Introduction
In the intricate world of medical device regulation, the concept of substantial equivalence stands as a pivotal benchmark for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of new products entering the market. Defined by the FDA, substantial equivalence allows manufacturers to demonstrate that their innovative devices are comparable to existing ones, known as predicate devices, thereby facilitating a streamlined approval process through the 510(k) pathway.
This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of substantial equivalence, exploring its critical role in regulatory submissions, the evaluation criteria that govern its determination, and the challenges manufacturers face in establishing it. By examining real-world examples and insights from industry experts, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how substantial equivalence shapes the landscape of medical device innovation and regulatory compliance.
Defining Substantial Equivalence in Medical Devices
Substantial equivalence medical device serves as a critical regulatory standard employed by the FDA to assess whether a new medical instrument can be deemed as safe and effective as an existing legally marketed instrument, referred to as a predicate instrument. The FDA defines a product as a substantial equivalence medical device if it shares the same intended use and technological characteristics as a predicate product, or if it possesses distinct technological features that do not introduce new questions regarding safety and effectiveness. This concept of a substantial equivalence medical device is essential for manufacturers aiming to launch new products to the market through the 510(k) application process, providing a streamlined pathway for expedited approval while maintaining patient safety and product effectiveness.
In 2024, the FDA reported a significant number of substantial equivalence approvals, with 1,041 products granted Breakthrough Device designation, of which 1,029 were granted by CDRH and 12 by CBER. For instance, the case study of Exablate, which received marketing authorization on 07/11/2016, exemplifies how successful 510(k) submissions can illustrate substantial equivalence medical device and its impact on market entry. Additionally, the recent approval of the UNIPURE SF6 Ophthalmic Gas systems for eye injection on 08/26/2024 highlights the ongoing relevance and importance of substantial equivalence medical device in facilitating access to innovative therapies.
In Colombia, the regulatory environment is similarly shaped by professionals like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, who utilizes her extensive background in biomedical engineering and health economics to navigate INVIMA’s supervision of medical products. INVIMA, acknowledged as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO, plays a crucial role in ensuring that medical products meet safety and efficacy standards before they can be marketed, paralleling the FDA's rigorous evaluation process. Specifically, INVIMA implements comprehensive guidelines for the classification, registration, and post-market surveillance of medical products, ensuring compliance with both national and international standards.
Ana Criado's contributions to INVIMA include her involvement in developing guidelines that streamline the approval process for innovative medical technologies, thereby enhancing patient access to essential health products.
Criteria for Evaluating Substantial Equivalence
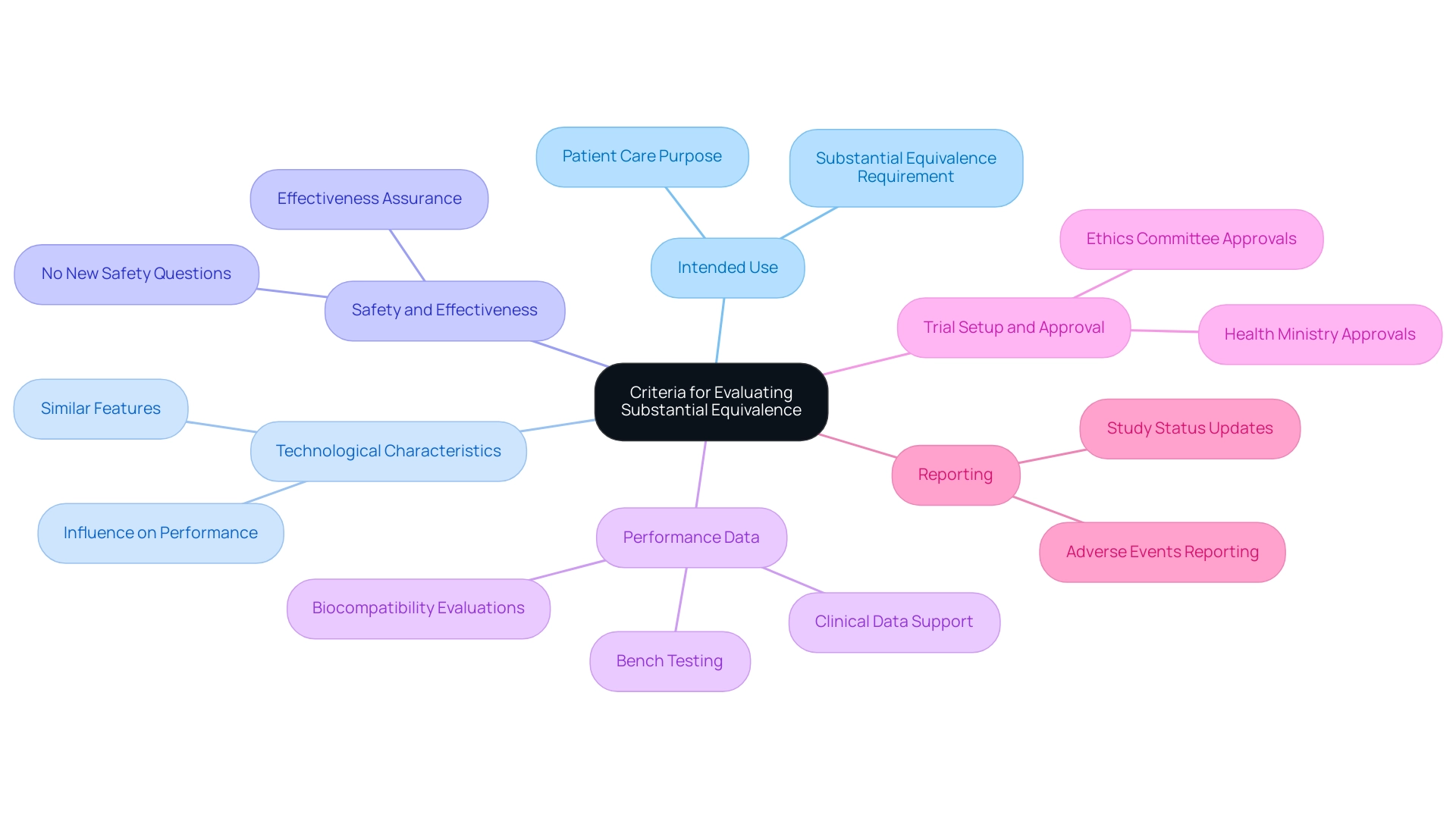
In navigating the complex landscape of medical equipment approval, particularly in the context of the FDA's stringent 510(k) submission process, it is essential to understand the comprehensive clinical trial management services available. Our capabilities include conducting feasibility studies, selecting appropriate research sites, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, and providing thorough review and feedback on study documents to meet country-specific regulations. Specifically, we focus on the following key elements:
- Intended Use: The new apparatus must qualify as a substantial equivalence medical device by sharing the same intended use as the predicate apparatus, ensuring that it serves a similar purpose in patient care.
- Technological Characteristics: The apparatus should possess the same or similar technological features to those of a substantial equivalence medical device, which can influence its performance and safety profile.
- Safety and Effectiveness: Any variations in technological characteristics must not introduce new questions concerning safety or effectiveness, especially in the context of a substantial equivalence medical device under the FDA's heightened scrutiny.
- Performance Data: Manufacturers must deliver comprehensive performance information, including elements like bench testing, biocompatibility evaluations, and clinical data that support the intended functionality of the substantial equivalence medical device.
- Trial Setup and Approval: We manage the trial setup process, ensuring timely approvals from ethics committees and health ministries.
- Reporting: We provide comprehensive reporting on study status, inventory, and both serious and non-serious adverse events.
With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® offers accelerated clinical study services across Latin America, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF). Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in compliance matters for medical equipment and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, spearheads our initiatives to guarantee adherence and positive results.
By adhering to these evaluation criteria and leveraging our expertise, we can facilitate regulatory approval and enhance trust in medical equipment. This approach is underscored by a recent analysis involving specimen collection from 220 subjects, which highlights the importance of comprehensive data in the evaluation process. Moreover, recent revisions to performance data requirements emphasize the need for accuracy; improper modifications in data evaluation can lead to incorrect calculations of sensitivity and specificity.
Thus, meeting these criteria is paramount for a successful 510(k) submission, reflecting the evolving expectations set forth by the FDA.
The Role of Predicate Devices in Substantial Equivalence
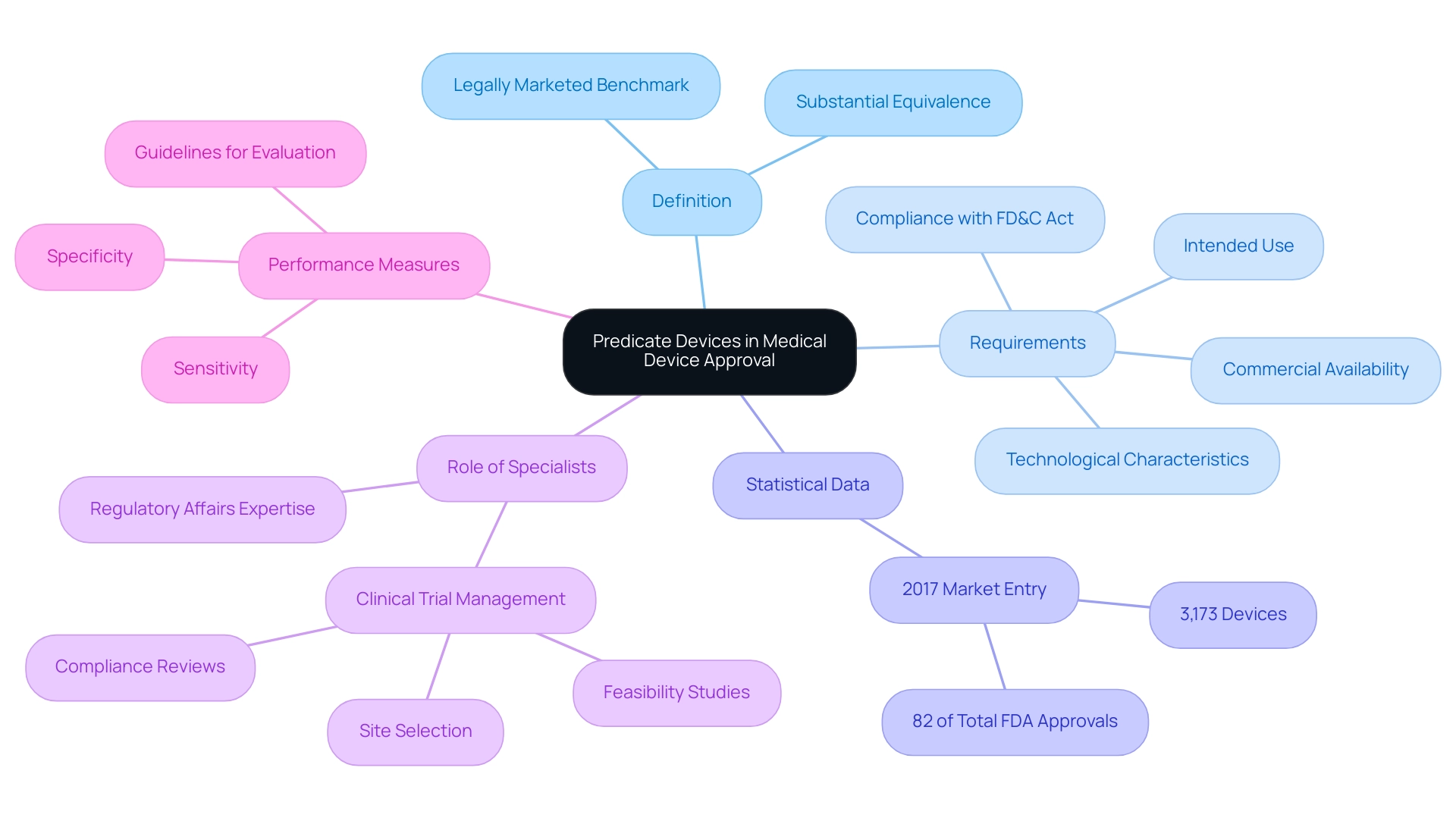
A predicate instrument serves as a legally marketed benchmark for demonstrating substantial equivalence medical device for new medical instruments. To qualify, a predicate product must be commercially available and cannot have been withdrawn from the market for safety or effectiveness reasons. In 2017, 3,173 items—accounting for 82% of the total FDA-approved or cleared products that year—entered the market via the 510(k) pathway, highlighting the critical role of predicate items in the approval process.
Manufacturers must ensure that the predicate shares the same intended use and technological characteristics as the new product. This comparison is vital, as it substantiates the new technology's safety and effectiveness as a substantial equivalence medical device using existing data from the predicate system. Furthermore, it is crucial to recognize that a predicate device cannot be one that violates the Federal Food Drug & Cosmetic (FD&C) Act, which further clarifies the framework surrounding these devices.
Importantly, specialists such as Ana Criado, Director of Compliance and CEO of Mahu Pharma, highlight the importance of comprehending these pathways, especially in relation to Colombia's evolving medtech landscape. Ana's extensive experience in Regulatory Affairs and her involvement in comprehensive clinical trial management services—including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, and project management—are crucial for navigating the complexities of the FDA approval process. Such insights emphasize the ongoing evolution of FDA processes and underscore the importance of predicate tools in facilitating a streamlined approval journey.
Furthermore, the FDA emphasizes the importance of presenting both sensitivity and specificity measures together to accurately reflect a test's performance, reinforcing the need for rigorous evaluation in the context of medical equipment approvals.
Steps to Demonstrate Substantial Equivalence in 510(k) Submissions
To successfully demonstrate substantial equivalence medical device in a 510(k) submission, it is crucial to meticulously follow these steps:
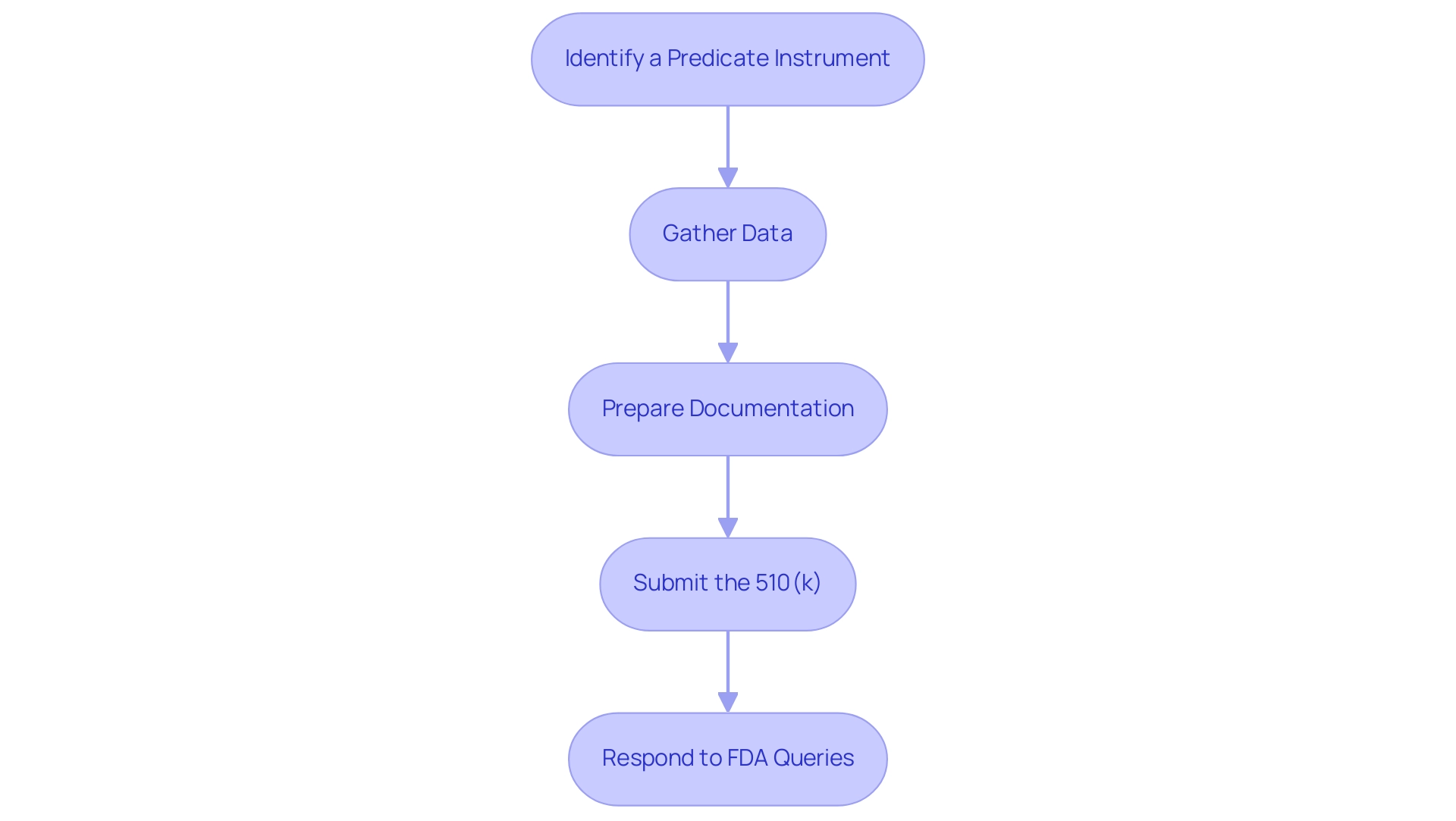
- Identify a Predicate Instrument: Conduct thorough research to select an appropriate predicate instrument that is legally marketed and closely relevant to your new product. This step forms the basis for demonstrating substantial equivalence medical device.
- Gather Data: Collect all necessary performance data, which includes both preclinical and clinical data, along with relevant testing results. This comprehensive data collection is essential for supporting your claims.
- Prepare Documentation: Compile detailed documentation that encompasses a complete device description, intended use, labeling, and a thorough comparison with the predicate device.
As noted by a regulatory expert, 'Technically no, but guidance documents reflect current FDA thinking on a topic, so you would be foolish to ignore them.' Adhering to these guidelines is essential for a successful application involving a substantial equivalence medical device, as they help reduce the risk of receiving a not substantially equivalent (NSE) letter, which can significantly delay the approval process. A case study titled 'Understanding the Clearance Process' illustrates the potential outcomes of entries and emphasizes the significance of thorough preparation.
- Submit the 510(k): Complete and submit the 510(k) application through the FDA’s electronic filing system. Ensure that all components of the application are well-prepared to facilitate an efficient review process. Additionally, the FDA offers an online monitoring system that enables official correspondents to follow the progress of their 510(k) applications, enhancing transparency and communication.
- Respond to FDA Queries: Be prepared to promptly respond to any requests for additional information from the FDA during their review process. The average review time for a 510(k) submission is approximately 120 days, making it imperative to maintain clear communication.
Furthermore, leveraging comprehensive clinical trial management services, such as those provided by bioaccess®, can enhance the efficiency of your submission process in Latin America. Their capabilities include trial setup, obtaining ethics committee approvals, and project management, all of which are crucial in navigating the complexities of compliance affairs.
Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in compliance matters for medical instruments and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, plays a crucial role in assisting you through these processes, ensuring adherence to local laws and standards. These steps are crucial in ensuring that your submission is comprehensive, adheres to compliance standards, and prepares your product as a substantial equivalence medical device for successful clearance.
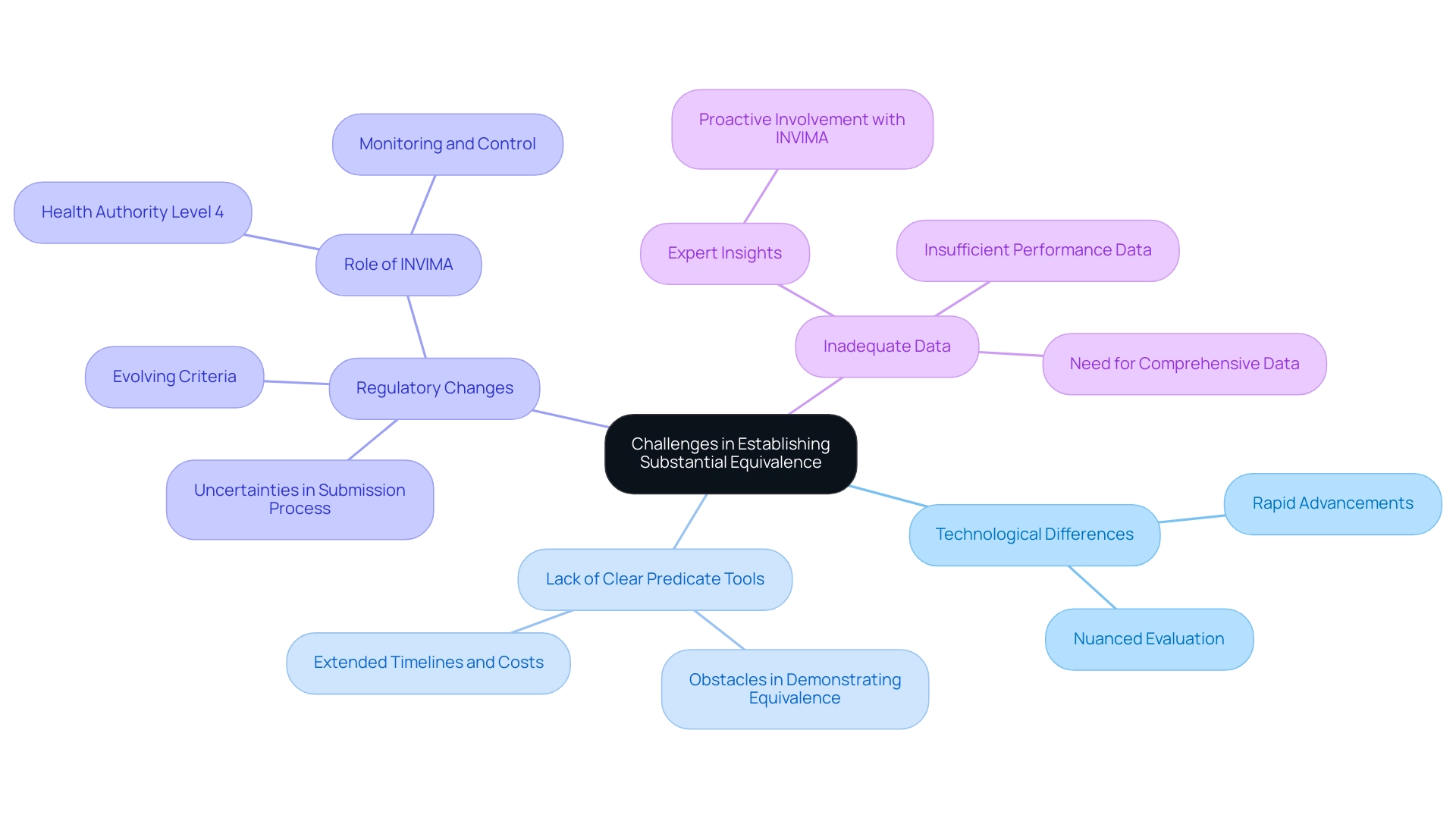
Challenges in Establishing Substantial Equivalence
Manufacturers must effectively navigate the numerous challenges presented by establishing substantial equivalence medical devices within the regulatory framework set by INVIMA (Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute). Key challenges include:
-
Technological Differences: Rapid advancements in medical equipment technology can introduce significant variations that complicate equivalence assessments.
Such innovations may render traditional comparisons inadequate, necessitating a more nuanced approach to evaluation.
-
Lack of Clear Predicate Tools: In instances where no suitable predicate tool is available, manufacturers face considerable obstacles in demonstrating equivalence.
This situation can lead to extended timelines and increased costs in the development process.
-
Regulatory Changes: An evolving regulatory landscape influenced by authorities like INVIMA can affect the criteria used to determine substantial equivalence, creating uncertainties for manufacturers during the submission process.
As emphasized by the Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization, INVIMA's designation as a Level 4 health authority highlights its proficiency in health regulation, which is essential for ensuring safety and efficacy.
The Directorate for Medical Equipment and other Technologies within INVIMA plays a pivotal role in monitoring and controlling medical products, suggesting technical standards for manufacturing, marketing, and quality assurance.
-
Inadequate Data: The presence of insufficient or ambiguous performance data can impede the demonstration of a device's safety and effectiveness.
Manufacturers must ensure that they provide clear and comprehensive data to support their proposals.
As Ana Criado, an expert in Regulatory Affairs and the Director of Regulatory Affairs at Mahu Pharma, emphasizes, understanding these regulatory challenges is vital for manufacturers.
She observes that proactive involvement with INVIMA can enable smoother applications and compliance.
Moreover, a study named "Regulatory Implications of Predicate Device Characteristics" examined the effects of the relationships discovered between predicate device traits and recall probabilities, indicating that the FDA might gain from gathering more detailed information concerning the recall status of predicate devices referenced in 510(k) filings.
By addressing these challenges proactively, manufacturers can enhance their submission success rates and ultimately improve patient safety outcomes.
Conclusion
The exploration of substantial equivalence in medical device regulation illuminates its critical role in ensuring both safety and efficacy for new products entering the market. This regulatory standard, defined by the FDA, allows manufacturers to demonstrate that innovative devices are comparable to existing predicate devices, thereby facilitating a more streamlined approval process through the 510(k) pathway. The insights provided throughout the article underscore the importance of understanding the criteria for evaluating substantial equivalence, including:
- Intended use
- Technological characteristics
- Performance data
Moreover, the challenges faced by manufacturers in establishing substantial equivalence cannot be overlooked. Rapid technological advancements, the availability of suitable predicate devices, evolving regulatory frameworks, and the need for robust performance data all present significant hurdles. The discussions surrounding these challenges highlight the necessity for manufacturers to engage proactively with regulatory bodies like the FDA and INVIMA to navigate this complex landscape effectively.
Ultimately, substantial equivalence serves as a cornerstone for medical device innovation, balancing the need for expedient market access with the imperative of patient safety. By adhering to established regulatory standards and addressing potential challenges, manufacturers can contribute to the advancement of healthcare technologies while ensuring compliance and fostering trust in their products. The ongoing evolution of these regulatory pathways will continue to shape the future of medical device development and patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a substantial equivalence medical device?
A substantial equivalence medical device is a regulatory standard used by the FDA to determine if a new medical instrument is as safe and effective as an existing legally marketed device, known as a predicate instrument. It must share the same intended use and technological characteristics or have distinct features that do not raise new safety or effectiveness concerns.
How does the FDA assess substantial equivalence?
The FDA assesses substantial equivalence by evaluating whether the new device has the same intended use and technological characteristics as a predicate device or if it has different technological features that do not introduce new safety or effectiveness questions.
What is the significance of the 510(k) application process?
The 510(k) application process provides a streamlined pathway for manufacturers to gain expedited approval for new medical devices while ensuring patient safety and product effectiveness.
Can you provide an example of a substantial equivalence medical device approval?
An example is the UNIPURE SF6 Ophthalmic Gas system, which was approved on 08/26/2024, and the Exablate device, which received marketing authorization on 07/11/2016, both illustrating successful substantial equivalence submissions.
What role does INVIMA play in Colombia regarding medical devices?
INVIMA, the Colombian regulatory authority, ensures that medical products meet safety and efficacy standards before market entry, similar to the FDA's evaluation process. It implements guidelines for classification, registration, and post-market surveillance.
Who is Ana Criado and what is her contribution to INVIMA?
Ana Criado is the Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma. She uses her background in biomedical engineering and health economics to develop guidelines that streamline the approval process for innovative medical technologies in Colombia.
What are the key elements considered in the 510(k) submission process?
The key elements include intended use, technological characteristics, safety and effectiveness, performance data, trial setup and approval, and comprehensive reporting on study status and adverse events.
What types of clinical studies does bioaccess® offer?
Bioaccess® offers a range of clinical study services including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF) across Latin America.
Why is accurate performance data important in the evaluation process?
Accurate performance data is crucial because improper modifications in data evaluation can lead to incorrect calculations of sensitivity and specificity, which can affect the overall assessment of the device's safety and effectiveness.




