Introduction
In the realm of medical devices, understanding shelf life is paramount to ensuring patient safety and product efficacy. Defined as the period during which a device is expected to function properly when stored under specified conditions, shelf life plays a crucial role in clinical outcomes.
The consequences of using expired devices can be dire, prompting regulatory bodies like INVIMA in Colombia to enforce stringent standards for compliance and oversight. This article explores the intricacies of medical device shelf life, including:
- The relevant ISO standards
- Testing methodologies
- Factors influencing longevity
By delving into these critical components, manufacturers and healthcare providers can better navigate the complexities of product management, ultimately fostering trust and safeguarding patient welfare.
Introduction to Medical Device Shelf Life and Its Importance
The longevity of medical equipment, as defined by medical device shelf life ISO standards, is characterized as the period during which a product is expected to operate safely and efficiently, assuming it is maintained and managed under designated circumstances. This concept is essential; expired equipment poses significant risks to patient safety and can jeopardize the integrity of clinical outcomes. Determining a clearly defined duration for products according to medical device shelf life ISO standards not only assists producers in adhering to safety and quality benchmarks but also enhances confidence among healthcare professionals and patients.
In Colombia, INVIMA (Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos) plays a vital role in ensuring that healthcare instruments comply with these standards as a Level 4 health authority acknowledged by the Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization. INVIMA is responsible for inspecting and supervising the marketing and manufacturing of health products, ensuring compliance with established regulations. A test plan should specify how much data needs to be gathered, including sample size, to ensure precise duration assessment.
Additionally, the case study titled 'Manufacturing Process and Shelf Life Determination' illustrates how the quality of materials and precision in the manufacturing process affect a healthcare product's stability and performance over time. As stated by a prominent specialist from Plastic Ingenuity, 'Our innovative, scalable healthcare solutions enable you to bring drug therapies, healthcare products, and diagnostic items to the market more quickly,' emphasizing the importance of strong durability assessment procedures. This tutorial will explore relevant ISO standards, including the medical device shelf life ISO standards, such as ISO 11607 for packaging, various testing methodologies like accelerated aging tests, and the numerous factors affecting product longevity, aiming to equip readers with a thorough understanding of this vital aspect in healthcare management, guided by regulatory excellence and oversight from authorities like INVIMA.
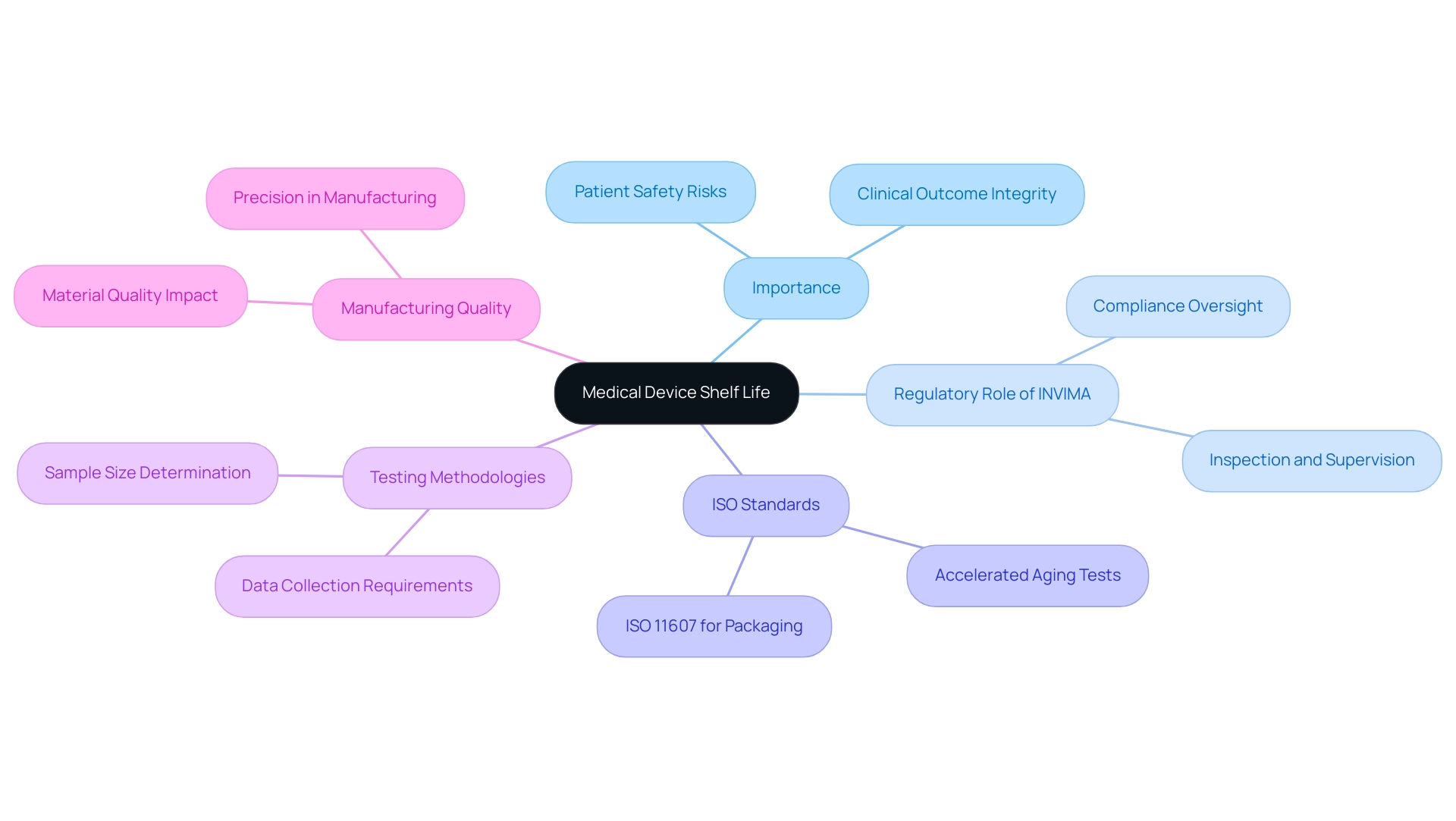
Key ISO Standards Governing Medical Device Shelf Life
Two crucial ISO standards that regulate the medical device shelf life iso standards of healthcare products are ISO 11607 and ISO 13485. ISO 11607 outlines the requirements for packaging used for terminally sterilized healthcare products, ensuring that the packaging preserves the integrity and sterility of the contents throughout their intended lifespan. Simultaneously, ISO 13485 creates a structure for a quality management system, requiring organizations to prove their ability to consistently deliver healthcare products and associated services that meet regulatory and client needs.
Compliance with the medical device shelf life iso standards is crucial, as it confirms the longevity of healthcare products, thereby ensuring their safety and effectiveness during use. Additionally, ISO 15883-2, released in 2006, offers historical background for the development of these standards, while ISO 22442-1 implements risk management principles to healthcare products that use animal tissues, highlighting the significance of thorough compliance. Furthermore, as emphasized in the case study on cybersecurity aspects in health software, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of healthcare instruments extends beyond storage testing to include data integrity and defense against possible cybersecurity risks.
This compliance not only improves patient safety but also strengthens confidence in healthcare technologies, as noted by Medistri, who highlights the significance of medical device shelf life iso standards:
We can help avert any negative health impacts or harm that may arise from the use of outdated instruments through shelf stability testing, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of healthcare tools and, ultimately, maintaining that the quality of these tools remains intact and patients are safeguarded.
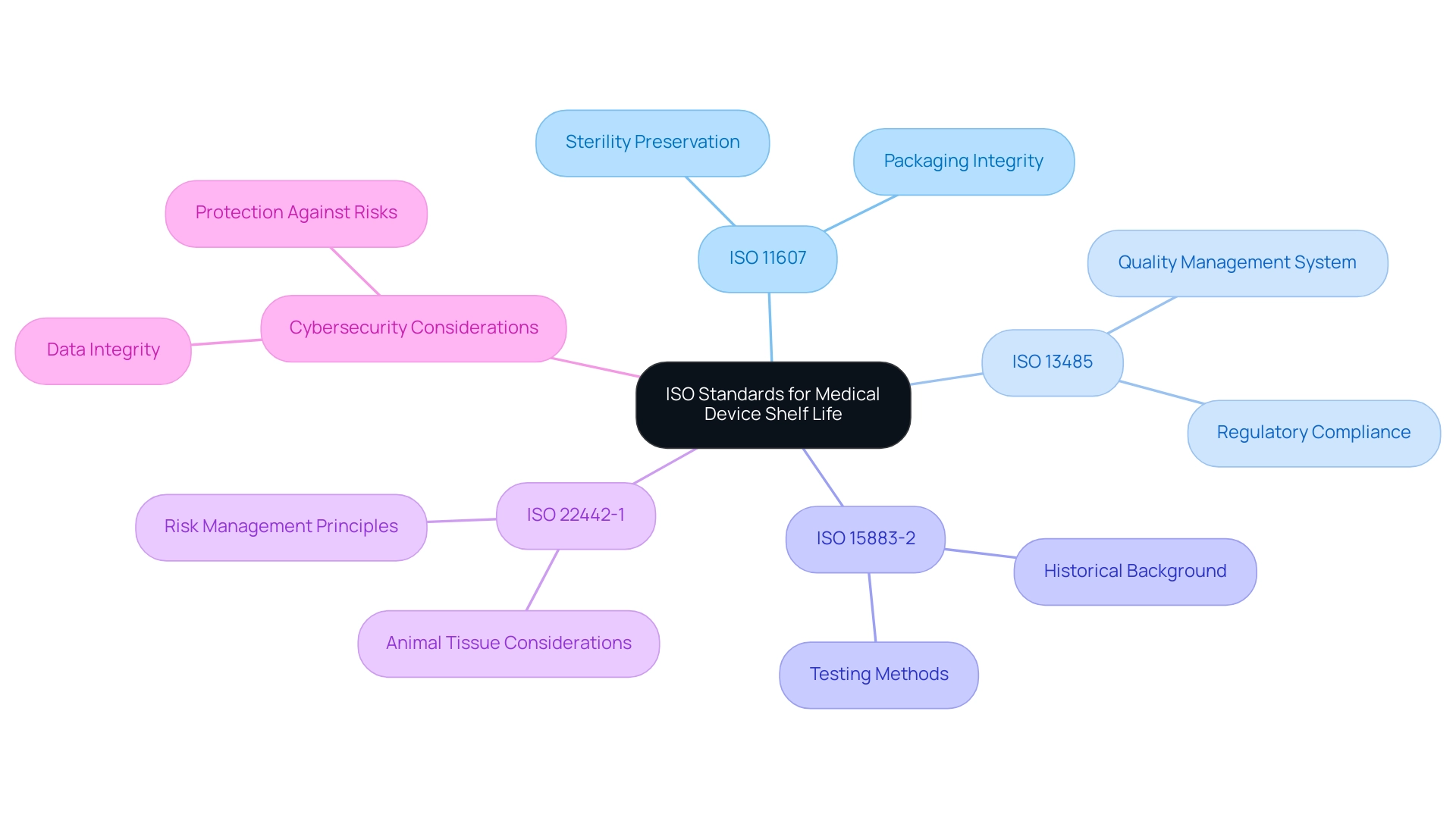
Shelf Life Testing Procedures and Methodologies
Shelf life testing is a critical process that often utilizes accelerated aging studies to ensure compliance with medical device shelf life ISO standards. In these evaluations, healthcare instruments are subjected to high temperatures and humidity levels to simulate the long-term impacts of aging on product quality. This methodology is enhanced by real-time testing, where items are stored under conditions that closely resemble actual usage scenarios.
Such thorough assessments are crucial in evaluating the physical, chemical, and microbiological stability of healthcare instruments as they pertain to the medical device shelf life ISO standards throughout their anticipated duration. Following validated testing protocols is vital, as it allows producers to assuredly determine and declare the longevity of their products, ensuring compliance with medical device shelf life ISO standards and strict regulatory standards. Recent estimates indicate a Cpk of 2.42 for these methodologies, with a 95% confidence interval ranging from 1.97 to 2.83, demonstrating the reliability of the testing processes employed.
By adopting innovations in storage duration testing techniques, the medical device sector can more effectively handle the intricacies of product stability and regulatory obligations in accordance with medical device shelf life ISO standards.
The significance of these techniques is highlighted by the perspectives of Abhay Gupta from the FDA, who has played a crucial role in the establishment of these standards. Moreover, a case study named 'A New Language for Duration' critiques the limited framework provided by ICH guidance documents regarding longevity and proposes a wider comprehension through clear terminology. This case study presents five unique terms associated with durability to avoid misunderstanding and advance development in the pharmaceutical sector.
For additional authoritative context, the PMCID for this discussion is PMC3429690 and the PMID is 22729779.
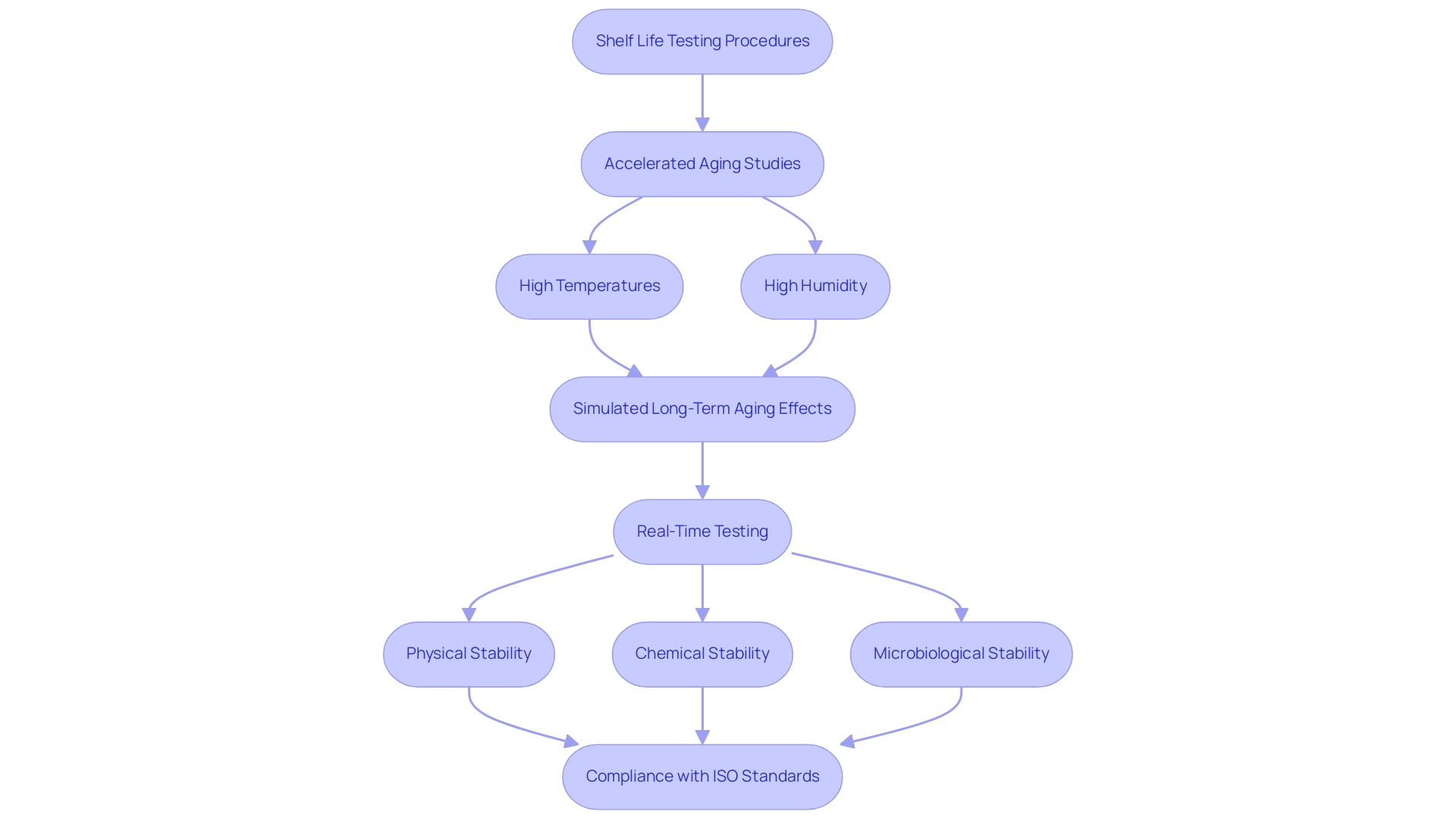
Factors Affecting Medical Device Shelf Life
The shelf life of medical equipment is intricately influenced by various factors, such as packaging materials and storage conditions, which must comply with medical device shelf life ISO standards. Packaging must be meticulously engineered to safeguard the equipment against environmental stresses while ensuring sterility is preserved. For instance, the selection of appropriate materials can significantly impact how well an apparatus ages, as certain plastics and composites may offer better barriers against moisture and oxygen than others.
Moreover, maintaining optimal storage conditions is crucial; deviations in temperature or humidity can accelerate degradation processes, leading to compromised product integrity. Recent findings emphasize the significance of these elements, with studies indicating that improper packaging can diminish an item's effective shelf life by up to 30%. By comprehending and tackling these essential factors, manufacturers can make informed decisions concerning product development and packaging solutions that align with medical device shelf life ISO standards, ultimately improving the durability and safety of their health-related products.
As mentioned by Plastic Ingenuity, one of the largest custom thermoforming companies in North America, "Our innovative, scalable healthcare solutions enable you to get drug therapies, medical products, and diagnostic offerings to the market faster." This highlights the significance of strategic packaging decisions in not only product longevity but also in expediting market readiness. Furthermore, case studies, like the one named 'Rounding of Data,' demonstrate how organizations can enhance their comprehension of data rounding methods to track product duration efficiently and implement required modifications to their packaging approaches.
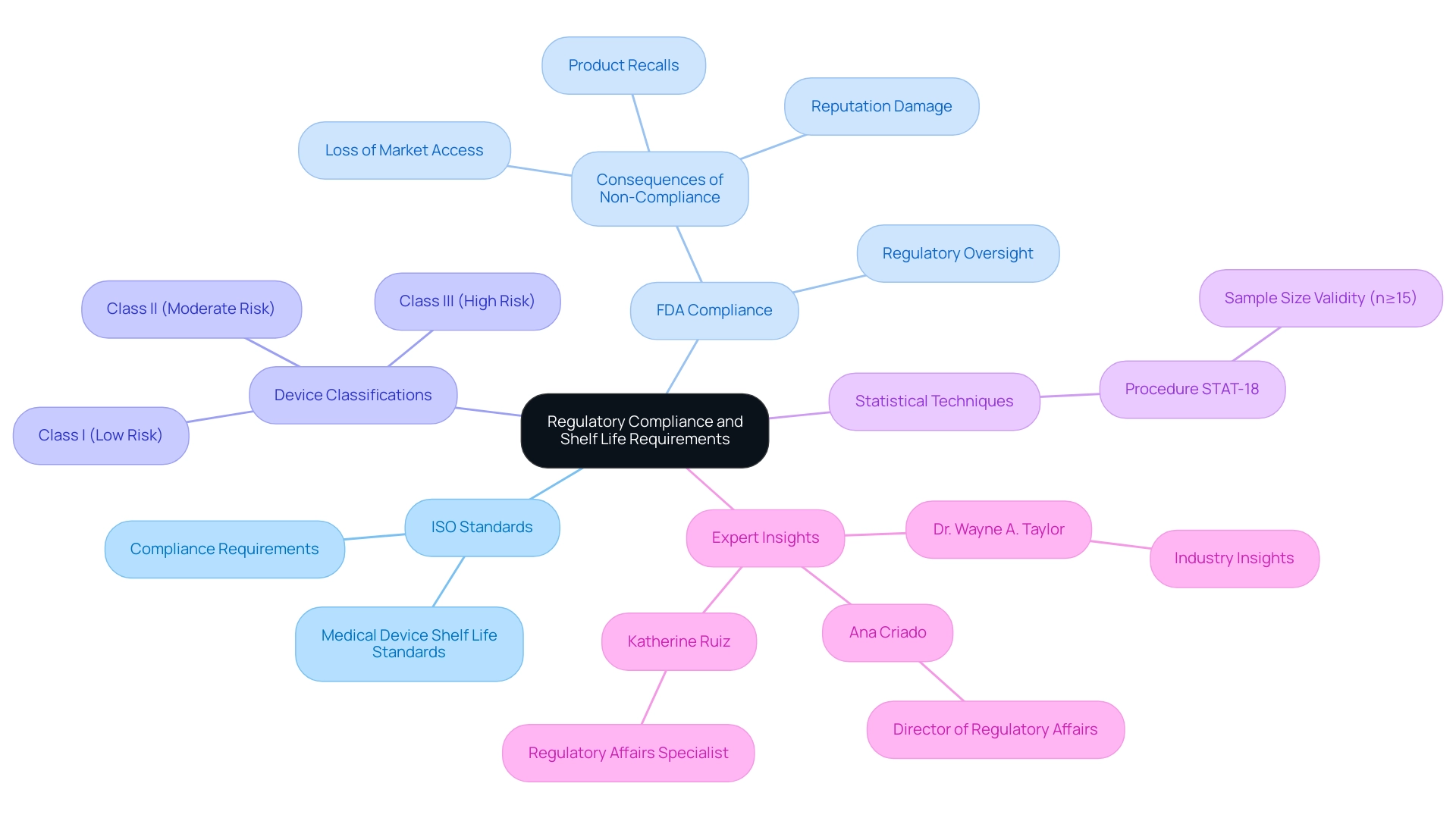
Regulatory Compliance and Shelf Life Requirements
Medical equipment producers must navigate a complex landscape of regulatory standards regarding longevity, especially focusing on medical device shelf life ISO standards to ensure compliance with FDA and ISO guidelines. According to Procedure STAT-18: Statistical Techniques for Normality Testing and Transformations, simulations demonstrate that statistical validity is achieved with sample sizes of n≥15, underscoring the importance of comprehensive testing in compliance with these regulations. Moreover, comprehending the categorization of healthcare devices—Class I (low risk), Class II (moderate risk), and Class III (high risk)—is essential, as each category involves different degrees of regulatory supervision that directly influence storage duration requirements.
With insights from experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, who has over five years of experience at INVIMA and holds advanced degrees in health economics and pharmacology, and Katherine Ruiz, who specializes in Regulatory Affairs for healthcare products and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, manufacturers can better navigate these complexities. They must ensure that their equipment remains both safe and effective for the duration of their specified shelf lives, adhering to medical device shelf life ISO standards, as failure to comply with these regulations can lead to severe legal and financial consequences, including product recalls, loss of market access, and damage to reputation. Consequently, a deep understanding of these compliance requirements is essential for manufacturers seeking to uphold their industry standing while prioritizing patient safety.
As Dr. Wayne A. Taylor emphasizes, 'This book is designed for engineers and scientists in the medical device industry,' highlighting the imperative for professionals in this field to engage with the evolving regulatory landscape and implement necessary practices to ensure compliance.
Conclusion
Medical device shelf life is essential for ensuring patient safety and product efficacy. This article has examined key aspects, including ISO standards like ISO 11607 and ISO 13485, which establish frameworks for packaging integrity and quality management. Compliance with these standards is crucial for manufacturers to validate their products' safety and effectiveness, thereby building trust with healthcare providers and patients.
Shelf life testing methodologies, such as accelerated aging studies and real-time evaluations, are vital for assessing the longevity of medical devices. These testing protocols help ensure that products remain stable and effective over their intended lifespan. Additionally, factors like packaging materials, environmental conditions, and storage practices significantly impact shelf life. Addressing these elements allows manufacturers to enhance product longevity and safety.
Regulatory compliance is another critical factor in managing medical device shelf life. Understanding FDA and ISO guidelines is essential for manufacturers to avoid serious consequences, including recalls and reputational damage. Collaborating with regulatory experts can provide valuable insights into maintaining safety standards throughout a device's lifecycle.
In conclusion, comprehending shelf life is indispensable for both manufacturers and healthcare providers. By prioritizing adherence to standards, implementing effective testing methodologies, and ensuring regulatory compliance, the industry can protect patient welfare and improve clinical outcomes. As medical technology evolves, focusing on shelf life will remain essential for effective product management and patient safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of the longevity of medical equipment?
The longevity of medical equipment is defined as the period during which a product is expected to operate safely and efficiently, assuming it is maintained and managed under designated circumstances.
Why is the concept of medical device shelf life important?
The concept of medical device shelf life is crucial because expired equipment poses significant risks to patient safety and can jeopardize the integrity of clinical outcomes.
What role does INVIMA play in Colombia regarding medical device shelf life?
INVIMA (Instituto Nacional de Vigilancia de Medicamentos y Alimentos) is responsible for ensuring that healthcare instruments comply with medical device shelf life ISO standards, inspecting and supervising the marketing and manufacturing of health products.
What are ISO 11607 and ISO 13485?
ISO 11607 outlines the requirements for packaging used for terminally sterilized healthcare products, ensuring the preservation of integrity and sterility. ISO 13485 establishes a quality management system framework for organizations to consistently deliver healthcare products that meet regulatory and client needs.
What is the significance of compliance with medical device shelf life ISO standards?
Compliance with these standards confirms the longevity of healthcare products, ensuring their safety and effectiveness during use, which ultimately improves patient safety and strengthens confidence in healthcare technologies.
How do testing methodologies like accelerated aging tests contribute to medical device shelf life?
Testing methodologies, such as accelerated aging tests, help assess the stability and performance of healthcare products over time, ensuring that they meet safety and quality benchmarks.
What other ISO standards are related to medical device shelf life?
Other related ISO standards include ISO 15883-2, which provides historical context for the development of shelf life standards, and ISO 22442-1, which implements risk management principles for healthcare products that use animal tissues.
What is the importance of strong durability assessment procedures in healthcare?
Strong durability assessment procedures are vital for ensuring that healthcare products remain safe and effective throughout their intended lifespan, as emphasized by industry specialists.




