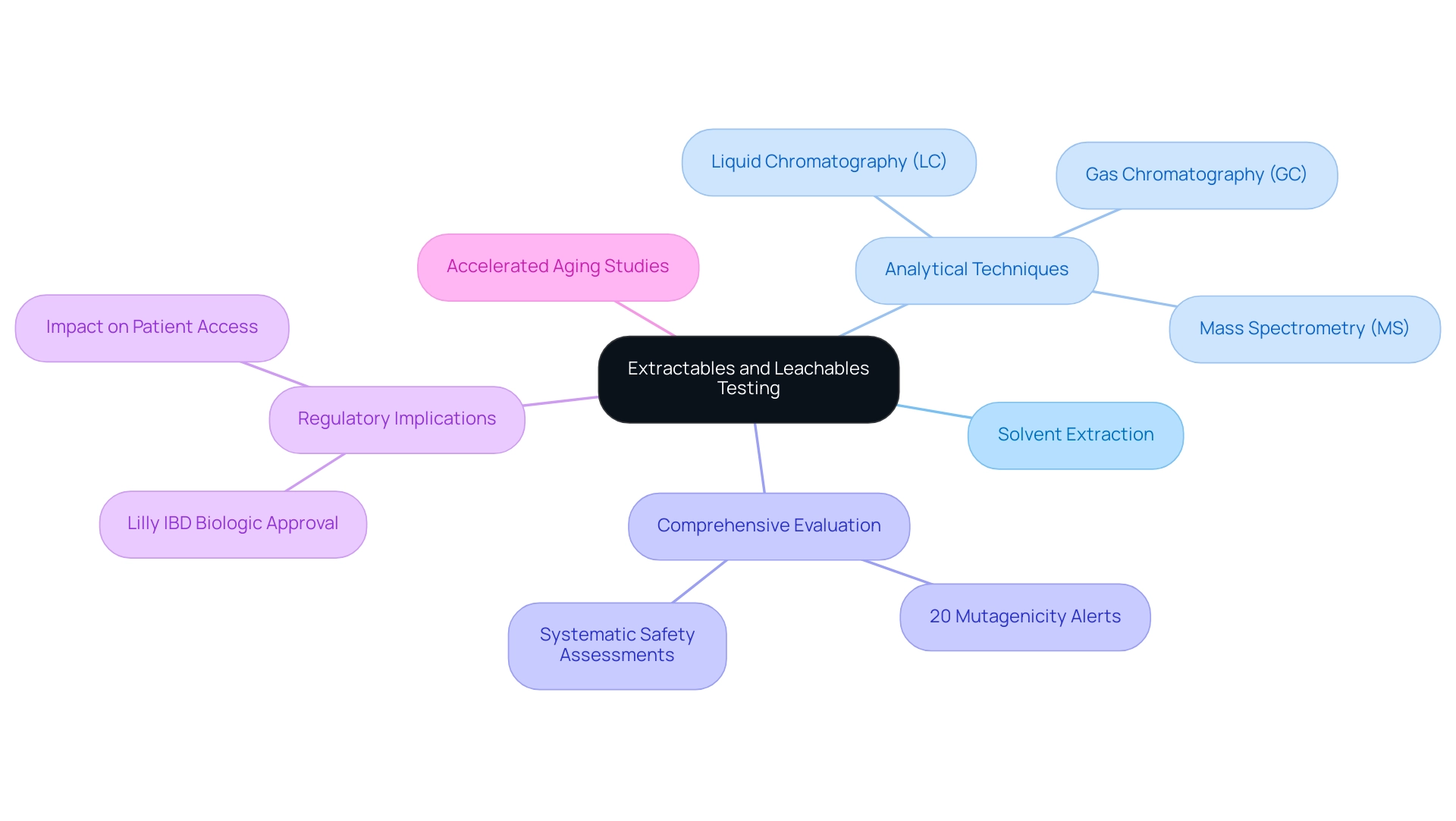
Regulatory guidelines for testing extractables and leachables vary by region and type of medical equipment, with ISO 10993-1 and ISO 10993-18 being the most commonly cited standards. ISO 10993-1 outlines critical requirements for biological evaluation, while ISO 10993-18 emphasizes the characterization of materials utilized in instruments. As noted by Clemens Guenther, Former Senior Expert Nonclinical Safety at Bayer AG, 'Compliance with these standards is crucial for ensuring product safety and efficacy in the market.'
The FDA further supplements these standards with specific guidance documents that delineate testing expectations across various classifications of equipment. Notably, professionals like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, and Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, emphasize the importance of these regulations in ensuring compliance for medical devices in Colombia. With her extensive background in biomedical engineering and regulatory consulting, Ana offers valuable insights into navigating the complexities of these standards.
Furthermore, the recent case study on Raman Spectroscopy as a substitute for conventional analytics demonstrates innovative methods in E&L studies, highlighting how Raman can analyze minute quantities of material without producing waste. Adhering to these established guidelines is imperative not only for achieving regulatory approval but also for fostering trust among healthcare professionals and patients alike. It is essential for manufacturers to remain vigilant and informed about ongoing updates to these regulations, particularly with the latest compliance statistics indicating a growing emphasis on ISO 10993-1 and ISO 10993-18 adherence to ensure that their products consistently align with the latest safety standards.

Common Methods for Extractables and Leachables Testing
A variety of common methods are employed for evaluating extractables and leachables, with solvent extraction standing out as a primary technique. This method entails exposing materials to specific solvents to identify potential leachables that could pose risks to safety or efficacy. In addition to solvent extraction, several analytical techniques are integral to this process, including:
- Gas chromatography (GC)
- Liquid chromatography (LC)
- Mass spectrometry (MS)
Significantly, approximately 20% of the extractables activated either an in vitro or in silico alert for mutagenicity, emphasizing the necessity of comprehensive evaluation. The choice of solvents is essential and frequently relies on the type of material and its intended use in medical tools. Furthermore, manufacturers are increasingly utilizing accelerated aging studies to simulate the long-term use of devices, thereby enhancing the reliability and relevance of their evaluation outcomes.
A systematic approach has been developed to assess the safety impact of extractables associated with pharmaceutical packaging materials, ensuring comprehensive evaluations. As noted by Ying Gao in the Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology:
Single-use technology has been adopted widely in bioprocess development and biopharmaceutical manufacturing in recent years.
This reflects the need for strong evaluation methodologies that can keep pace with innovation.
Furthermore, the recent broadened authorization of Lilly's biologic for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) highlights the real-world implications of extractables analysis in regulatory contexts, enhancing patient access to effective therapies. Comprehending these methodologies enables researchers and manufacturers to select the most appropriate approaches for their specific products, ensuring thorough evaluations that meet regulatory expectations.
Challenges in Extractables and Leachables Testing
Evaluating for extractables and leachables (E&L) in medical equipment presents considerable difficulties arising from the varied materials used in their manufacturing and the intrinsic intricacy of assessment methods. Recent advancements have underscored the importance of employing sensitive analytical equipment to accurately detect low-level contaminants that can complicate the identification process. In light of this, a systematic approach is imperative.
This involves:
- Meticulous material characterization
- Identifying, quantifying, and minimizing impurities from E&L
- Validation of assessment methods to enhance [reliability
PCA results](https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01208) indicate that three principal components represent 94.8% of the observed variance in the sample set, highlighting the complexity of analyzing various materials. Diane Paskiet, Chair of the Product Quality Research Institute (PQRI) L&E Working Group, noted,
If organic chemicals are above the AET, these must be identified and assessed for safety; however, certain compounds of concern that would be lower than the AET may need to be specifically targeted.
Collaborating with experienced laboratories can significantly bolster the accuracy of results while ensuring compliance with regulatory expectations. Moreover, creating strong evaluation procedures customized for particular equipment is essential for reducing risks and guaranteeing safety. Case studies, like the creation of Quantitative Structure Toxicity Relationships (QSTR) for phenols, demonstrate how predictive models can assist in assessing the safety of materials and tackle the challenges of E&L evaluation, thereby improving the overall efficiency of E&L evaluation.
As the terrain of healthcare tools changes, tackling these challenges through creative evaluation methods will be essential for enhancing product safety and effectiveness.
Future Trends in Extractables and Leachables Testing
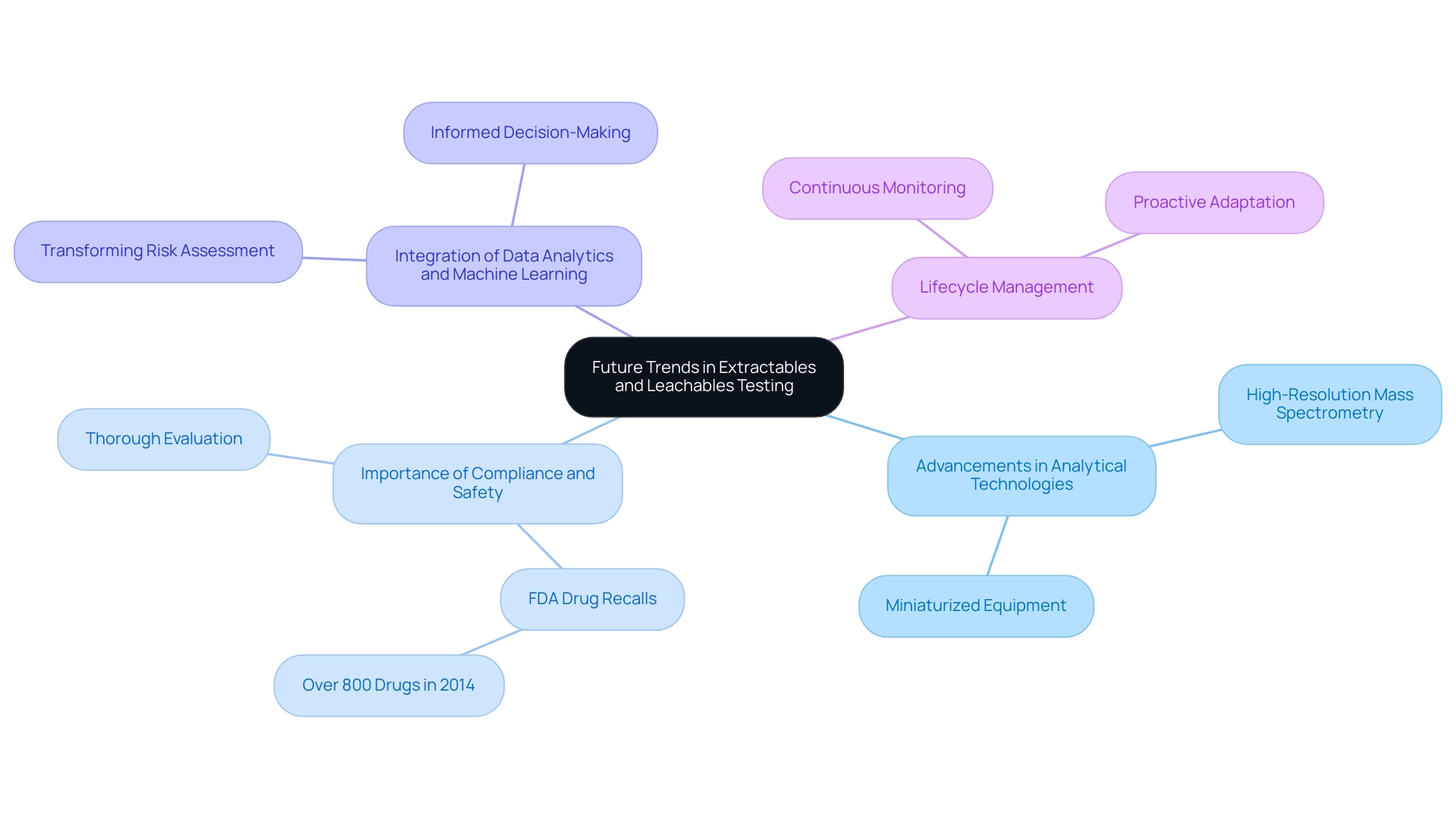
The medical device sector is experiencing considerable change, and various key trends are influencing the future of extractables and leachables medical devices evaluation. Notable advancements in analytical technologies, including high-resolution mass spectrometry and miniaturized equipment, are significantly enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of evaluation methods. These innovations allow for more accurate identification of potential contaminants, which is essential for safety.
In fact, the FDA recalled over 800 drugs in 2014, underscoring the importance of thorough evaluation and compliance in the medical device industry. Furthermore, the integration of data analytics and machine learning is poised to transform risk assessment processes, enabling more robust and informed decision-making concerning safety and compliance. As stated by ORACLE,
'MarkWide Research is a trusted partner that provides us with the market insights we need to make informed decisions.
Their reports are thorough, accurate, and delivered on time.'
This highlights the significance of reliable market insights in the context of extractables and leachables medical devices testing. Regulatory agencies are increasingly concentrating on lifecycle management, emphasizing the necessity for continuous monitoring of extractables and leachables medical devices throughout an item's lifecycle.
This shift emphasizes that manufacturers must remain proactive in adapting to these evolving trends to ensure compliance and maintain the highest standards of product safety, especially as the regulatory landscape continues to evolve. Client testimonials from companies like IBM, Microsoft, KPMG, INTEL, and ORACLE further demonstrate the reliability and quality of advancements in analytical technologies, reinforcing the practical implications of these innovations.
Conclusion
Understanding extractables and leachables (E&L) is critical for ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices. The distinctions between extractables and leachables highlight the complexities involved in evaluating materials used in medical devices, emphasizing the necessity for rigorous testing protocols. Comprehensive testing not only adheres to stringent regulatory guidelines, such as those established by ISO and the FDA, but also protects patient health by identifying potentially harmful substances.
As the industry progresses, the importance of advanced analytical methodologies cannot be overstated. Techniques such as gas chromatography and mass spectrometry are pivotal in detecting low-level contaminants, while emerging technologies promise to enhance sensitivity and accuracy in testing. The integration of data analytics and machine learning is set to refine risk assessments, facilitating more informed decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Addressing the challenges associated with E&L testing is essential for manufacturers aiming to uphold product integrity and patient safety. By adopting innovative testing approaches and maintaining vigilance regarding regulatory updates, stakeholders can navigate the evolving landscape of medical device safety. Ultimately, a proactive stance in E&L management will not only foster trust among healthcare professionals and patients but will also contribute to the advancement of safer and more effective medical devices in the marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are extractables and leachables in medical devices?
Extractables are compounds that can be identified and quantified during controlled laboratory testing, while leachables are compounds that can migrate into a product under typical usage conditions. Both can pose risks to patient safety and the integrity of healthcare instruments.
Why is testing for extractables and leachables important in the medical sector?
Testing ensures adherence to regulatory standards, protects patient health, and maintains the integrity of medical devices. It helps identify potentially harmful substances that could lead to toxicity, allergic reactions, or device failure.
What regulatory organizations oversee the assessment of extractables and leachables?
Regulatory organizations such as the FDA and ISO have established stringent guidelines to assess extractables and leachables in medical devices.
How can the manufacturing process affect extractables and leachables?
The manufacturing process, such as the nozzle temperature during production, can influence the release of extractables and leachables. For example, a recorded nozzle temperature of 270 °C for a polycarbonate item can impact the compounds released.
What methodologies are used in the evaluation of extractables and leachables?
Various methodologies, including solvent extraction, gas chromatography, and mass spectrometry, are employed to rigorously test for extractables and leachables in medical devices.
What recent developments are influencing the market for extractables and leachables testing services?
Recent mergers and acquisitions among key companies in the U.S. and Europe indicate substantial growth in the market for extractables and leachables testing services, highlighting the importance of compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
How do case studies contribute to understanding the impact of extractables and leachables?
Case studies, such as those conducted by SCHOTT Pharma, demonstrate the use of ISO 17025 accreditation and FDA registration in E&L analysis, emphasizing the significance of thorough evaluations to ensure safety and compliance.
What is the significance of ongoing research and compliance in extractables and leachables testing?
Continuous research and compliance with the latest FDA guidelines are crucial for managing extractables and leachables in healthcare products, especially with the evolving landscape of allogeneic therapies and CRISPR Therapeutics.




