Introduction
Navigating the intricate landscape of medical device regulation is crucial for the success of clinical trials under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). As the industry grapples with a complex web of compliance requirements, particularly for startups facing unique challenges, understanding the nuances of these regulations becomes paramount.
This article delves into essential strategies for ensuring compliance, effective data management, and ethical oversight throughout the lifecycle of MDR clinical trials. By addressing key considerations such as:
- Informed consent
- Ongoing monitoring
- Adaptive marketing strategies
medical professionals can enhance their trial outcomes and maintain a competitive edge in the evolving healthcare landscape.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Frameworks in MDR Clinical Trials
MDR clinical trials are subject to a multifaceted regulatory landscape, primarily governed by the Medical Device Regulation (EU) 2017/745, alongside various national laws that can influence the execution of these studies. Navigating these regulations is imperative for ensuring compliance and achieving successful outcomes, particularly for medical device startups facing unique challenges such as regulatory hurdles, competition, recruitment issues, and financial constraints. Key considerations include:
- Understanding MDR Requirements: Familiarizing yourself with the specific stipulations detailed in the MDR, including aspects such as risk classification and clinical evaluation processes, is fundamental to the study's design and execution.
- Navigating National Regulations: Each EU member state may impose additional regulations that can influence how experiments are conducted. Understanding these local nuances is crucial for seamless implementation and compliance in MDR clinical trials.
- Engagement with regulatory bodies, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA), is essential for ensuring that your MDR clinical trials align with regulatory expectations and for preemptively addressing any compliance issues.
- Documentation and Reporting: Timeliness and accuracy in documentation and reporting to regulatory bodies cannot be overstated, as these elements are critical for maintaining study integrity and fulfilling compliance obligations.
Alongside these factors, our offerings include feasibility and selection of research locations and principal investigators (PIs), setup, and thorough study project management. In a recent presentation titled Time to Evolve—How to Better Support Medical Device Study Builds, Execution, and Data Acquisition, Walker Bradham emphasized the challenges faced in medical device research, advocating for solutions that enhance efficiency and adaptability in operational processes. The conversation emphasized Zelta’s research platform as a valuable resource to simplify procedures and enhance speed to insights in studies.
Furthermore, the importance of patient information in research studies is highlighted by the MAUDE Patient Information statistics:
- 134032KB compressed
- 1130935KB uncompressed
- A total of 20457749 records
This emphasizes the extent to which patient information can influence clinical research outcomes. Nicole Latimer, CEO of Medrio, stated, "Utilizing patient-reported outcomes in Medical Device Trials can provide invaluable insights that shape your commercialization plans."
This authoritative viewpoint emphasizes the significance of ePRO information in navigating the complexities of MDR clinical trials. Furthermore, it is essential to recognize that the file associated with these data does not comply with accessibility standards, a crucial compliance factor that must be addressed in the context of MDR studies. Integrating these components will enable healthcare professionals, including authorities like Ana Criado and Katherine Ruiz, to manage the intricacies of MDR assessments more efficiently.
For additional help, we invite you to SCHEDULE A MEETING with our team to discuss how we can assist with your research requirements.
The Role of Data Management and Integration in Successful MDR Trials
Successful medical device research (MDR) studies depend on strong information management and integration strategies. At bioaccess®, we specialize in comprehensive clinical study management services, ensuring that every aspect of the study is meticulously handled. Our expertise encompasses a range of studies, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF).
Key considerations include:
- Information Gathering: Implementing standardized methods for information gathering is crucial to ensure consistency and reliability across all trial sites. This not only enhances the integrity of the information but also supports accurate comparisons and analyses. For instance, in the old age subgroup, the response rate for the new therapy is 0.7 compared to 0.35 for the control, underscoring the importance of effective information management in achieving reliable outcomes.
- Integrated Information Systems: Utilizing integrated information management systems streamlines entry, monitoring, and reporting processes. Such systems, as facilitated by bioaccess®, enable the secure movement of over 60 million healthcare records across thousands of organizations, which is essential for successful clinical studies.
- Real-Time Information Access: Ensuring that researchers have access to real-time information is vital for timely decision-making and risk mitigation. This capability allows for immediate responses to emerging issues, thus minimizing disruptions during the test.
- Information Security and Compliance: Establishing stringent protocols for information security is essential for compliance with regulations such as GDPR, which protect patient information. Data security not only protects participant confidentiality but also boosts the credibility of the study results. Dr. John Griffin emphasizes the importance of these practices, stating, "Effective information management strategies are the backbone of successful clinical trials."
- Discrepancy Management: Real-world applications of information management practices are illustrated through case studies, such as the discrepancy management approach where inconsistencies in information are identified and managed through clarification from investigators or self-evident corrections. The CDM team at bioaccess® regularly reviews discrepancies, ensuring resolutions are documented and maintaining the accuracy of the data, although some discrepancies may remain unresolved.
By prioritizing these strategies and leveraging our specialized services, medical professionals can significantly enhance the quality and compliance of their MDR clinical trials. Moreover, the significance of confidence intervals in assessing effect size cannot be overstated, as low p-values alone do not indicate practical relevance. Incorporating these practices establishes the foundation for successful outcomes and guarantees compliance with best practices in research.
Ensuring Compliance with Good Clinical Practice in MDR Trials
Following Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is essential for the successful execution of mdr clinical trials. The following key aspects are essential:
-
Informed Consent: It is essential that all participants provide informed consent, ensuring they fully comprehend the study's nature, associated risks, and potential benefits.
Current statistics indicate that informed consent rates in clinical studies have fluctuated, with recent data showing that only 65% of participants fully understand the consent they provide. This highlights the need for continued focus on effective consent processes.
-
Protocol Compliance: Strict adherence to the study protocol is necessary to maintain the integrity and reproducibility of results.
Variations from the protocol can compromise the validity of the results.
-
Training and Qualification of Staff: All personnel involved in the study must be adequately trained and qualified for their specific roles. Regular staff training is a strategy that upholds compliance and ensures that team members are well-versed in GCP requirements.
-
Monitoring and Auditing: Implementing systematic monitoring and auditing processes is crucial for proactively identifying and addressing compliance issues. Recent news underscores the importance of these practices in maintaining adherence to GCP guidelines.
-
Quality Management Systems: Establishing robust quality management systems is essential for ensuring that all study processes meet regulatory standards and enhance the overall integrity of the research.
-
Fostering a Culture of Compliance: Encouraging a culture of compliance within the research team promotes ethical practices and adherence to GCP, further safeguarding participant rights and data integrity.
-
Experiment Setup and Import Authorizations: Effective experiment setup and obtaining necessary import authorizations are crucial steps that ensure compliance with local regulations and facilitate the smooth conduct of research studies.
-
Reporting: Comprehensive reporting on study status, inventory, and both serious and non-serious adverse events is essential for maintaining transparency and accountability throughout the research process.
By emphasizing these GCP elements in mdr clinical trials, medical professionals can uphold ethical standards and enhance the credibility of their research. Moreover, the extensive research management services we provide, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance evaluations, setup, import permits, project oversight, and reporting, align with the regulatory requirements established by INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute. These principles provide a roadmap for researchers to conduct studies that respect participants and uphold scientific integrity, as noted in the case study titled '5 Essential Ethical Guidelines for Accurate Research in 2024.'
As highlighted by Stocken DD, GCP but not as you know it, this emphasizes the evolving nature of compliance in clinical trials.
Post-Market Surveillance and Ethical Oversight in MDR Clinical Trials
Post-market surveillance is a vital aspect of the device lifecycle, ensuring that safety and effectiveness are maintained long after a product's initial approval. In Colombia, the INVIMA (Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos) plays a crucial role in this process as the national regulatory authority responsible for overseeing health products, including medical devices. Key components of an effective post-market surveillance strategy include:
- Ongoing Monitoring: Developing comprehensive strategies for the continuous assessment of device performance and safety is essential. INVIMA's Directorate for Medical Devices and other Technologies monitors pre- and post-market programs through systematic data collection and analysis to ensure compliance with health standards.
- Adverse Event Reporting: Establishing a robust system for promptly reporting and addressing adverse events to regulatory authorities is crucial. This system not only fulfills regulatory obligations but also demonstrates a manufacturer’s commitment to patient safety. Compliance with regulations, such as those mandated by INVIMA, is necessary for effective monitoring of device performance.
- Ethics Committee Involvement: Engaging with ethics committees during the post-market phase is critical to ensuring that ethical standards are maintained. These committees play an essential role in overseeing the ethical implications of ongoing trials and surveillance efforts.
- Patient Feedback Mechanisms: Creating effective channels for collecting patient feedback enables manufacturers to incorporate real-world experiences into safety evaluations. This patient-centered approach helps inform device improvements and enhances overall safety outcomes.
- Regulatory Compliance Case Study: For instance, a case study titled "Regulatory Compliance in PMS" illustrates how compliance with INVIMA’s regulations is essential for manufacturers to demonstrate their commitment to patient safety and effective monitoring of device performance. This case study highlights specific methodologies employed by INVIMA in monitoring and evaluating health devices post-market.
- Industry Insights: As industry leaders emphasize, a proactive stance on post-market surveillance is fundamental for the future of health devices in the digital health and MedTech sectors. Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs, notes that continuous improvement in these areas is vital for addressing emerging challenges in public health.
These elements together guarantee that healthcare practitioners follow safety regulations and ethical methods during their examinations, ultimately aiding in enhanced public health results. Recent statistics indicate that adverse event reporting rates have significantly increased in 2024, highlighting the growing emphasis on transparency and accountability in post-market surveillance, further supported by INVIMA's classification as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
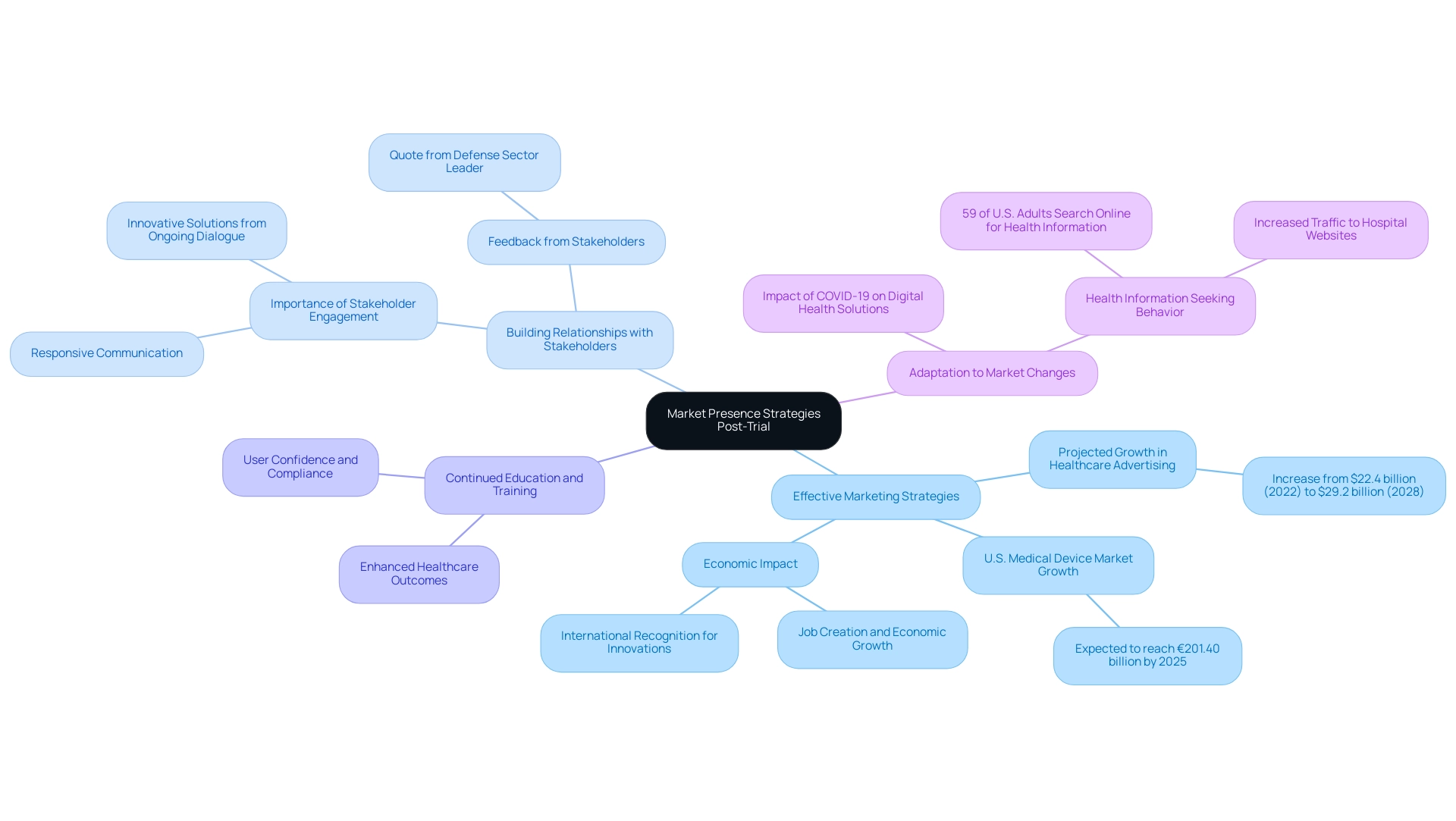
Strategies for Maintaining Market Presence Post-Trial
Following the completion of MDR clinical trials, maintaining a robust market presence for healthcare devices demands a multifaceted strategic approach:
-
Effective Marketing Strategies: It is crucial to develop targeted marketing campaigns that not only highlight the unique benefits and safety of the device but also resonate with potential users. The IMARC Group has projected a significant increase in U.S. healthcare advertising, from $22.4 billion in 2022 to $29.2 billion by 2028, indicating a growing willingness among healthcare companies to invest in effective content and lead generation strategies. Furthermore, the U.S. medical device market is expected to reach €201.40 billion by 2025, presenting a substantial opportunity for growth. Importantly, the ripple effects of Medtech clinical studies extend beyond the companies themselves, contributing to job creation and economic growth in local communities while also enhancing international recognition for the innovations developed.
-
Building Relationships with Stakeholders: Establishing and nurturing strong relationships with key stakeholders—such as healthcare providers, payers, and regulatory bodies—is essential for facilitating market access. As one leader in the defense sector observed,
Thank you for sending the market report and information. It looks quite comprehensive and the data is exactly what I was looking for. I appreciate the timeliness and responsiveness of you and your team.
This feedback underscores the value of responsive stakeholder engagement. Additionally, experts emphasize that ongoing dialogue with stakeholders can lead to innovative solutions and improved market strategies, further enhancing the international collaboration aspect of Medtech initiatives.
-
Continued Education and Training: Providing ongoing education and training for users ensures that they understand the proper use and application of the device. This initiative is critical in enhancing user confidence and compliance, which ultimately contributes to successful adoption and improved healthcare outcomes in the communities served.
-
Adaptation to Market Changes: Staying attuned to industry trends and regulatory requirements is imperative. The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly accelerated the adoption of digital health solutions, emphasizing the need for device companies to adapt their marketing strategies accordingly. For instance, a study conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics revealed that 59% of U.S. adults seek health or wellness information online, emphasizing the importance of a strong online presence. Health-related searches significantly drive traffic to hospital websites, indicating that effective online engagement can enhance market visibility while also promoting healthcare improvement within local economies. By adapting to these changes, companies can not only improve healthcare outcomes but also solidify their position in the international market.
By implementing these strategic considerations, medical professionals can effectively navigate the post-trial landscape, ensuring that their devices remain competitive, compliant, and responsive to market needs, all while contributing positively to the economic fabric of the regions they engage with.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of medical device regulation is essential for the success of clinical trials under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The article outlines several critical strategies that medical professionals and startups must adopt to ensure compliance and enhance trial outcomes. Understanding the specific requirements of the MDR, engaging with regulatory bodies, and maintaining rigorous documentation practices are foundational to successful trial execution.
Moreover, effective data management and integration play a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity and reliability of clinical trials. By implementing standardized data collection methods and utilizing integrated data systems, researchers can foster a robust environment for decision-making and risk management. This is further complemented by a strong commitment to Good Clinical Practice (GCP), which safeguards ethical standards and participant rights throughout the trial lifecycle.
Post-market surveillance and ethical oversight are equally important, as they ensure ongoing compliance and safety of medical devices after approval. The emphasis on continuous monitoring, adverse event reporting, and patient feedback mechanisms reflects a proactive approach to maintaining product efficacy and public trust.
Finally, the strategies discussed for maintaining market presence post-trial highlight the necessity for effective marketing, stakeholder engagement, and adaptability to industry changes. By prioritizing these elements, medical professionals can not only enhance their competitive edge but also contribute positively to the healthcare landscape.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of MDR requirements, coupled with strategic planning and ethical oversight, is vital for the success of clinical trials. Embracing these practices will empower medical professionals to navigate the regulatory landscape effectively, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and sustained market presence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What governs MDR clinical trials?
MDR clinical trials are primarily governed by the Medical Device Regulation (EU) 2017/745, along with various national laws that can influence the execution of these studies.
Why is it important to navigate the regulatory landscape for MDR clinical trials?
Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for ensuring compliance and achieving successful outcomes, especially for medical device startups that face unique challenges such as regulatory hurdles, competition, recruitment issues, and financial constraints.
What are the key considerations for conducting MDR clinical trials?
Key considerations include understanding MDR requirements, navigating national regulations, engaging with regulatory bodies like the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and ensuring timely and accurate documentation and reporting.
How can understanding MDR requirements benefit a clinical trial?
Familiarizing oneself with specific stipulations in the MDR, such as risk classification and clinical evaluation processes, is fundamental to the design and execution of the study.
What role do national regulations play in MDR clinical trials?
Each EU member state may impose additional regulations that influence how experiments are conducted, making it essential to understand these local nuances for seamless implementation and compliance.
Why is engagement with regulatory bodies important?
Engaging with regulatory bodies ensures that MDR clinical trials align with regulatory expectations and helps preemptively address any compliance issues.
What is the significance of documentation and reporting in MDR studies?
Timeliness and accuracy in documentation and reporting are critical for maintaining study integrity and fulfilling compliance obligations with regulatory bodies.
What challenges do medical device researchers face according to recent discussions?
Challenges include regulatory hurdles, competition, recruitment issues, and financial constraints, emphasizing the need for solutions that enhance efficiency and adaptability in operational processes.
How can patient information impact clinical research outcomes?
Patient information, particularly patient-reported outcomes, can provide invaluable insights that shape commercialization plans and influence clinical research outcomes.
What is the importance of information management in MDR clinical trials?
Effective information management is crucial for ensuring consistency, reliability, and compliance with regulations, thereby enhancing the quality of clinical trials.
What strategies can enhance information management in clinical studies?
Key strategies include standardized information gathering, integrated information systems, real-time information access, stringent security protocols, and effective discrepancy management.
How does effective information management contribute to clinical trial success?
It enables timely decision-making, enhances data integrity, and ensures compliance with regulations, ultimately leading to successful outcomes in MDR clinical trials.

