Overview
The article focuses on the significance of transparency and accountability in clinical research, emphasizing their role in enhancing trust, credibility, and patient engagement in studies. It supports this by discussing how comprehensive sharing of information, adherence to regulatory frameworks, and the use of clinical trial registries can improve the integrity of research processes and encourage participation from underrepresented groups.
Introduction
In the realm of clinical research, transparency and accountability stand as fundamental pillars that ensure the integrity and credibility of scientific inquiry. As the landscape evolves, particularly with the increasing emphasis on diversity and ethical standards, understanding the nuances of these principles becomes imperative.
This article delves into the definitions of transparency and accountability, exploring their critical roles in fostering trust among stakeholders, including patients, researchers, and regulatory bodies. Furthermore, it examines the significance of clinical trial registries in promoting research integrity, outlines best practices for enhancing transparency, and highlights the impact of regulatory frameworks in supporting these essential concepts.
By illuminating the interconnectedness of these elements, the discussion aims to underscore the necessity of a commitment to transparency in advancing clinical research and improving patient outcomes.
Defining Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research
Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research is characterized by the comprehensive sharing of information concerning study protocols, outcomes, and potential conflicts of interest. This practice is crucial for promoting Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research, as it allows stakeholders—including patients, researchers, and sponsors—to access vital data necessary for making informed decisions. Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research enhances this by ensuring researchers and organizations remain answerable for their actions and choices throughout the cycle.
Together, these principles of Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research foster an atmosphere of trust and strengthen the credibility of findings, ultimately resulting in improved patient outcomes. In light of the impending FDA requirement for diversity inclusion plans, which underscores the need for transparency and accountability in clinical research, it is clear that a commitment to these principles is not merely ethical but essential for propelling forward medical knowledge. Recent statistics from the FDA highlight that only 10% of research participants represent underrepresented groups, emphasizing a critical area for enhancement.
Media coverage, including that from Clinical Leader, has been crucial in highlighting advancements in health studies in Latin America and Colombia, leading to greater transparency and accountability in clinical research as well as promoting ethical practices in examinations. For example, the article by the Clinical Leader on the issues of diversity in medical studies addresses how the absence of representation can distort findings. As noted by Peter Steffensen, 'It has been a pleasure to partner with Columbia Science, Health, and Information Clinic and UAEM on their vital efforts to keep pressure on the FDA to improve FDAAA enforcement.'
This sentiment reflects a growing agreement on the necessity of Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research, particularly as we strive to dismantle barriers that have historically hindered participation among underrepresented groups. A recent case analysis titled 'Underlying Factors Creating Barriers to Diversity in Research' reveals that despite interest in participation among underrepresented groups, various obstacles deter engagement, including fears of discrimination and historical exploitation. Pragmatic constraints like limited access, time, and financial resources contribute to low participation rates, necessitating targeted efforts to address these challenges.
Furthermore, the regulatory oversight of INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, plays a crucial role in addressing these barriers. As a Level 4 health authority as designated by PAHO/WHO, INVIMA's roles include ensuring adherence and promoting ethical standards in clinical evaluations, which is essential for fostering an inclusive and effective clinical development environment.
The Role of Clinical Trial Registries in Enhancing Research Integrity
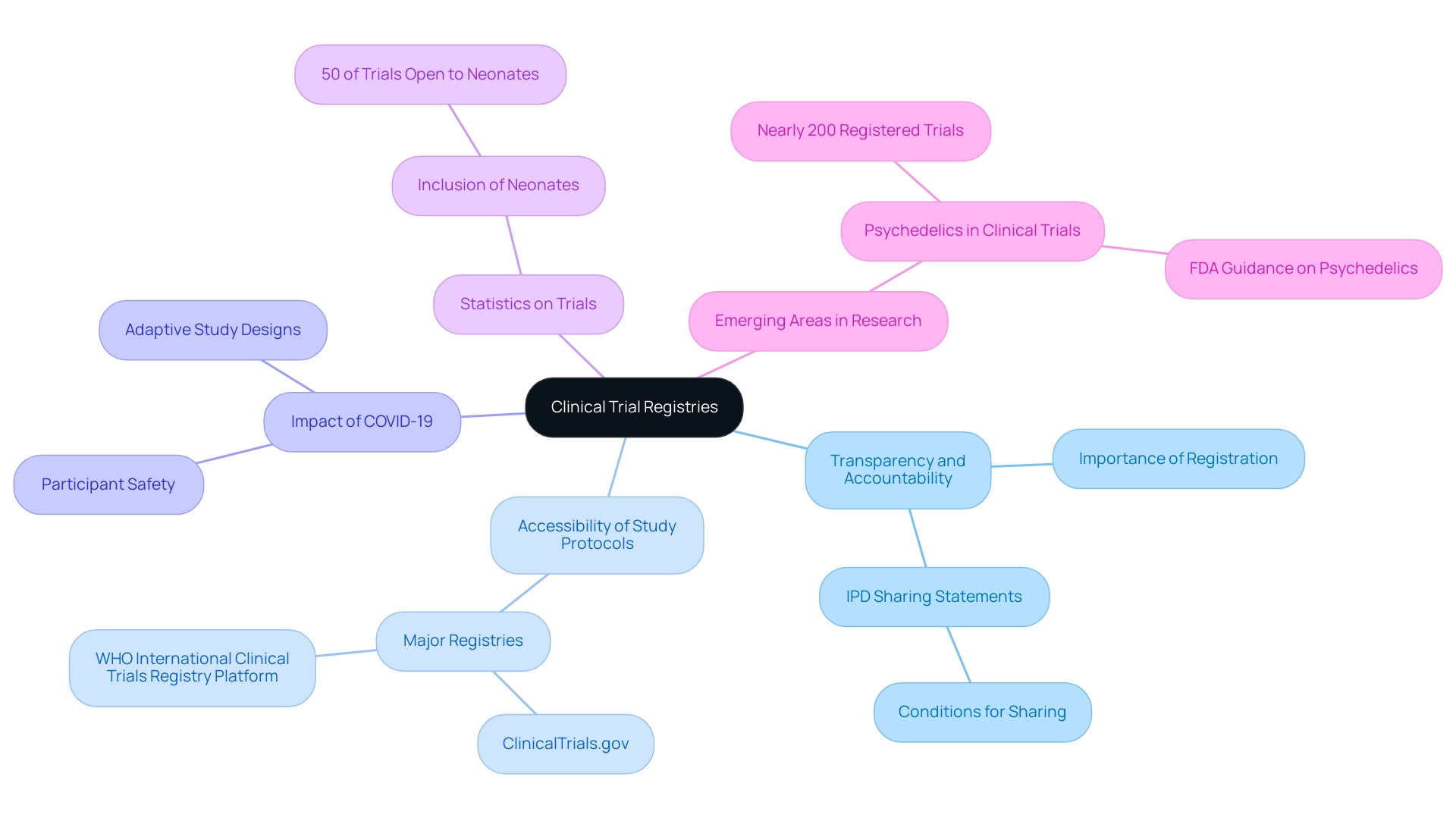
Clinical registries are vital tools for enhancing integrity, acting as public platforms where investigators are mandated to register their projects before commencement. This practice significantly enhances transparency and accountability in clinical research, as it allows for the accessibility of study protocols. Importantly, it ensures transparency and accountability in clinical research by holding researchers accountable for reporting all outcomes, regardless of their favorability.
Major registries, including ClinicalTrials.gov and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, offer stakeholders the capability to search for information about both ongoing and completed studies, thereby fostering trust in the research process. Furthermore, these registries play a critical role in mitigating selective reporting and publication bias, ensuring that all data—including negative results—are made accessible for thorough examination.
Recent statistics indicate that in 2024, approximately 50% of studies including children in their inclusion criteria also extended eligibility to neonates, reflecting an evolving understanding of diverse participant needs. The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on research studies in Thailand, highlighting the need for adaptive study designs and innovative methods to maintain participant safety and data integrity during unprecedented times. Moreover, the landscape of trial registries is continually advancing, as evidenced by the emergence of nearly 200 registered trials focused on psychedelics.
This shift is especially significant as it addresses substantial unmet medical needs in central nervous system (CNS) disorders, illustrating a real-world example of how registries support inquiry in emerging areas. As these practices develop, it is essential for researchers to follow strong registration protocols, which ultimately improve the dependability of trials and safeguard the interests of patients and the wider community. Considering the current developments, especially concerning individual participant data (IPD) sharing statements, which must specify whether data will be shared and the conditions for sharing, the dedication to transparency and accountability in clinical research remains a cornerstone of integrity.
Implementing Best Practices for Transparency and Accountability
To enhance transparency and accountability in clinical research, it is essential for researchers to create a well-defined protocol that outlines clear objectives, methodologies, and data management plans. Our extensive clinical research management services include:
- Feasibility assessments
- Site selection
- Compliance evaluations
- Setup and approval processes
- Import permits
- Project management
- Thorough reporting
All of which guarantee adherence to regulatory standards. Specifically, our trial setup process includes thorough reviews and feedback on research documents to comply with country requirements, as well as the management of both serious and non-serious adverse events throughout the research.
All data from the research is available on the OSF repository, promoting transparency and accountability in clinical research. Regular training on ethical conduct must be provided for all team members, ensuring that everyone is equipped with the necessary knowledge to uphold these principles. Effective communication strategies with stakeholders—including patients, sponsors, and regulatory authorities—should be prioritized.
This can involve providing consistent updates on research progress, addressing challenges encountered, and noting any changes in protocols. Between November 2020 and July 2021, 14 individual participants were recruited from 11 different institutions, illustrating the collaborative nature of clinical studies. Furthermore, fostering a culture that encourages team members to express concerns and report issues without the fear of repercussions is vital in promoting accountability.
As Dhruva et al. have requested a mandate for registration of SU/HD inquiries, similar accountability measures should be considered in protocols. A notable case analysis, titled 'Balancing Diversity and Privacy in IPD Anonymization,' underscores the challenges of anonymizing individual participant data while preserving privacy and ensuring data diversity, particularly concerning minority groups.
It emphasizes the need for strategies that enhance data quality while ensuring transparency and accountability in clinical research amidst these complexities. Additionally, the role of INVIMA as the Colombian regulatory authority is crucial in overseeing compliance and ensuring the safety of investigational devices. By embracing these optimal methods, including acknowledging the influence of Medtech trials on local economies—such as job creation, economic growth, and healthcare enhancement—research organizations can strengthen their credibility and the overall reliability of their initiatives.
The Impact of Transparency on Patient Engagement
Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research are crucial for enhancing patient engagement within clinical studies. When patients are thoroughly informed about the project's purpose, procedures, potential risks, and benefits, their likelihood of participation and sustained commitment to the trial significantly increases. Research indicates that well-informed patients exhibit higher engagement levels, which is crucial given the recent findings that patient satisfaction in hospitals has generally declined across most domains during the pandemic.
This underscores the need for effective communication strategies that promote transparency and accountability in clinical research. Gelareh Sadigh emphasizes:
Improving price transparency where patients are responsible for a portion of the cost of care aims to improve patients’ decision-making and financial planning, and decrease prices through increased competition, and thus decrease overall healthcare spending.
Furthermore, involving patients in the decision-making process cultivates a sense of ownership and trust in the study.
Researchers should utilize various communication methods—such as informational sessions, brochures, and digital platforms—to effectively reach a wider audience. The UK's National Health Service (NHS) serves as a pertinent case study; while it offers free healthcare, including advanced imaging, the inconsistency in price disclosure compliance among private providers underlines the complexities of transparency. Notably, the emergence of startups aimed at improving access to healthcare pricing information reflects ongoing efforts to enhance transparency and accountability in clinical research.
Furthermore, the suggestion 25-A-07-008.03 to CMS emphasizes the regulatory consequences of Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research. Ultimately, involving patients as partners in studies not only enhances recruitment rates but also enriches the quality of data gathered, leading to improved health outcomes. Moreover, identifying leadership and influential figures in this area, along with recognizing accolades such as the 2022 HX NDNQI Award recipients and the 2022 HX Guardian of Excellence Award recipients, can offer additional context to the conversation on quality in healthcare management.
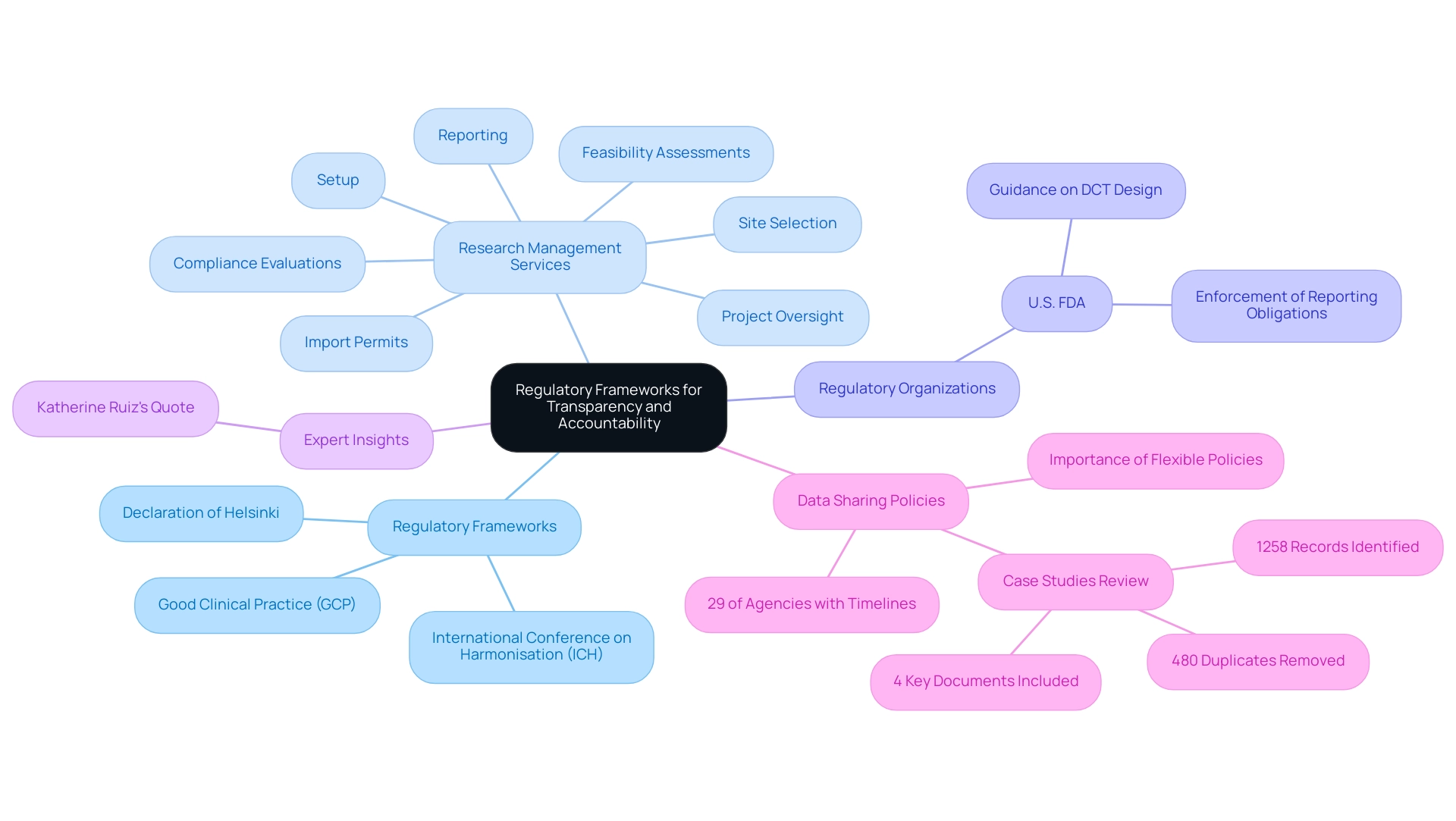
Regulatory Frameworks Supporting Transparency and Accountability
Regulatory frameworks, notably the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and the Declaration of Helsinki, are crucial for fostering transparency and accountability in clinical research. These guidelines outline the ethical principles crucial for carrying out investigations involving human subjects, requiring researchers to reveal important information about objectives, methodologies, and potential risks. Adherence to these regulations not only safeguards participant welfare but also enhances the credibility and reliability of research findings.
Our extensive research management services encompass:
- Feasibility assessments
- Site selection
- Compliance evaluations
- Setup
- Import permits
- Project oversight
- Reporting
Ensuring that all facets of the experiment conform to regulatory standards. We also provide thorough review and feedback on study documents to ensure compliance with country requirements, as well as detailed reporting on study status, inventory, and both serious and non-serious adverse events. Recent analysis indicates that 29% of research agencies have established timelines for sharing data, reflecting a growing commitment to transparency.
Regulatory organizations like the U.S. FDA play a crucial role in enforcing strict reporting obligations for research studies, ensuring that transparency is fundamental to the research process. The U.S. FDA has also provided guidance on decentralized research (DCT) design and execution, highlighting the significance of electronic systems in medical investigations.
'Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, has expressed the importance of evaluating regulatory documents, stating,
With this intention, we conducted a scoping review of the literature with the following objectives: to identify regulatory documents that have guided trial investigators in trial data sharing and to explore the key elements of data-sharing mechanisms in these regulatory documents.
Moreover, the recent evaluation of data-sharing policies emphasized the necessity for adaptable yet thorough frameworks to improve practices and promote cross-border collaboration. This review involved identifying a total of 1258 records, removing 480 duplicates, and including 4 key documents for data coding, highlighting the limited academic publications on regulatory frameworks and the necessity for gray literature searches. By strictly adhering to these established guidelines and frameworks, researchers can maintain the integrity of their studies and cultivate trust among stakeholders, thereby reinforcing the overarching goal of transparency and accountability in clinical research.
Conclusion
Transparency and accountability are essential to the integrity of clinical research, fostering trust among stakeholders such as patients, researchers, and regulatory bodies. By sharing information about study protocols, outcomes, and conflicts of interest, these principles empower informed decision-making, ultimately improving patient outcomes. The push for diversity in clinical trials further emphasizes the need for inclusive practices that dismantle barriers to participation.
Clinical trial registries enhance research integrity by ensuring that study information is accessible and that all outcomes, positive or negative, are reported. This practice reduces selective reporting and strengthens trust in the research process. Adopting best practices, including effective communication and rigorous protocols, is critical for enhancing transparency and accountability.
Moreover, transparency boosts patient engagement, as informed patients are more likely to participate in trials and contribute valuable data. Engaging patients as partners not only enriches the research experience but also leads to better health outcomes. Regulatory frameworks, such as ICH guidelines and Good Clinical Practice, provide vital support for maintaining ethical standards and safeguarding participant welfare.
In summary, the interplay of transparency, accountability, and regulatory oversight is crucial for advancing clinical research. A steadfast commitment to these principles enhances research credibility and cultivates trust among all stakeholders. Prioritizing transparency is essential for navigating the complexities of modern medical inquiries and ultimately improving patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is meant by Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research?
Transparency and Accountability in Clinical Research refers to the comprehensive sharing of information regarding study protocols, outcomes, and potential conflicts of interest, which is essential for promoting informed decision-making among stakeholders, including patients, researchers, and sponsors.
Why is Transparency and Accountability important in clinical research?
These principles foster trust, strengthen the credibility of findings, and ultimately lead to improved patient outcomes by ensuring that researchers and organizations are answerable for their actions throughout the research cycle.
What recent FDA requirement emphasizes the need for transparency in clinical research?
The impending FDA requirement for diversity inclusion plans underscores the necessity for transparency and accountability in clinical research, highlighting the importance of diverse representation in research studies.
What statistics highlight the lack of diversity in research participation?
Recent statistics from the FDA indicate that only 10% of research participants represent underrepresented groups, pointing to a critical area for improvement.
How has media coverage contributed to transparency in clinical research?
Media coverage, such as that from Clinical Leader, has highlighted advancements in health studies, particularly in Latin America, promoting ethical practices and greater transparency and accountability in clinical research.
What barriers hinder participation among underrepresented groups in clinical research?
Barriers include fears of discrimination, historical exploitation, limited access, time constraints, and financial resources, which deter engagement from underrepresented groups despite their interest in participation.
What role does INVIMA play in addressing barriers to diversity in research?
INVIMA, Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, ensures adherence to ethical standards in clinical evaluations and promotes an inclusive clinical development environment as a Level 4 health authority designated by PAHO/WHO.
How do clinical registries enhance transparency and accountability in clinical research?
Clinical registries require investigators to register their projects before commencement, allowing for public access to study protocols and holding researchers accountable for reporting all outcomes, thereby mitigating selective reporting and publication bias.
What are some major clinical registries mentioned in the article?
Major registries include ClinicalTrials.gov and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, which enable stakeholders to search for information about ongoing and completed studies.
What recent trends have been observed in clinical trial registrations?
Approximately 50% of studies including children in their inclusion criteria now also extend eligibility to neonates, reflecting an evolving understanding of diverse participant needs. Additionally, nearly 200 registered trials focused on psychedelics have emerged, addressing unmet medical needs in central nervous system disorders.
What is the significance of individual participant data (IPD) sharing statements in clinical research?
IPD sharing statements must specify whether data will be shared and under what conditions, emphasizing the ongoing commitment to transparency and accountability as a cornerstone of integrity in clinical research.

