Introduction
Navigating the complex landscape of medical device development requires a thorough understanding of the structured phases that guide the evaluation and approval process. Each phase, from the foundational preclinical studies to the critical post-market surveillance, serves a distinct purpose in ensuring the safety and efficacy of new medical technologies.
As organizations strive to bring innovative devices to market, they must contend with rigorous regulatory requirements, the intricacies of clinical trial management, and the ongoing challenges of patient recruitment and resource allocation.
This article delves into the essential phases of medical device studies, highlighting the objectives and regulatory considerations that shape each stage, while also examining the pivotal role of specialized clinical trial management services in facilitating successful outcomes.
Through a comprehensive exploration of these elements, the significance of effective study design and execution in advancing healthcare solutions becomes clear.
Overview of Medical Device Study Phases
Medical equipment studies are structured into several critical phases, each serving distinct purposes in the evaluation and development process:
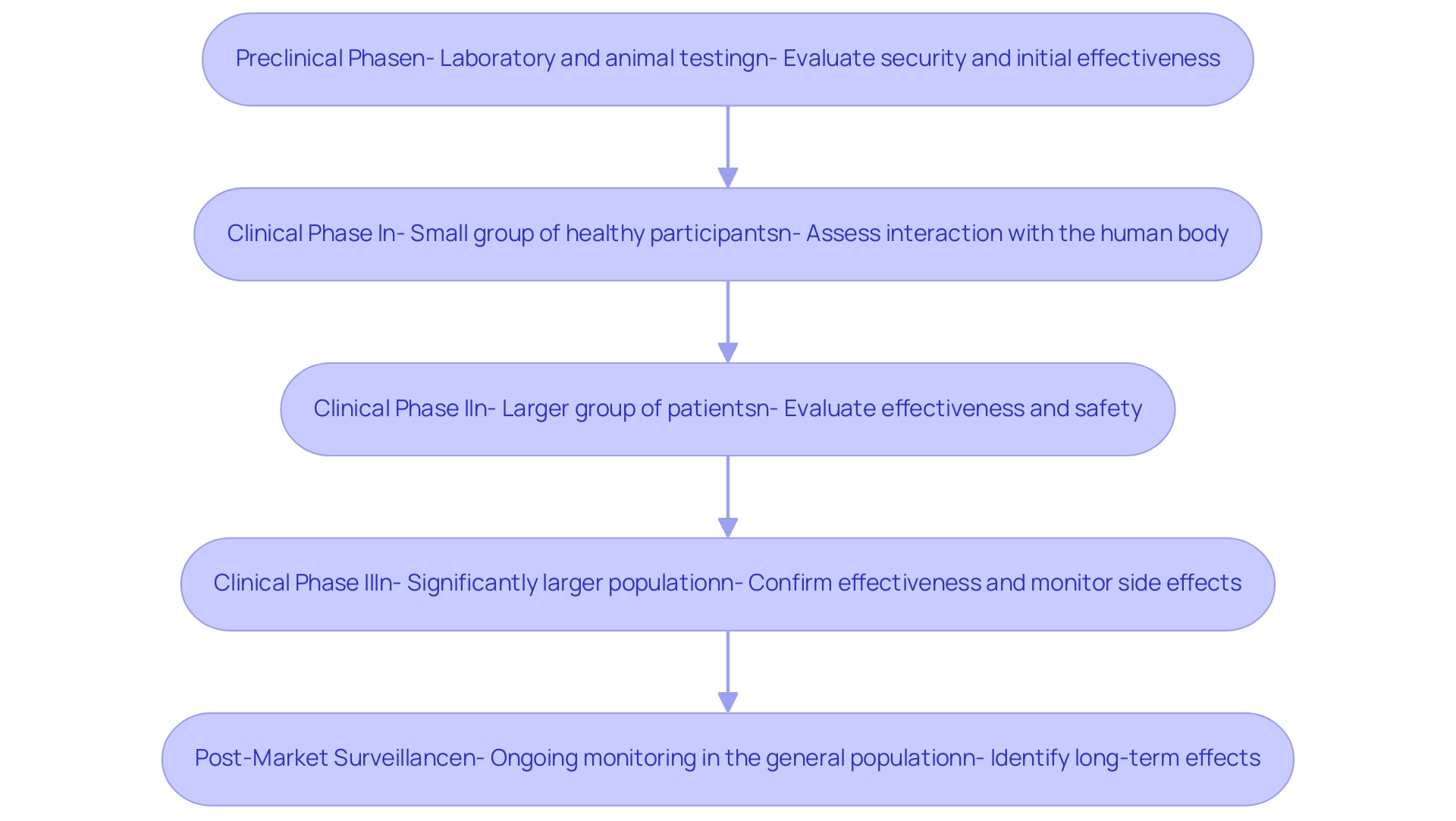
- Preclinical Phase: This essential stage includes laboratory and animal testing to thoroughly evaluate the security and initial effectiveness of the apparatus before human trials. It aims to identify any potential risks and establish preliminary effectiveness.
- Clinical Phase I: Concentrated mainly on well-being, this phase includes a small group of healthy participants. The goal is to assess how the apparatus interacts with the human body, determining its risk profile and identifying any negative responses.
- Clinical Phase II: Expanding the participant pool, this phase includes a larger group of patients to evaluate the effectiveness of the equipment while continuing to assess safety. This dual focus is crucial for determining how well the apparatus performs in a patient population.
- Clinical Phase III: Conducted on a significantly larger population, this phase is designed to confirm the effectiveness of the technology, monitor side effects, and compare its performance against standard treatments. The outcomes of this phase are critical for regulatory submissions.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Following regulatory approval, ongoing monitoring of the product's performance in the general population is essential. This monitoring aims to identify any long-term effects or rare complications that may emerge once the apparatus is in widespread use.
In the context of Latin America, companies like bioaccess® provide accelerated clinical research services, leveraging over 20 years of expertise in managing investigations such as Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Follow-Up Research. Their extensive clinical research management services include feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, setup, import permits, project oversight, and reporting. This specialized approach is crucial for navigating the regulatory landscape, particularly the oversight provided by INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, recognized as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
Recent advancements in these phases, particularly in 2024, highlight the FDA's recommendation for electronic submissions of calculations and analytical programs, significantly streamlining the process.
The opportunity cost of capital in medical device study phases is approximately 10.4%, underscoring the financial implications of timely and efficient studies. Furthermore, the PARCADIA study exemplifies the contemporary approach to clinical investigations, focusing on the intersection of ICD intervention and imaging in the context of ischemic cardiomyopathy. This trial illustrates the evolving landscape of medical equipment research and the importance of integrating advanced imaging techniques within clinical phases.
Additionally, the VenoValve research presented by Dr. Jorge Hernando Ulloa at the Charing Cross International Symposium serves as a key example of successful first-in-human data, showcasing the practical applications of these clinical phases. As mentioned by Aylin Sertkaya, PhD, from Eastern Research Group Inc., the use of Bayesian interim analysis facilitates improved efficiency and responsiveness, illustrating the increasing complexity in medical instruments and the necessity of adhering to best practices in clinical research. The impact of Medtech clinical research on local economies, including job creation and healthcare improvement, further emphasizes the significance of these trials in fostering international collaboration and economic growth.
Objectives and Regulatory Requirements of Each Study Phase
Each stage of the medical device study phases is defined by particular goals and regulatory criteria that direct the development process.
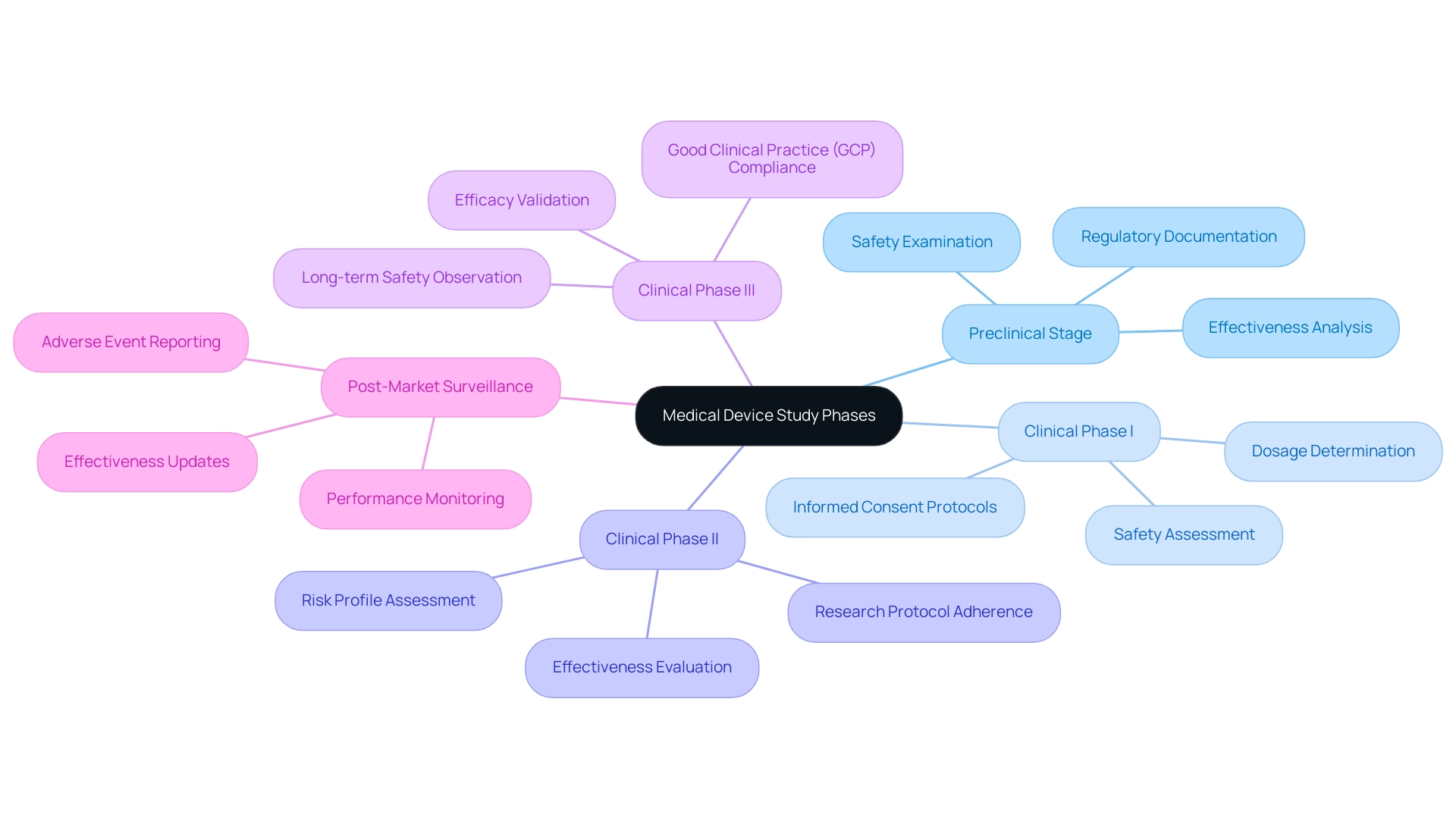
- Preclinical Stage: The main aims during this stage focus on examining security and analyzing potential effectiveness, particularly within the medical device study phases, especially in relation to existing standard treatments. Regulatory agencies require detailed documentation of laboratory and animal testing outcomes, ensuring that all preclinical findings are rigorously examined before advancing to clinical trials.
- Medical device study phases: This initial clinical phase concentrates on assessing the safety of the investigational instrument and determining suitable dosages. Regulatory requirements during this phase include rigorous informed consent protocols, which are essential for safeguarding participant rights, as well as ongoing monitoring to address any potential adverse effects in real-time. Here, bioaccess® guarantees a tailored approach to enhance communication and adherence, tackling typical obstacles for US Medtech firms in Latin America, including language issues and regulatory intricacies.
- Clinical Phase II: In this phase of the medical device study phases, the objectives shift to evaluating the effectiveness of the apparatus while still assessing its risk profile. Regulatory requirements necessitate detailed research protocols, which must be adhered to meticulously, along with regular reporting of any adverse events to ensure comprehensive oversight. The partnership between bioaccess® and regional facilities improves the efficiency of these investigations, especially in maneuvering through local regulatory environments and tackling the obstacles encountered by Medtech firms in Latin America.
The medical device study phases include Clinical Phase III, which is a vital stage that seeks to validate the efficacy of the instrument and observe its long-term safety in a broader population. Regulatory requirements are extensive, demanding thorough documentation and strict adherence to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, which are crucial in maintaining the integrity of the research. Bioaccess®'s expertise in crucial research enables streamlined processes that conform to global standards, including Early-Feasibility Evaluations (EFS) and First-In-Human Trials (FIH).
Post-market surveillance is a critical aspect of the medical device study phases, focusing on the consistent observation of a product's performance in actual environments after it has been approved and is available. Regulatory agencies demand continuous reporting of adverse occurrences and regular effectiveness updates to ensure patient well-being and instrument efficacy. Bioaccess® offers crucial assistance in post-market clinical follow-up research, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
Since the start of the fiscal year 2003, medical equipment user fees have been imposed on original PMAs and specific categories of PMA supplements, which highlights the financial aspects in medical equipment assessments. As emphasized in the case analysis on Investigational Device Exemption (IDE), this exemption permits investigational instruments to be utilized in clinical trials to gather data on efficacy and security for PMA or 510(k) submissions, necessitating approval from both the FDA and an Institutional Review Board (IRB) for significant risk instruments. Clinical research can only begin after obtaining the required approvals, ensuring adherence to security regulations.
As highlighted by Adnan Ashfaq, a Quality, Regulatory & Validation Specialist, > Our comprehensive medical equipment development solution speeds up your product development initiatives, enabling you to foster collaboration, unlock traceability, and obtain visibility into essential information throughout your product’s lifecycle. This emphasizes the significance of organized development procedures that conform to regulatory expectations, ensuring the successful launch of innovative medical products.
The Role of Preclinical Studies in Medical Device Development
Preclinical research is essential to the advancement of medical instruments, fulfilling several vital roles:
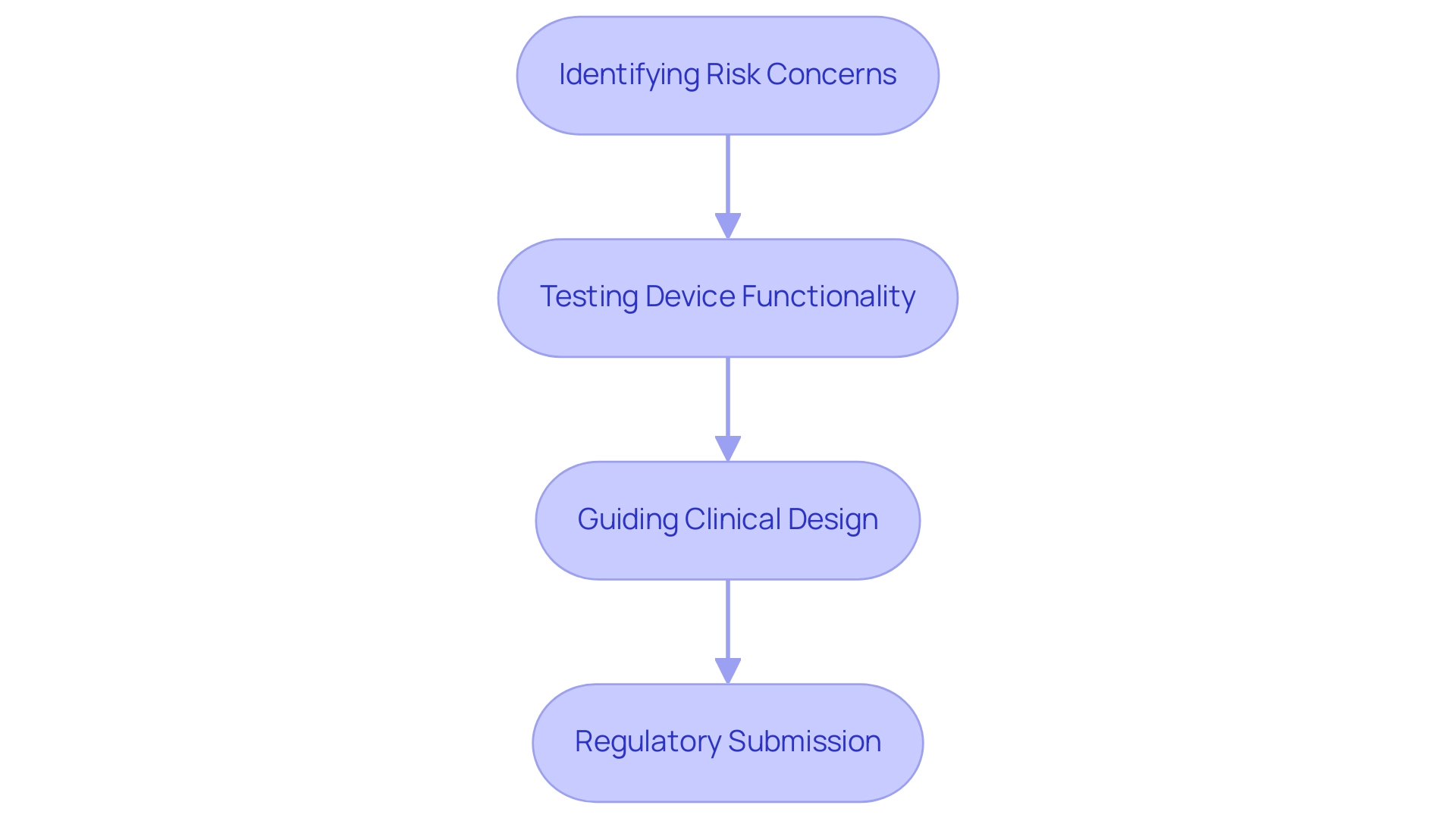
- Identifying Risk Concerns: These investigations are key in revealing possible risk issues before human trials, thus reducing hazards linked with instrument use. Recent statistics show that approximately 30% of medical devices fail due to safety concerns recognized during preclinical evaluations, highlighting their significance.
- Testing Device Functionality: By assessing device performance in controlled environments, researchers obtain valuable insights into its efficacy and potential for success in clinical applications. For example, Dynamic Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (DSIMS) is utilized to examine drug distribution and release behavior from coatings, offering essential information that guides design choices.
- Guiding Clinical Design: The information obtained from preclinical evaluations is crucial in forming clinical research frameworks during the medical device study phases, influencing important decisions such as patient selection and the formulation of outcome measures. Research comparisons between parametric and non-parametric tests demonstrate how statistical methods are utilized to analyze preclinical data, ensuring strong conclusions that inform experimental designs.
- Regulatory Submission: Comprehensive results from the medical device study phases are essential for regulatory submissions. They show that the apparatus complies with strict security criteria prior to progressing to human testing. As Dr. Julien Namur of Archimmed SARL emphasizes, > Images courtesy of Dr. Julien Namur, Archimmed SARL, France <, the thorough documentation of these investigations establishes the foundation for successful regulatory approval.
Our clinical management services enhance these processes by ensuring feasibility and selection of research locations, compliance reviews, project setup, import permits, and ongoing project oversight and reporting. These services are crucial for maintaining adherence to regulatory requirements, including oversight from INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, recognized as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO. The reporting and monitoring elements of our services are crucial in tracking study status, inventory, and significant and minor adverse events, which are important for informed decision-making throughout the research process.
Overall, the insights obtained from preclinical studies not only improve the risk profile of medical instruments but also guarantee their functionality, ultimately directing the development process towards more effective and secure healthcare solutions.
From Clinical Trials to Post-Market Surveillance: Ensuring Device Safety
The shift from clinical trials to post-market monitoring includes several essential steps that are crucial for guaranteeing the security and efficacy of medical instruments:
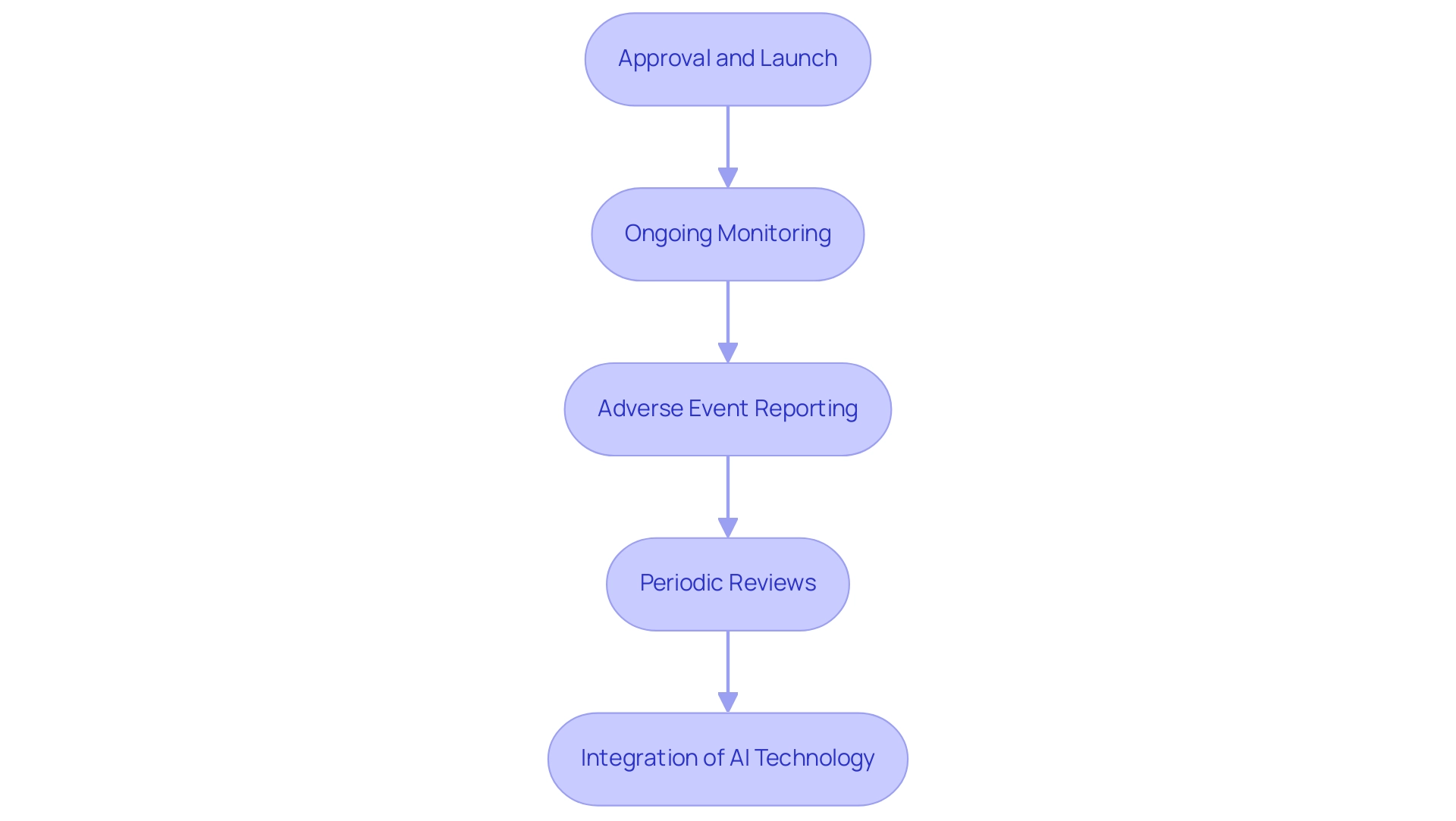
- Approval and Launch: After successful clinical trials, instruments receive regulatory approval from authorities like INVIMA, permitting them to enter the market. This signifies an important milestone in the product lifecycle, ensuring adherence to Colombia’s strict health regulations.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuous post-market surveillance plays a crucial role in evaluating the long-term effects of medical products within the broader population. INVIMA, classified as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO, actively oversees these products to ensure security and effectiveness, utilizing various information sources, including spontaneous adverse event reports and routinely gathered healthcare data, to guarantee that any potential issues are quickly identified and resolved.
- Adverse Event Reporting: It is crucial for manufacturers to swiftly report adverse events or product failures to regulatory bodies like INVIMA. Recent statistics show that roughly 30% of medical equipment encounter adverse events within the first year of market introduction, emphasizing persistent challenges in managing equipment security. This process not only promotes transparency but also strengthens the dedication to patient well-being.
- Periodic Reviews: Regular assessments of equipment performance and risk data are essential for identifying and reducing emerging threats. Adherence to post-market surveillance (PMS) regulations, as required by entities such as INVIMA and the FDA, showcases a manufacturer's commitment to continuous oversight and patient well-being. Specifically, the FDA mandates producers to perform yearly evaluations of equipment information, as highlighted in the case study on PMS compliance, which demonstrates that following these regulatory obligations is essential for maintaining equipment reliability and effectiveness.
- Integration of AI Technology: Recent frameworks have been proposed to evaluate the preparedness of AI models for real-world applications, mitigating potential risks linked to their use in medical instruments. This highlights the increasing convergence of technology and regulatory adherence in the MedTech arena.
According to industry expert Pedro Sancha, strong monitoring systems are crucial for the credibility and security of medical products after launch. His insights highlight the necessity of rigorous post-market surveillance to ensure that products not only meet initial safety standards but continue to perform safely throughout their lifecycle. Furthermore, it is important to note that INVIMA, established in 1992 under Colombia's Ministry of Health and Social Protection, has a dedicated Directorate for Medical Equipment and other Technologies.
This directorate is responsible for overseeing the monitoring and control of medical equipment, tracking pre- and post-market programs, and suggesting technical standards for manufacturing, marketing, and quality assurance.
Challenges and Considerations in Medical Device Study Phases
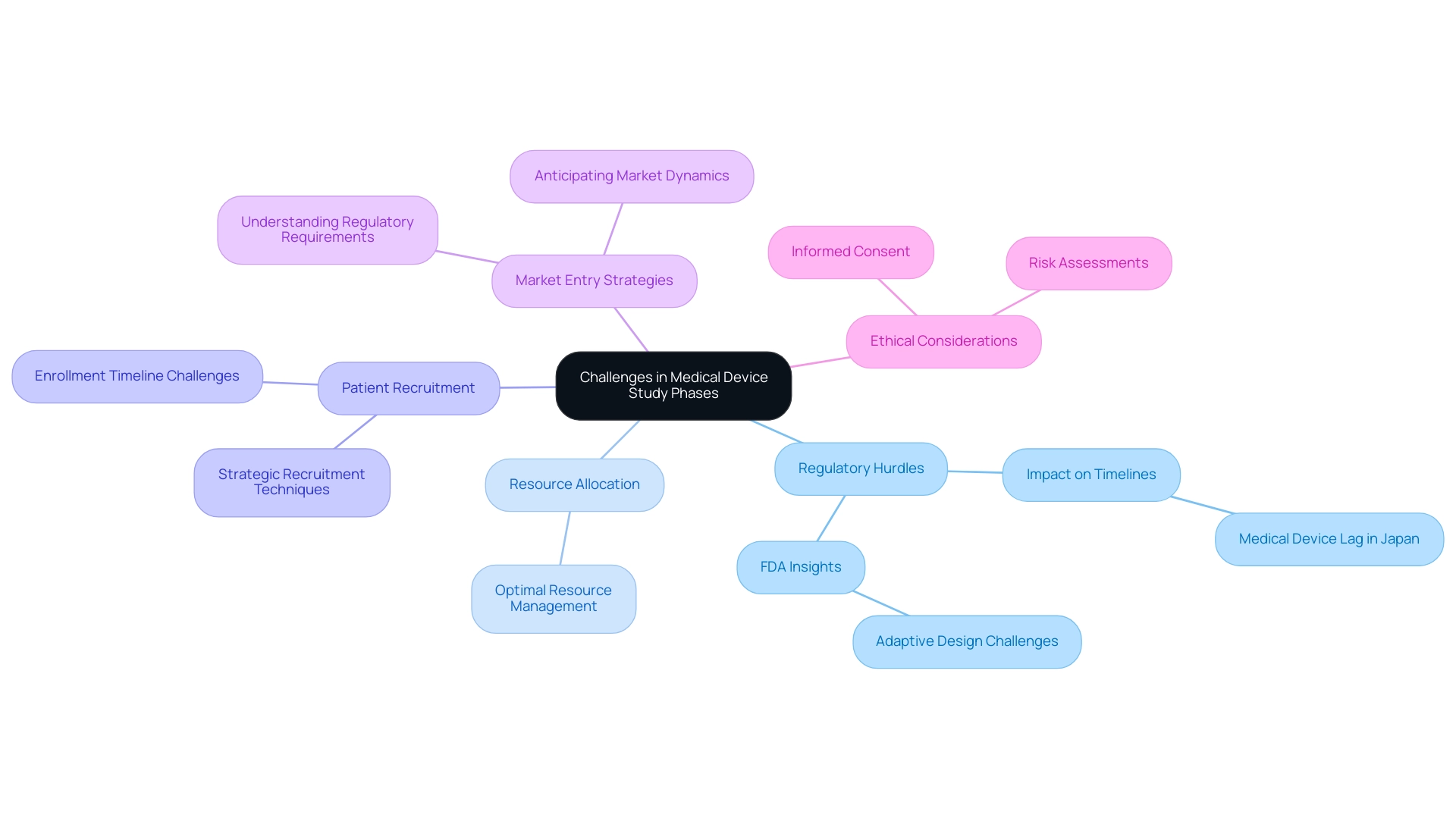
The journey through medical device study phases is fraught with several challenges that significantly impact the development timeline and overall success of clinical studies. Key hurdles include:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The complexities of navigating regulatory frameworks can result in considerable delays and increased costs. For instance, in Japan, the medical device lag reached nearly 3 years in the early 2000s, underscoring the impact of regulatory hurdles on timelines.
Insights from the FDA CDRH emphasize that 'adaptive design refers to a type of design in which modifications are made to one or more aspects of a clinical study during the process, utilizing accumulated data that are preplanned in the protocol.' However, these adaptations often face scrutiny, complicating the approval process. bioaccess® leverages its 20+ years of Medtech experience to navigate these regulatory complexities effectively, ensuring smoother testing processes.
- Resource Allocation: Effectively managing multiple projects within the constraints of time and resources is a critical challenge. Organizations must ensure that adequate resources are allocated to each phase of the research without compromising quality or compliance. 'bioaccess®'s tailored approach ensures optimal resource allocation across all medical device study phases.
- Patient Recruitment: Identifying and enrolling suitable candidates for clinical trials remains a significant hurdle. Expert opinions highlight that recruitment difficulties can lead to extended enrollment timelines, which may jeopardize the overall study schedule. bioaccess® utilizes strategic recruitment techniques to improve participant enrollment, thus reducing delays.
- Market Entry Strategies: A clearly defined market entry strategy is essential for the successful commercialization of medical instruments. This involves not only understanding regulatory requirements but also anticipating market dynamics and potential barriers to entry. bioaccess® provides comprehensive market entry strategies, ensuring clients are well-prepared for commercialization.
- Ethical Considerations: Upholding ethical standards throughout the research process is vital to safeguarding patient rights and ensuring their safety. This includes obtaining informed consent and conducting thorough risk assessments to mitigate potential harm. bioaccess® emphasizes ethical factors in all its research, ensuring adherence to the highest standards.
In this context, bioaccess® distinguishes itself with its expedited medical equipment clinical research services in Latin America, utilizing over 20 years of Medtech expertise. Their expertise encompasses the various medical device study phases, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF), ensuring a tailored approach to navigate these challenges effectively. Additionally, Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, plays a crucial role in addressing regulatory hurdles, enhancing compliance, and facilitating smoother study processes.
Recent advancements, such as user-friendly Bayesian interfaces like BEANZ, aim to streamline Bayesian analysis for subgroup analysis, which may alleviate some regulatory challenges by providing clearer insights into study data. Furthermore, a recent study titled 'Study Limitations' acknowledged the potential underestimation of adaptive randomized controlled trials (RCTs) due to incomplete database registrations, indicating that the current understanding of adaptive designs in medical device trials may be limited, further complicating the regulatory landscape as we move into 2024.
Conclusion
Navigating the multifaceted landscape of medical device development necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the critical phases involved in the evaluation and approval process. Each phase—from preclinical studies to post-market surveillance—serves a distinct purpose, ensuring that new medical technologies meet stringent safety and efficacy standards. The detailed examination of these phases reveals the importance of structured methodologies and regulatory compliance in advancing healthcare solutions.
The preclinical phase establishes the foundation by identifying potential safety concerns and guiding the design of subsequent clinical trials. As devices progress through the clinical phases, the focus shifts from safety to efficacy, with each stage building upon the findings of the previous one. Successful navigation of these phases is crucial not only for regulatory approval but also for the long-term success of medical devices in real-world settings.
Post-market surveillance is equally vital, allowing for continuous monitoring of device performance and the identification of any emerging safety issues. The integration of advanced technologies and ongoing regulatory compliance efforts underscores the commitment to patient safety throughout the product lifecycle. Ultimately, the collaboration between clinical trial management services and regulatory bodies is essential in mitigating challenges such as patient recruitment and resource allocation, ensuring that innovative medical devices can be brought to market effectively and efficiently.
In conclusion, the structured approach to medical device studies, combined with a thorough understanding of regulatory requirements, fosters a pathway for innovation that enhances patient care and drives advancements in healthcare technology. As the medical device landscape continues to evolve, the emphasis on rigorous study design and execution will remain critical in shaping the future of medical technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main phases of medical equipment studies?
Medical equipment studies are structured into five critical phases: Preclinical Phase, Clinical Phase I, Clinical Phase II, Clinical Phase III, and Post-Market Surveillance. Each phase serves distinct purposes in the evaluation and development process.
What occurs during the Preclinical Phase?
The Preclinical Phase involves laboratory and animal testing to evaluate the safety and initial effectiveness of the medical apparatus before human trials. It aims to identify potential risks and establish preliminary effectiveness.
What is the focus of Clinical Phase I?
Clinical Phase I concentrates on safety and involves a small group of healthy participants. The goal is to assess how the apparatus interacts with the human body, determine its risk profile, and identify any negative responses.
How does Clinical Phase II differ from Clinical Phase I?
Clinical Phase II expands the participant pool to a larger group of patients to evaluate the effectiveness of the equipment while continuing to assess safety. This phase is crucial for determining how well the apparatus performs in a patient population.
What is the purpose of Clinical Phase III?
Clinical Phase III is conducted on a significantly larger population to confirm the effectiveness of the technology, monitor side effects, and compare its performance against standard treatments. The outcomes of this phase are critical for regulatory submissions.
What is involved in Post-Market Surveillance?
Post-Market Surveillance involves ongoing monitoring of the product's performance in the general population after regulatory approval. This monitoring aims to identify any long-term effects or rare complications that may emerge once the apparatus is widely used.
How do companies like bioaccess® contribute to clinical research in Latin America?
Companies like bioaccess® provide accelerated clinical research services, leveraging over 20 years of expertise in managing various types of investigations. Their services include feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, and project oversight, which are essential for navigating the regulatory landscape.
What recent advancements have been made in medical equipment studies?
Recent advancements include the FDA's recommendation for electronic submissions of calculations and analytical programs, which streamline the process. Additionally, studies like PARCADIA exemplify contemporary approaches to clinical investigations, integrating advanced imaging techniques.
What are the financial implications of medical device study phases?
The opportunity cost of capital in medical device study phases is approximately 10.4%, highlighting the financial implications of conducting timely and efficient studies.
What regulatory requirements are essential during the medical device study phases?
Each phase has specific regulatory requirements, including rigorous informed consent protocols, detailed research protocols, adherence to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, and continuous reporting of adverse occurrences and effectiveness updates.

