Overview
The article focuses on the regulatory environment for early-feasibility studies (EFS) in Latin America, addressing the complexities and variations in regulations across different countries in the region. It explains that understanding local regulations, such as those enforced by agencies like ANVISA in Brazil and INVIMA in Colombia, is crucial for researchers to navigate the approval processes effectively, ensuring ethical compliance and participant safety while also benefiting from financial incentives and support services available in these countries.
Introduction
The landscape of clinical trials in Latin America is characterized by a unique blend of regulatory frameworks, ethical considerations, and cultural dynamics that shape the research environment. As the region gains prominence in global clinical research, understanding the intricacies of local regulations becomes essential for researchers aiming to conduct successful trials.
From Colombia's efficient approval processes to Brazil's stringent oversight by ANVISA, navigating these diverse requirements presents both opportunities and challenges. Furthermore, ethical imperatives, such as informed consent, take on added complexity within the context of local customs and patient expectations.
This article delves into the regulatory landscape, ethical considerations, and the operational hurdles faced by researchers in Latin America, providing insights that are crucial for anyone looking to engage with this evolving market.
Overview of Regulatory Framework for Clinical Trials in Latin America
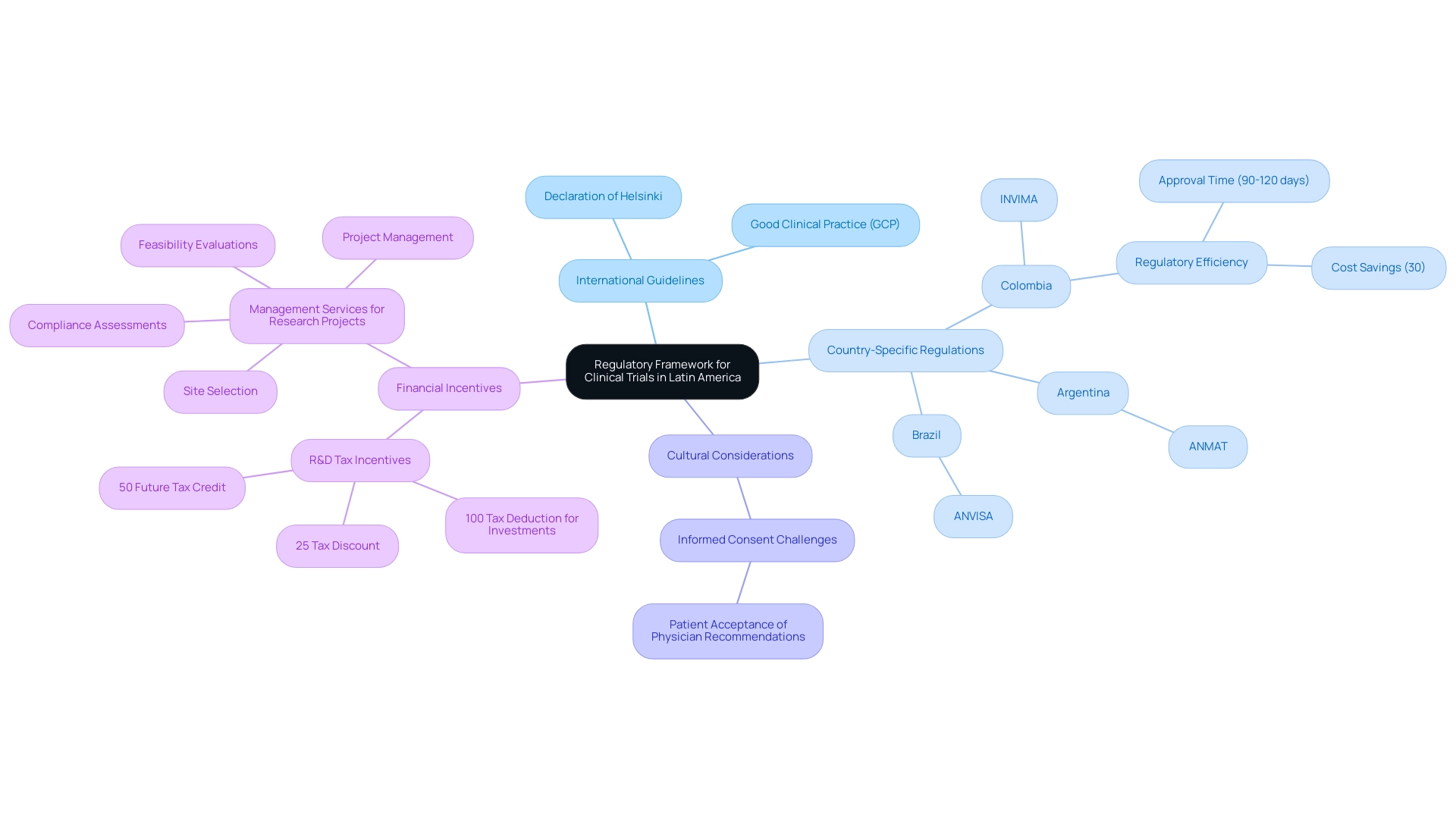
The governing structure that oversees clinical studies in Latin America is shaped by the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America, which involves a complicated interaction of international guidelines and local rules. In Colombia, companies benefit from a highly efficient regulatory process, with IRB/EC and INVIMA approvals typically completed within 90-120 days, offering significant cost savings of over 30% compared to studies in North America or Western Europe. Adherence to the Declaration of Helsinki remains paramount, as it establishes ethical principles for conducting medical research involving human subjects, alongside compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines to ensure studies are designed and conducted ethically and scientifically.
Each country in the region has its own health authority dictating specific protocols; for instance:
- Brazil operates under the National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA)
- Argentina mandates compliance with the National Administration of Drugs, Food and Medical Technology (ANMAT)
- In Colombia, the National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute (INVIMA) serves as a Level 4 health authority, overseeing medical device regulations and ensuring compliance with rigorous standards.
Considering that nearly 30% of the population in Latin America is under 14 years old, understanding and applying these regulations is essential for researchers aiming to protect participant safety and ensure ethical research conduct.
Cultural differences also play a significant role in informed consent procedures; patients in Latin America may accept physician recommendations without question, complicating the process for foreign sponsors. A recent review titled 'Need for Regular Updates in LATAM Regulations' emphasizes that the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America shows a significant delay in the updating of drug registration and research requirements compared to reference health authorities. This emphasizes the need for more regular updates of regulations to support the implementation of novel study designs within the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America and improve the marketing approval procedures for new medications.
Strengthening the role of the FDA as a reference agency could further assist LATAM countries in modernizing their drug approval processes. As Gómez et al. highlighted in their survey of medical oncologists from developing nations, grasping the local governance environment is essential for carrying out successful research in these distinct contexts.
Additionally, Colombia offers attractive R&D tax incentives, including:
- A 100% tax deduction for investments in science, technology, and innovation projects
- A 25% tax discount
- A 50% future tax credit
This makes it financially appealing for medical device companies. Moreover, extensive management services for research projects are available, which encompass:
- Feasibility evaluations
- Site selection
- Compliance assessments
- Setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
This ensures that researchers receive the essential support throughout the research process.
Ethics and Informed Consent in Latin American Clinical Trials
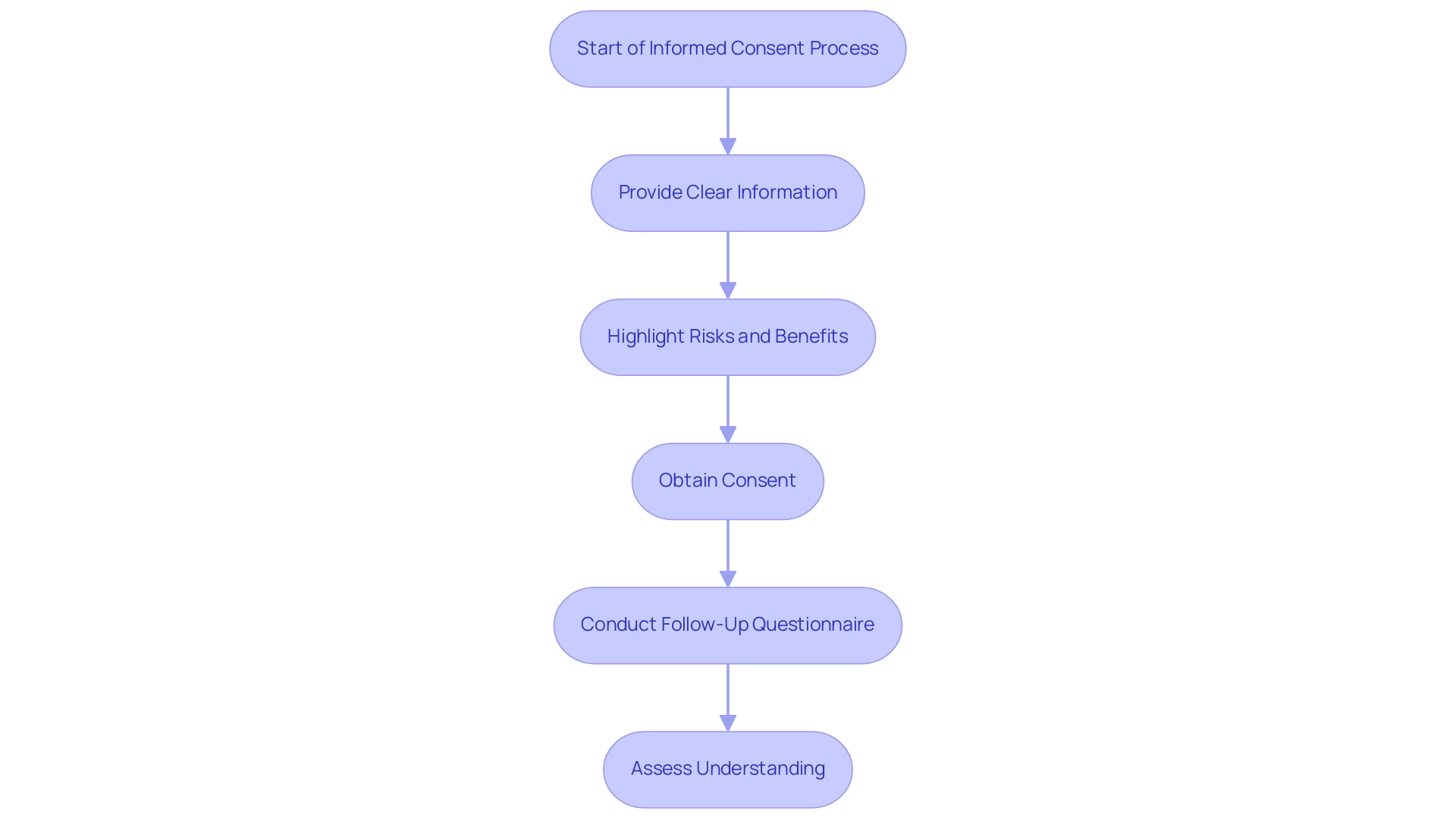
In Latin America, the regulatory environment for efs studies governs ethical considerations in clinical trials through national ethics committees and regulatory guidelines that emphasize the necessity of obtaining informed consent from all participants prior to enrollment. This process requires researchers to provide participants with clear and concise information regarding the objectives of the research, potential risks, benefits, and their rights as participants. Notably, a significant research conducted by Hereu et al. in 2010 highlights that the use of closed-ended questions during the consent process is associated with higher rates of understanding of the purpose of the research, the voluntary nature of participation, and the freedom to withdraw.
Additionally, a research examination by Verheggen in 1996 assessed informed consent among 198 adult patients across 26 experiments, utilizing a questionnaire distributed four weeks after the initial consent process. The findings underscored the importance of assessing understanding through follow-up questionnaires, revealing that addressing language barriers and cultural differences is crucial for ensuring that the consent process is ethical and culturally sensitive.
In comparison, the research in Americaninhas found that most participants agreed or strongly agreed with the consent process (p = 0.02), providing a contrasting perspective on participant understanding in different contexts. As part of our extensive research management services, we concentrate on:
- Feasibility assessments
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Setup procedures
- Acquiring necessary import permits
to ensure adherence to INVIMA regulations, which oversee medical device compliance as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO. Our services also encompass comprehensive project management and monitoring, along with meticulous reporting on progress, inventory, and adverse events to ensure compliance and transparency throughout the process.
The current conversation surrounding informed consent practices in clinical trials in Latin America highlights the regulatory environment for efs studies, reflecting a growing recognition of these ethical imperatives and the need for greater efforts to ensure that participants achieve a comprehensive understanding of informed consent, thereby safeguarding their interests while contributing to local economies through job creation and healthcare improvements.
Navigating the Approval Process for Early-Feasibility Studies
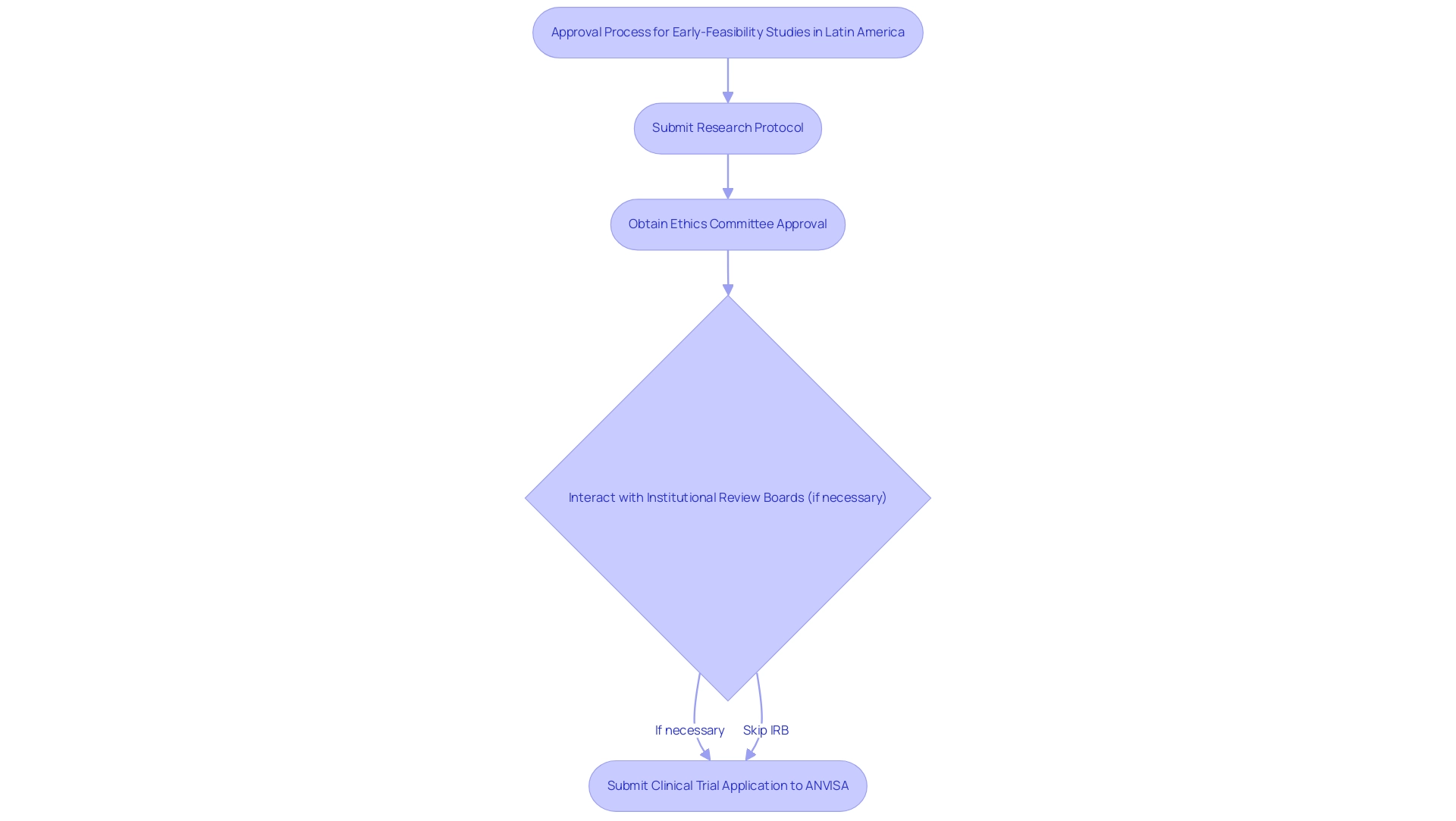
Navigating the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America during the approval process for early-feasibility assessments is a critical undertaking that encompasses several essential stages. In the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America, researchers must begin by submitting a detailed research protocol to the relevant regulatory body, followed by obtaining ethics committee approval. In certain scenarios, interactions with institutional review boards (IRBs) may also be necessary.
Detailed documentation is essential, encompassing objectives, design methodologies, and thorough risk assessments. For example, Brazil's requirements for the submission of a Clinical Trial Application (CTA) to ANVISA, the national health surveillance agency, highlight the importance of understanding the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America to streamline the approval process and expedite the commencement of research.
Early-feasibility assessments, along with:
- First-In-Human Trials
- Pilot Trials
- Pivotal Trials
- Post-Market Medical Follow-Up Assessments
not only contribute to successful health outcomes but also play a significant role in local economies by creating jobs and promoting economic growth.
The insights from the APHINITY investigation further emphasize the significance of these timelines, with a median approval duration of 53 days and ethics committee endorsement averaging 56 days, facilitating swift patient enrollment and efficient execution. As Julio Martinez-Clark, CEO and co-Founder of Bioaccess, advises, 'Pay attention to the Pacific Alliance, pay attention to the OECD,' emphasizing the importance of these economic contexts in compliance and the overall success of research studies. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, Bioaccess brings specialized knowledge and flexibility to navigate these processes efficiently.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Their Roles in Clinical Trials
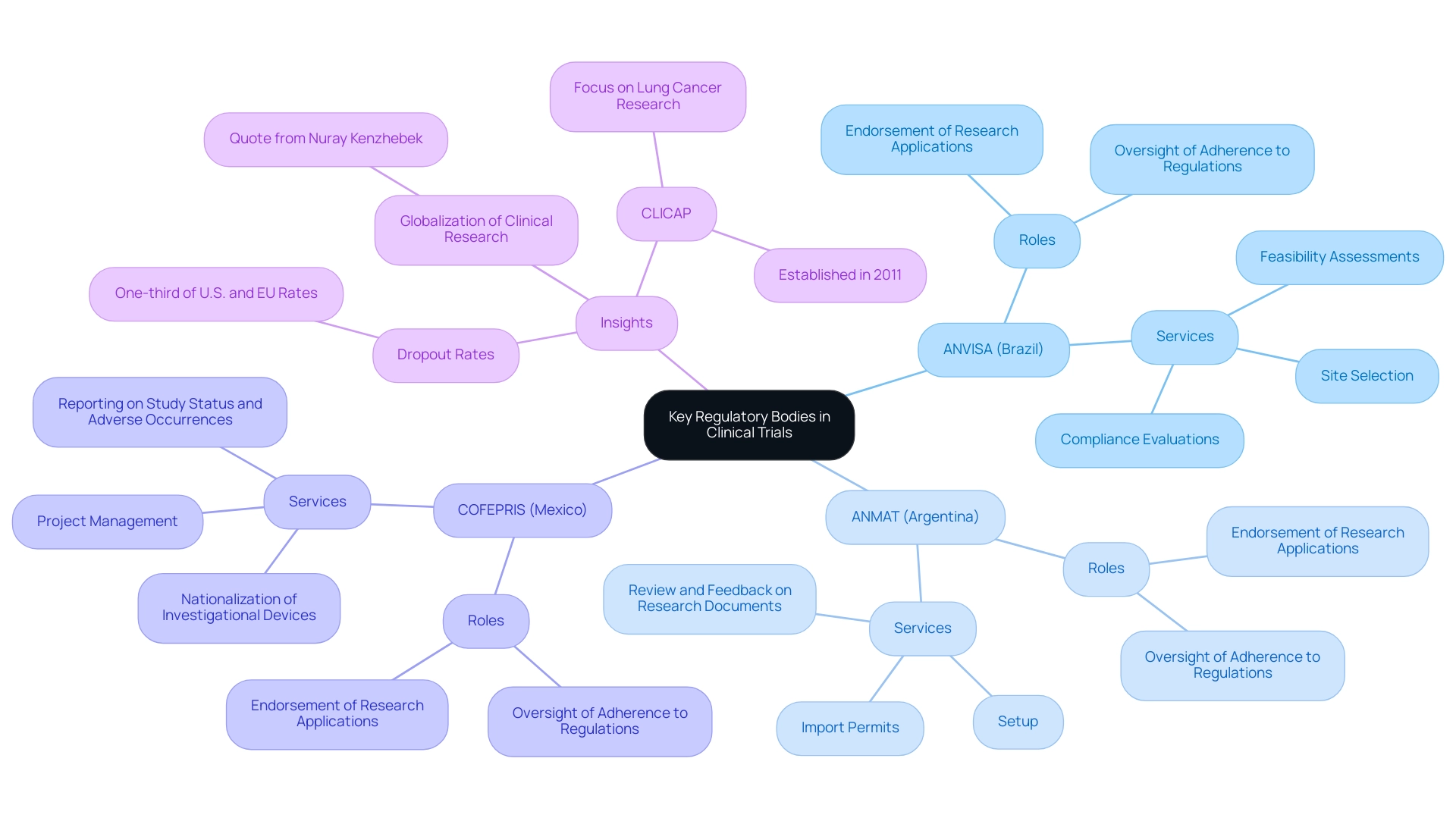
Key regulatory agencies, including ANVISA in Brazil, ANMAT in Argentina, and COFEPRIS in Mexico, are crucial in shaping the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America. These organizations are tasked with the endorsement of research applications and the rigorous oversight of adherence to local regulations, ensuring the safety and welfare of study participants. They also provide guidance on best practices and adapt to the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America to facilitate innovative research approaches.
Our extensive study management services include:
- Feasibility assessments
- Site selection
- Compliance evaluations
- Review and feedback on research documents
- Setup
- Import permits
- Nationalization of investigational devices
- Project management
- Reporting on study status and adverse occurrences
For example, recent expert insights indicate that the growing involvement of Latin America in FDA-regulated studies reflects a significant trend in the globalization of medical research. Nuray Kenzhebek, Marketing Director at Cyberdise, noted, 'And, maybe, Latin America’s growing role in FDA-regulated trials highlights a broader trend: the globalization of clinical research?'
Notably, dropout rates in this region are one-third of those in the U.S. and EU, underscoring the potential for successful study execution. Furthermore, global guidelines and public health initiatives are advancing pediatric drug development for rare diseases, emphasizing the importance of compliance in this area. The Latin American Consortium for the Investigation of Lung Cancer (CLICAP), established in 2011, illustrates joint efforts to enhance lung cancer research in the region, emphasizing the crucial role of governing organizations.
Moreover, comprehending the revised profile of cancer burden, patterns, and trends in Latin America and the Caribbean is crucial for researchers, as it contextualizes the important functions and regulations governed by ANVISA, ANMAT, and COFEPRIS, which are part of the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America, allowing them to navigate the oversight landscape more efficiently and improve the efficacy of their research studies.
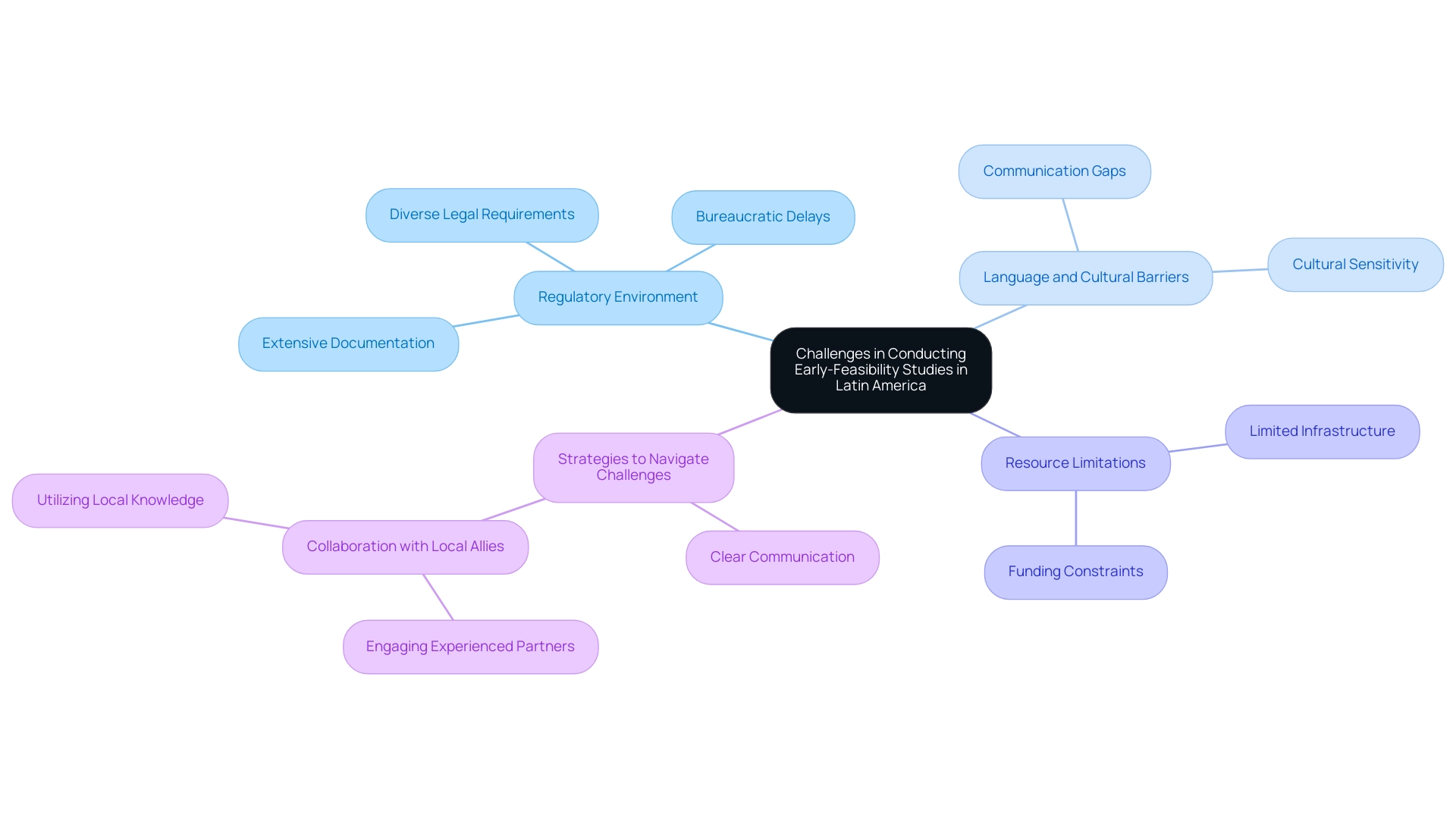
Challenges in Conducting Early-Feasibility Studies in Latin America
Conducting early-feasibility studies in Latin America is challenging due to the regulatory environment for efs studies in Latin America, which includes diverse legal requirements that vary from one country to another, potential language and cultural barriers, and significant resource limitations. Notably, 52% of global clinical trials are now conducted outside the U.S., reflecting a shift towards regions like Latin America as preferred sites for clinical research. Researchers often encounter bureaucratic delays in obtaining approvals, which can be exacerbated by the need for extensive documentation, thus slowing progress.
In Colombia, substantial R&D tax incentives for medtech firms, such as a 50% tax rebate on research investments, exemplify a supportive legislative environment that facilitates faster market entry for non-FDA-approved devices through local partnerships. To successfully navigate these challenges, specialists suggest:
- Creating clear communication with local governing bodies at the beginning of the research.
- Collaborating with knowledgeable local allies, like bioaccess®, which has more than 20 years of experience in Medtech. This can be extremely beneficial; their personalized strategy guarantees that research protocols are adjusted to the cultural settings of the participant population while retaining the adaptability needed to respond to the changing environment of trials.
Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, highlights the significance of comprehending the regulatory environment to improve compliance and enable smoother project execution. Julio G. Martinez-Clark, CEO of bioaccess®, highlights that 'Colombia stands out as a noteworthy hub for clinical research, offering many advantages that make it an attractive choice for medtech companies.' By implementing these strategies, researchers can enhance collaboration and significantly improve their chances of successful study execution, ultimately addressing the ongoing challenges faced in conducting early-feasibility studies in Latin America.
Conclusion
The regulatory landscape for clinical trials in Latin America is both intricate and dynamic, shaped by a mix of local regulations and international guidelines. Understanding the specific requirements of each country, such as:
- Colombia’s efficient approval processes
- Brazil’s rigorous oversight by ANVISA
is essential for researchers. The emphasis on ethical considerations, particularly informed consent, highlights the need for culturally sensitive approaches to ensure participant understanding and safety.
Navigating the approval process for early-feasibility studies presents its own set of challenges, including:
- Bureaucratic delays
- The necessity for comprehensive documentation
Despite these hurdles, the potential for successful clinical research in Latin America remains strong, bolstered by attractive R&D incentives, a commitment to ethical standards, and the active involvement of key regulatory bodies like:
- ANVISA
- ANMAT
- COFEPRIS
These organizations not only facilitate compliance but also promote innovative research practices that align with global standards.
As Latin America continues to gain prominence in the global clinical research arena, fostering collaboration with local partners and maintaining open communication with regulatory authorities will be crucial. By leveraging the region's unique advantages while addressing its challenges, researchers can enhance the effectiveness of their clinical trials, ultimately contributing to advancements in medical science and improved healthcare outcomes. The ongoing evolution of this landscape underscores the importance of staying informed and adaptable in order to navigate the complexities of conducting clinical research in this vibrant region.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the regulatory environment for clinical studies in Latin America?
The regulatory environment for clinical studies in Latin America is shaped by a complex interaction of international guidelines and local rules, with each country having its own health authority that dictates specific protocols.
How does the regulatory process in Colombia compare to North America and Western Europe?
Colombia has a highly efficient regulatory process, with IRB/EC and INVIMA approvals typically completed within 90-120 days, resulting in significant cost savings of over 30% compared to studies in North America or Western Europe.
What ethical guidelines must researchers adhere to when conducting studies in Latin America?
Researchers must adhere to the Declaration of Helsinki, which establishes ethical principles for conducting medical research involving human subjects, as well as comply with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines to ensure studies are conducted ethically and scientifically.
Which health authorities oversee clinical studies in specific Latin American countries?
Brazil: National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA), Argentina: National Administration of Drugs, Food and Medical Technology (ANMAT), Colombia: National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute (INVIMA).
Why is understanding regulations important for researchers in Latin America?
Understanding and applying regulations is essential for protecting participant safety and ensuring ethical research conduct, especially given that nearly 30% of the population in Latin America is under 14 years old.
What challenges do cultural differences present in the informed consent process in Latin America?
Cultural differences may lead patients to accept physician recommendations without question, complicating the informed consent process for foreign sponsors.
What recent findings highlight the need for updates in Latin American regulations?
A review titled 'Need for Regular Updates in LATAM Regulations' emphasizes significant delays in updating drug registration and research requirements, indicating a need for more regular updates to support novel study designs and improve marketing approval procedures.
How could the FDA's role assist LATAM countries in drug approval processes?
Strengthening the FDA's role as a reference agency could help LATAM countries modernize their drug approval processes.
What tax incentives does Colombia offer for research and development?
Colombia offers attractive R&D tax incentives, including a 100% tax deduction for investments in science, technology, and innovation projects, a 25% tax discount, and a 50% future tax credit.
What management services are available for research projects in Colombia?
Management services include feasibility evaluations, site selection, compliance assessments, project setup, import permits, project management, and reporting to ensure essential support throughout the research process.

