Introduction
In the intricate landscape of medical device regulation, understanding the pathways to FDA approval is essential for manufacturers aiming to ensure safety and efficacy in their products. The FDA categorizes medical devices into three classes based on risk, each with distinct regulatory requirements that dictate the approval process.
From the minimal oversight of Class I devices to the rigorous scrutiny faced by Class III devices, the journey through regulatory compliance is fraught with challenges and nuances. As technological advancements continue to reshape the industry, navigating these regulatory frameworks becomes increasingly complex.
This article delves into the classifications, approval processes, and post-approval compliance necessary for medical devices, while also exploring emerging trends that influence the regulatory environment. By equipping stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of these critical aspects, the aim is to facilitate a smoother path toward successful market entry and ongoing device safety.
Understanding FDA Approval: Classifications and Regulatory Pathways
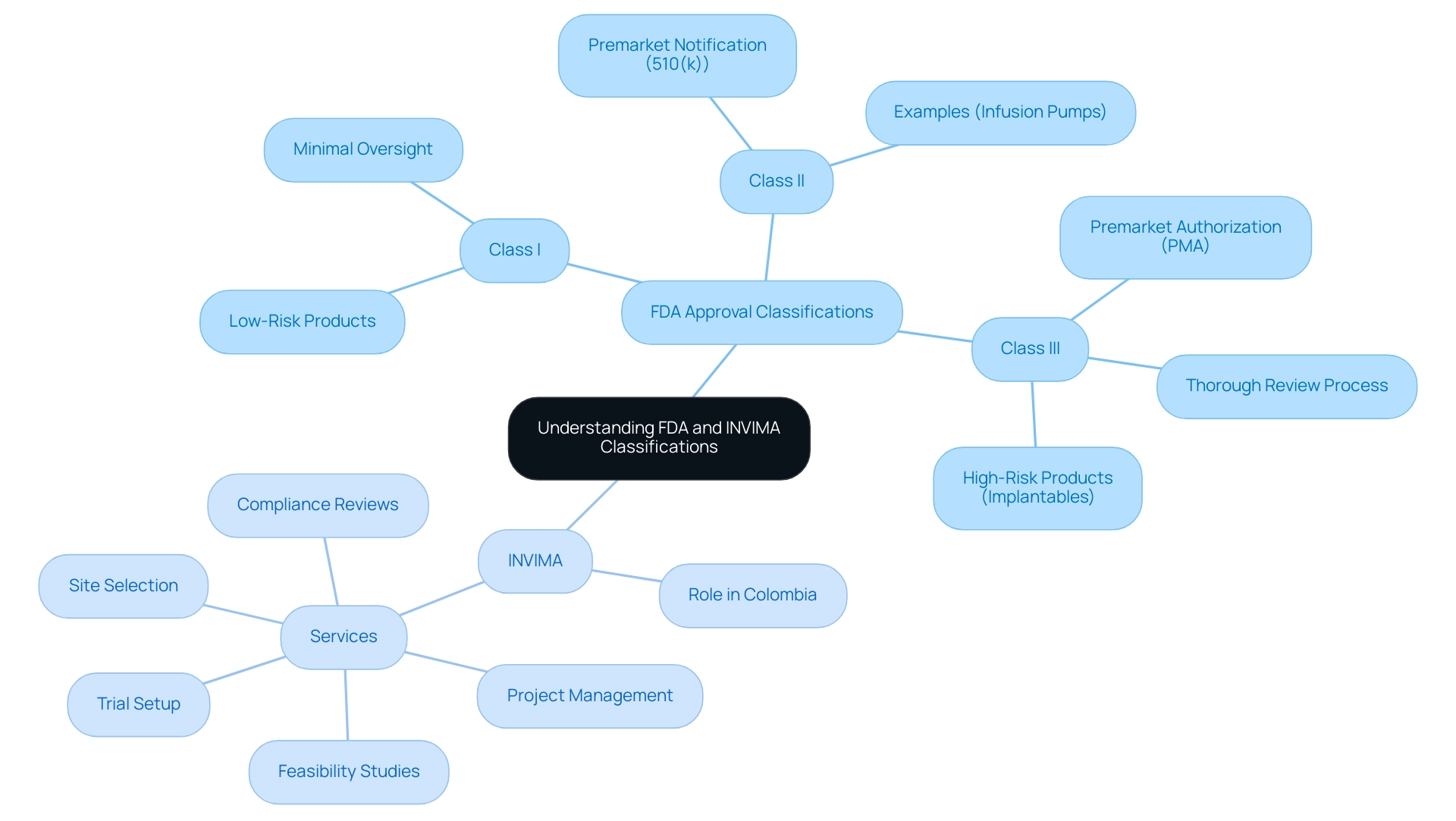
The FDA categorizes medical instruments into three distinct classifications—Class I, Class II, and Class III—based on the associated risk levels of their use. Class I items, which include low-risk products such as bandages, are subject to minimal regulatory oversight. In contrast, Class II products, such as infusion pumps, necessitate a premarket notification (510(k)) to demonstrate their substantial equivalence to existing items already on the market.
Class III products represent the highest risk category and include implantable items like pacemakers; these necessitate premarket authorization (PMA), which involves a thorough and rigorous review process. In Colombia, the INVIMA (Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos) plays a crucial role similar to that of the FDA, overseeing the marketing and manufacturing of health products, and ensuring compliance with safety and efficacy standards. As a Level 4 health authority acknowledged by PAHO/WHO, INVIMA grants medical authorization for the import and export of products, including medical equipment.
INVIMA also offers essential services related to clinical trial management, including:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Project management
Recent statistics indicate that the FDA has classified over 20,000 medical instruments across these categories as of 2024, reflecting the growing complexity of the market. Furthermore, a case study emphasizes the prolonged wait times for De Novo and Panel Track processes, with De Novo wait times escalating to 420 days and Panel Track wait times to 289.62 days in the first half of 2024.
This highlights ongoing challenges in the validation process for Class III devices. For producers, understanding these classifications is vital not only for choosing the suitable compliance route but also for ensuring adherence to FDA standards through the use of FDA approved materials for medical devices, ultimately enabling a more efficient validation process. As noted by Katie Hobbins, Managing Editor at MD+DI, 'Understanding the nuances of FDA classifications is essential for navigating the regulatory landscape effectively.'
For those operating in Colombia, understanding INVIMA's comprehensive processes for feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, and trial setup is equally critical to ensure successful market entry.
Navigating the FDA Approval Process for Medical Devices
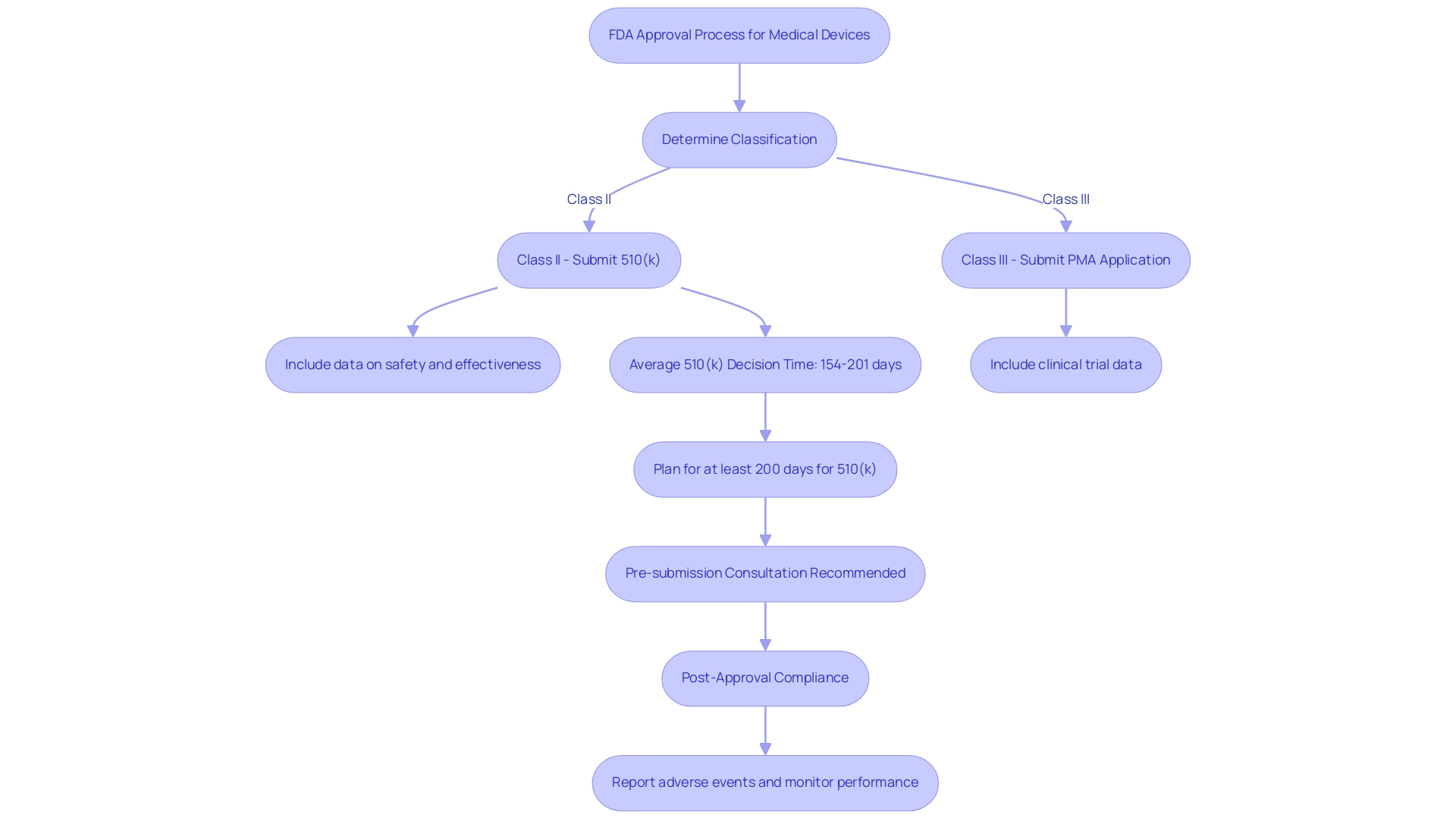
Navigating the FDA approval process begins with determining the classification of the medical product, particularly when considering FDA approved materials for medical devices. For Class II products, manufacturers are required to submit a premarket notification known as a 510(k), which demonstrates substantial equivalence to an already marketed item. This submission must include comprehensive data on the equipment's safety and effectiveness concerning FDA approved materials for medical devices.
In contrast, Class III devices require a premarket authorization (PMA) application, which must include clinical trial data to support safety and efficacy claims. The FDA meticulously reviews these applications to ensure that they involve FDA approved materials for medical devices and adhere to established safety and efficacy standards. Recent insights indicate that the average time to receive a 510(k) decision for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) products varies significantly, ranging from 154 days for Quality Management Framework (QFM) submissions to 201 days for Quality Improvement Health (QIH) submissions.
This extended timeline underscores the importance of preparing for potential requests for additional information, which can pause the 90-day countdown. Manufacturers should thus plan for at least 200 days for their 510(k) submissions, particularly if they involve FDA approved materials for medical devices linked to investment milestones or commercial agreements. Additionally, a formal pre-submission consultation is advised to prevent Not Substantially Equivalent (NSE) situations, which can postpone the endorsement process.
Dr. Hugh Harvey notes that the slowest 510(k) submission was from BrainLab, taking 287 days for their BOLD MRI Mapping tool. Furthermore, recent news emphasizes that Panel Track wait times have risen from an average of 285.80 days in 2023 to 289.62 days in 2024, reflecting the changing landscape of FDA authorization timelines. Proactive engagement through pre-submission consultations is thus crucial for manufacturers to streamline the process.
Once devices are approved, manufacturers must also be vigilant about post-approval compliance, which involves reporting any adverse events and monitoring device performance, particularly when using FDA approved materials for medical devices, as this is an essential aspect of maintaining compliance with regulations. Leveraging the comprehensive clinical trial management services offered by bioaccess®, including:
- Early-Feasibility Studies
- First-In-Human Studies
- Pilot Studies
- Pivotal Studies
- Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies
can greatly enhance the efficiency and success of navigating the FDA approval process. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® provides the expertise and customized approach needed to ensure a smooth journey through regulatory requirements.
FDA-Cleared vs. FDA-Approved: Key Differences Explained
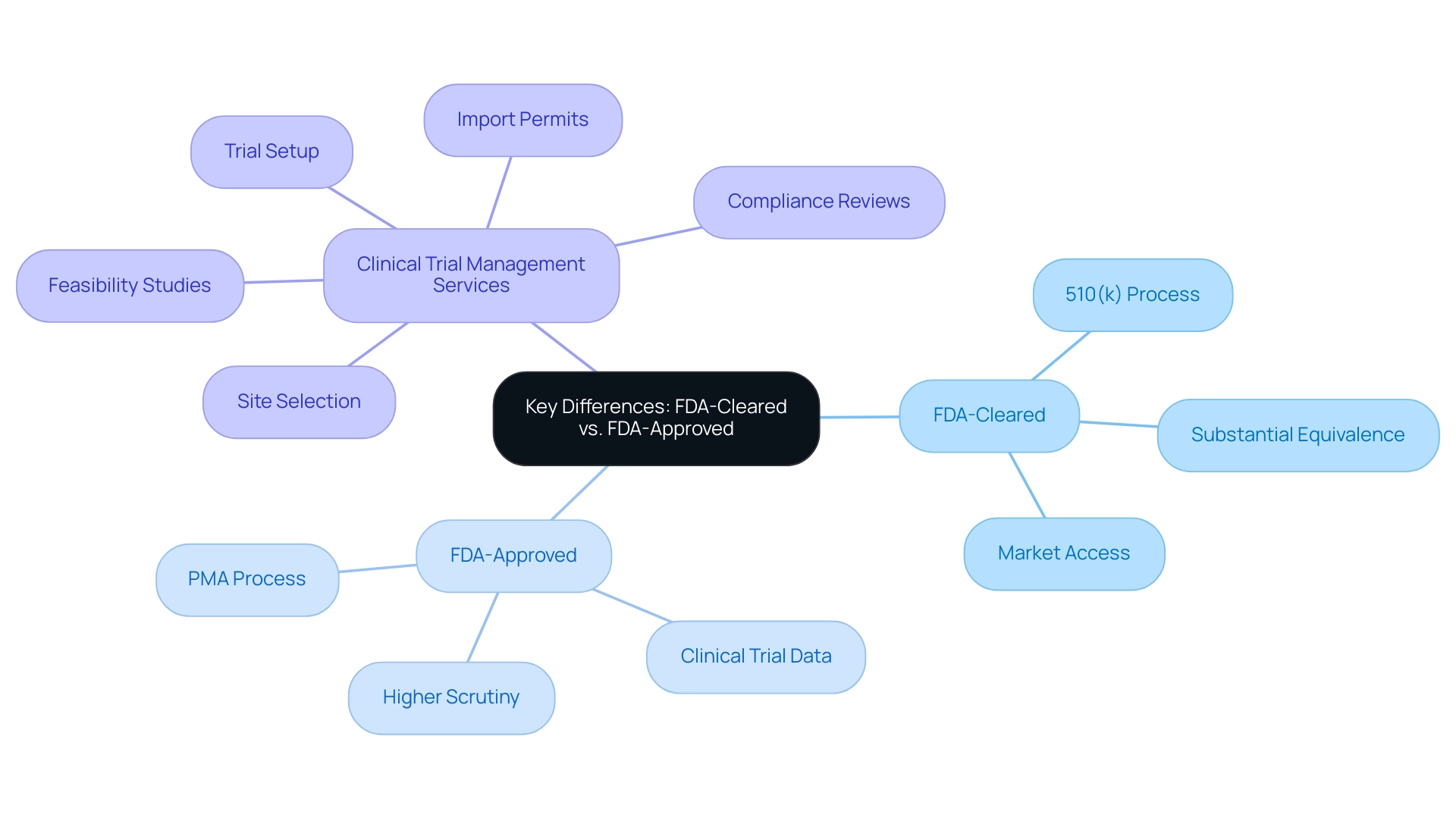
FDA-cleared products have successfully navigated the 510(k) process, demonstrating substantial equivalence to existing items on the market. This pathway verifies that the apparatus is safe and effective for its intended use, allowing for quicker market access. In contrast, FDA-approved products undergo a more stringent evaluation through the Pre-Market Approval (PMA) process, which requires comprehensive clinical trial data to substantiate their safety and efficacy.
This rigorous review leads to formal endorsement, indicating a higher level of scrutiny. Stakeholders must recognize the critical differences between these two pathways, as they significantly impact marketing and product discussions. A notable example is the recent approval of the Annalise Enterprise CXR Triage Trauma system on 03/28/2023, highlighting the importance of thorough evaluation in enhancing trauma diagnostics.
Moreover, with the expertise of Katherine Ruiz, who specializes in Regulatory Affairs for medical products and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, we navigate the complexities of these regulations. Our comprehensive clinical trial management services include:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
ensuring that all aspects of the study are meticulously managed. Additionally, we offer project management and reporting on study status, inventory, and serious and non-serious adverse events, which are essential for maintaining compliance in the medical equipment industry.
As researcher Chouffani El Fassi articulates, 'You learned something new; you saw how that tool actually functions in real life.' We see that as the most valuable kind of data. This insight highlights the practical implications of understanding these distinctions, which are essential for navigating regulatory landscapes and ensuring compliance in the medical equipment industry, particularly in the context of accelerated clinical study services offered by bioaccess® across Latin America.
Post-Approval Compliance: Ensuring Ongoing Safety and Efficacy
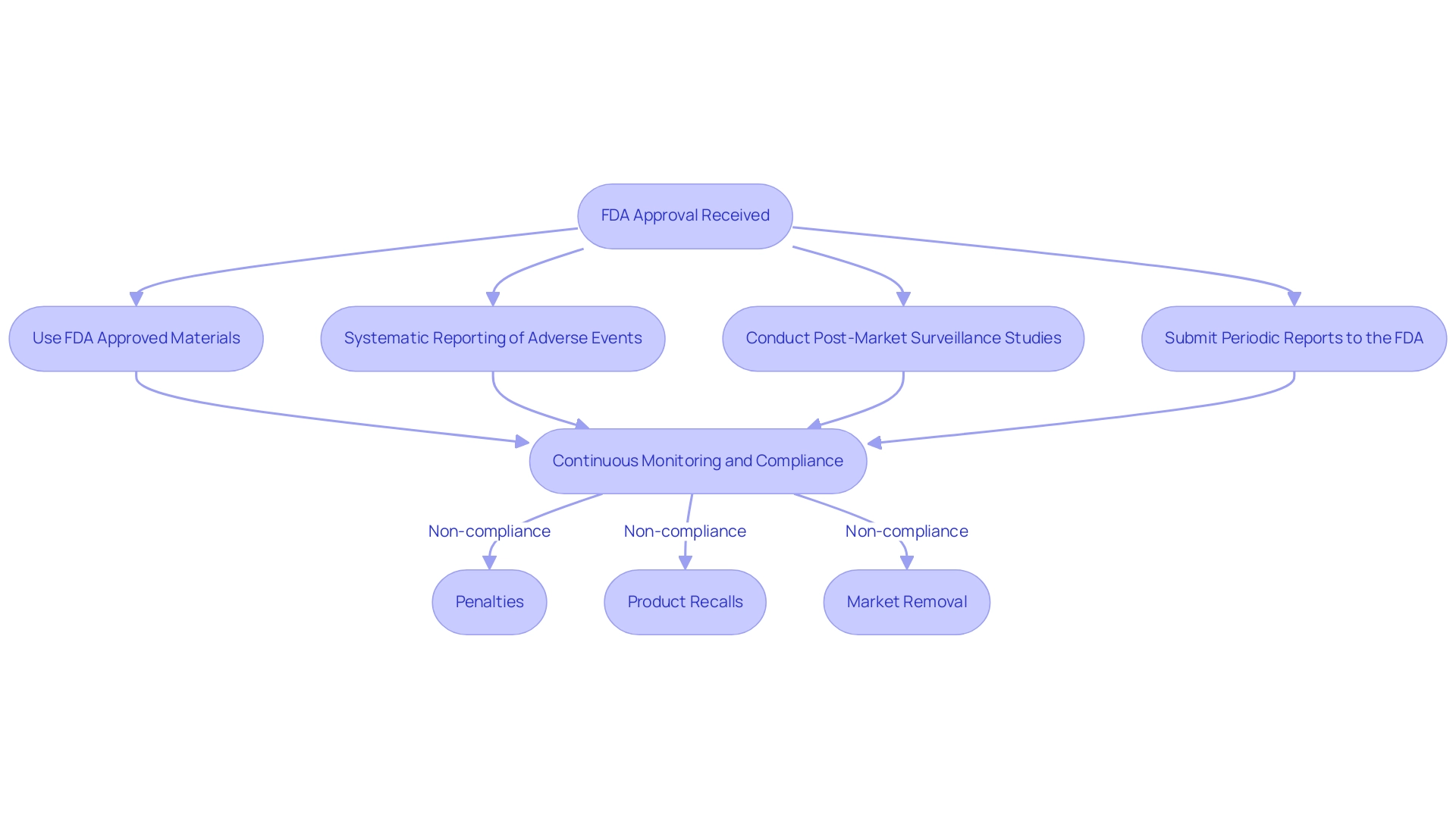
Upon receiving FDA approval, manufacturers must ensure they use FDA approved materials for medical devices while adhering to rigorous ongoing regulations to guarantee the continued safety and efficacy of their medical products. This entails a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Systematic reporting of adverse events
- Conducting post-market surveillance studies
- Submitting periodic reports to the FDA
A robust monitoring system is essential for tracking performance and promptly addressing any safety concerns that arise.
Notably, our service capabilities encompass:
- Feasibility studies
- Selection of research sites
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting on study status and adverse events to ensure that all requirements are met efficiently
Recent statistics indicate that a significant number of adverse event reports are submitted to the FDA annually, with 104 complaints designated as potentially serious injuries or deaths; however, only 49% of these high-risk complaints were escalated for further investigation. This low escalation rate underscores the necessity for manufacturers to maintain vigilance in compliance efforts to prevent potential safety issues from going unaddressed.
Non-compliance with regulations concerning FDA approved materials for medical devices can lead to severe repercussions, including:
- Penalties
- Product recalls
- The outright removal of the item from the market
Therefore, it is imperative for manufacturers to prioritize ongoing compliance to safeguard public health and maintain their market standing. As Dr. Van Norman points out, 'Continuous oversight is crucial to ensuring that the products remain safe and effective after they hit the market.'
Furthermore, the importance of diverse stakeholder input, as highlighted by the mixed methods approach to stakeholder recruitment, emphasizes the need for comprehensive perspectives in compliance discussions. In this context, Katherine Ruiz's knowledge in compliance matters for medical products and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia further illustrates the advantages of informed supervision. The centralized approach of the FDA provides benefits in handling these compliance requirements efficiently, highlighting the difficulties encountered by decentralized systems in other areas.
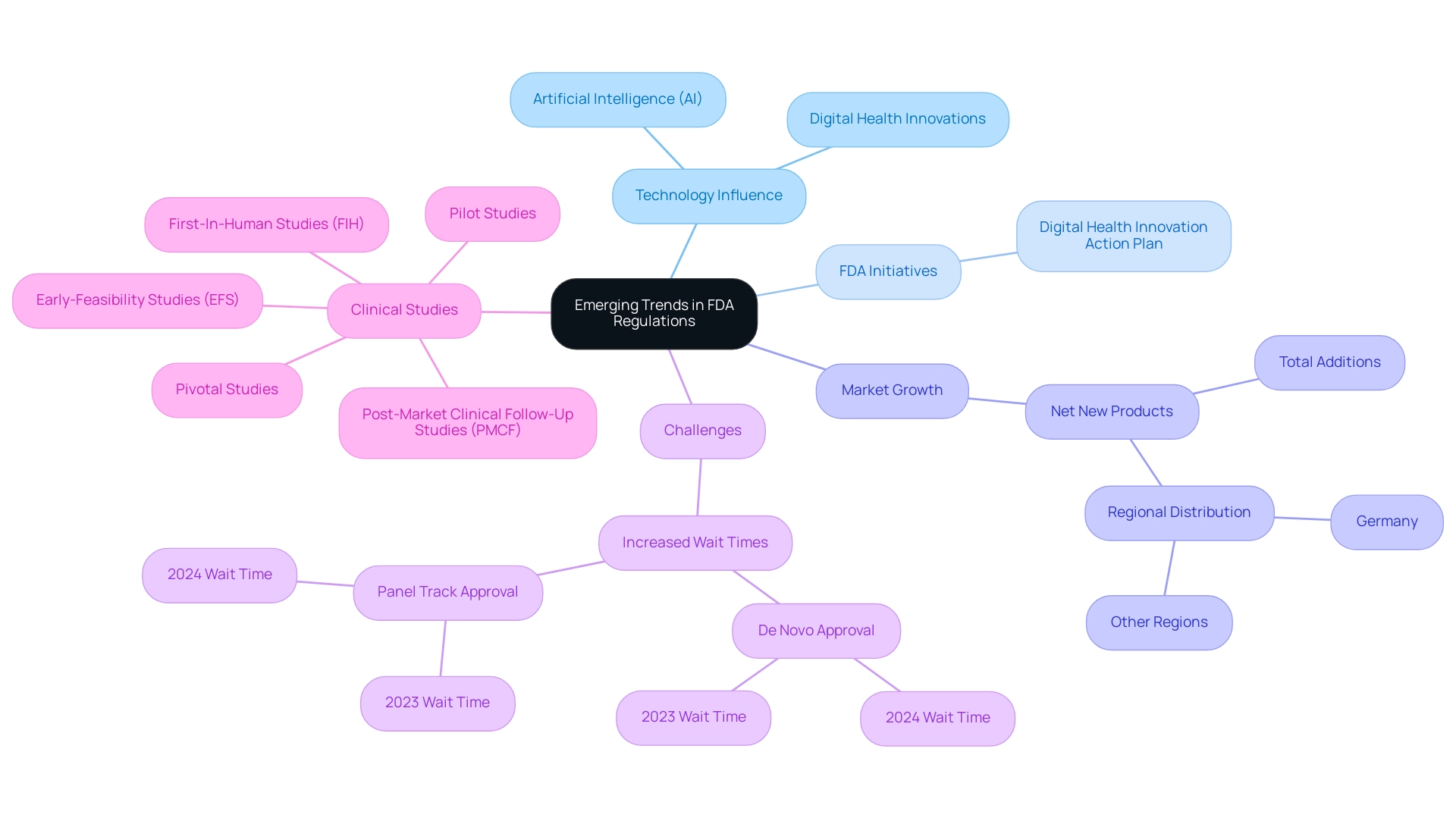
Emerging Trends in FDA Regulations: The Role of Technology and Innovation
Recent advancements in technology, especially in artificial intelligence (AI) and digital health, are significantly influencing the use of FDA approved materials for medical devices in FDA regulations for medical products. In reaction to this swift rate of innovation, the FDA is modifying its regulatory structures to simplify authorization procedures for different types of equipment. A notable initiative is the FDA's Digital Health Innovation Action Plan, designed to promote the development of software-based medical devices while ensuring their safety and effectiveness.
Since May 2021, the digital therapeutic market has seen 87 net new product additions, with 46 in Germany and 41 in other regions, underscoring the growth and importance of digital health innovations. Despite this progress, challenges persist; for example, De Novo approval wait times have increased slightly from 415 days in 2023 to 420 days in 2024, while Panel Track wait times rose from 285.80 days to 289.62 days. These figures illustrate the ongoing hurdles within the oversight landscape.
As these technological advancements continue to evolve, it is essential for manufacturers, like those advised by experts such as Ana Criado and Katherine Ruiz, to stay informed about emerging trends and compliance adaptations. Katherine Ruiz's expertise in compliance affairs for medical devices further complements the insights provided by Ana. According to Iseult McMahon, an analyst at BTIG, 'We think that this is a directional positive for the broader medical technology space as it provides both improving certainty to companies (and investors) as well as reduces cash burn during the interim period when a company is awaiting a decision.'
By utilizing new compliance pathways and enhancing their innovation strategies in product development with FDA approved materials for medical devices, manufacturers can strategically position themselves within the dynamic healthcare landscape. Additionally, bioaccess® specializes in managing various clinical studies, including:
- Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS)
- First-In-Human Studies (FIH)
- Pilot Studies
- Pivotal Studies
- Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF)
These studies are crucial for navigating the complexities of regulatory approval.
Conclusion
Understanding the regulatory pathways to FDA approval is paramount for medical device manufacturers striving to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products. The classification of devices into Class I, Class II, and Class III highlights the varying levels of risk and the corresponding regulatory requirements that must be met. Each class presents unique challenges, particularly for Class III devices, which require rigorous premarket approval processes. The statistics indicating increased wait times for approvals reflect the complexities manufacturers face in an evolving regulatory landscape.
Furthermore, the distinction between FDA-cleared and FDA-approved devices underscores the importance of navigating these pathways effectively. While FDA-cleared devices benefit from a streamlined process, FDA-approved devices undergo more comprehensive scrutiny, necessitating a thorough understanding of the regulatory framework. This knowledge is crucial not only for achieving market entry but also for maintaining compliance post-approval, where ongoing monitoring and reporting are vital to ensuring device safety.
Emerging trends in technology, particularly in digital health and artificial intelligence, are reshaping the regulatory environment. As the FDA adapts its frameworks to accommodate these innovations, manufacturers must remain vigilant and informed to leverage new opportunities while navigating potential challenges. The role of expertise in regulatory affairs cannot be understated, as it provides invaluable guidance in managing compliance and facilitating smoother approval processes.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of FDA classifications, approval processes, and post-approval compliance is essential for medical device manufacturers. By staying informed about regulatory changes and leveraging expert insights, stakeholders can better navigate the complexities of the medical device landscape, ultimately contributing to the safety and efficacy of innovative healthcare solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the classifications of medical instruments according to the FDA?
The FDA categorizes medical instruments into three classifications: Class I, Class II, and Class III, based on the associated risk levels of their use.
What is the regulatory oversight for Class I medical devices?
Class I items, which include low-risk products such as bandages, are subject to minimal regulatory oversight.
What requirements must Class II medical devices meet?
Class II products, such as infusion pumps, require a premarket notification (510(k)) to demonstrate their substantial equivalence to existing items already on the market.
What distinguishes Class III medical devices from the other classes?
Class III products represent the highest risk category and include implantable items like pacemakers; they require premarket authorization (PMA), which involves a thorough review process.
What role does INVIMA play in Colombia regarding medical products?
INVIMA (Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos) oversees the marketing and manufacturing of health products in Colombia, ensuring compliance with safety and efficacy standards.
What services does INVIMA provide related to clinical trials?
INVIMA offers services such as feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, and project management for clinical trials.
How many medical instruments has the FDA classified as of 2024?
As of 2024, the FDA has classified over 20,000 medical instruments across the three categories.
What are the wait times for De Novo and Panel Track processes?
De Novo wait times have escalated to 420 days, while Panel Track wait times have reached 289.62 days in the first half of 2024.
Why is understanding FDA classifications important for producers?
Understanding these classifications is vital for choosing the suitable compliance route and ensuring adherence to FDA standards, which facilitates a more efficient validation process.
What insights are provided about the FDA approval process for Class II and Class III devices?
Class II devices require a 510(k) submission demonstrating substantial equivalence, while Class III devices require a PMA application that includes clinical trial data to support safety and efficacy claims.
How long does it typically take to receive a 510(k) decision for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) products?
The average time varies significantly, ranging from 154 days for Quality Management Framework (QFM) submissions to 201 days for Quality Improvement Health (QIH) submissions.
What is advised to prevent delays in the 510(k) submission process?
A formal pre-submission consultation is recommended to avoid Not Substantially Equivalent (NSE) situations, which can delay the endorsement process.
What must manufacturers monitor after device approval?
Manufacturers must report any adverse events and monitor device performance, particularly when using FDA approved materials for medical devices, to maintain compliance with regulations.
What services does bioaccess® provide to assist in the FDA approval process?
Bioaccess® offers clinical trial management services, including early-feasibility studies, first-in-human studies, pilot studies, pivotal studies, and post-market clinical follow-up studies.




